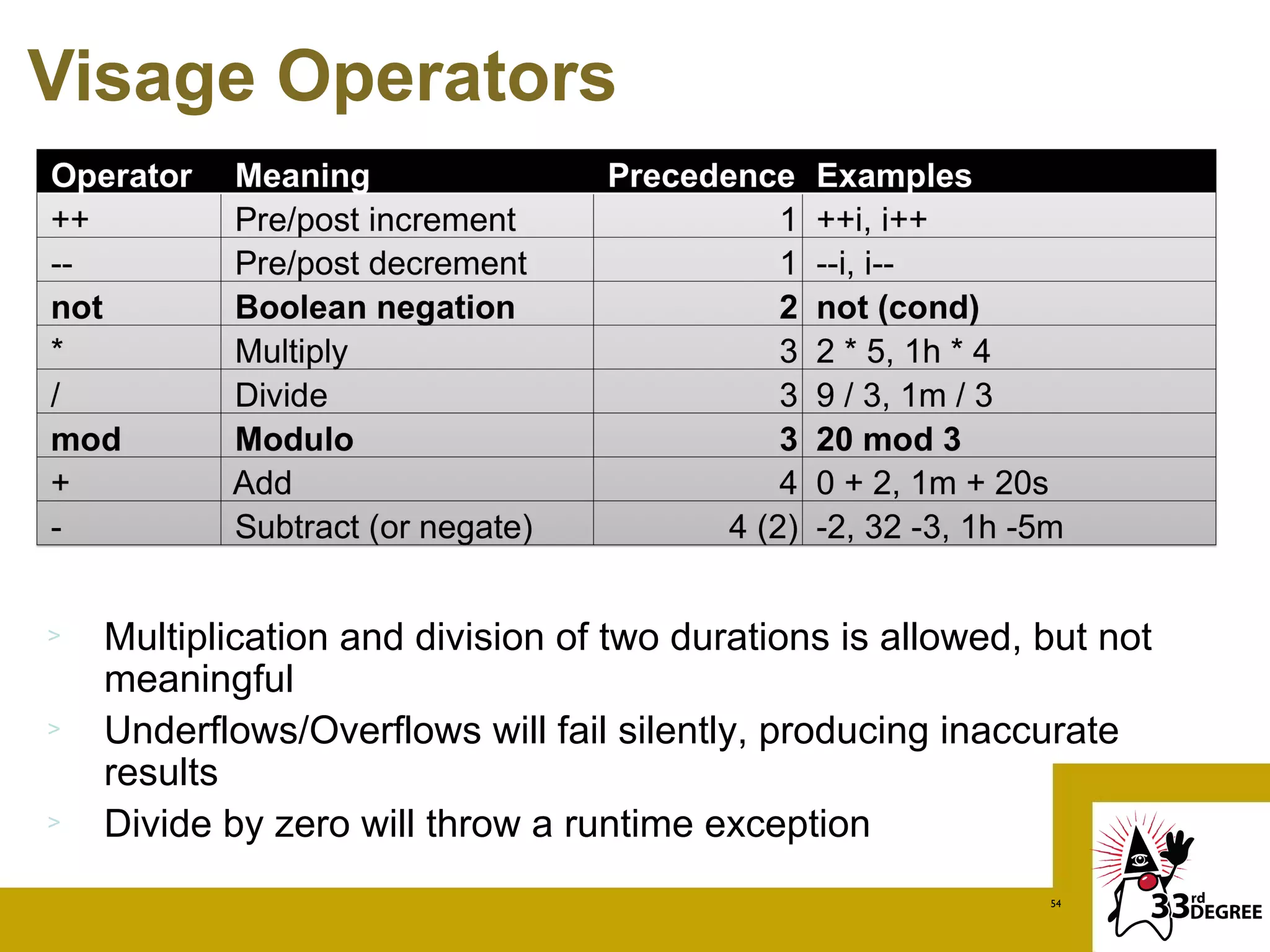
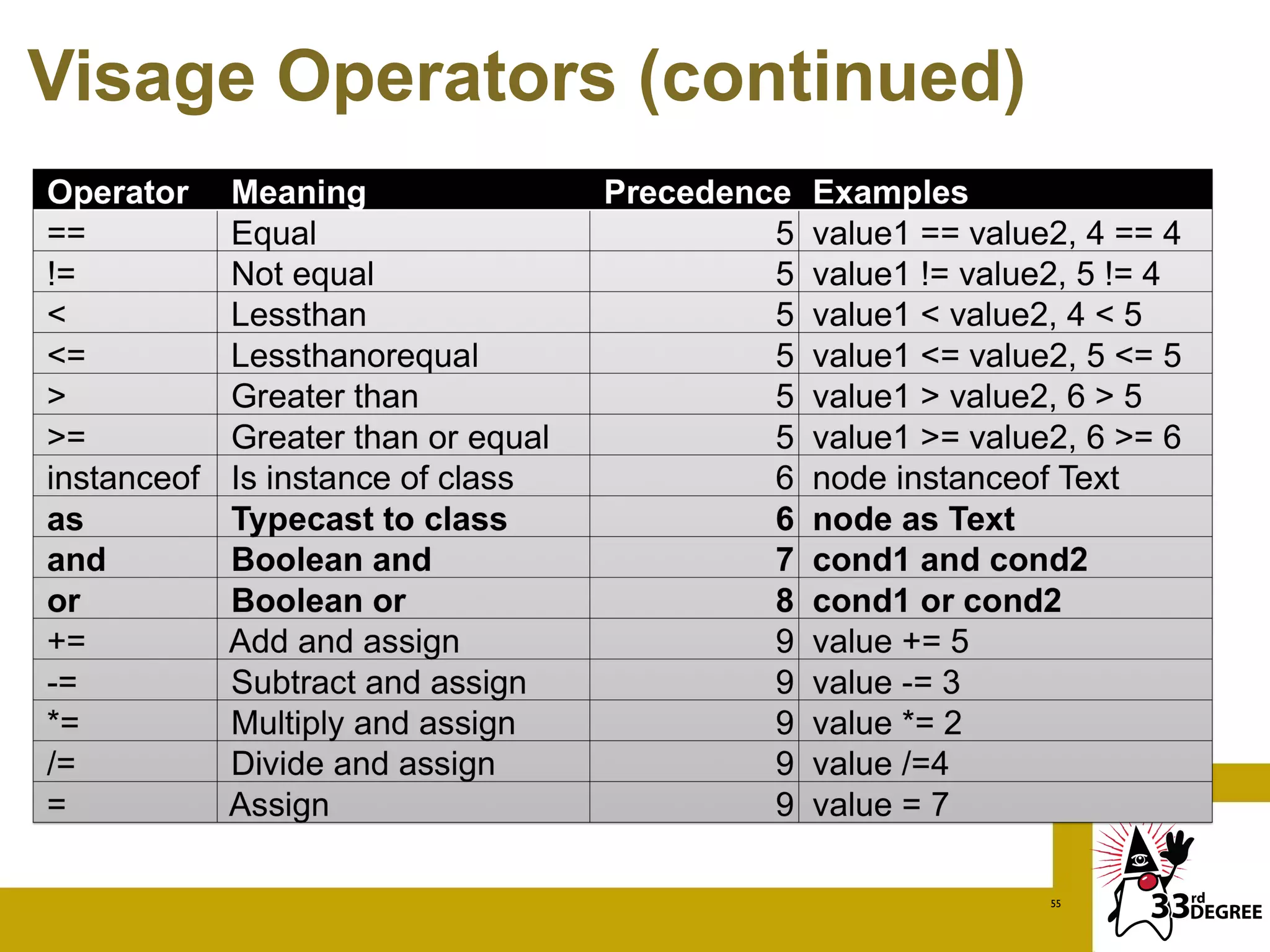
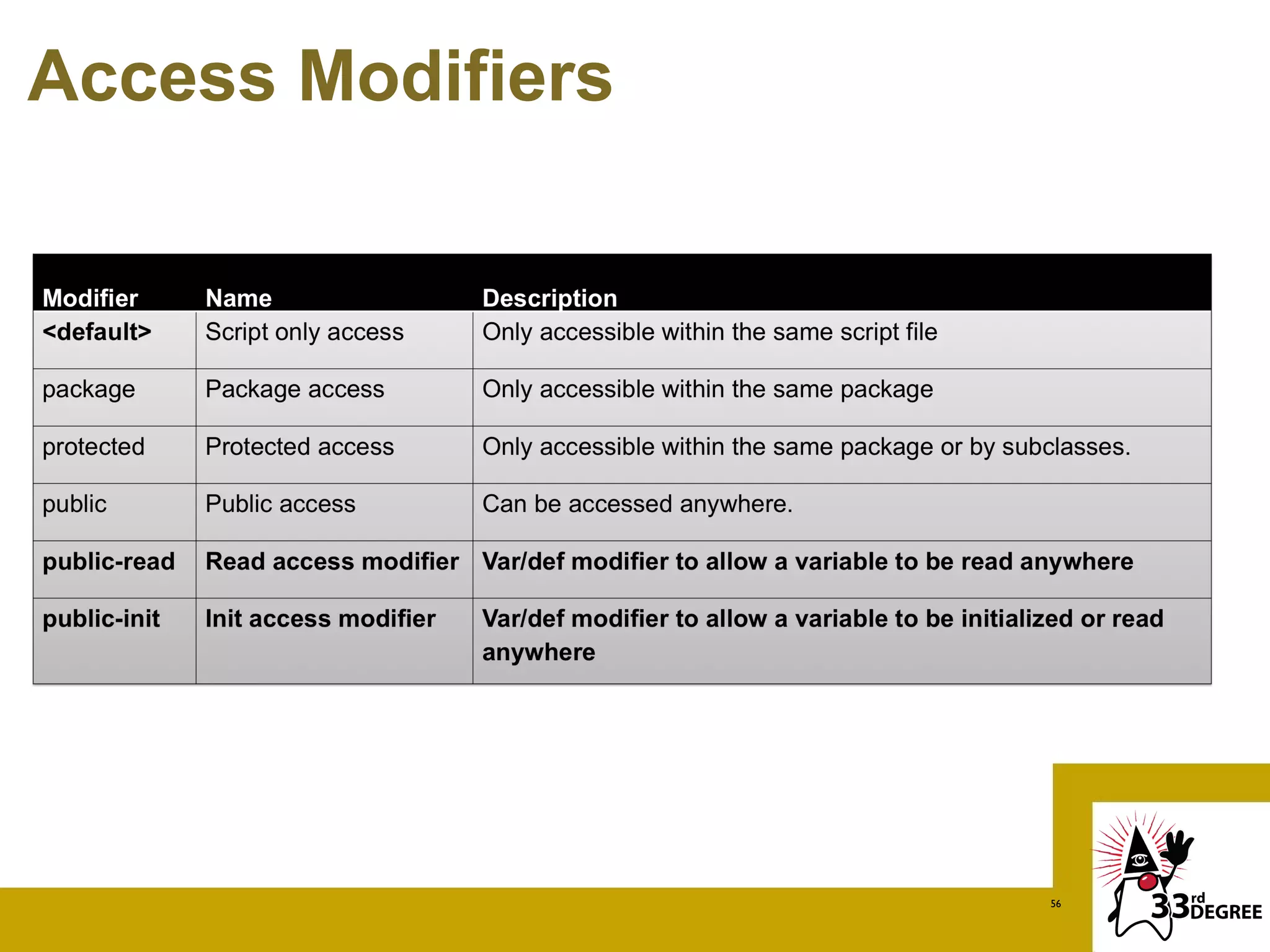
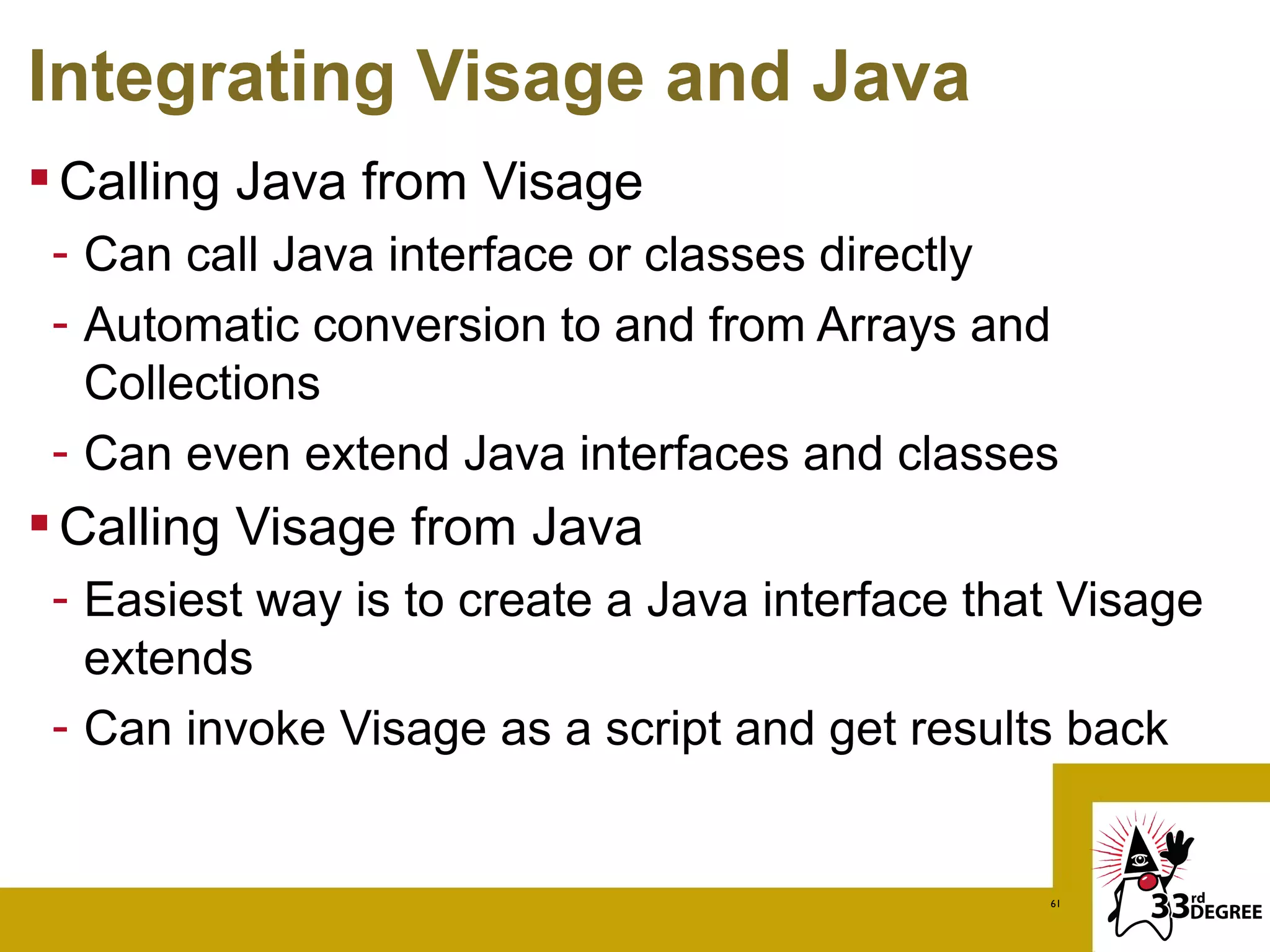
The document discusses the Visage programming language, a domain-specific language designed for creating user interfaces, particularly for JavaFX and Vaadin platforms. It showcases examples of Visage syntax, data binding, and how Visage integrates with Android and Java, highlighting its unique features such as automatic UI updates and rich control integration. Additionally, it covers advanced topics like creating sequences and accessing Java methods within Visage.






![Java vs. Visage DSL
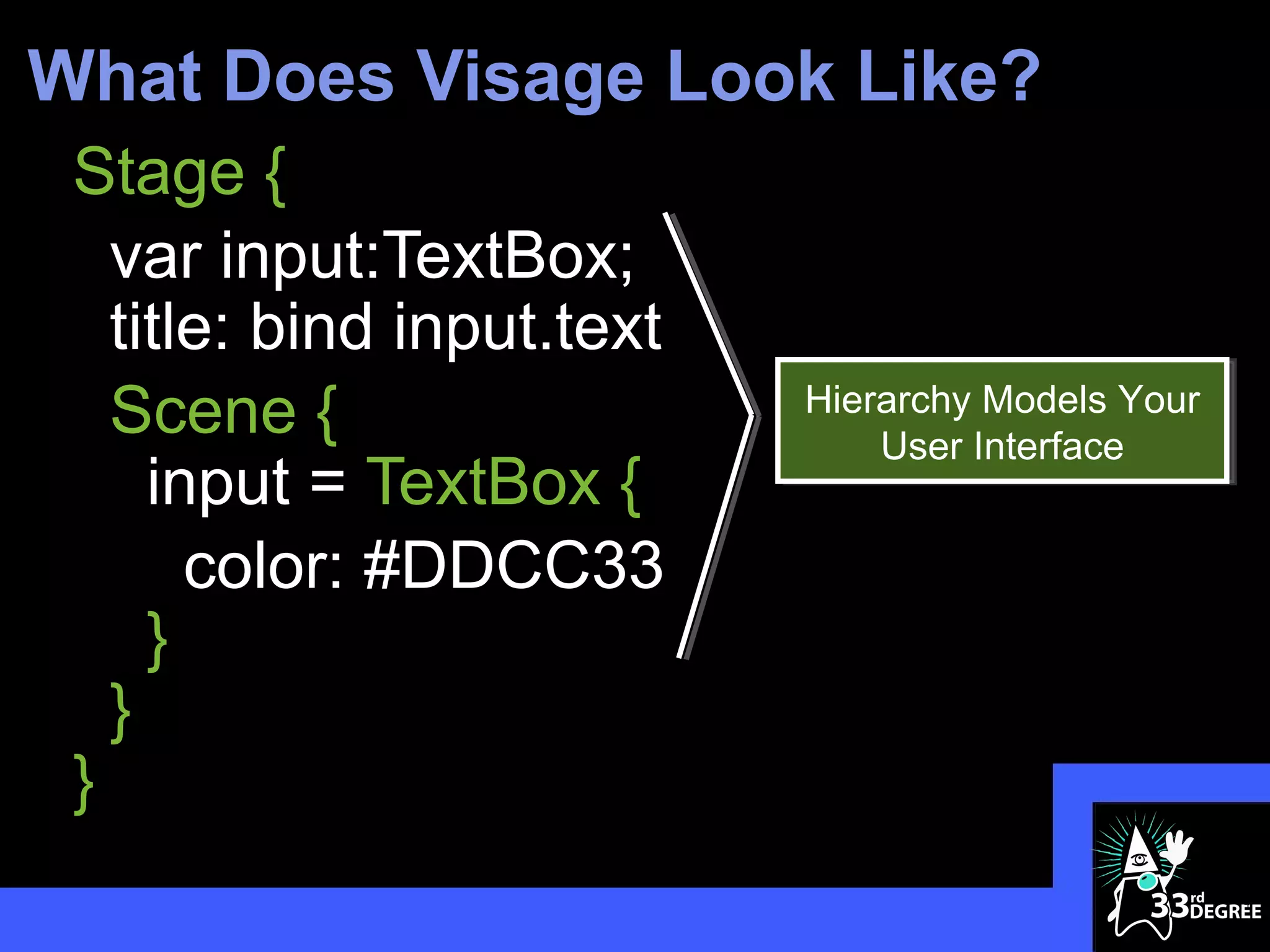
var circles:Circle[];
ublic class VanishingCircles extends Application { Stage {
title: "Vanishing Circles"
Scene {
public static void main(String[] args) { width: 800
height: 600
Application.launch(args); fill: BLACK
Group {
} circles = for (i in [1..50]) {
def c:Circle = Circle {
centerX: random() * 800
centerY: random() * 600
@Override radius: 150
fill: color(random(), random(), random(), .2)
public void start(Stage primaryStage) { effect: BoxBlur {
height: 10
primaryStage.setTitle("Vanishing Circles"); width: 10
iterations: 3
40 Lines
Group root = new Group();
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 800, 600, Color.BLACK);
}
35 Lines
stroke: WHITE
strokeWidth: bind if (c.hover) 5 else 0
1299 Characters 487 Characters
onMouseClicked: function(e) {
List<Circle> circles = new ArrayList<Circle>(); Timeline {at (3s) {c.radius => 0}}.play()
}
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { }
}
final Circle circle = new Circle(150); }
}
circle.setCenterX(Math.random() * 800); }
circle.setCenterY(Math.random() * 600); Timeline {
for (circle in circles) at (40s) {
circle.setFill(new Color(Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), .2)); circle.centerX => random() * 800;
circle.centerY => random() * 600
circle.setEffect(new BoxBlur(10, 10, 3)); }
}.play()
circle.addEventHandler(MouseEvent.MOUSE_CLICKED, new
EventHandler<MouseEvent>() {
public void handle(MouseEvent t) {
KeyValue collapse = new KeyValue(circle.radiusProperty(), 0);
new Timeline(new KeyFrame(Duration.seconds(3), collapse)).play();
}
});
circle.setStroke(Color.WHITE);
10
circle.strokeWidthProperty().bind(Bindings.when(circle.hoverProperty())](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-10-2048.jpg)
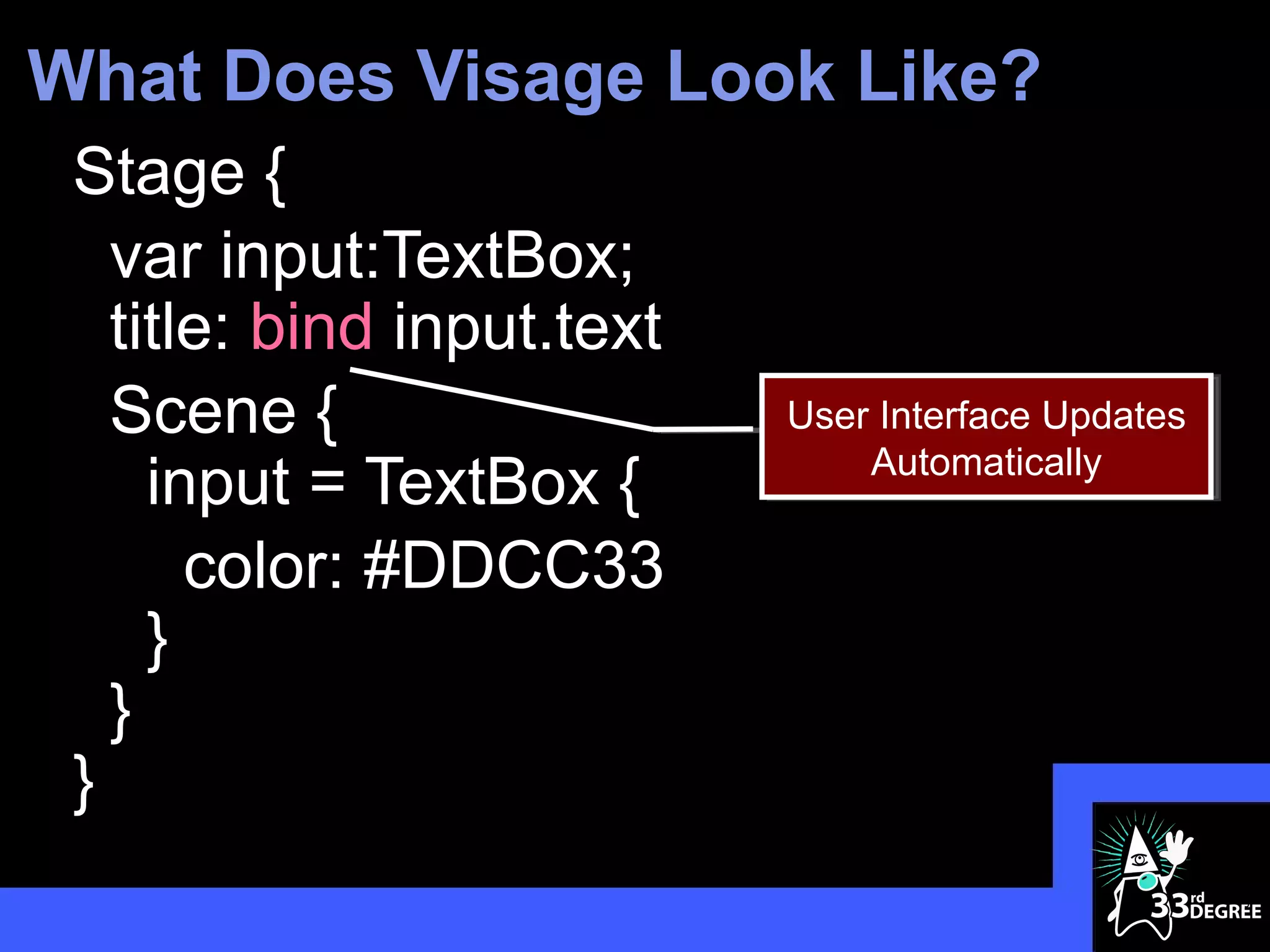
![How about JavaFX on… Visage
Stage {
title: "Vanishing Circles"
scene: Scene {
width: 800
height: 600
fill: BLACK
content: Group {
circles = for (i in [1..50]) {
Circle {
centerX: random() * 800
centerY: random() * 600
}
}
}
}
}
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-11-2048.jpg)
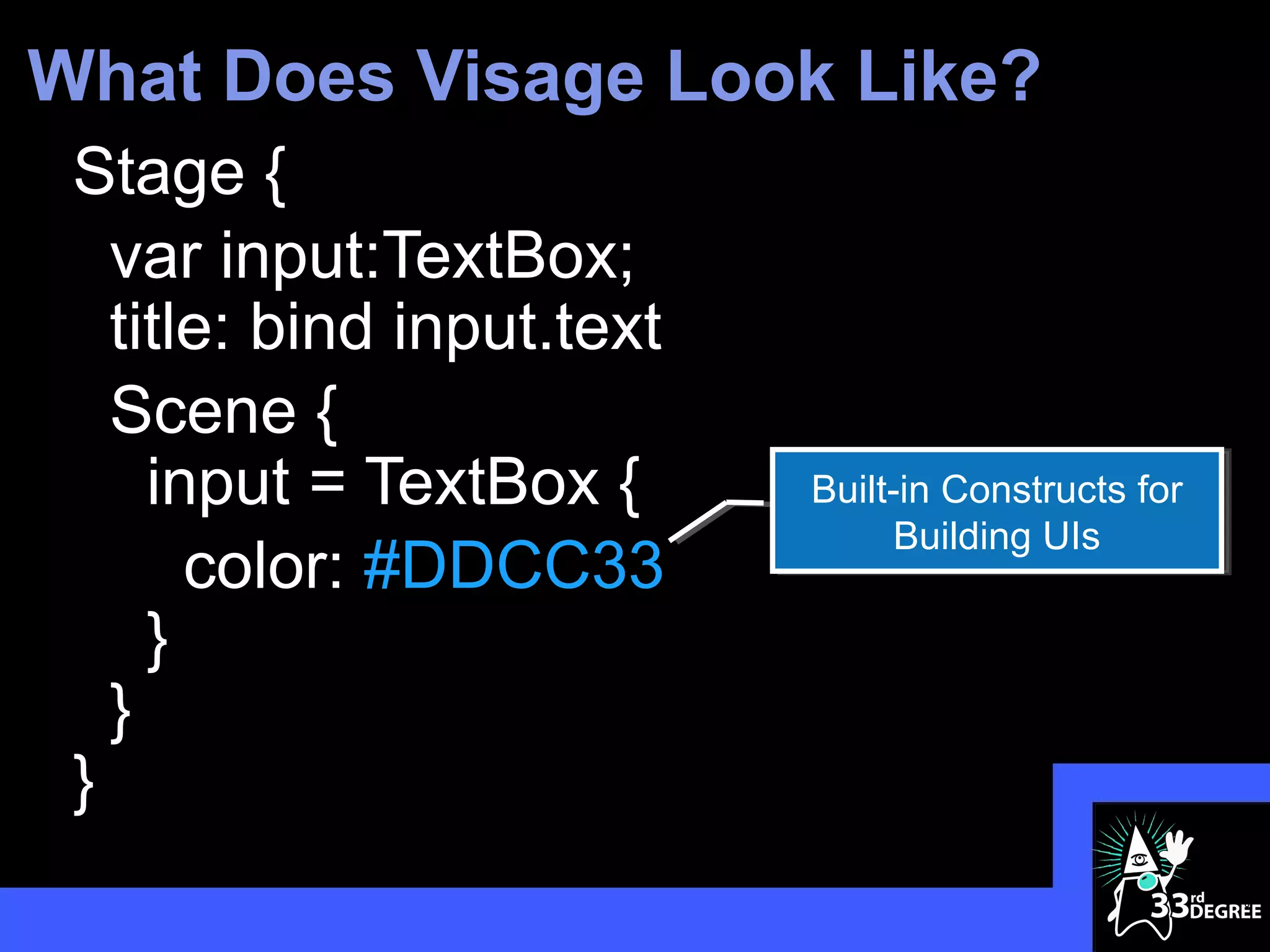
![How about JavaFX on… Visage
Stage {
title: "Vanishing Circles"
scene: Scene {
width: 800
height: 600
fill: BLACK
content: Group {
circles = for (i in [1..50]) {
Circle {
centerX: random() * 800
centerY: random() * 600
}
}
}
}
}
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-12-2048.jpg)
![How about JavaFX on… Visage
Stage {
title: "Vanishing Circles"
Scene {
width: 800
height: 600
fill: BLACK
Group {
circles = for (i in [1..50]) {
Circle {
centerX: random() * 800
centerY: random() * 600
}
}
}
}
}
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-13-2048.jpg)

![Visage is JavaFX Script++
Default Parameters
New Literal Syntax For:
- Angles – 35deg, 4rad, 1turn
- Colors – #DDCCBB, #AA33AA|CC
- Lengths – 5px, 2pt, 3in, 4sp
Null-check Dereference
- var width = rect.!width
Built-in Bindable Maps (coming soon!)
- var fruitMap = ["red" : apple, "yellow" : banana]
- var fruit = bind fruitMap["red"]
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-15-2048.jpg)





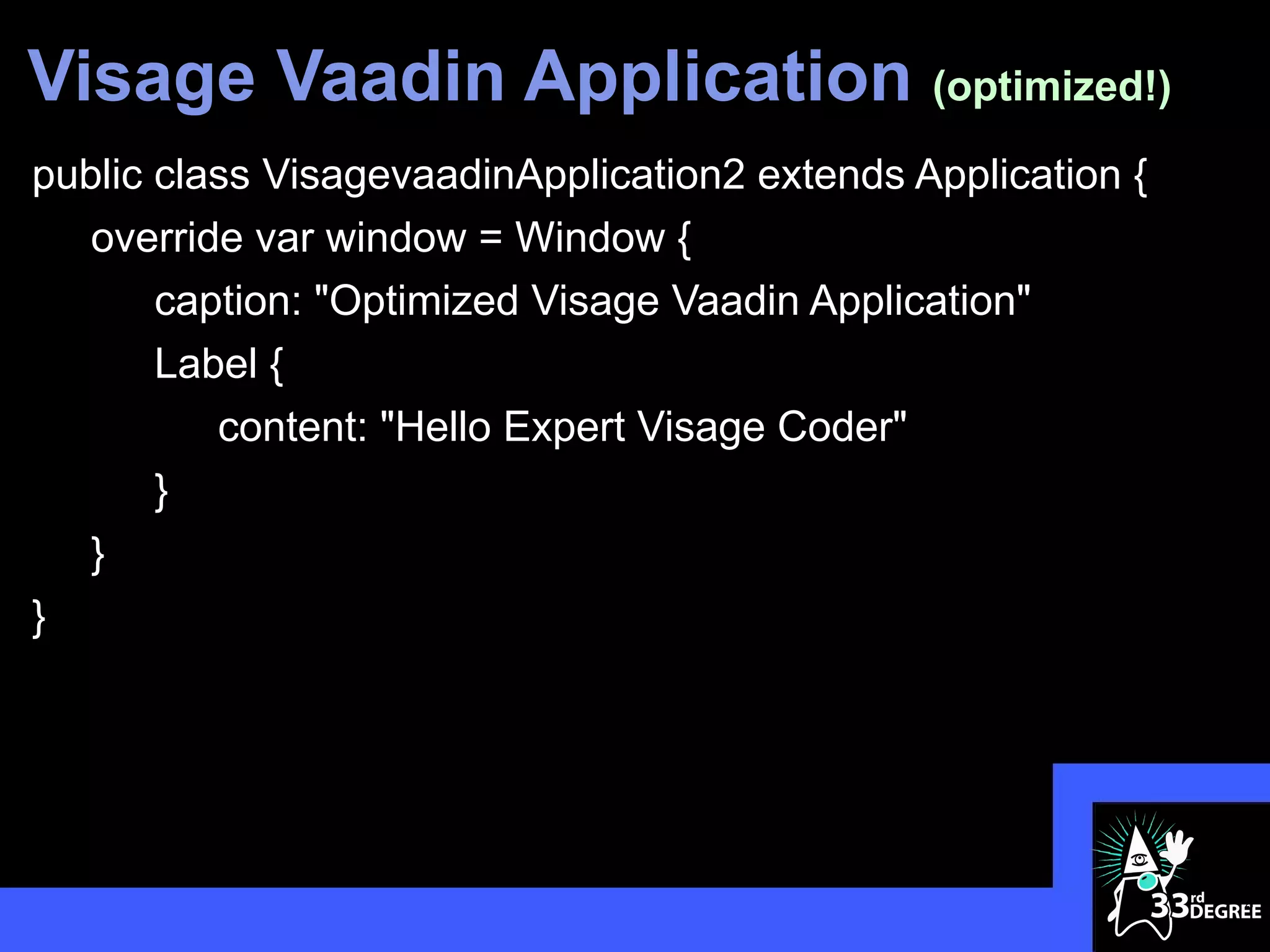













![Bound Controls (2)
}
TextView {
text: "Is Revealed!!!"
}
TextView {
text: bind secret
}
]
}
41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-41-2048.jpg)






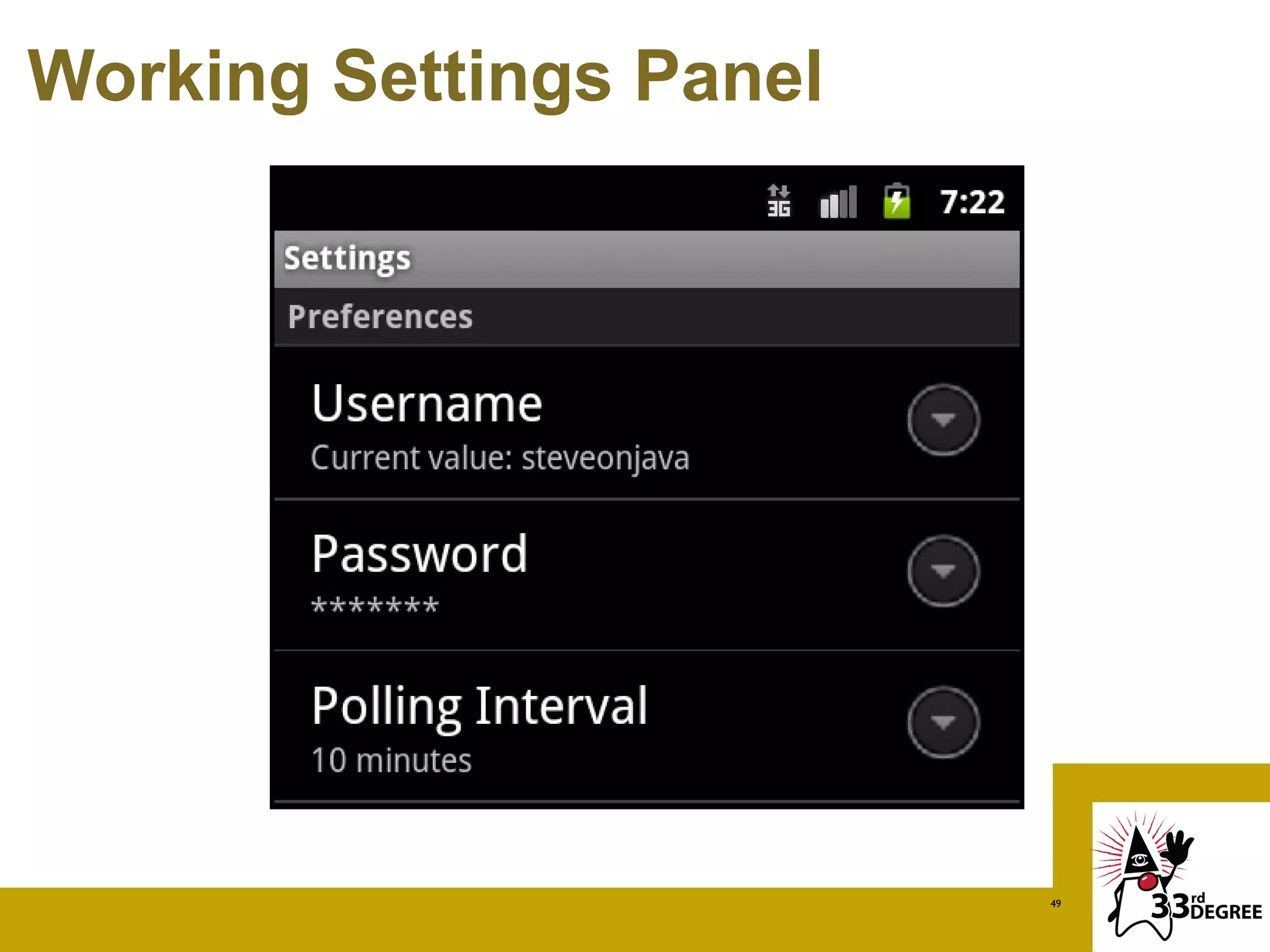
![List Preference
pollingPref = ListPreference {
title: "Polling Interval"
key: "pollingPref"
defaultValue: "60000"
entries: ["30 seconds", "1 minute", "5 minutes",
"10 minutes", "15 minutes", "30 minutes", "1 hour"]
entryValues: ["30000", "60000", "300000",
"600000", "900000", "1800000", "3600000"]
summary: bind pollingPref.entry
}
48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-48-2048.jpg)
![Sequence Puzzlers
What is the size of this sequence:
[1..10 step -1]
What does this evaluate to:
[10..<20 step 2][k|k>17]
What is the size of this sequence:
sizeof [20..1 step -3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-50-2048.jpg)



![What Bind Updates
var x = bind if(a) then b else c
x is updated if a or b or c changes
var x = bind for (i in [a..b]) { i * i }
Not everything is recalculated
If a = 1 and b = 2, x is [1, 4]
If b changes to 3, only the added element is
calculated
1 4 9
58](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-58-2048.jpg)



![Creating Sequences
Explicit sequence expression
- [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
Elements are separated by commas
Comma may be omitted if element ends with
brace
1 3 5 7 9
64](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-64-2048.jpg)
![Creating Sequences
Numeric sequence with range expressions:
- [1..10] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Can have a step:
- [1..10 step 2] 1 3 5 7 9
- [0.0..0.9 step 0.1] 0 .1 .2 .3 .4 .5 .6 .7 .8 .9
Can be decreasing:
- [10..1 step -3] 10 7 4 1
Beware of step that goes opposite direction:
- [10..1] is []
Exclusive right end
- [1..<5] 1 2 3 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-65-2048.jpg)
![Getting Info from Sequences
ints = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
1 3 5 7 9
[0] [1] [2] [3] [4]
sizeof ints is 5
ints[0] is 1, ints[1] is 3, ..., ints[4] is 9
ints[-1] is 0 (default value of Integer), so is
ints[5]
Object sequence has a default of null
66](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-66-2048.jpg)
![Getting Slices from Sequences
ints = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
1 3 5 7 9
[0] [1] [2] [3] [4]
ints[0..2] is [1, 3, 5]
ints[0..<2] is [1, 3]
ints[2..] is [5, 7, 9]
ints[2..<] is [5, 7]
ints[2..0], ints[-2..-1], ints[5..6] are all []s
67](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-67-2048.jpg)
![Getting Subsets from Sequences
ints = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
1 3 5 7 9
[0] [1] [2] [3] [4]
ints[k | k > 6] is:
- [7, 9] (k > 6 is a condition)
ints[k | indexof k < 2] is:
- [1, 3]
ints[k | k > 10] is:
- []
68](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-68-2048.jpg)
![Inserting into Sequences
ints = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] 1 3 5 7 9
insert 20 into ints 1 3 5 7 9 20
insert 30 before ints[2] 1 3 30 5 7 9 20
insert 40 after ints[4] 1 3 30 5 7 40 9 20
insert [50, 60] into ints 1 3 30 5 7 40 9 20 50 60](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-69-2048.jpg)
![Deleting from Sequences
ints = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] 1 3 5 7 9
delete 7 from ints 1 3 5 7 9
delete ints[0] 1 3 5 9
delete ints[0..1] 3 5 9
delete ints: ints becomes [] 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleanerapiscleaneruiswithvisage33rddegrees-120325100955-phpapp01/75/Cleaner-APIs-Cleaner-UIs-with-Visage-33rd-Degrees-70-2048.jpg)