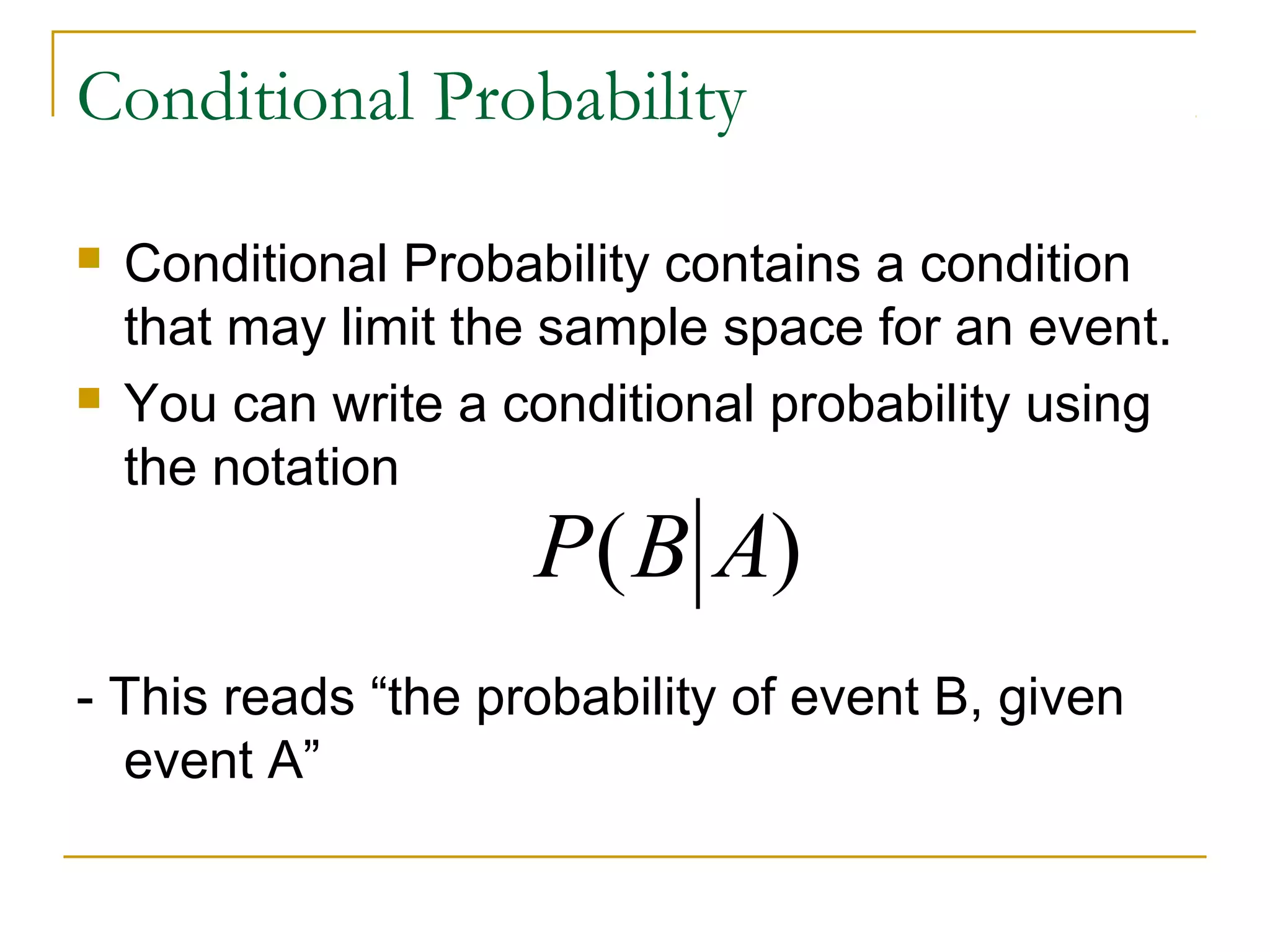
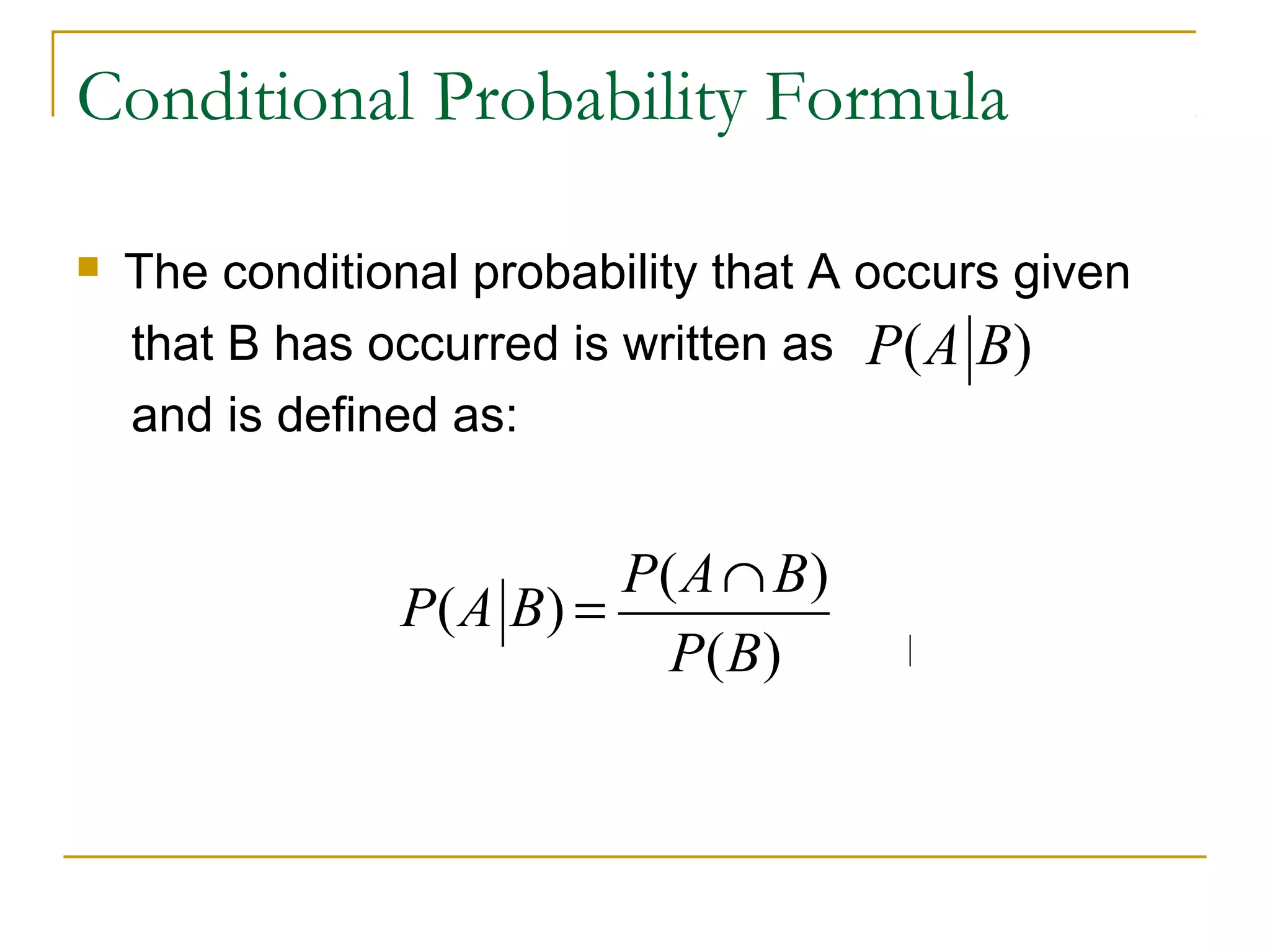
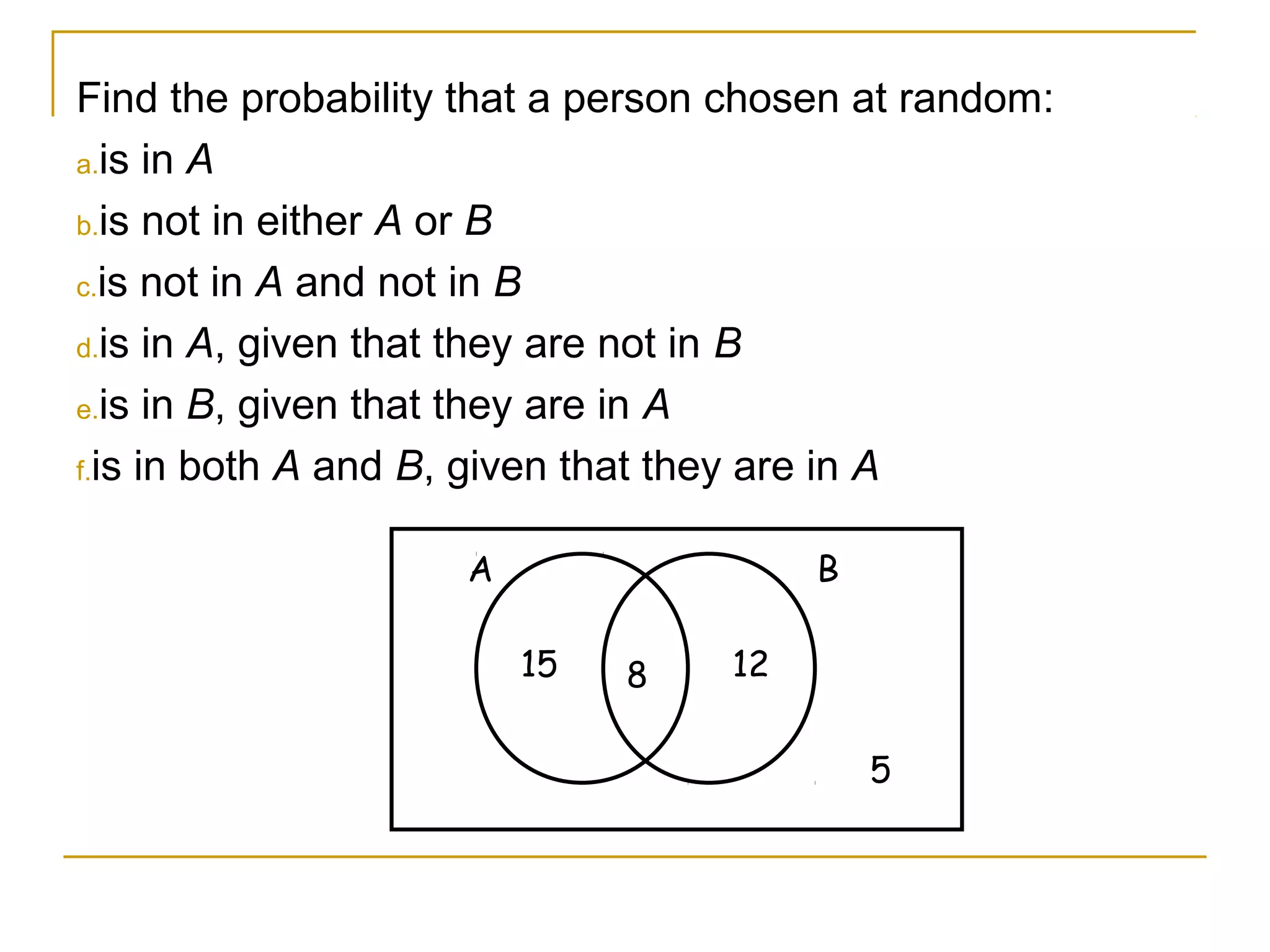
Conditional probability describes the probability of an event occurring given that another event has occurred. It is calculated as the probability of the events intersecting (both occurring) divided by the probability of the conditioning event. Venn diagrams can be used to visualize sample spaces and intersections of events to calculate conditional probabilities. Conditional probabilities limit the sample space based on a specified condition.