This document provides an overview of Splunk, including:
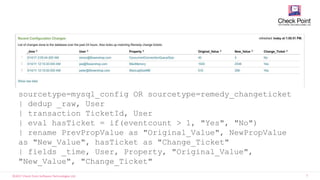
- Splunk's main functionality is real-time log collection, indexing, and analytics of time series data through search queries and data exploration/visualization capabilities.
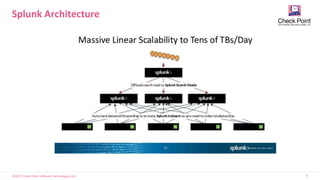
- Reasons to use Splunk include its proven success in the field, flexible and user-friendly interface, and ability to handle large volumes of data from various sources through infinite scaling.
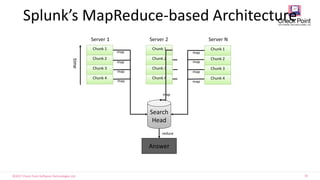
- Splunk uses a MapReduce-based architecture to index and search large volumes of data across multiple servers.