Road of construction
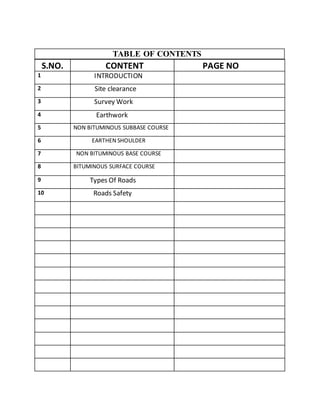
- 1. S.NO. CONTENT PAGE NO 1 INTRODUCTION 2 Site clearance 3 Survey Work 4 Earthwork 5 NON BITUMINOUS SUBBASE COURSE 6 EARTHEN SHOULDER 7 NON BITUMINOUS BASE COURSE 8 BITUMINOUS SURFACE COURSE 9 Types Of Roads 10 Roads Safety TABLE OF CONTENTS
- 2. INTRODUCTION Developmentof a country depends on the connectivityof various places with adequate road network. Roads constitute the most important mode of communication in areas where railways have not developed much. India has one of the largest road networks in the world (over 3 million km at present).For the purpose of managementand administration,roads in india are divided into followingfive categories: 1. National Highways (NH) 2. State Highways (SH) 3. MajorDistrict Roads (MDR) 4. Other District Roads (ODR) 5. Village Roads (VR) Site Clearance Two Types Of Methods C & G (CLEARING & GRUBBING) ENCROACHMENT CLEARING a.) C & G (CLEARING & GRUBBING) :- A good construction practice to follow cutting, removingand disposing of all unsuitablematerials such as trees, bushes shrubs,stump, roots, grass, weeds,top organic soils up to a minimum depth of 150mm from the road construction area known as site clearance-clearingand
- 3. grubbing(C&G).grass, weeds,top organic soils up to a minimum depth of 150mm from the road construction area known as site clearance- clearing and grubbing(C&G). b.) ENCROACHMENT CLEARING :- Decidingon the matter of whetherconstruction of a religious structure (Temple)and attemptingto encroach upon the public land is a fundamental or legal right, Survey Work Two Types Of Methods CENTERLINE & CHAINAGE MARKING OGL (ORIGINAL GROUND LEVEL ) RECORDINIG a) CENTERLINE & CHAINAGE MARKING :- Centerline markingis the primary survey part in road construction.Centerline is useful while setting out for any road construction work. So it is very essential markingcentre line first, before any construction work. b). OGL (ORIGINAL GROUND LEVEL ) RECORDINIG :- Verification of existingground level prior to work commencing.This is essential as the basis for all future measurementon site. EARTHWORK EMBANKMENT SUBGRADE a.) EMBANKMENT:- Usually consistof soil but may also include aggregate, rock, or crushed paving material.Al- Mardoofis specialized & famous in embankmentwork based
- 4. on his competentengineers,supportive staff & big fleet of modern equipment.Recently,Mardoofhas completed four projects with a huge quantityof embankment7,509,786 m3. Al-Mardoofstandard of work is fantastic and is example amongother companies engaged in construction industry. While embankment,Al-Mardoofmanagementtakes no compromise and select good qualitymaterial that meets required standards of MOT. During embankment,Al- Mardoof engineers & lab technician also take special care on type of material,material gradation,material gravity and densityto achieve optimum results. Al- Mardoofis specialized in common fill, rock fill and sand fill. b.)SUBGRADE :- The sub-grade will need some basic preparation to make it fit for construction purposes and this process is known as 'sub-grade formation'.Al- Mardoof engineers are well versed with sub-grade formulation because.
- 5. On every Al-Mardoofproject, subgrade beingcarried out by separate team. The team is consist of engineers,foreman’s, surveyor’s,lab technician and a set of latest equipment’s i.e. graders, rollers, water trailers. Our engineers ensurethat subgrade able to support loads transmitted from the pavementstructure.Our lab technicians take special care on verifying degree of compaction,moisture content, and type of material beingused. Currently, subgrade beingcarried out on our four ongoingprojects and Alhamdulillah ourwork performance is excellent. NON BITUMINOUS SUBBASECOURSE GSB (GRANULAR SUB BASE) Granular sub-base (GSB)
- 6. SUB BASE (GSB)– The full form of GSB is granular sub base.itis beinglaid in road work because it plays two major roles 1- it works as drainage layer 2- it provides a good sub base to laid base layer on it. Material – The material to be used for the work shall be natural sand, crushed gravel, crushed stone, crushed slag, or combination thereofdependingupon the grading required use of material like brick metal, kankar and crushed concrete shall be permitted in the lower sub base.The material shall be free from organic or other deleterious constituents. Grading III and IV shall be used in lower sub base. Grading V and VI shall be used as sub-base-cum-drainage layer. Where the sub-base is laid in two layers as upper sub- base and lowersub-base,the thickness of each layer shall not be less than 150mm.If the water absorption of the aggregates determined as per IS: 2386(part-3)is greater than 2 %, the aggregates shall be tested for wet aggregate impact value (AIV) (IS: 5640).Soft aggregates like kankar, brick ballastand laterite shall also be tested for wet AIV.
- 7. Physical Requirements Of Granular Sub Base CONSTRUCTION OPERATION :- Spreadingand compacting- the sub base material of the specified grading shall be mixed homogenously with the help of motor grader .the required water content shall be determined in accordance with IS:2720 (part 8). Moisture contentof the mix shall be checked in accordance with IS: 2720 (part 8) and adjusted so that, at the time of compaction,it is from 1 to 2 % below the OMC.
- 8. Immediatelyspreadingthe mix, rollingshall be done.If the thickness of the compacted layer does not exceed 100mm,a smooth wheeled rollerof 80 to 100 KN weight may be used.For a compacted single layer up to 200mm the compaction shall be done with the help of a vibratory roller of min. 80 to 100KN.Rollingshall commence at the lower edge and proceed towards the upper edge longitudinallyfor portion having unidirectional cross fall or on super elevation.For carriage way having cross fall on both sides, Rolling shall commence at the edges and progress towards the crown. WET MIX MACADAM (WMM) sub – base /base:-
- 9. Wet mix macadam (WMM) act as a base course just below the bituminous layer(bitumen base course or surface course). The thickness of a single compacted Wet mix macadam(WMM) layer shall not be less than 75mm.when vibrating or other approved types of compacting equipment are used, the compacted depth of a single layer of the sub-base course may be up to 200mm. Each pass of the roller shall uniformly overlap not less than one –third of the track made in the preceding pass. The speed of roller shall not exceed 5 KM per hour. Rolling shall be continued till the density achieved is at least 98% of the max. Dry density for the material determined as per IS: 2720 (part8). All loose, segregated or other defective areas shall be made good to the full thickness and re-compacted. Measurement- Granular sub –base shall be measured as finished work in position in cubic metres.
- 10. Types of treatment for soil to make suitable for sub- base :- (1) Lime treated soil for improved sub-grade/sub-base (2) Cementtreated soil and cement-fly ash treated sub- base/base (3) Crushed cementconcrete sub-base EARTHEN SHOULDER Earthen Shoulder Construction on Both Side Shoulder:- is an emergencystoppinglane by the verge of a road or motorway,on the right side in countries which drive on the right, and on the left side in countries which drive on the left. Many wider U.S. freeways have shoulders on both sides of each directional carriageway—in the median,as well as at the outer edges of the road, for additional safety. Shoulders are not intended for use by through traffic, although there are exceptions. NON BITUMINOUS BASE COURSE WMM (WET MIX MACADAME) Wet Mix Macadam consistof laying spreadingand compactingof clean, crushed,well-graded granularmaterials on a prepared and approved Granularsub-Base.The material is well mixed with water and rolled to a dense mass.It shall be laid on one or more layers as per line and level, grade and cross section shown in the drawing or as directed by the Engineer.The thickness of single compacted Wet Mixed Macadam (WMM) Base shall not be less than 75 mm. Maximum thickness of single compacted layer base can be up to 250 mm upon approval of Engineer.
- 11. 1. Reference 2. Setting Out. 3. Selection of Material. 4. Equipments. 5. Methods of Operation. 6. QualityControl. 7. Work Safety. 8. Environmental Safety. 1. Reference :- I) Ministry of Road Transport& Highways Specifications II) Technical Specifications III) RelevantDrawings. IV) IS 2720 Codes. 2. Setting Out.:- After the layer of GSB Sub-Base has been approved,then line and level are carried out to fix the Wet Mix Macadam base layer (herein after called WMM Base). Pegs are fixed at regular intervals on the safe side of the road edge where blade of grader should not disturb the peg while blendingof the Base materials.On each peg’s top level of Base layer is marked. The chainage boards and working bench mark shall be set out side the limits of construction areas. 3. Selection of Material. :- 3.1 ) Aggregate
- 12. Coarse aggregate shall be crushed stone or crusherrun as per IRC 109 or clause 406.2.1 of MORT&H specification. 3.2) Physical requirement The constituents of the aggregates shall be produced by integrated crushing and screeningplant (Impact or Cone type) and,unless otherwise instructed by the Engineer,crushingshall be carried out in at least two stages. The fraction of material passingthrough 4.75mm sieve shall also be crusher run screeningonly. The aggregate shall conform to the physical requirements setforth in Table 400-12 ofMORT&H.or IRC 109 clause .If the water absorption value testof coarse aggregate is greater than 2 per cent, the soundness testshall be carried out on the materials delivered to site. 3.3) Grading Requirement The aggregate shall conform to the grading given in table 406.2.1.2 of technical specification or IRC 109 -2015.Material finer than 425 micron, shall have Plasticity Index(PI) less than 6. The final gradation approved within these limits shall be well graded from coarse to fine and shall not vary from low limit on one sieve to high limit of adjacent sieve or vice versa. 4. Equipments.:- 1. Wet Mix Macadam Plant 2. Dumper/ Tippers. 3. Vibro Roller (80 to 100 KN) 4. Water Tanker 5. Pavercapable of pavingmore than 9 meter width. 6. Survey kit / instrument 5. Methods of Operation.:-
- 13. 5.1) Provision of lateral confinement of aggregates Proper arrangementshall be made for the lateral confinementof wet mix during laying. This shall be done by laying materials on adjoining shoulderalongwith that of WMM layer. The preparation of mix, spreadingof mix and compaction are done sequentially. The sequence ofoperation shall be followed as described in clause: 406.3.3 of MORT&H. 5.2) Preparation of mix Wet mix Macadam shall be prepared in an approved WMM mixing plant havingprovision for controlled addition of water and forced/positive mixing arrangement.Optimum moisture for mixing shall be determined in accordance with IS: 2720 (Part 8) after replacing the aggregate fraction retained on 22.4 mm sieve with materials of passing from 22.4 and retained on 4.75 mm. While addingwater, evaporation loss shall also be taken into account. The mixed material should be uniformlywet and no segregation shall be permitted. 5.3) Spreading of mix Immediatelyafter mixing, the aggregate shall be spread uniformlyand evenlyupon the approved GSB layer. Materials should neitherbe dumped in heap nor their haulingover a partly completed stretch. The first layer will be laid by motor grader and the second layer mix shall be spread by a WMM paver finishercapable of pavingminimum 4.5m to 9.0m width. The layer may be tested by depth block during construction.No segregation of materials are allowed.The aggregates should be of uniform gradation with no pockets of fine materials. 5.4) Compaction After the mix has been laid on site to the required thickness,grade and camber, then compaction is carried out with suitable rollerto the full depth. For a thickness up to 200mm in a single layer, compaction shall
- 14. be done with vibratory roller of 80 to 100 KN static weights with plain drum or equivalentcapacity roller. Rollingis done from loweredge towards upper edge longitudinallyfor the portion havingunidirectional cross fall and superelevation. 5.5) Opening to traffic After testing the compaction & level of WMM course the road shall be allowed to dry for 24 hours. Preferablyno vehicular traffic should be allowed on the finished WMM surface till it has dried and covered with wearingcourse. 6. QualityControl. :- Table 400-12 Physical Requirementof coarse aggregate for Wet Mix Macadam for Sub-base/Base Courses 406 WET MIX MACADAM SUB BASE /BASE
- 15. Table 400-13: GradingRequirementof Aggregate for Wet Mix Macadam 1. Control Tests for GranularWMM Base: PostConstruction 2. Tolerance in Surface Level : +10 mm 3. permissible undulation(with 3 m straight edge) : 8 mm 4. no. of undulations permitted in any 300 m length, exceeding12 mm: 20 5. Control on quality of materials and works shall be in accordance to section 900 of MORT&H 7.Work Safety. :- 1.Safety will be provided location specific safety plan. 8. Environmental Safety. :- 1.NearbyStreams, water courses,lakes, reservoir shall be protected from contamination bythe soil erosion from areas exposed during excavation by constructing temporaryberms, dykes, sedimentBasins, slopes,drains & by the use of temporarymulches,seedingor other control devices. 2.Vehicles tracks shall be kept moist to preventflying of dust particles with the vehicle movement.
- 16. BITUMINOUS SURFACECOURSE PRIMECOAT DBM (DENSEBITUMINOUS MACADAM) TACK COAT BC (BITUMINOUS CONCRETE) a) PRIMECOAT:- A prime coat is an application of a low viscosity asphaltto a granularbase in preparation for an initial layer (or surface course layer) of asphalt.The purpose of the prime coat is; to coat and bond loose material particles on the surface of the base,to harden or toughen the base surface to provide a work platform for construction equipment,to plug capillary voids in the base course surface to preventmigration of moisture,and to provide adhesion between the base course and succeedingasphalt course.After applyingthe prime coat, it must cure for a minimum of 48-72 hours before asphaltis placed,with no rain in the forecast. There are four primary purposes for the application of a prime coat on an aggregate base course;.
- 17. 1-Coatand bond loose material particles on the surface of the base. 2-Harden or toughen the base surface to provide a work platform for construction equipment. 3-Plug capillary voids in the base course surface to prevent migration of moisture. 4-Provide adhesionbetween the base course and succeedingasphalt course. Prime coat penetrates b) DBM (DENSE BITUMINOUS MACADAM) :- The full-scale laying and compaction of Dense Bituminous Macadam shall be carried out with the help of approved material, and mix design proposed for the permanentworks using the Plants, Equipment,Machineryand approved methodology. Dense Bituminous Macadam (DBM) Construction
- 18. 1) Bitumen for DBM work :- PavingBitumen of penetration grade S- 65 complyingwith Indian Standard Specifications for Paving Bitumen IS:73 and Contract Technical Specification shall be used. 2) Specificationof Coarse Aggregates for DBM :- Coarse Aggregates shall be of crushed rock retained on the 2.36 mm sieve. Aggregates shall be as per specified in table 500-8,of MORTH for DBM and satisfy the physical requirements 3) Specificationof Fine Aggregates for DBM :- Fine Aggregates shall be of crushed stone passingon 2.36 mm sieve and retained on 75.00-micron sieve.It should be clean, hard, durable,dry and free from dust and soft or friable matter, organicand other deleterious matter.Fine Aggregates shall have a sand equivalent value of not less not than 50 when tested in accordance with IS:2720 part-37,and PI shall not exceed 4.0 when tested in accordance with IS:2720 part-5. This shall comply with the requirements as per clause 507.2.3 of MORTH. 4) FillerSpecification for DBM :- Filler shall conform to 507.2.4 of MORTH specification and consist of finely divided mineral matter such as cement,rock dust, hydrated lime. 5) The fillergradation limits forDBM :- IS Sieve % Passingby weight 600 micron 100 300 micron 95-100 075 micron 85-100 The filler material shall be free from organiccontaminants and have plasticity Indexnot greater than four. The plasticity index(PI)requirementshall not implementif the filler is cement or lime. AggregateGradation forDense BituminousMacadam :- The combined coarse,fine aggregates and filler shall satisfy the grading requirements as indicated in table 500-9 of MORTH.The
- 19. grading of the aggregate mix as used in work, shall be a smooth curve within and approximatelyparallel to the envelopein . Job Mix Design Requirementsfor Dense BituminousMacadam :- In addition to the grading and qualityrequirements of individual ingredients,the Job Mix shall meet the followingrequirements as per Table 500-10 ofMORT&H technical specification. The permissible variations of actual mix from the job mix design shall be within the specified limits of Table 500-13 of MORT&H specification. Prime Coat/ Tack Coat for Dense Bituminous Macadam :- It shall be Bitumen Emulsion of grade- CSS 1h as per ASTM D – 2397 from an approved source (As per clause 502.2.3 & 503.2.1 of Contract Technical Specification). Plants and Equipmentfor DBM Operation :-
- 20. Self-propelled Bitumenpressure sprayerequipped for spraying emulsionof 7000 ltr capacity – 01 No. Mobile Air compressor – 01 No. Hot Mix Plant of capacity 150 TPH -01 No. AutomaticSensorPaver – 01 No Smooth wheel Rollers,Cap 8 to 10 mt. dead wt – 02 Nos Pneumatictyre Rollers, Cap 12 to 15 mt. dead wt – 02 Nos. Tipper/Dumpers of capacity. 15 mt. – Adequate nos as per the site requirement Water Tanker,capacity – 10,000 lit – 1 No. Survey related accessories and equipment Other accessories as per the site requirements. Smooth wheel Rollers Site Trials for DBM :- The full-scale laying and compaction trials shall be carried out with the approved mix design of DBM materials proposed for the permanentworks using the Plants,Equipment,Machineryand
- 21. methods proposed.The trials shall be done with the consentand underthe supervisionof the Engineeror his representative. The trial shall be carried out to demonstrate the suitabilityof the Plants,Equipment,machineryand work procedures to provide and compact the material to the specified proportions,densityand voids content and to confirm that the other specified criteria of the finished AsphaltPavementcan be achieved.The trial length shall be for the full construction width and depth for the layer. The trial of pavementlayershall be undertaken ahead ofthe proposed work to commence full-scale work on that layer. Data to be recorded during the site trial of DBM :- Type and grade of bitumen used shall be recorded The composition and grading of the construction material, The temperature of bitumen and aggregate shall be recorded immediatelyprior to enteringthe mixer, and the temperature of the mix after discharge from the mixer prior to dispatch from the plant, on commencementof laying, on commencementof compaction and on completion of compaction. The type, mass, numberof wheels,frequencyof vibration and the numberof passes of the compaction equipment,as appropriate for each roller type. The per cent air voids in the mix at the lab, voids in mineral aggregate (VMA), voids filled with bitumen (VFB), stability and flow, The air voids achieved at site, the compacted thickness of the layer, per cent compaction achieved and any other important, relevantinformation as required by the Supervision Consultant. Surveys and Setting out Works for DBM :-
- 22. After completion of the Wet Mix Macadam layers as per the construction drawings,the limits of Dense Bituminous Macadam shall be marked as per established grid lines and Bench Marks etc. Preparation of Base for DBM :- Where DBM is to be laid over WMM surface, The tack coat shall be applied over the previouslyprimed surface or even previouslylaid Bitumen surface before laying of DBM in accordance with the provisions of clause 503 of MORTH The base on which DBM is to be laid shall be prepared, Edges Protection Work :- Edges on shoulderside or on the side where Kerb has not been provided shall be well protected and aligned by fixing angles of size 100 mm x 100 mm properly anchored.It shall be ensured that mix at edges is well compacted, and proper line and levels are maintained. c) TACK COAT:- Whatis tack coat :- Tack coat (also known as bond coat) is a light application of asphalt emulsion betweenhot mix asphaltlayers designed to create a strong adhesive bond withoutslippage.Heavierapplicationsmay be used under porous layers or around patches where it also functions as a seal coat. Why use tack coat :- Withouttack coat the asphaltlayers in a road way may separate which reduces the structural integrity of the road and may also allow water to penetrate the structure. What type of emulsion should be used for tack coats :- The type of emulsionused for tack coats varies from country to country. Normal practice in the USA is to use a slow-setting emulsion thatis diluted with water before application. Why use prime coat :-
- 23. Prime coats protect the integrity of the granular base during construction and help reduce dust. In the case of a base which is to be covered with a thin hot mix layer or a chip seal for a low volume roadway,priming ensures a good bond betweenthe seal and the underlyingsurface which otherwise would have a tendencyto delaminate. Why use asphaltemulsionprime :- Compared to cut back asphaltprimes, emulsion primes are environmentallyfriendlier. What type of emulsion is mostsuitable for emulsionprime :- Slow-settinggrades of asphaltemulsions (diluted with water before application)are suitable.With dense granularbases,or stabilized bases the surface may need to be broken up by scarifying before application,to ensure good penetration. d) BC (BITUMINOUS CONCRETE) :- Report Highlights Analysis is provided for the international markets including development trends, competitive landscape analysis, and key regions development status Development policies and plans are discussed as well as manufacturing processes and cost structures arealso analysed The report provides key statistics on the state of the industry and is a valuable sourceof guidance and direction for companies. Report Details The Global Bituminous Concrete Paver Sales Market Report 2016 is a professionaland in-depth study on the current state of the Bituminous Concrete Paver Sales industry. The report provides a basic overview of the industry including definitions, classifications, applications and industry chain structure. The Bituminous Concrete Paver Sales market analysis is provided for the international marketincluding development history, competitive
- 24. landscapeanalysis, and major regions’ development status. The report focuses on Global major leading industry players with information such as company profiles, productpicture and specification, capacity, production, price, cost, revenue and contact information. The report covers the development policies and plans as well as manufacturing processes and coststructures. This reportalso states import/export, supply and consumption figures as well as cost, price, revenue and gross margin by regions (United States, EU, Global and Japan), and other regions can be added. Types Of Roads :- 1.) Earthen Roads. 2.) Gravel Roads. 3.) Murrum Roads. 4.) Kankar Roads. 5.) WBM Roads. 6.) Bituminous Roads. 7.) Concrete Roads. Earthen Roads. :- The roads which are laid with the available soil at the site are called Earthen Roads.These are the cheapestroads amongall the roads.Earthen roads are designed for very low volume traffic. Available soil is laid in two-three layers and surface of the road is compacted with the rammer to expel the excess voids present in the soil. These roads are also called as temporary roads usuallylaid for movingconstructing vehicles while buildinga structure or for movingarmy vehicles during war times.
- 25. it is not recommendedto go with Earthen roads in monsoonas the soil may runoff during rain. Gravel Roads. :- Gravel roads are the second cheapest among all the types of roads and they are also better than Earthen roads. In this type of roads, the mixture of gravel and earth (available soil at the site) is paved on the surface and compacted. Gravel
- 26. roads are also called as metal roads. These types of roads are easilybuilt and generallylaid in villages. Murrum Roads. :- Murram is a gravelly lateritic material which is occurred during the disintegration of igneous rocks by weathering agencies. The roads which are laid using Murram as primary material is called as a Murram road. The density of murram is higher than the gravel which also provides good surface finish and compaction than above two types of roads. Kankar Roads. :-
- 27. The word Kankar is derived from India which means an Impure form of Limestone. This type of roads usually recommended at places having a good quantity of lime. Kankar road is one of the low-quality roads but better than Earthen roads and gravel roads. Water bound Macadam Roads (WBM). :- This type of road is also called as WBM road. The crushed stone (aggregate) is used as a base course. WBM roads are laid as layers. Aggregates are spread on the surface as a layer having 10cm thickness, water is sprinkled on each layer and then rolled for a better finish. These roads are better than the Murram, Earth and Kankar roads. In cities WBM is usually laid in pit holes. Bituminous Roads. :- The bituminous is a black viscous and adhesive material occurred during the distillation of petrol. Bituminous roads are
- 28. primarily used all over the world which is very easy to lay and provides smooth and good surface finish. The thickness of bitumen road depends upon the subgrade soil at the site. It is always recommended to lay the bitumen roads in two layers. Concrete Roads. :- The roads which are laid using the cement concrete material is called concrete roads. These are the costlier roads among all type of roads. This type of roads are recommended at the places of the high volume of traffic and it takes more time to construct the concrete roads as the concrete requires proper curing. The average life of a concrete road is 40 years whereas bituminous road has an average life of 3 years.
- 29. Roads Safety ( Cautionary Signs ) :- right hand curve : This sign cautions you about a Right Hand Curve on the road ahead. This helps you in maneuvering vehicle accordingly and nullifies the possibility of accident due to sudden appearance of turn. left hand curve :- This sign cautions you about a Left Hand Curve on the road ahead. This also helps you in maneuvering vehicle accordingly. You get time to slow your speed and set your eyes on the curve. It also reduces the possibility of accident due to sudden appearance of turn. Right Reverse Band :- This road sign indicates the actual design i.e., a sort of Z formation of the road ahead.It cautions the driver aboutthe
- 30. zigzag turn towards Right. The driver should reduce the speed at the sight of this sign and maneuverthe vehicle cautiously. Left Reverse Band :- This road sign indicates the actual design i.e., a sort of Z formation of the road ahead.It cautions the driver aboutthe zigzag turn towards Left. The driver should reduce the speed at the sight of this sign and maneuverthe vehicle cautiously. Steep Ascent :- This road sign indicates that there is steep ascent ahead and driver should get ready to climb and put the vehicle in relevantgear. Most of the times, these signs are found on hilly road where steep ascentand descentare normal part of travel. Steep Descent :- This road sign indicates that there is steep descent ahead and driver should get ready to descentby putting the vehicle in relevantgear. One should not try to speed up on descentas it loosens the grip on vehicle. Most of the times, these signs are found on hilly road where steep ascentand descentare normal part of travel.
- 31. Narrow Road Ahead :- When the width of the road decreases and the road merges into a narrow road, there is a possibilitythat a speeding vehicle may get collide with oncomingtraffic. This sign cautions the driver to be careful as the road ahead is narrow. Road Widens Ahead :- This sign signifies that the road ahead is wide. The width of the road widens after this sign and thus traffic should adjustaccordingly. Narrow Bridge :- Sometimes road converges to a bridge which is of less width than that of road. This sign is erected before such bridges which are narrowerthan the road. The driver should reduce the speed and watch for oncomingtraffic for safe drive. Slippery Road :- This sign indicates the slippery condition of the road ahead.This condition could be due to seepage of water or oil spill etc. The driver should invariablyslow down the vehicle at sight of this sign to avoid accident.
- 32. Cycle Crossing:- This road sign indicates that there is a cycle path intersectingthe major road. The driver should carefully cross this intersection as cyclist could cross the majorroad safety. Pedestrian Crossing :- Pedestrian is the king of traffic. This sign cautions the driver to eitherslow down or stop the vehicle and allow the pedestrian to cross the road. The part of road is also demarcated in white strips known as zebra crossing. At zebra crossing the Pedestrian has first right on the road. Men At Work :- This sign shows that there is some repair/cleaning etc.beingundertaken on the road and labouris involved in it. People working on road need safety from the traffic and hence this sign is erected before the site of repair on road. The driver should drive slowly and carefully by diverting to ensure the safety of labour. Cross Road : - This sign tells that there is a crossing of roads ahead. This sign advices that the vehicle should be slowed and intersection should be crossed cautiouslyby lookingon both sides.
- 33. This road sign depicts the actual formation of road ahead.The road is divided into two forming a shape of Y. This helps driver in managing the intersection carefully. Round About:- Round-Aboutis a substitute of a road intersection.It allows smooth flow of traffic without the aid of traffic lights. This sign indicates that there is a round-aboutaheadand the driver to take relevantlane well before maneuveringthe round-about. Roads Safety (Mandatory / Regulatory) Stop :- This is one of the most important and prominentRoad Sign. This sign indicates that Driver should immediatelystop. Usually Police,traffic and toll authorities use this signs at check posts. Give Way :- This is one of the most importantand prominent Road Sign. This sign indicates that Driver should immediately
- 34. stop. Usually Police, traffic and toll authorities use this signs at check posts. No Entry :- Certain pockets of an area or road are demarcated as no entry areas for traffic. This could be entry to a restricted area or no traffic zone. So the driver should obeyit and divert his route. One Way :- This indicates that the traffic flow is allowed in only one direction. The way beyond this sign restricts entry of the traffic however,the oncomingtraffic flow remains normal. All Motor Vehicles Prohibited :- This sign signifies that there should no movementof traffic in the designated area eitherfrom outside or within.This is used to decongestthe area.It is also used at pedestrian areas.
- 35. Pedestrians Prohibited :- This sign restricts the movementof pedestrian on road or the adjoiningarea.This could be lane for fast movingvehicles,highways etc. This could be installed at intersection where alternate crossingarrangements like underpass,footover bridge etc are there for crossing the road. Right Turn Prohibited :- This sign directs driver not to turn towards right side in any circumstance. Left Turn Prohibited : - This sign directs driver not to turn towards left side in any circumstance. U-Turn Prohibited :- This sign can be seen at some of the busy intersection on roads. The U turn at these intersections could result in major accidents or traffic jams.The driver should not violate this sign to avoid fine and any untoward incident. OvertakingProhibited :- With superhighways and advancement in automobiletechnologyspeed of vehicles has increased
- 36. manifold.With this overtaking has come as a maneuverto save time on road. But some place where the roads are narrow,at bridges, at turns Overtakingbecomes dangerous.At these place this sign is installed which prohibitovertakingensuringsafety. Speed Limit :- This sign designates the speed, as specified in the sign, of traffic on road. The limit specified must be invariable followed to avoid penal action and accidents on the road. Length Limit :- This sign on road indicates that length of the vehicle, which can be maneuveredthrough that passage.It could be a sharp turn, a hairpin bend etc. This is meantfor long and oversized vehicle,which cannotnegotiate a safe turn. CompulsoryCycle Track :- This indicates that the traffic flow is allowed in only one direction. The way beyond this sign restricts entry of the traffic however,the oncomingtraffic flow remains normal.