5.2 - Internal Resistance, Power & Combining Resistors
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
4 likes•6,297 views
Electricity
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Magnetic Circuit & Energy Stored In Magnetic Field

Magnetic Circuit & Energy Stored In Magnetic Field
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (17)
Similar to 5.2 - Internal Resistance, Power & Combining Resistors
Similar to 5.2 - Internal Resistance, Power & Combining Resistors (20)
More from simonandisa
More from simonandisa (16)
Recently uploaded
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? webinar
Thursday 2 May 2024
A joint webinar created by the APM Enabling Change and APM People Interest Networks, this is the third of our three part series on Making Communications Land.
presented by
Ian Cribbes, Director, IMC&T Ltd
@cribbesheet
The link to the write up page and resources of this webinar:
https://www.apm.org.uk/news/making-communications-land-are-they-received-and-understood-as-intended-webinar/
Content description:
How do we ensure that what we have communicated was received and understood as we intended and how do we course correct if it has not.Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...Association for Project Management
Mehran University Newsletter is a Quarterly Publication from Public Relations OfficeMehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024

Mehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024Mehran University of Engineering & Technology, Jamshoro
https://app.box.com/s/7hlvjxjalkrik7fb082xx3jk7xd7liz3TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Recently uploaded (20)
ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.

ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.
This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.

This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...
Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx

Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx
TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...
Food safety_Challenges food safety laboratories_.pdf

Food safety_Challenges food safety laboratories_.pdf
HMCS Max Bernays Pre-Deployment Brief (May 2024).pptx

HMCS Max Bernays Pre-Deployment Brief (May 2024).pptx
Vishram Singh - Textbook of Anatomy Upper Limb and Thorax.. Volume 1 (1).pdf

Vishram Singh - Textbook of Anatomy Upper Limb and Thorax.. Volume 1 (1).pdf
5.2 - Internal Resistance, Power & Combining Resistors
- 1. 5.2 - Internal Resistance, Electrical Power, Resistors in Series & Parallel 1
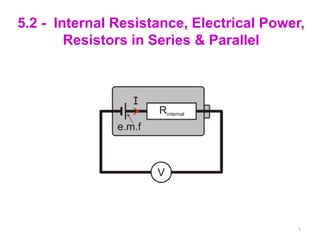
- 2. Internal Resistance All cells are made of materials that have resistance, this is called Internal Resistance (r) If the cell is connected to an External Resistor (R) then some of the energy is converted from electrical energy to heat energy inside the cell. The PD available for the circuit is EMF (E) therefore less than the EMF of the cell. This picture shows that some of the EMF is lost before the charges even leave the battery. PD (V) 2
- 3. Internal Resistance (cont) I Using Ohms Law: E= Ir + IR I For the main Resistance in the circuit: V=IR Missing volts: Ir 3
- 4. More Internal Resistance If you connected a wire directly from one end of the I battery to the other then the Resistance (R) would be very small. The Current (I) that flows would be enormous. I This would cause loads of heat to be wasted by the current as it moves through the Internal Resistance of the battery. The battery would get very hot and run out of energy very fast. This is called a short circuit. Try it with the PhET Circuit Construction Kit: http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/circuit- construction-kit-dc or click on the picture OR connect some steel wool across a battery. 4
- 5. Electrical Power (P) Power means the energy per second (Watts or Js-1) Remember some definitions: By substitution: 5
- 6. More Electrical Power Equations (P) Using: and Ohms Law: We can find the Power DISSIPATED (converted to heat) by a resistor. By substituting from Ohms Law: V=RI OR I=V/R 6
- 7. Combining Resistors 1. Series Circuits Putting two resistors together is like putting two separate flights of stairs one after the other. The stairs are harder to climb 7
- 8. Combining Resistors 2. Parallel Circuits Because there are more ways of getting round the circuit this is like making the stairs wider. The Resistance is less. 8
- 9. See how combinations of Resistors work: http://www.walter-fendt.de/ph14e/combrlc.htm or click on the picture Add Resistors and then highlight areas of the circuit to see the total resistance. Impedance is another word that can be used for Resistance 9