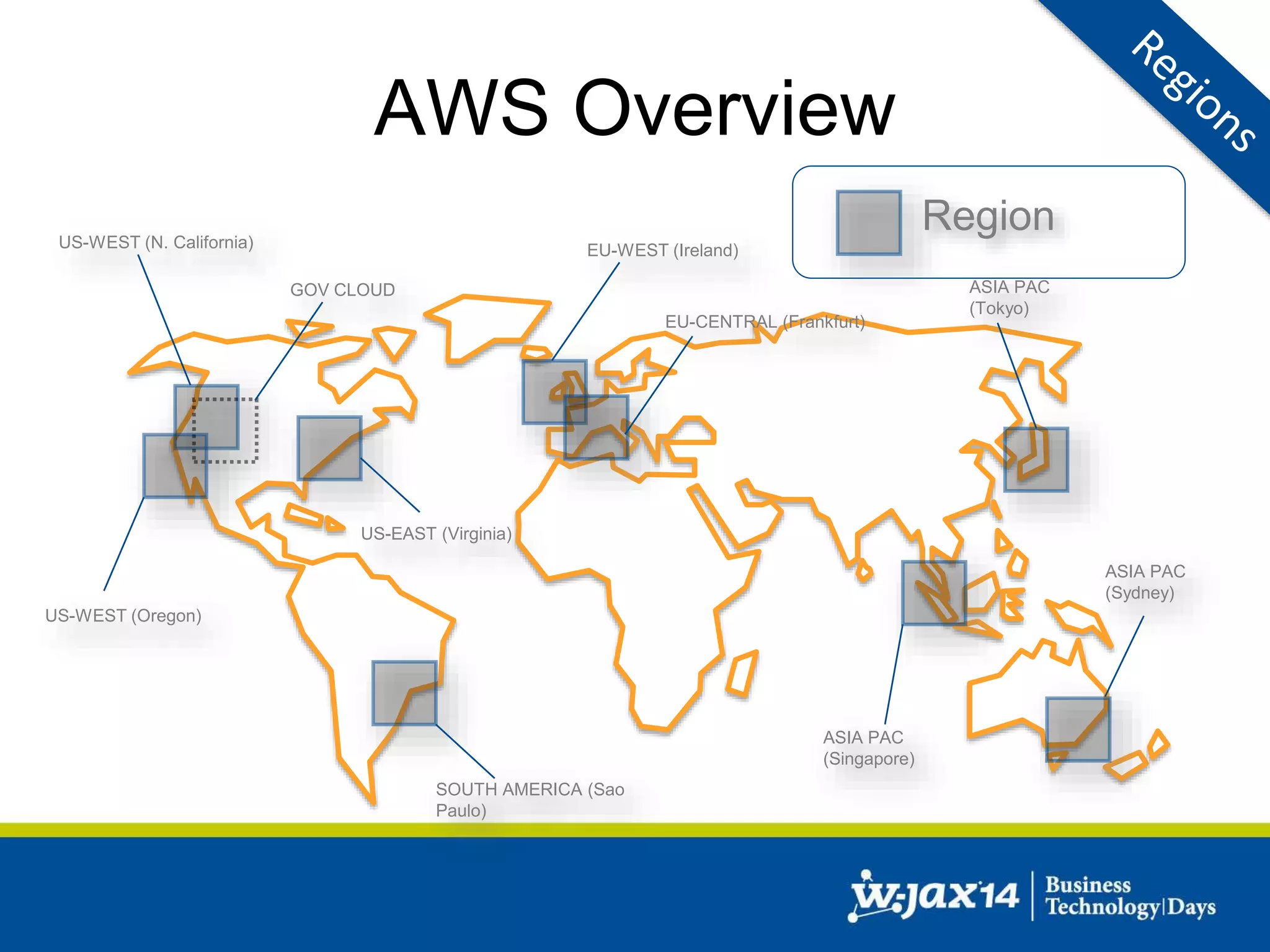
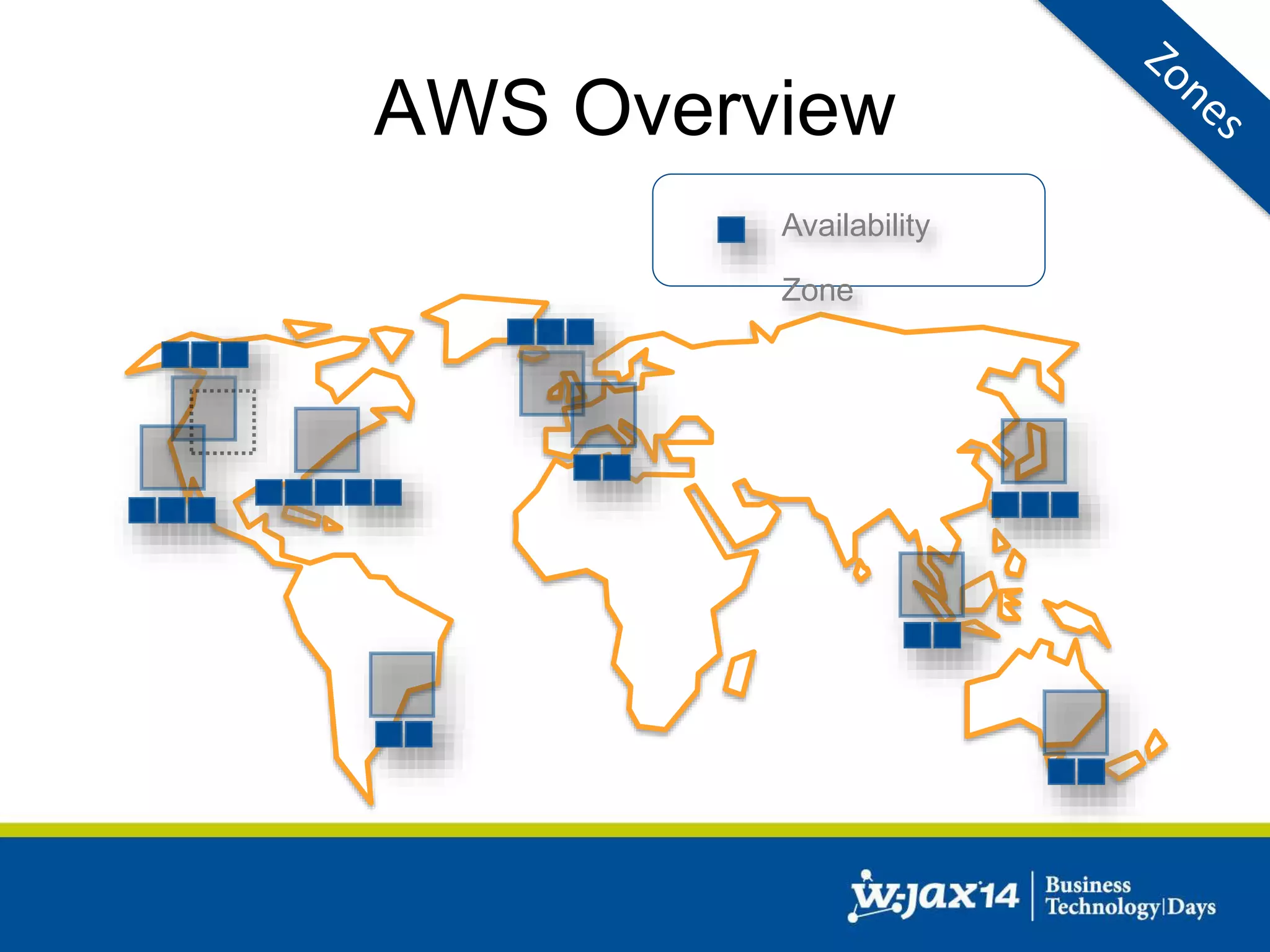
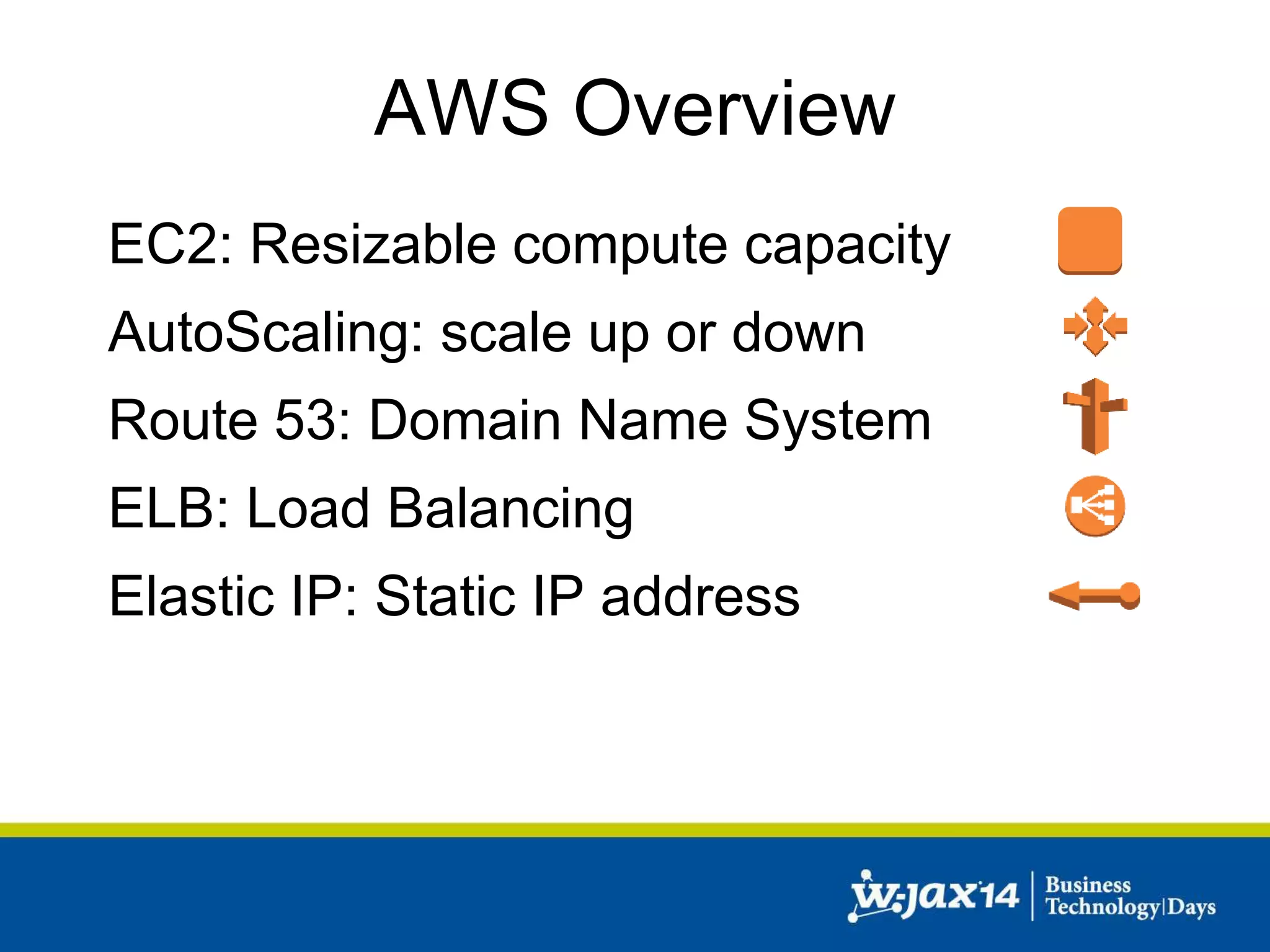
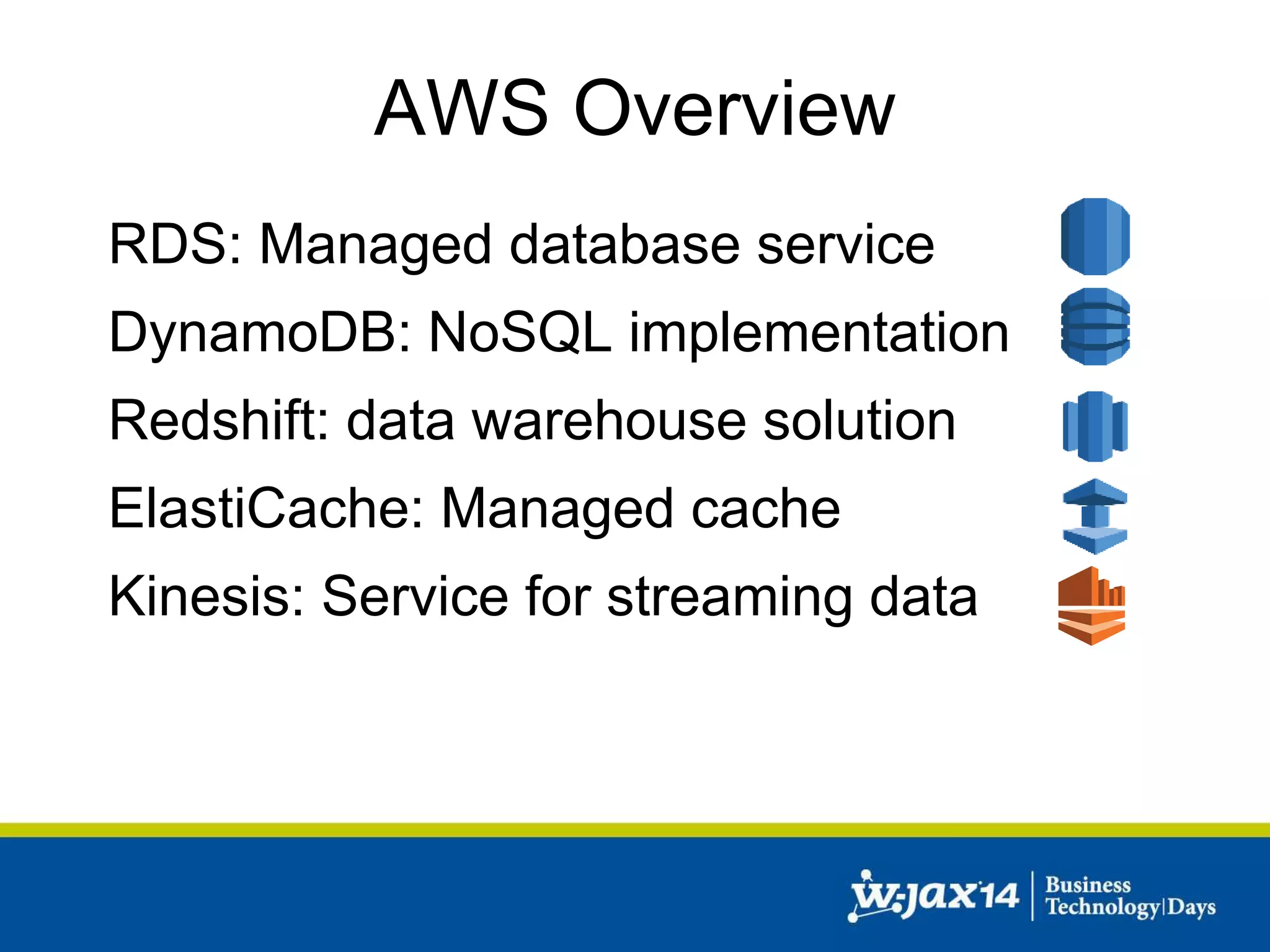
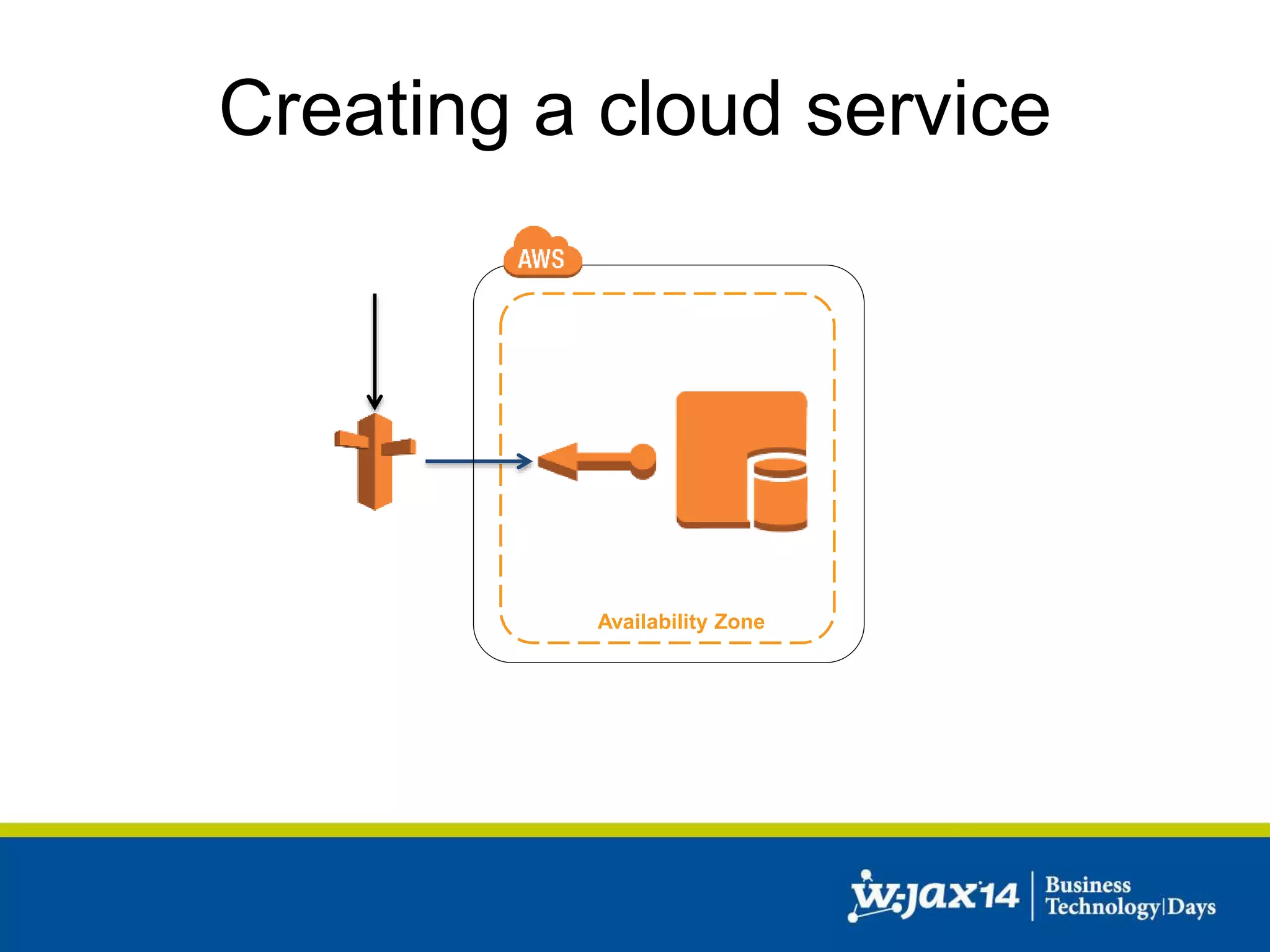
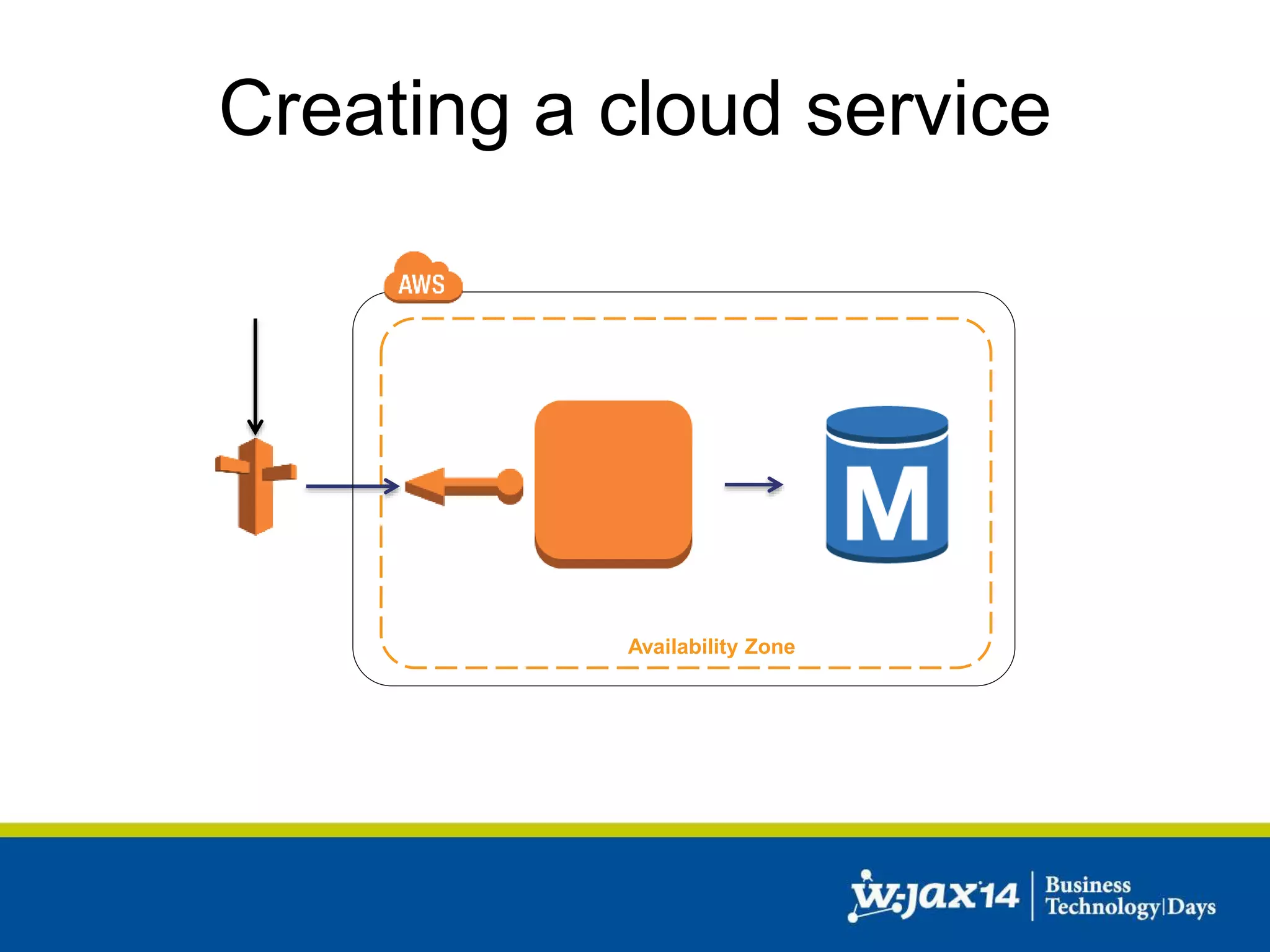
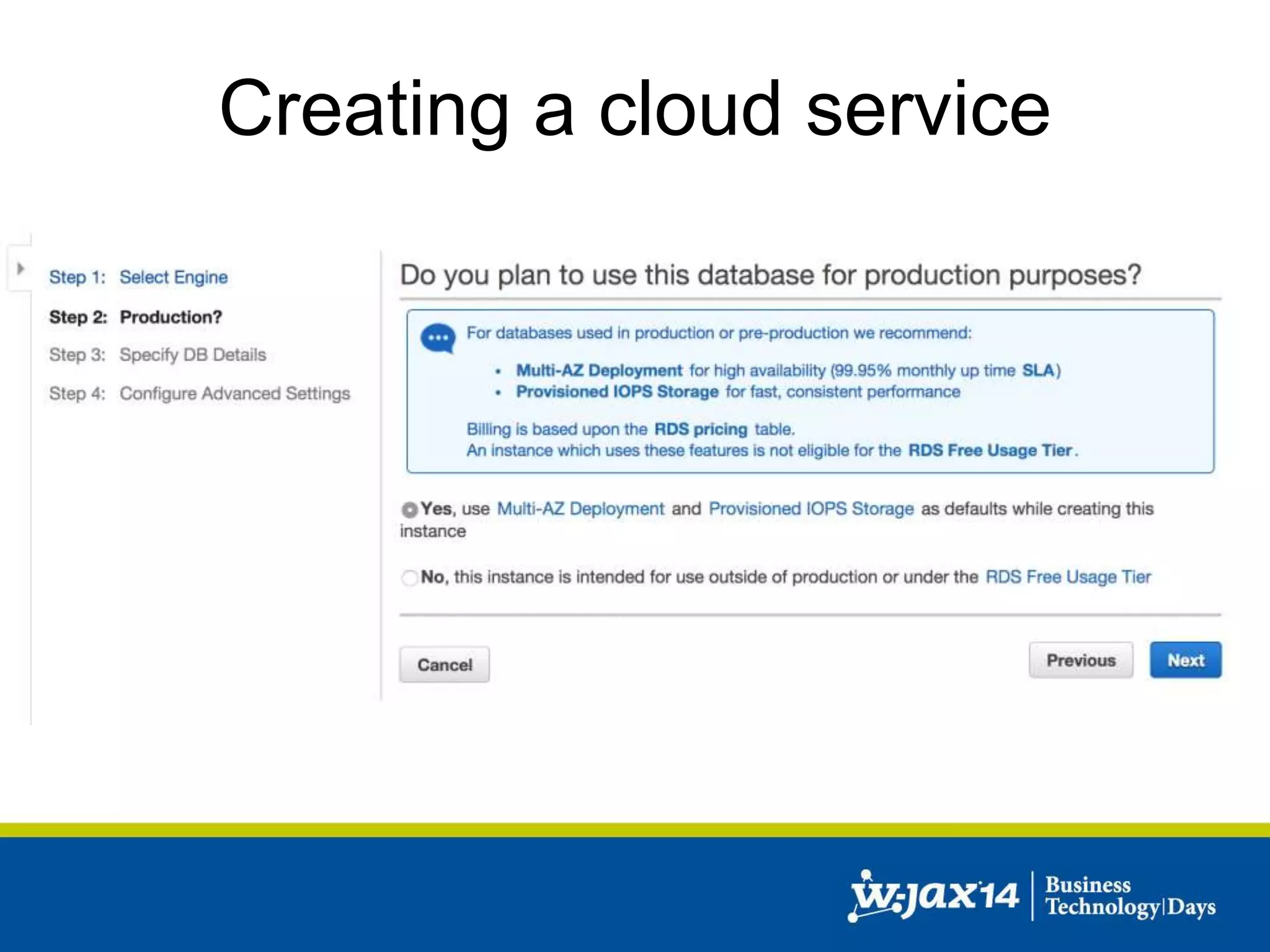
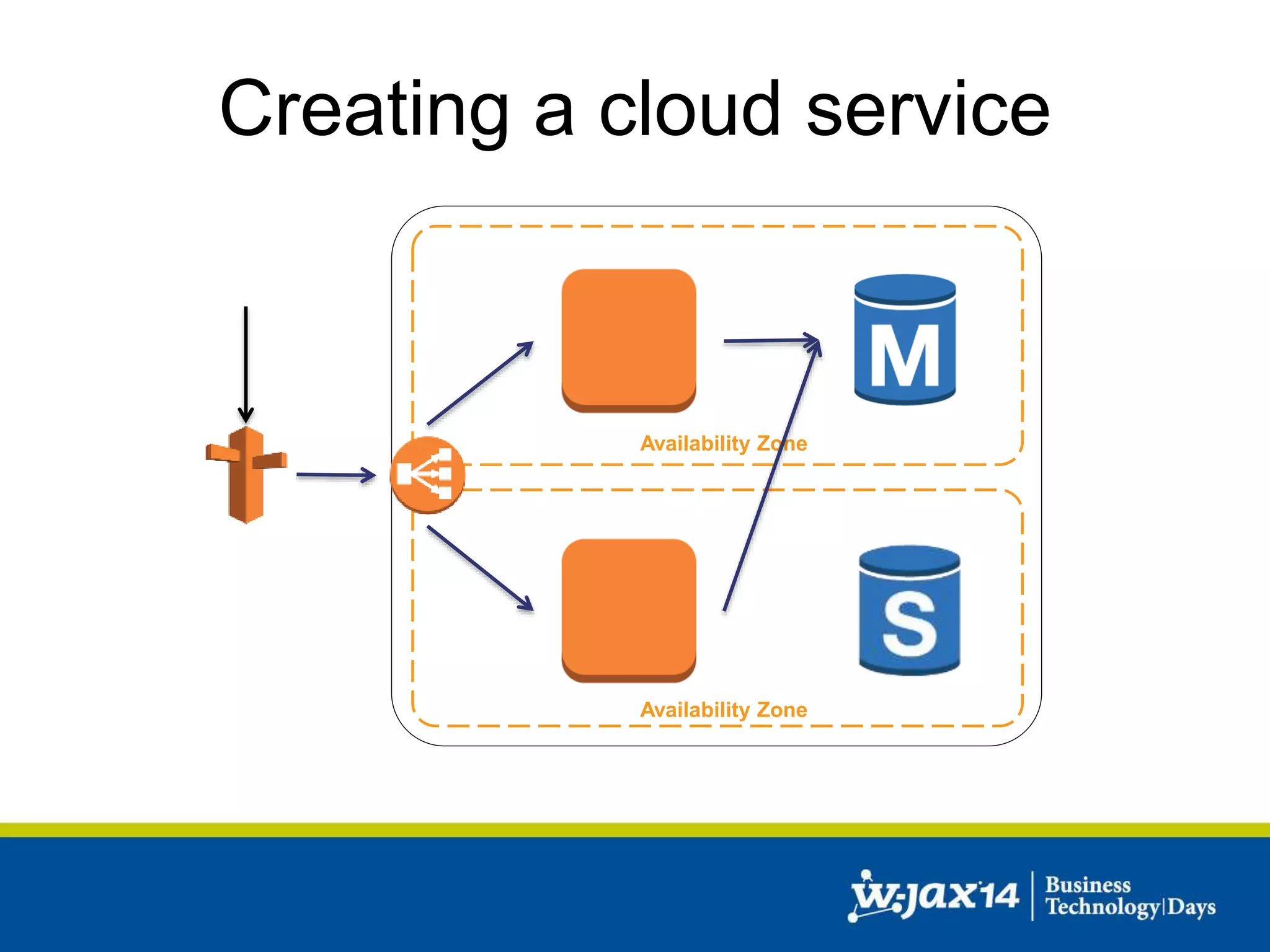
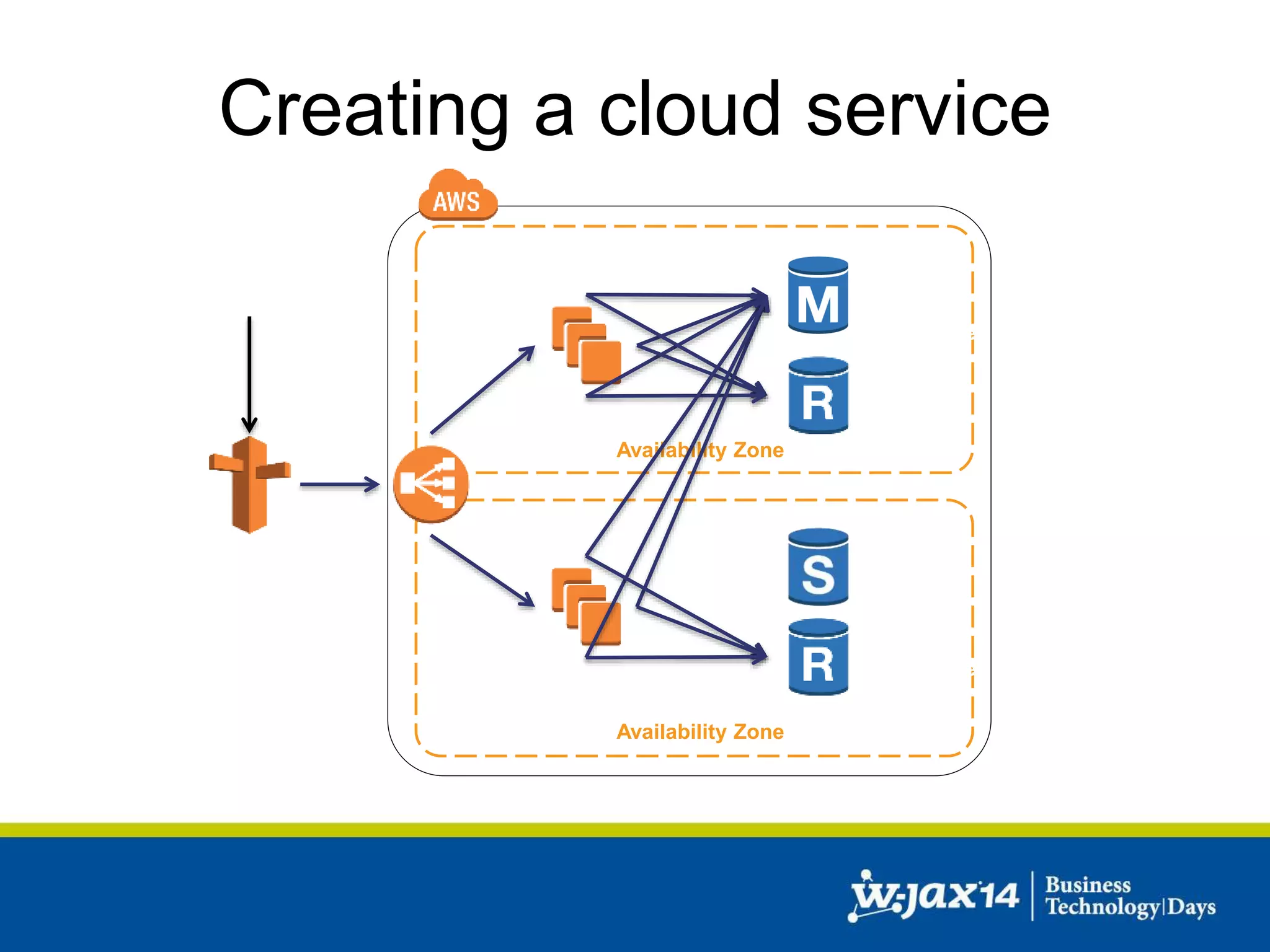
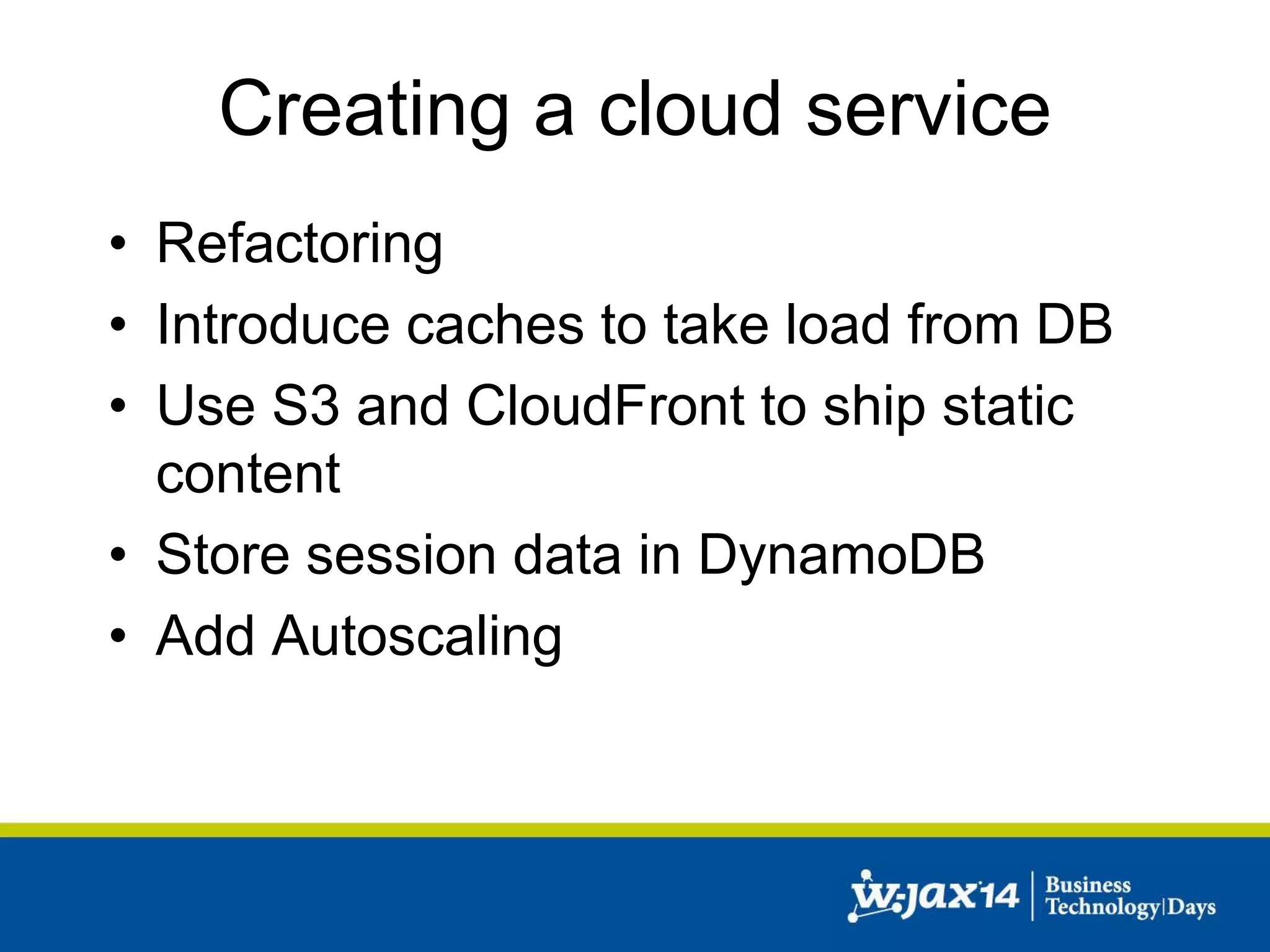
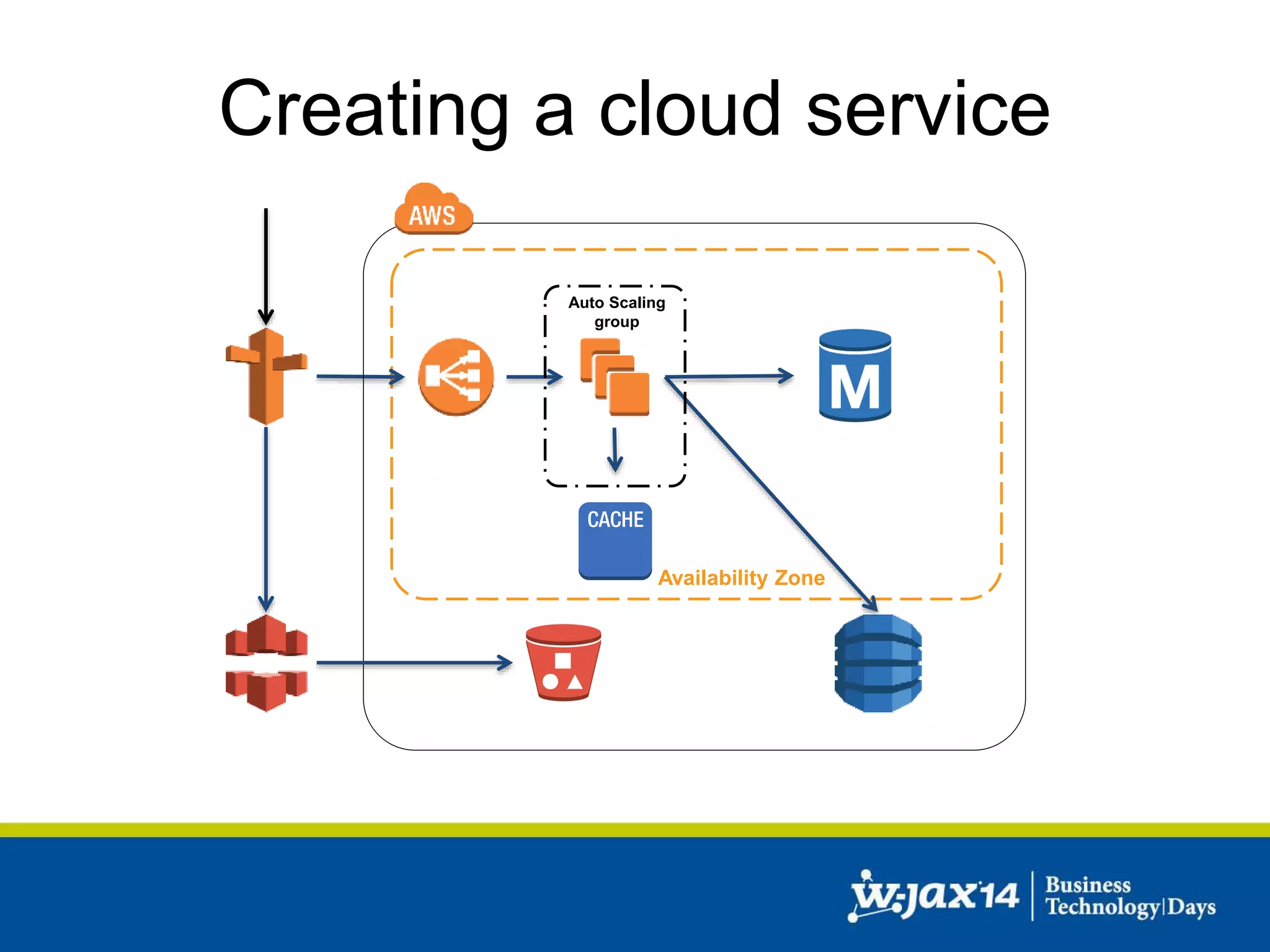
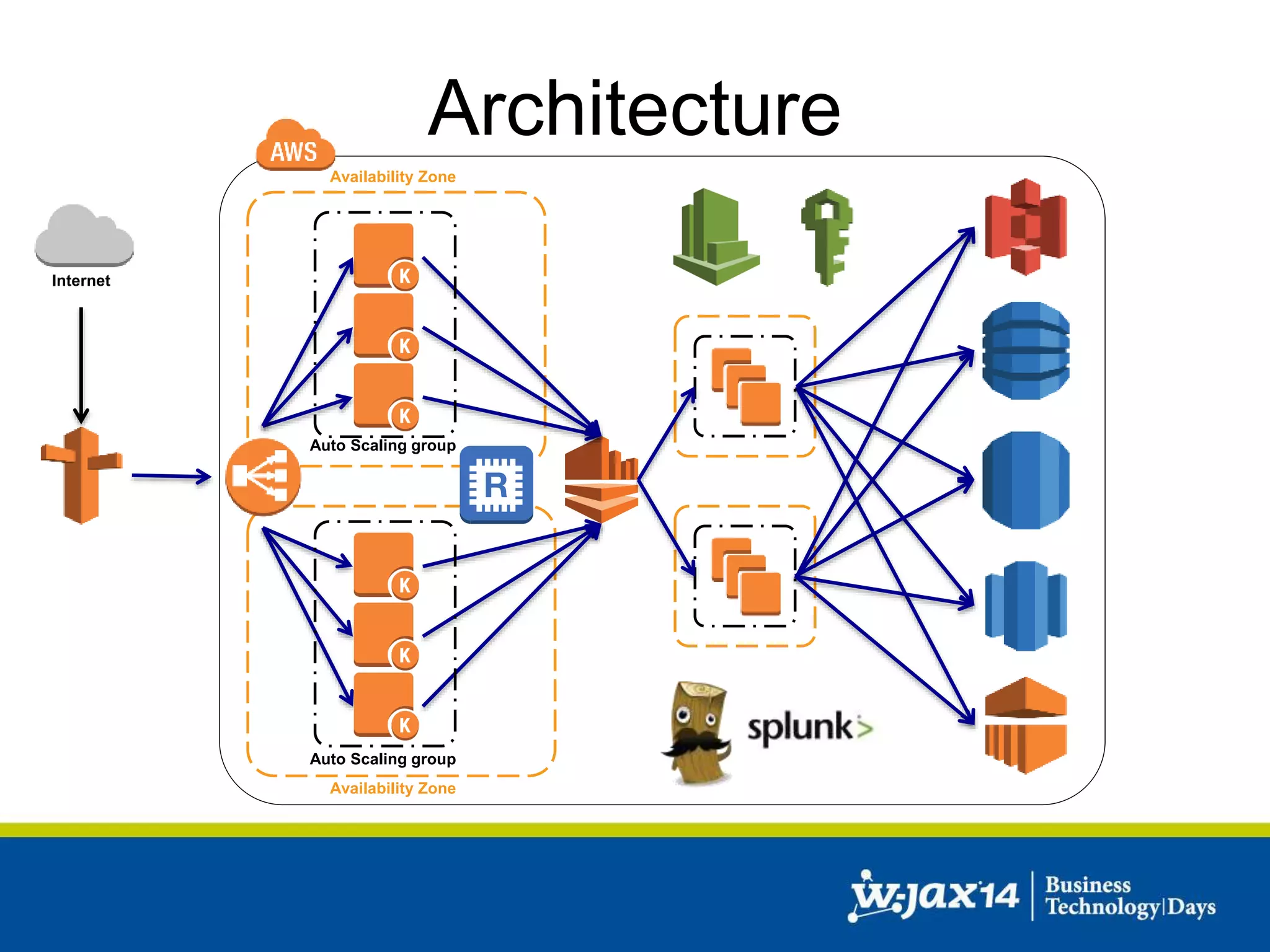
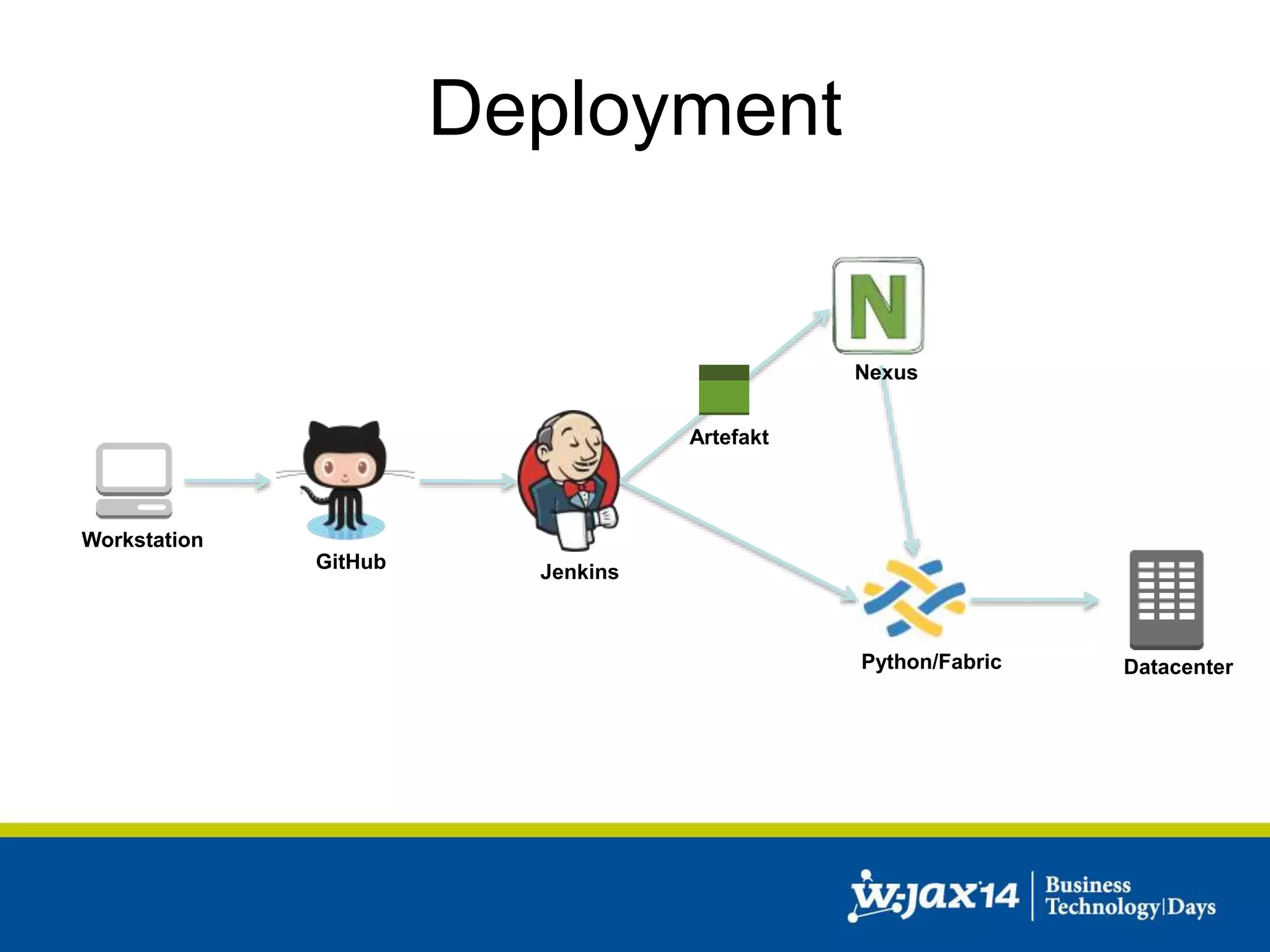
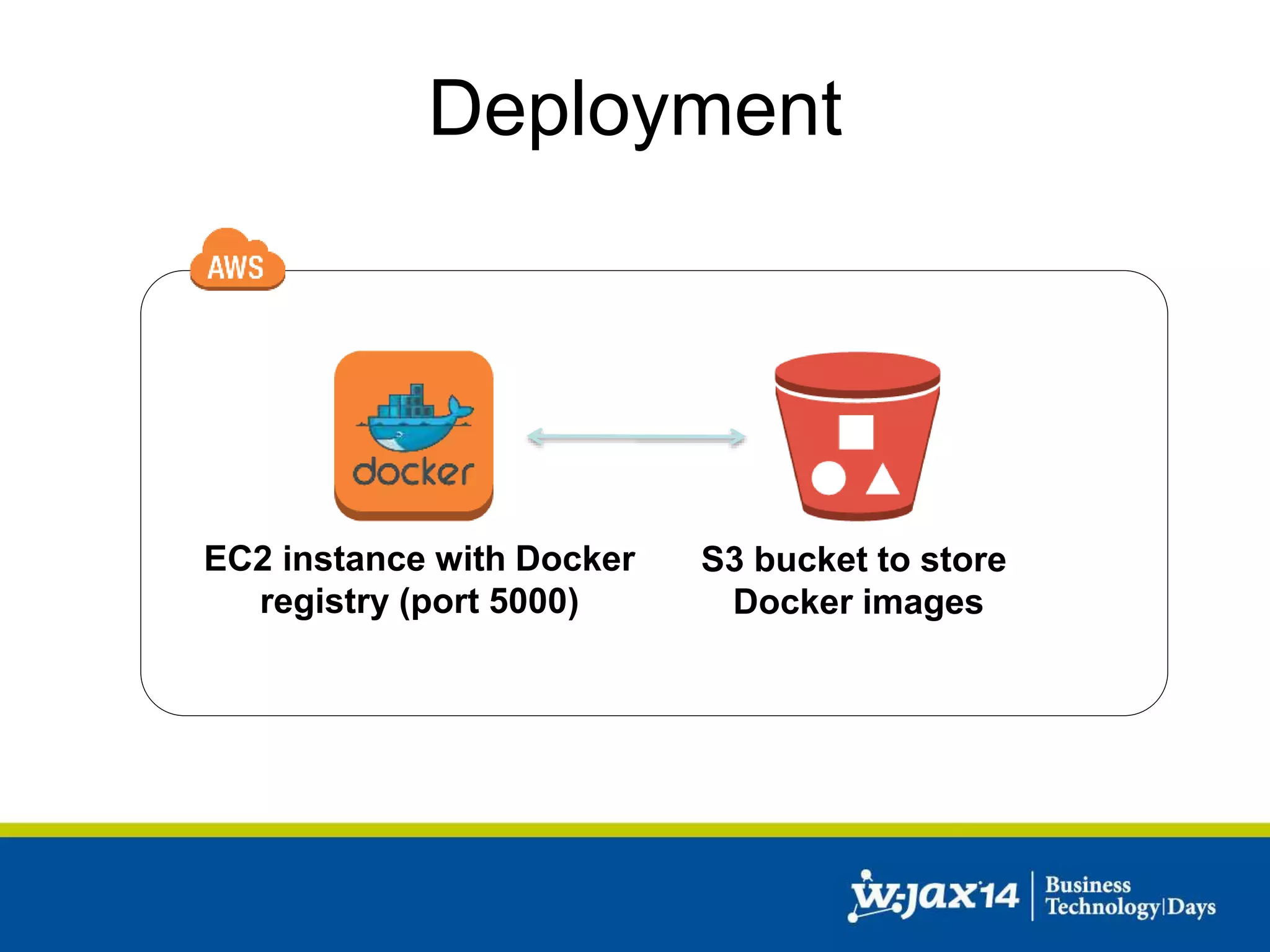
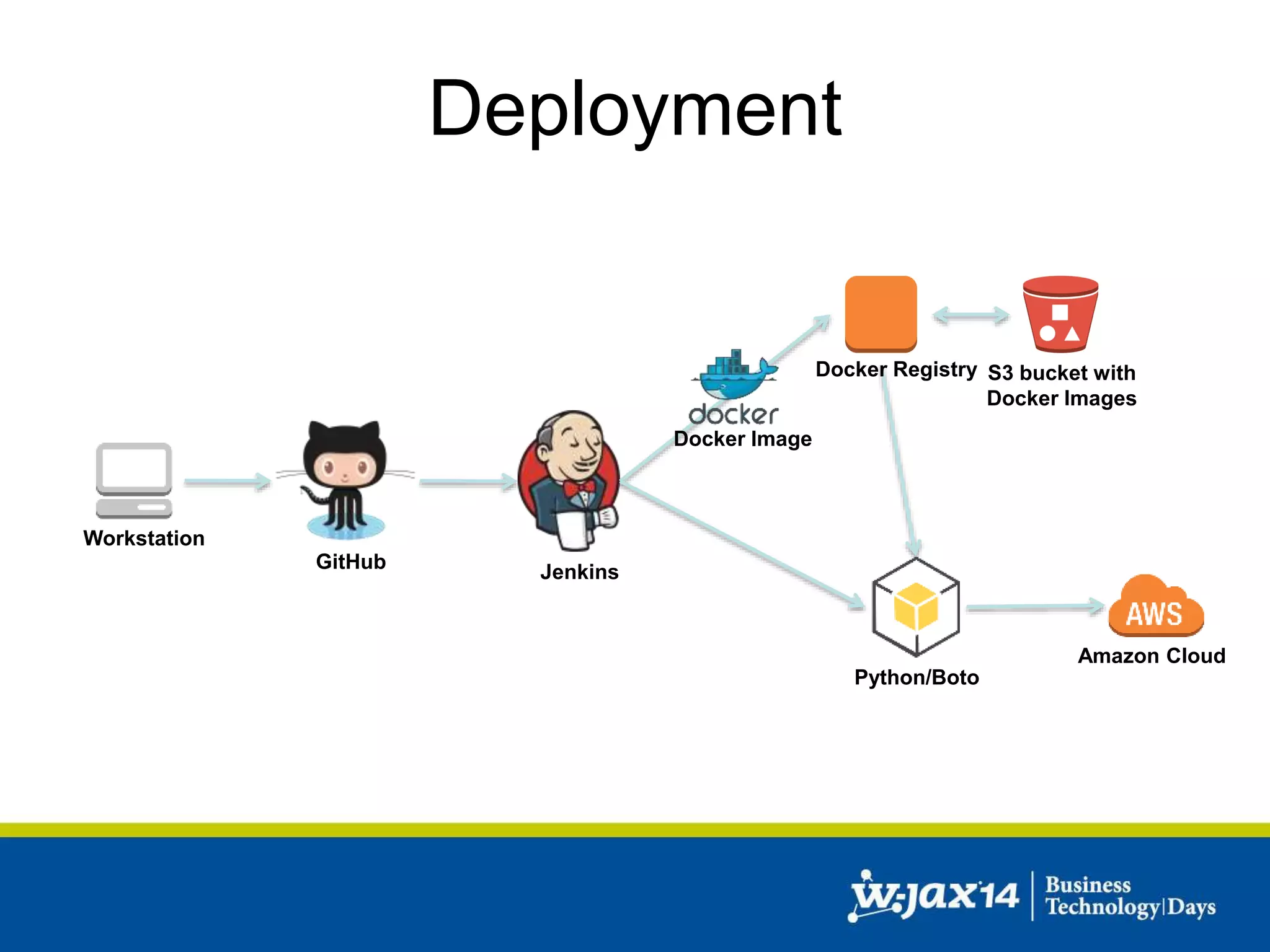
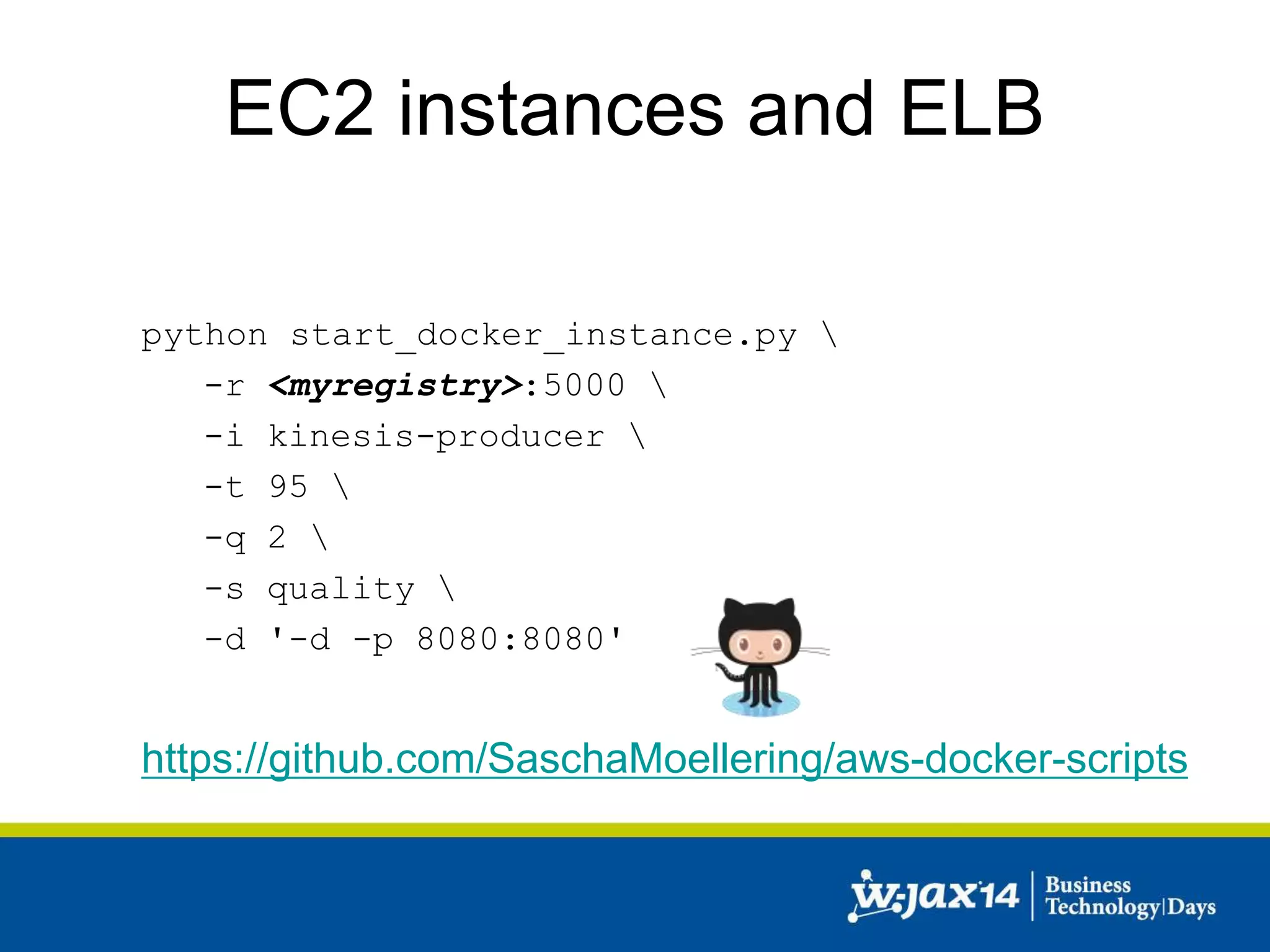
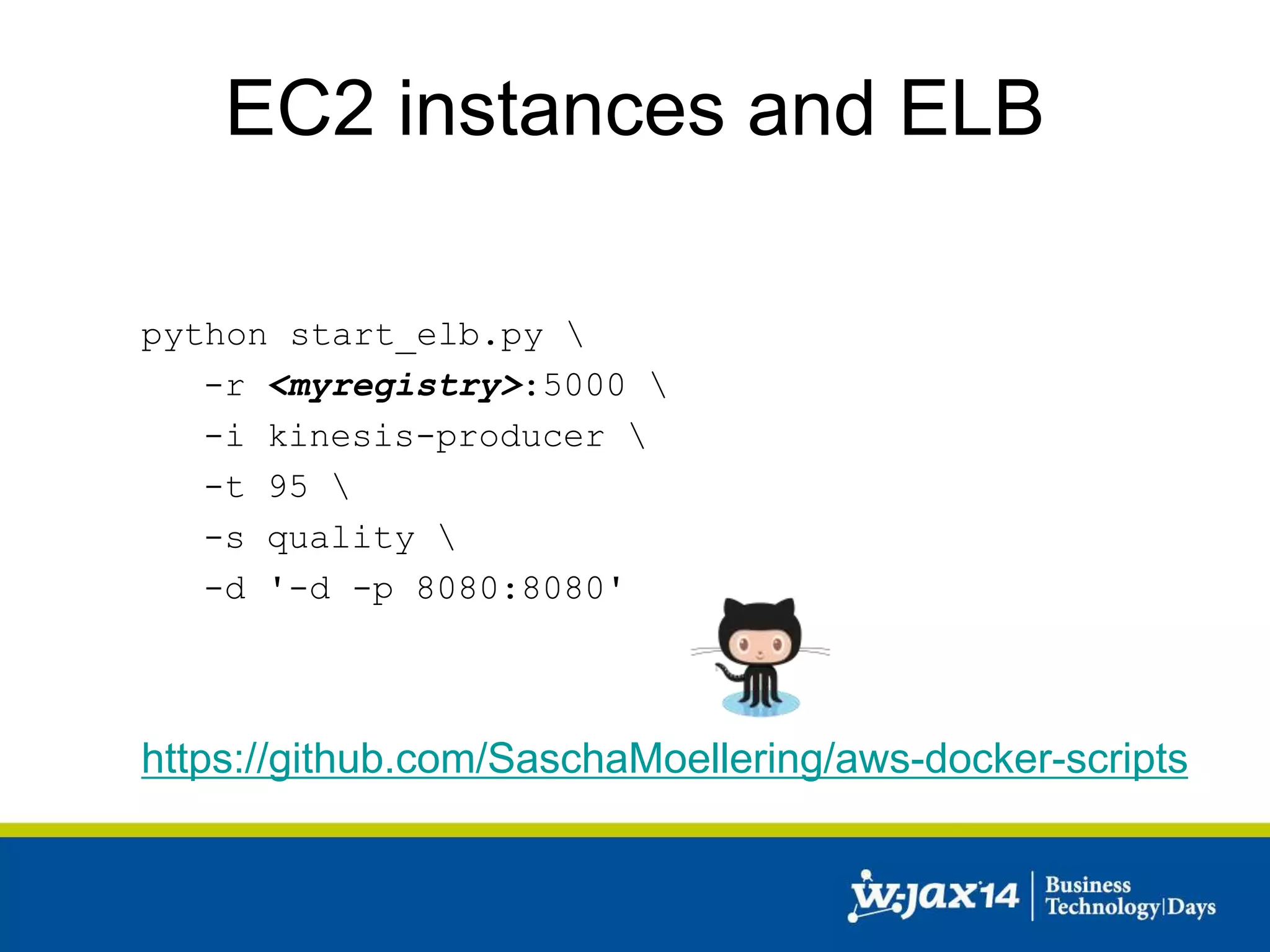
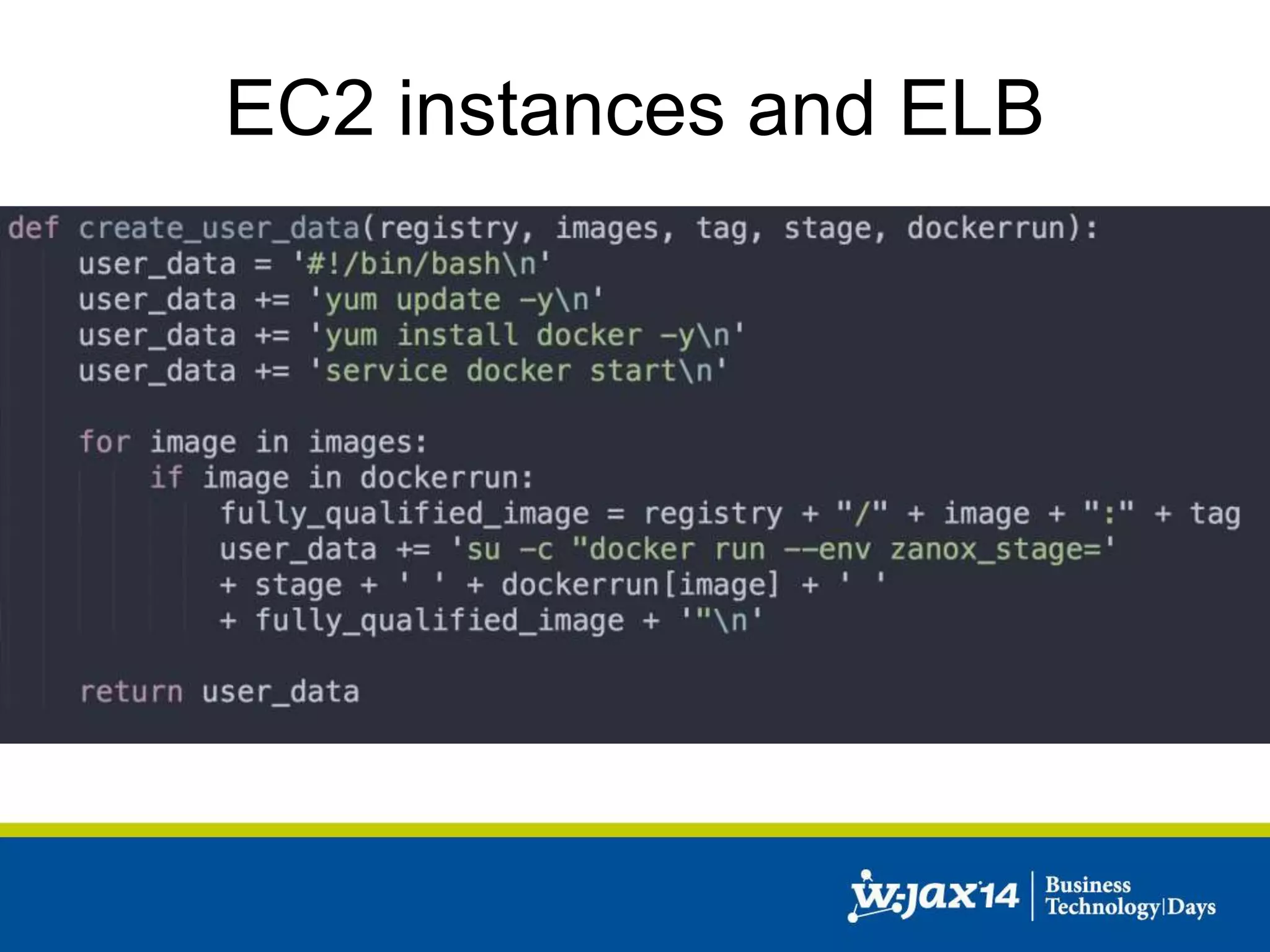
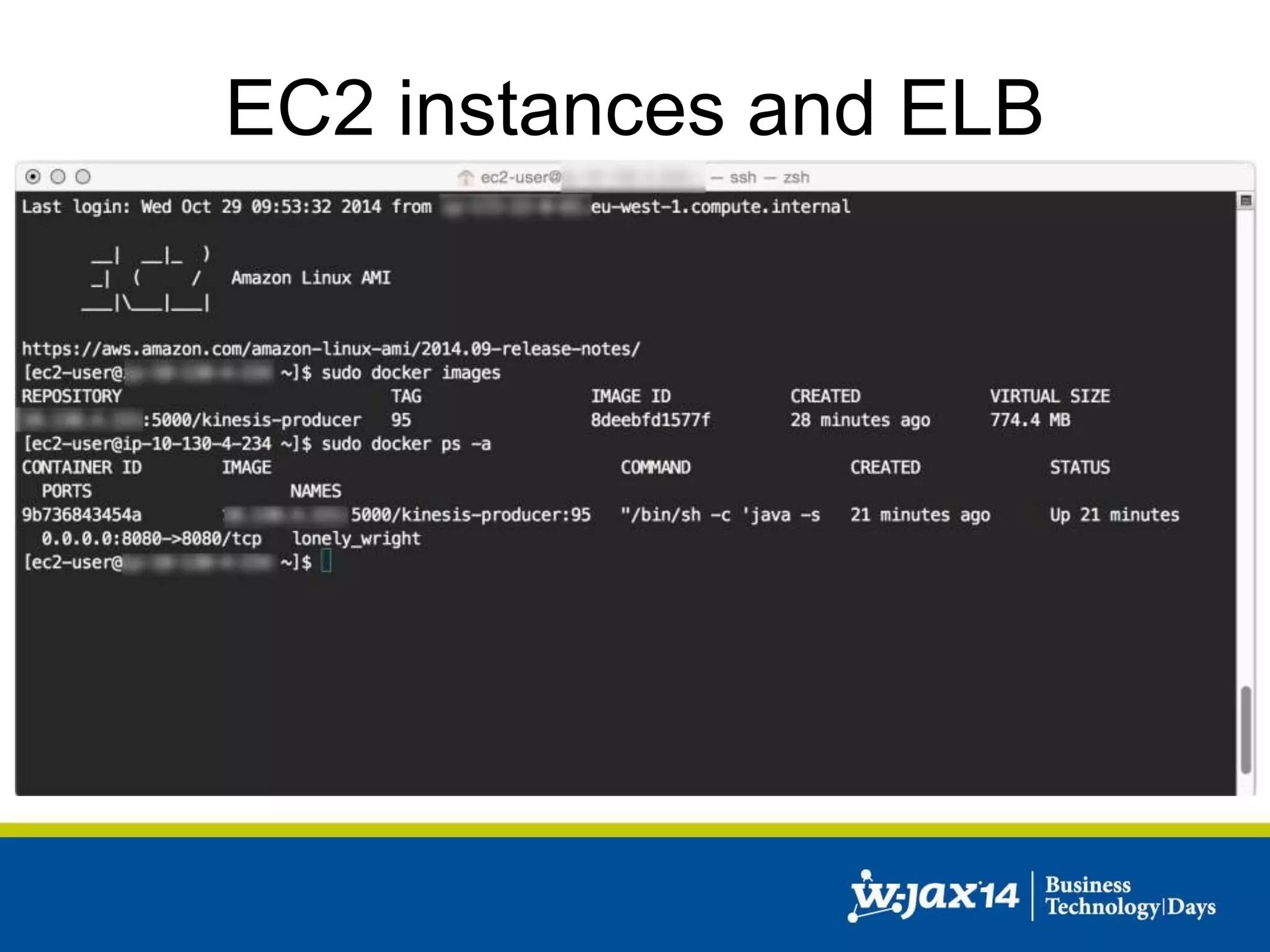
This document discusses scaling applications in the AWS cloud. It begins with an overview of AWS services like EC2, S3, RDS, and ELB. It then walks through creating a simple cloud application and database, and improving it by separating components, adding redundancy, caching, and autoscaling. A real-world example is shown using Vert.x, Kinesis, Docker, and deployment scripts to dynamically scale a streaming data application across Availability Zones.