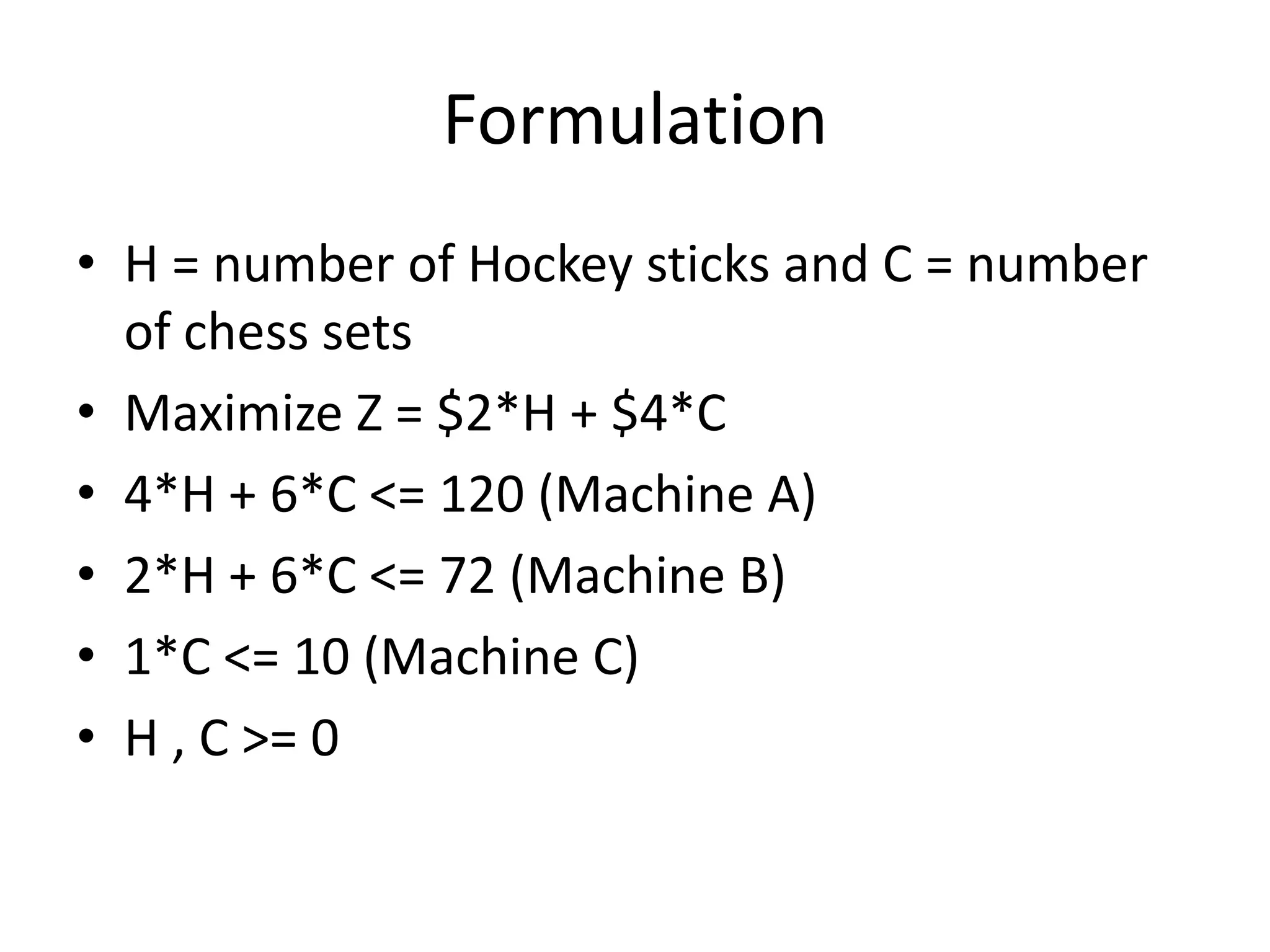
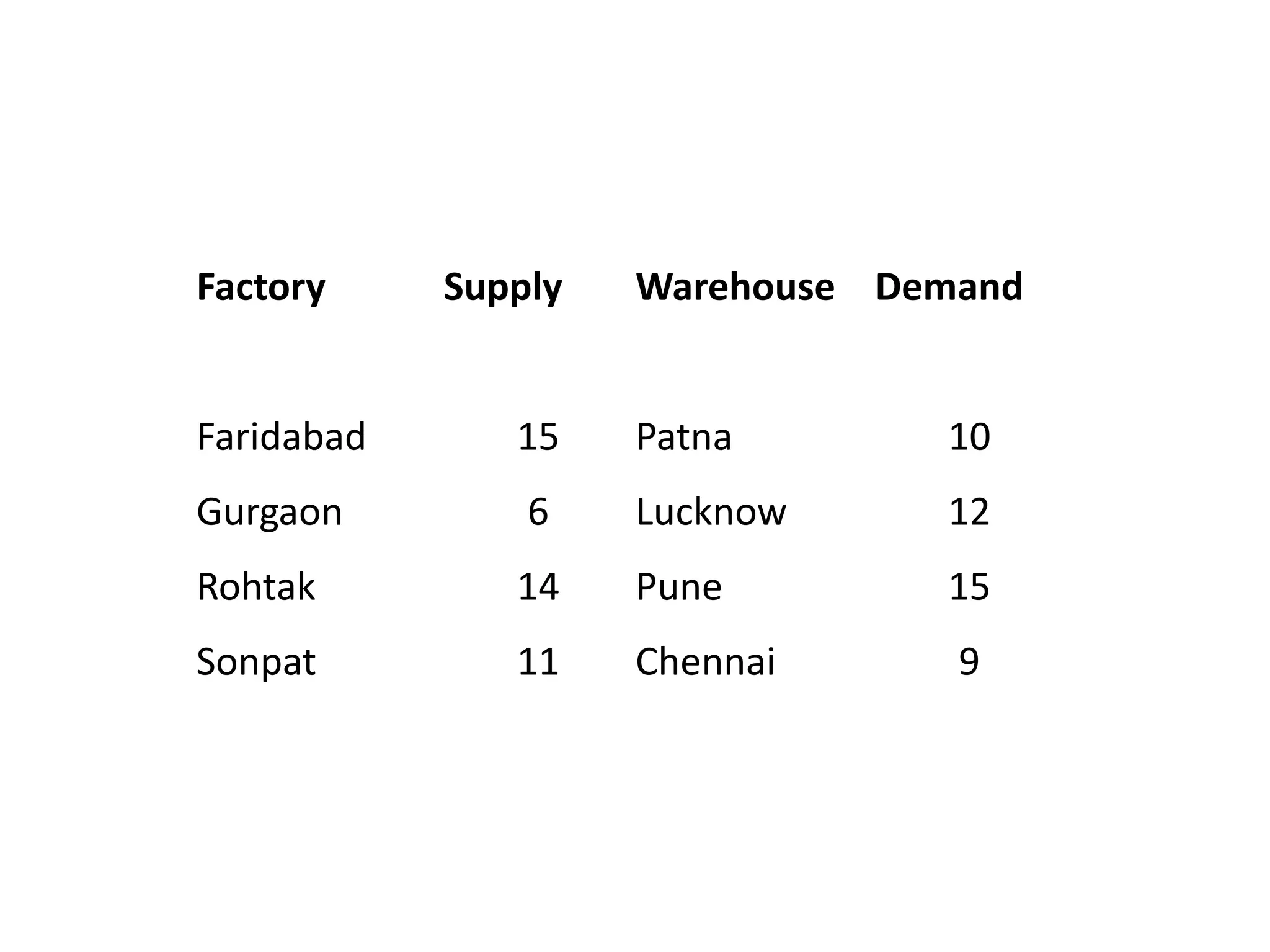
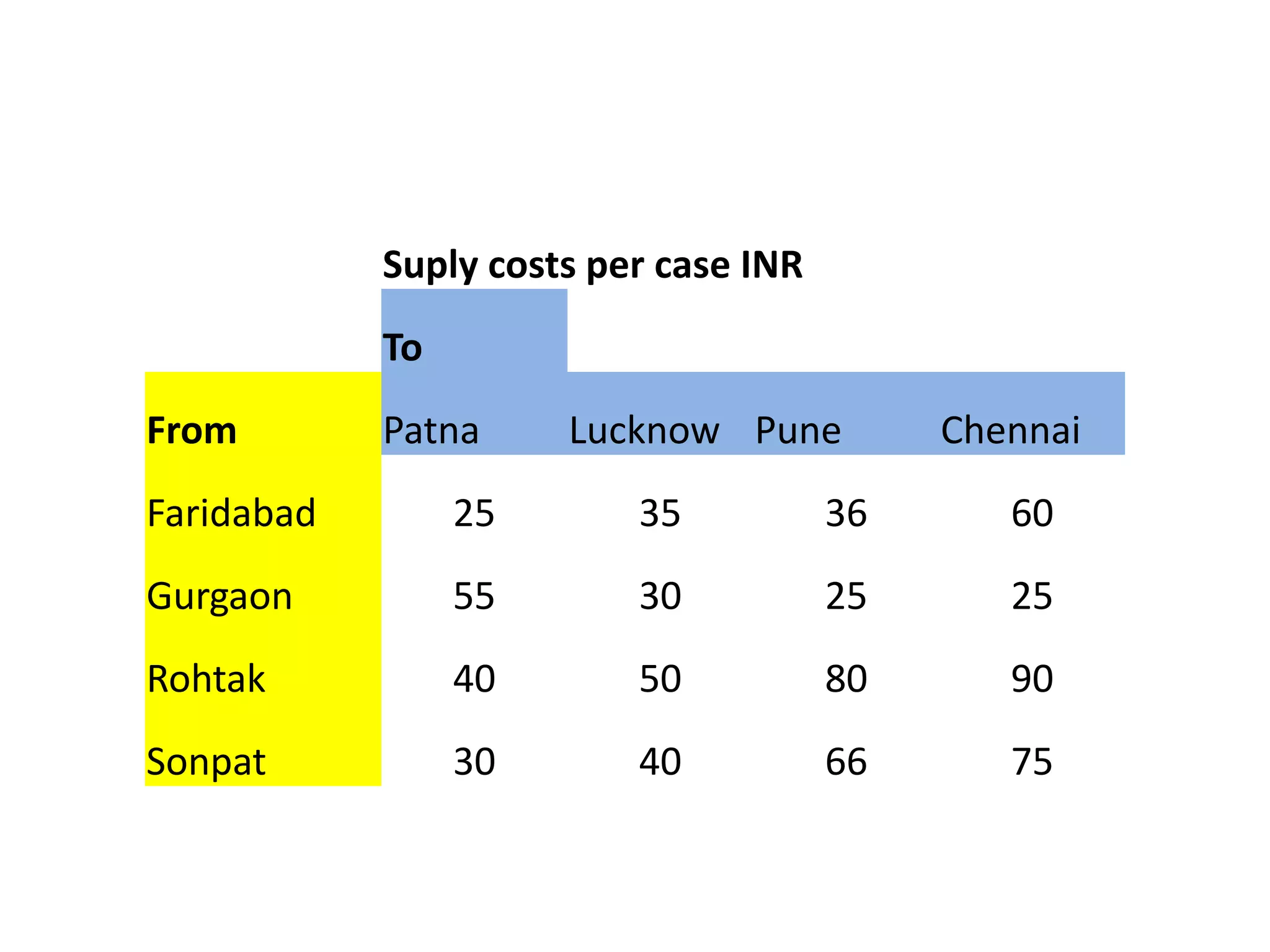
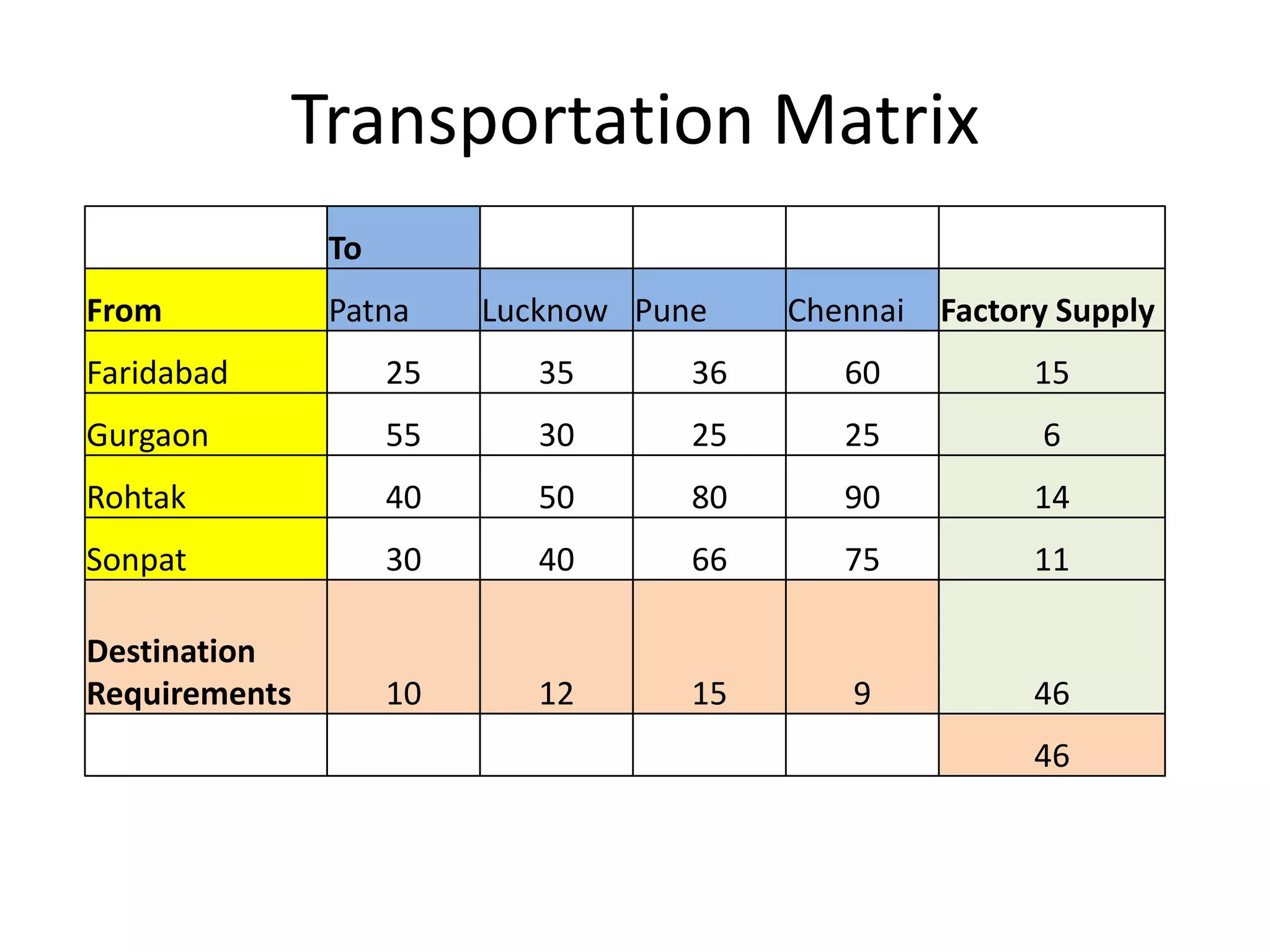
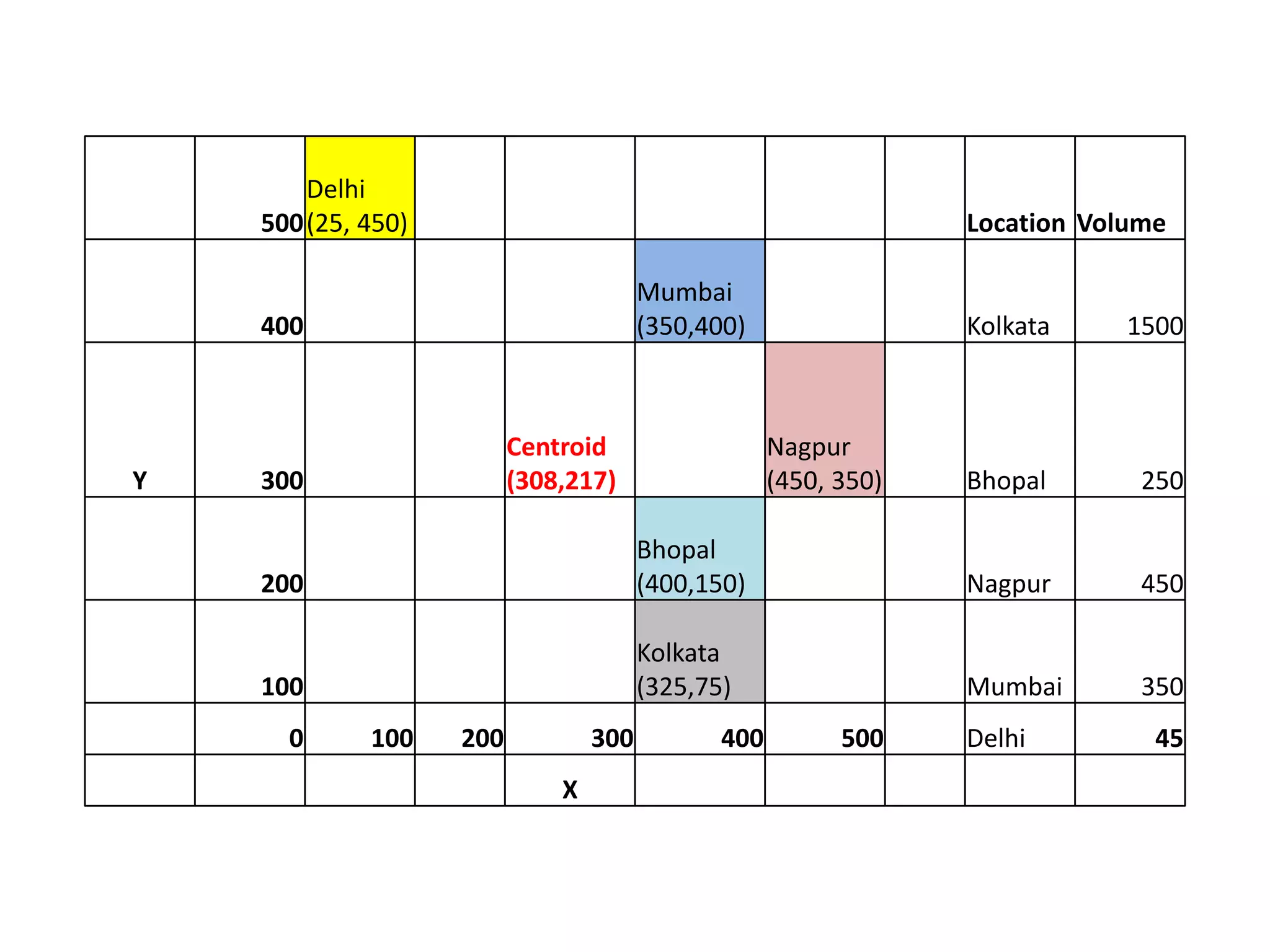
The document describes linear programming and transportation problems. It provides an example of using linear programming to optimize production at a company making hockey sticks and chess sets given machine capacity constraints. It then describes how transportation problems can be formulated as a special case of linear programming to minimize shipping costs given supply, demand, and per-unit shipping costs. The document includes a numerical example of solving a transportation problem to allocate supply across multiple destinations to meet demand at lowest cost.