Breastfeeding Benefits and Techniques
- 2. Breastfeeding is the best natural feeding and breast milk is best milk. The basic food of infant is mother's milk. Breastfeeding is the most effective way to provide a baby with a caring environment and complete food. INTRODUCTION
- 3. It meets the nutritional as well as emotional and psychological needs of the infant. Recently there is tendency to replace the natural means of infant feeding and introduction of breast milk substitutes Breastfeeding deserves encouragement from all concerned in the welfare of children.
- 4. INCIDENCE RATE UNICEF stated that every year over one million infants die and millions of others are impaired, because they are not adequately breastfed. Everyday between 3000 to 4000 infants die from diarrhea and acute respiratory infections because the ability to feed them adequately has been taken
- 5. Family and Community Benefits Maternal Benefits Psychological Benefits Protective Value Digestibility Nutritive Value A D V A N T A G E S Advantages of Breastfeeding
- 6. • Breastfeeding is the safest, cheapest and best protective food for infants. • Superiority of human milk is due to its superior nutritive and protective value. • It is perfect food for infants and provides total nutrient requirements for the first six months of life. Advantages of Breastfeeding
- 7. NUTRITIVE VALUE • Breast milk contains all the nutrients in the right proportion which are needed for optimum growth and development of the baby up to 6 months. • It is essential for brain growth of the infant because it has high percentage of lactose and galactose which are important components of galactocerebroside. • It facilitates absorption of calcium which helps in bony growth.
- 8. • It contains amino acids like taurine and cysteine which are important as neurotransmitters. • Breast milk fats are polyunsaturated fatty acids which are necessary for the myelination of the nervous system. • It has vitamins, minerals, electrolytes and water in the right proportion for the infant which are necessary for the maturation of the intestinal tract.
- 9. • It provides 66 calories per 100 mL and contains 1.2 g protein, 3.8 g fat, 7 g lactose and vitamin A 170 to 670 IU, vitamin C 2 to 6 mg, vitamin D 2.2 IU, calcium 35 mg, phosphorus 15 mg in 100 mL. • The total amount of milk secretion per day is about 600 to 700 mL, which is sufficient for the baby. • Its composition is ideal for an infant. • It provides specific nutrition for preterm baby in preterm delivery.
- 10. DIGESTIBILITY • Breast milk is easily digestible. • The proteins of breast milk are mostly lactoalbumin and lactoglobulin which form soft curds that is easy to digest. • The enzyme lipase in the breast milk helps in the digestion of fats and provides free fatty acids.
- 11. PROTECTIVE VALUE • Breast milk contains IgA, IgM, macrophages, lymphocytes, bifidus factors, unsaturated lactoferrin, lysozyme, complement and interferon. • Thus, breastfed baby is less likely to develop infections especially gastrointestinal and respiratory tract infections, e.g. diarrhea and ARI.It also provides protection against malaria and various viral and bacterial infections like skin infections, septicemia, etc.
- 12. • Breastfeeding protects the infant from allergy and bronchial asthma. • It also protects against neonatal hypocalcemia, tetany, necrotizing enterocolitis, deficiencies of vitamin E and zinc, neonatal convulsions and sudden infant death syndrome. • Exclusive breastfeeding baby has less chance of developing malnutrition, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, arteriosclerosis, ulcerative colitis, appendicitis, • childhood lymphoma, liver disease; celiac disease and dental caries.
- 13. PSYCOLOGICAL BENEFITS • Breastfeeding promotes close physical and emotional bondage with the mother by frequent skin-to-skin contact, attention and interaction. • It stimulates psychomotor and social development. • It leads to better parent child adjustment, fewer behavioral disorders in children and less risk of child abuse and neglect. • Breastfeeding promotes development of higher intelligence and feeling of security in infant.
- 14. MATERNAL BENEFITS • Breastfeeding reduces the chance of postpartum hemorrhage and helps in better uterine involution. • Lactational amenorrhea promotes in recovery of iron stores. • It can protect from pregnancy for first 6 months if exclusive breastfeeding is carried out.
- 15. • Breastfeeding improves metabolic efficiency and satisfaction with sense of fulfilment of the mother. • It reduces the risk of breast and ovarian cancer of the mother. • It improves slimming of the mother by consuming extra fat which accumulated during pregnancy.
- 16. • It is more convenient and time saving for the mother. • Mother can provide fresh, pure, readymade, clean uncontaminated milk to her baby at right temperature without any preparations. • Mother feels comfortable to feed the baby especially at night.
- 17. FAMILY AND COMMUNITY BENEFITS • Breastfeeding is economical in terms of saving of money, time and energy. • Family has to spend less on milk, health care and illness. • Community expenditure on health care and contraception are reduced. • It is economic for the families, hospitals, communities and for countries.
- 18. PREPARATION FOR BREASTFEEDING In the antenatal period, examination of breast and identification of problems, like retracted nipple should be done with necessary advice for interventions. Preparation for breastfeeding must begin in the antenatal period.
- 19. Adequate diet in prenatal period should be consumed in terms of energy and nutrients. Prevention of micronutrient deficiencies, rest, regular exercise, hygienic measures, etc. should be advised for better health in antenatal period.
- 20. • Antenatal counseling, family support, mother support group also should be emphasized as the preparation of mothers for breastfeeding. • Mother should be psychologically prepared to feed her baby immediate after birth.
- 21. INITIATION OF BREAST FEEDING • Breastfeeding should be initiated within first half an hour to one hour of birth or as soon as possible. • It should also be initiated within one hour even after cesarean section delivery, if the mother and baby, both are having no problem.
- 22. CONTI…. • Early suckling provides warmth, security and 'colostrum, the baby's first immunization. • Although little in amount, the first milk, colostrum, is most suitable and contains a high concentration of protein and other nutrients, the baby needs. • It is rich in anti-infective factors and protects the baby from respiratory infections and diarrheal diseases.
- 23. • Mothers should be demonstrated about the techniques of breast feedings. • Rooming-in or bedding-in should be done with infant and mother as soon as possible to prevent separation.
- 24. Mother should be advised for exclusive breastfeeding up to 6 months and as demand feeding. No food or drink other than breast milk should be given to neonates. No water, glucose water, animal milk, gripe water, indigenous medicines, vitamins and minerals drops or syrup should be given. No bottle and pacifier are allowed. In case of preterm babies or sick babies, being in special care unit, they should be fed with expressed breast milk EBM). Nursing staff is responsible to ensure that nothing except breast milk is given.
- 25. Mother should be instructed to assess the indicators of adequacy of breastfeeding and importance of increasing her own dietary intake with extra 550 cal and to drink fluids in response to her thirst. Rest and relaxation of mother are important for recovery from delivery and successful lactation in postnatal period
- 26. INDICATORS OF ADEQUACY OF BREASTFEEDING Audible swallowing sound during the feed Let down sensation in mother's breast Breast is full before feed and softer afterward Wet nappies 6 or more in 24 hours Frequent soft bowel movements, 3 to 8 times in 24 hours Average weight gain of 18 to 30 g/day Baby sleeps well and does not cry frequently Baby has good muscle tone and healthy skin
- 27. Note: Passage of urine 6 to 8 times per day and average weight gain are considered as most important criteria.
- 28. DIFFERENT COMPOSITION OF BREAST MILK Transitional Milk Colostrum Mature Milk Preterm Milk Hindmilk Foremilk
- 29. Colostrum • It is secreted during first three days after delivery. • It is thick, yellow and small in quantities. • It contains more antibodies and cells with higher amount of proteins and fat-soluble vitamin (A, D, E, K). • It is sufficient and protective for the baby and should not be discarded. Transitional Milk • It follows the colostrum and secretes during first two weeks of postnatal period. • It has increased fat and sugar content and decreased protein and immunoglobulin content.
- 30. Mature Milk • It is secreted usually from 10 to 12 days after delivery. • It is watery but contains all nutrients for optimal growth of the baby. Preterm Milk • The breast milk secreted by a mother who has delivered a preterm baby is different from milk of a mother who has delivered a full-term baby. • This milk contains more proteins, sodium, iron, immunoglobulins and calories appropriate for the requirements of the preterm neonates.
- 31. Foremilk • It is secreted at the starting of the regular breastfeeding. • It is more watery to satisfy the baby's thirst and contains more proteins, sugar, vitamins and minerals. Hindmilk • It is secreted towards the end of regular breastfeeding and contains more fat and energy. • The mother should feed the baby allowing one breast to empty to provide both foremilk and hindmilk, before offering other breast. • For optimum growth and to fulfil adequate fluid and nutritional requirements, both foremilk and hindmilk are needed for the baby.
- 32. TECHNIQUE OF BREASTFEEDING • Mother should be comfortable and relaxed physically and mentally before giving breastfeed. • She should wash her hands and can have a glass of water or milk. • Mother should have no due work in her hands. • Baby should be cleaned and dried before feeding; otherwise baby may feel discomfort or may non-cooperate during feeding.
- 33. Correct positioning of mother and baby is an important aspect of successful breastfeeding. Mother can be in sitting or side lying position
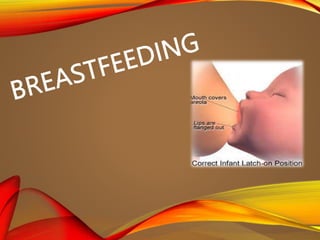
- 34. • Even mother can be lying flat with infant on top of the mother, especially following lower uterine cesarean section (LUCS) delivery. • Baby should be supported by the mother's forearm in slight head elevated position and with head, neck and back in a straight line. • Baby should be hold close to mother with trunk-to-trunk in touch and facing towards breast • After proper positioning, when baby's chin touches the breast, cheek touches the nipple; baby will open the mouth in 'rooting reflex.
- 35. • Then the baby will be quickly moved on to the breast with the lower lip below the nipple; so that the nipple and most of the areola go into the baby's mouth. • The suckling of breast stimulates the 'milk secretion or prolactin reflex' which promotes the milk production and secretion. • Then by the 'milk ejection or oxytocin reflex', milk flows out from the glands into the lactiferous sinuses and ducts and then to the baby's mouth. • When baby suckles again and again in regular slow deep sucks with good 'sucking reflex, the adequate milk flows out and then baby's cheeks become full with milk.
- 37. • The mother may hear the swallowing sound and does not feel pain in the nipple. • All these indicate favorable signs of good attachment or latching and breastfeeding. • The baby should have good 'swallowing reflex' to take adequate feed with sufficient flow of milk. • Baby's rooting, sucking and swallowing reflexes help the baby to take secreted milk from the breast successfully • If the baby falls asleep after few sucks, mother should arouse the baby by gentle tap behind the ear or on the sole of the foot.
- 38. • Initially breastfeeding can be given at 1 to 2 hours interval and then on 'self-demand' by the baby. • A baby usually cries when feel hungry and then must be put into the breast. • Duration of feeding should be continued till the baby is satisfied. • The duration of sucking depends upon the vigor of the baby and on the 'let-down reflex. • One breast should be emptied completely before starting with another breast.
- 40. • Next feeding should be started with opposite breast, i.e. which was fed last in the previous feeding. Burping to be done gently. • It is usually not necessary, if the baby is having good latching and attachment during feeding which prevent air entry into the baby's mouth. • Baby should be placed on right side after feeding. Usually the baby falls asleep. Mother should make the baby dry and comfortable. • Breastfeeding should be continued exclusively up to 4 months of age or preferably may be up to 6 months if adequate breast milk is available.
- 42. • The baby should be given only breast milk and nothing else, not even water for first 4 months of life, even in summer months. • Frequent suckling helps to have adequate amount of milk for the baby. • Complementary foods can be started at 6 months, exact age may vary, but breastfeeding should be continued up to 2 years of age or beyond and especially at night. • Mother should maintain hygienic measures, take daily bath and wash her breast during bath and wear clean blouse during this period to prevent contamination of breast milk.
- 43. CONTRAINDICATIONS OF BREASTFEEDING • The true contraindications of breastfeeding are galactosemia and phenylketonuria. • Maternal conditions which can be considered as 'REAL' contraindications are Radiotherapy, Ergot therapy, Antimetabolites therapy and Lithium therapy. • Maternal illness should not result in interruption of breastfeeding. Expressed breast milk (EBM) can be given to the baby, whenever needed, from the mother or mother's substitute.
- 46. THE BABY WHO DOES NOT SUCKLE • No unneeded drugs to be given to breastfeeding mothers • No artificial food or water to be given to the baby. • Breastfeeding to be given when the baby is alert and ready. • Milk to be expressed into the nipple just prior to feed the baby. • Nipple should be placed slightly upward towards the roof of the baby's mouth. • Keeping the baby's nose free during breastfeeding.
- 47. THE BABY WHO DOES NOT SUCKLE • Baby should be hold in comfortable position with good attachment to the breast and should be kept dry and warm. • Avoiding pressure on potentially painful areas during feeding. • Express breast milk to maintain lactation in both breasts. • Allowing the baby to feed only one breast.
- 48. INVERTED NIPPLES • Treatment should be started after birth of the baby. The nipple is manually stretched and rolled out several times a day. • A pump or a plastic syringe (10 mL) is used to draw out the nipple and the baby is then put to the breast • Precautions should be taken to prevent injury of breast and nipple during the traction with the syringe.
- 49. SORE NIPPLE • Correct positioning and latching of the baby to the breast. • Frequent washing with soap and water should be avoided. • Baby should not be pull off the breast while still sucking. • Hindmilk to be applied to the nipple after a feeding. • Nipples should be aired and allowed to heal in between feeds.
