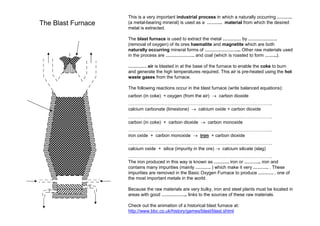
Blast Furnace Process Extracts Iron
- 1. The Blast Furnace This is a very important industrial process in which a naturally occurring ………. (a metal-bearing mineral) is used as a ………. material from which the desired metal is extracted. The blast furnace is used to extract the metal ………… by ………………. (removal of oxygen) of its ores haematite and magnetite which are both naturally occurring mineral forms of …………………... Other raw materials used in the process are ………………. and coal (which is roasted to form ……..). ………… air is blasted in at the base of the furnace to enable the coke to burn and generate the high temperatures required. This air is pre-heated using the hot waste gases from the furnace. The following reactions occur in the blast furnace (write balanced equations): carbon (in coke) + oxygen (from the air) → carbon dioxide ………………………………………………………………………………….. calcium carbonate (limestone) → calcium oxide + carbon dioxide ………………………………………………………………………………….. carbon (in coke) + carbon dioxide → carbon monoxide ………………………………………………………………………………….. iron oxide + carbon monoxide → iron + carbon dioxide ………………………………………………………………………………….. calcium oxide + silica (impurity in the ore) → calcium silicate (slag) ………………………………………………………………………………….. The iron produced in this way is known as ………. iron or ……….. iron and contains many impurities (mainly ………. ) which make it very ………. . These impurities are removed in the Basic Oxygen Furnace to produce ………. , one of the most important metals in the world. Because the raw materials are very bulky, iron and steel plants must be located in areas with good …………….. links to the sources of these raw materials. Check out the animation of a historical blast furnace at: http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/games/blast/blast.shtml
- 2. The Basic Oxygen Furnace The Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Process is the UK's major method for making steel. Modern furnaces will take a charge of up to 350 tonnes and convert it into steel in less than 40 minutes. Basic Oxygen Steelmaking (BOS) makes steel from Blast Furnace iron and up to 20% of scrap metal. The hot ………………. metal from the Blast Furnace contains up to 4.5% of ……….…. Other elements such as phosphorus and silicon are also present as impurities. Steelmaking reduces the carbon content to a level that matches the customer’s requirements (often less than 0.1%) and reduces the level of other impurities. Treating the hot metal with ………………. before it goes into the BOS furnace reduces the percentage of ………………. . This is called desulphurization. ………………. is blown into the furnace or BOS vessel through a water cooled oxygen lance. This oxidises carbon and the other unwanted elements in the hot metal. Carbon is oxidised to carbon monoxide gas, which passes from the converter to a cleaning plant. After cleaning, it can be re-used as a fuel gas. The rest of the elements in the metal are converted to ………………. oxides. They combine with the ………………. and other fluxes that are added during the blow. This produces a ………………. that floats on the surface of the metal. Write balanced equations for the following reactions occurring in the furnace. carbon [impurity] + oxygen → carbon monoxide [gas] ………………………………………………………………………………….. silicon [impurity] + oxygen → silicon dioxide [acidic] ………………………………………………………………………………….. silicon dioxide [acidic] + calcium oxide [basic] → calcium silicate [slag] ………………………………………………………………………………….. High carbon steel is ………………. but ………………. . Low carbon steel is softer and more easily worked. Stainless steel is an alloy of iron with chromium and nickel. 18/8 stainless steel (used in cutlery) contains 18% Cr and 8% Ni. http://www.schoolscience.co.uk/content/4/chemistry/steel/
