pdf&rendition=1-1.pdf
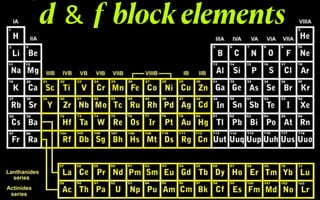
- 1. d & f block elements .IE#fgfT-tfnft-EEf
- 2. 1 - 2 1- 10ns 2n - d 3d 15T.S 4d 2ndTS sa 30d4.5 6d 2MTs (n- 2)f( - 14(n- 1)d0ns
- 3. Elements of groups 3-12 in the periodic table Also called transition metals Last electron enters in the penultimate d - orbital
- 4. Electronic configuration of the d-Block elements Scooty vicraman feco nicuzen amfar -
- 6. Scandium, Sc Titanium, Ti Vanadium, V Chromium, Cr Manganese, Mn Iron, Fe Cobalt, Co Nickel, Ni Copper, Cu Zinc, Zn [Ar] 3d 4s 1 2 [Ar] 3d 4s 2 2 [Ar] 3d 4s 3 2 [Ar] 3d 4s 5 1 [Ar] 3d 4s 5 2 [Ar] 3d 4s 6 2 [Ar] 3d 4s 7 2 [Ar] 3d 4s 8 2 [Ar] 3d 4s 10 1 [Ar] 3d 4s 10 2
- 7. Exceptional Electronic Configuration Chromium : Copper : “Half filled and fully filled configuration is more stable than partially filled configuration”. 36545' 3d9451
- 8. Q. Cr, (n.
- 9. All transition elelments are d- block elements, but all d - block elements are not transition elements ? Fe = 3d"as 23a+ = 3d" Fe
- 10. Transition metals A transition metal is defined as the one which has incompletely filled d orbital in its ground state or in any one of its oxidation states Zinc, cadmium and mercury are not regarded as transition metals General electronic configuration is ♻ ♻ ( n-1)d ns 1-10 1-2 r I ⑩
- 11. Zn (atomic number = 30) is not a transition element, though it is a d block element. Why? Q. 32 = 361452 2n2 + = 3d10
- 12. Q. zn, cd, Ag.
- 13. General Characteristics Atomic and ionic radii Melting point and boiling point lonisation enthalpy Oxidation states Magnetic properties
- 14. Formation of complexes Formation of coloured compounds Catalytic properties Interstitial compounds formation Alloy formation Electrode potential ♻
- 15. Atomic and ionic radii In a given transition series, the atomic and ionic radii first decreases, then become constant and increases towards the end of the series. The atomic and ionic radii of 2nd and 3rd row transition metals are quite similar. This is due to the Lanthanide contraction. 1 · x. ⑨
- 17. Q. h.c.
- 18. Melting point and boiling point In a given transition series the melting and boiling points 1st increases up to the middle and then decreases. As the number of unpaired electron increases, the metallic bond strength increases. Hence the melting point also increases. In a given transition series, the number of unpaired electrons increases up to the middle and then decreases. ♻ ♻ ♻ ⑩ X
- 19. High enthalpy of atomisation _
- 20. Why do the transition elements exhibit higher enthalpies of atomisation? Due to the presence of unpaired electrons, they have strong interatomic interaction. Thus they have high enthalpy of atomisation.
- 21. Ionisation enthalpy The ionisation enthalpy of transition elements generally increases from left to right. This is due to increase in nuclear charge. But the increase is not regular. The first ionisation enthalpies of Cr and Cu are low. This is because the removal of one electron does not change their d configuration. ♻
- 22. l Cr = 3d545' 1st1.E = loue. (n = 3d104512nd1.E=hish 1st I.E =lush. Mr = 3d5452 2 2nd1.7-lare. 24 = 3d1045
- 23. The 2nd ionisation energy of Cr and Cu are very high. This is because the removal of one more electron from these metals disrupted their stable configuration (d or d ) The 2nd ionisation enthalpies of Mn and Zn are lower than the 1st Ionisation enthalpies, this is because after the removal of one more electron, they attain the stable half filled or completely filled electronic configuration. 5 10 ♻
- 24. Oxidation State Transition metals show variable oxidation states. This is because in chemical reactions along with s-electrons, d-electrons also participate. 3dkS ② o o ②
- 25. Common on state (d block)s = + 2 -
- 26. Magnetic Properties Spin Magnetic moment : Paramagnetism is due to the presence of unpaired electrons. As the number of unpaired electrons increases paramagnetism increases. -> paramagnetic -> piamagnetic. BM. Iwoympaised is
- 27. n(n + 2 m = aS n = r 3 M. = 3d5452 = ⑤(5 + a) 2+ = 365450 M = 55Bm - ⑭ 1 (1/7 - 15 n = 5.
- 28. Formation of coloured ions or compounds Due to the presence of unpaired electrons in d orbitals. When an electron from a lower energy d orbital is excited to a higher energy d orbital, (d-d transition) the energy of excitation corresponds to the frequency of light absorbed.
- 29. .IT
- 30. d10or do - - - - 2n = 3d'4S 2 30 2n2+ = 3d10. -> HiL T fulyhiled dd tons asovi = 3d5452 Niat = 3d8. ↑k n = 2,1 coloured.
- 31. Ti2+ = 32482n= 21 - 4i = 362452 414+ = 3d045 o d colonless = =
- 32. Formation of Complexes Transition metals form a large no. of complexes. This is due to: 1. Comparatively smaller size 2. High ionic charge 3. Presence of partially filled d orbitals 4. Ability to show variable oxidation state ⑤ 2 ⑨ v
- 33. Catalytic Property Transition metals act as catalysts in a large no. of chemical reactions. This is due to their large surface area and their ability to show variable oxidation state. haber = Fe. Conduct = v205
- 34. n
- 35. B.
- 36. Interstitial Compound Formation These are formed when smaller atoms like H, N, C, B etc. are trapped inside the crystal lattice of the metal. They are usually non-stoichiometric and neither typically ionic nor covalent. Examples: Fe3H, Mn4N, TiC, VH0.56, TiH1.7 etc ♻ ♻ ♻
- 37. 1) They have high melting point. 2) They are very hard. 3) They retain metallic conductivity. 4) They are chemically inert. 00000000 000000000 00000000
- 38. Alloy Formation Alloys are homogeneous solid solutions of elements in which at least one element is a metal. Because of similar radii and other characteristics of Transition metals, they readily form alloys. The alloys formed are hard and have high m.p. Examples: Bronze (Cu, Zn), Stainless steel (Fe, C, Ni, Mn and Cr). ♻ Reason
- 39. M /M Electrode Potential Copper has positive potential - The high energy to transform Cu(s) to Cu (aq) is not balanced by its hydration enthalpy 2+ 2+ (u2+/cn = 0.34 cu -> (ya+ 2 Snydeation 1123z-
- 40. ⑭ cu2t stable. - cut in (as) sain unstable. Reason, lane hydration enthalpy ofcution. - hydratin a stability. hydration I range enthalpy. Siz
- 41. thank goin