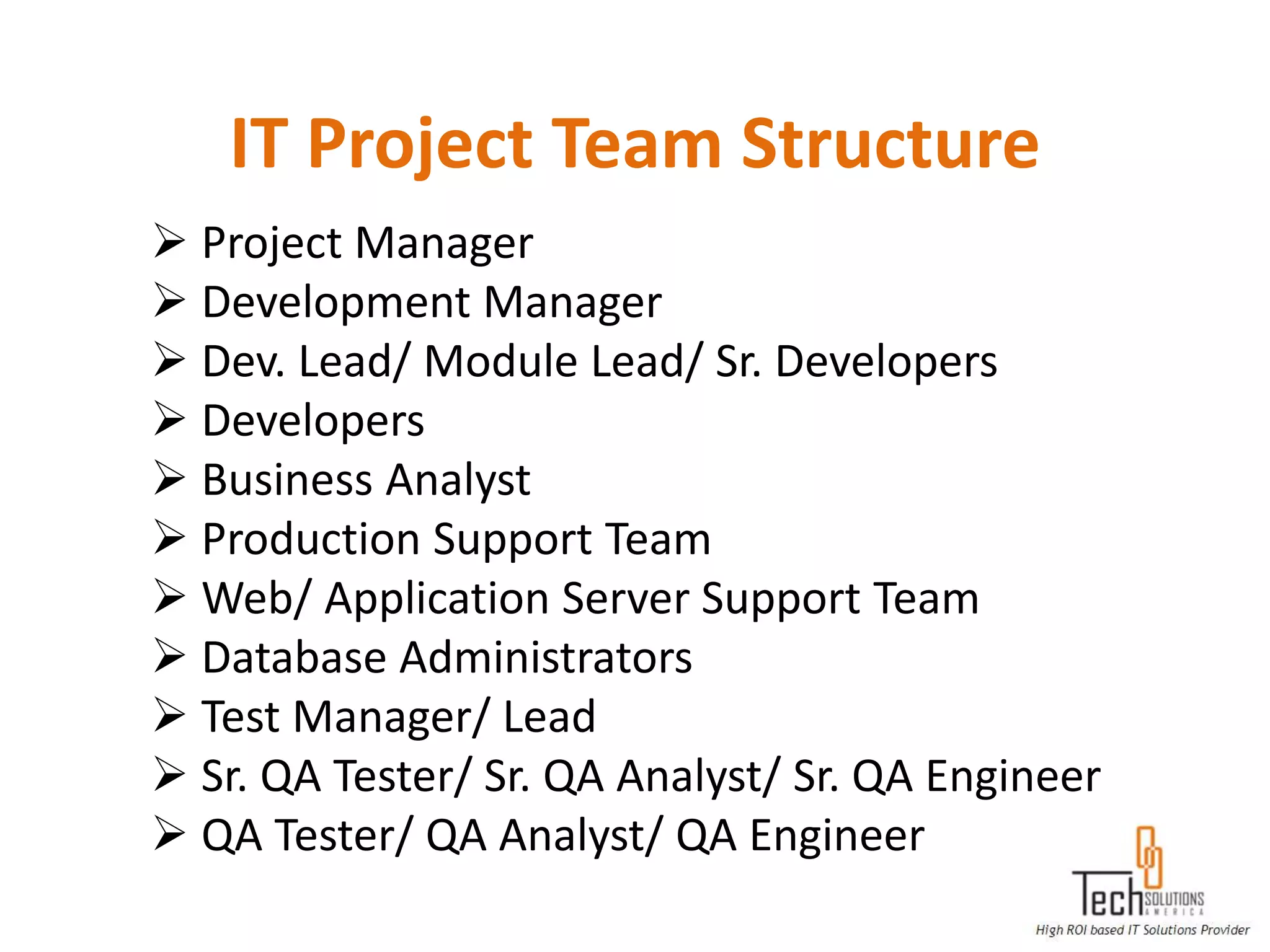
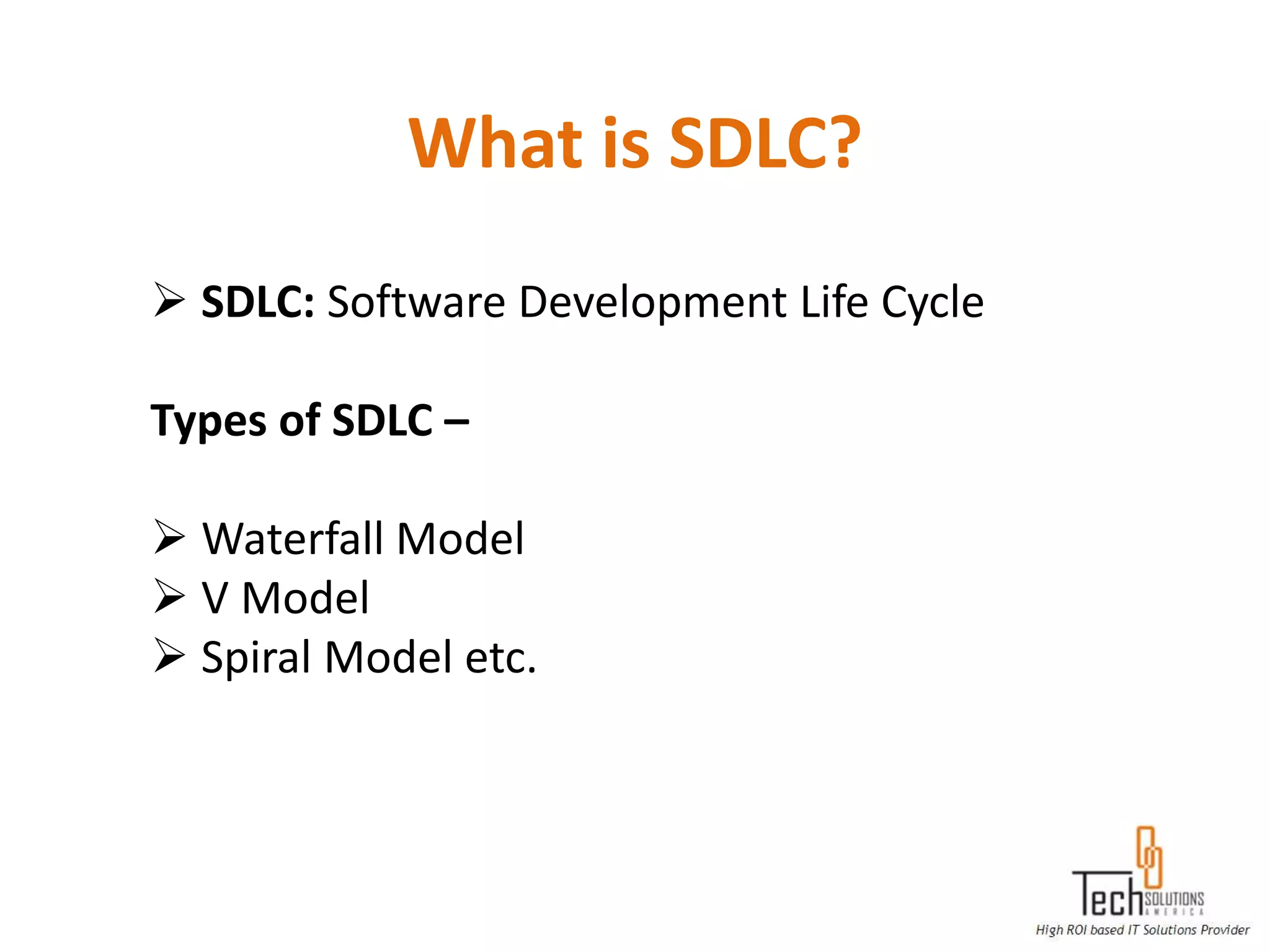
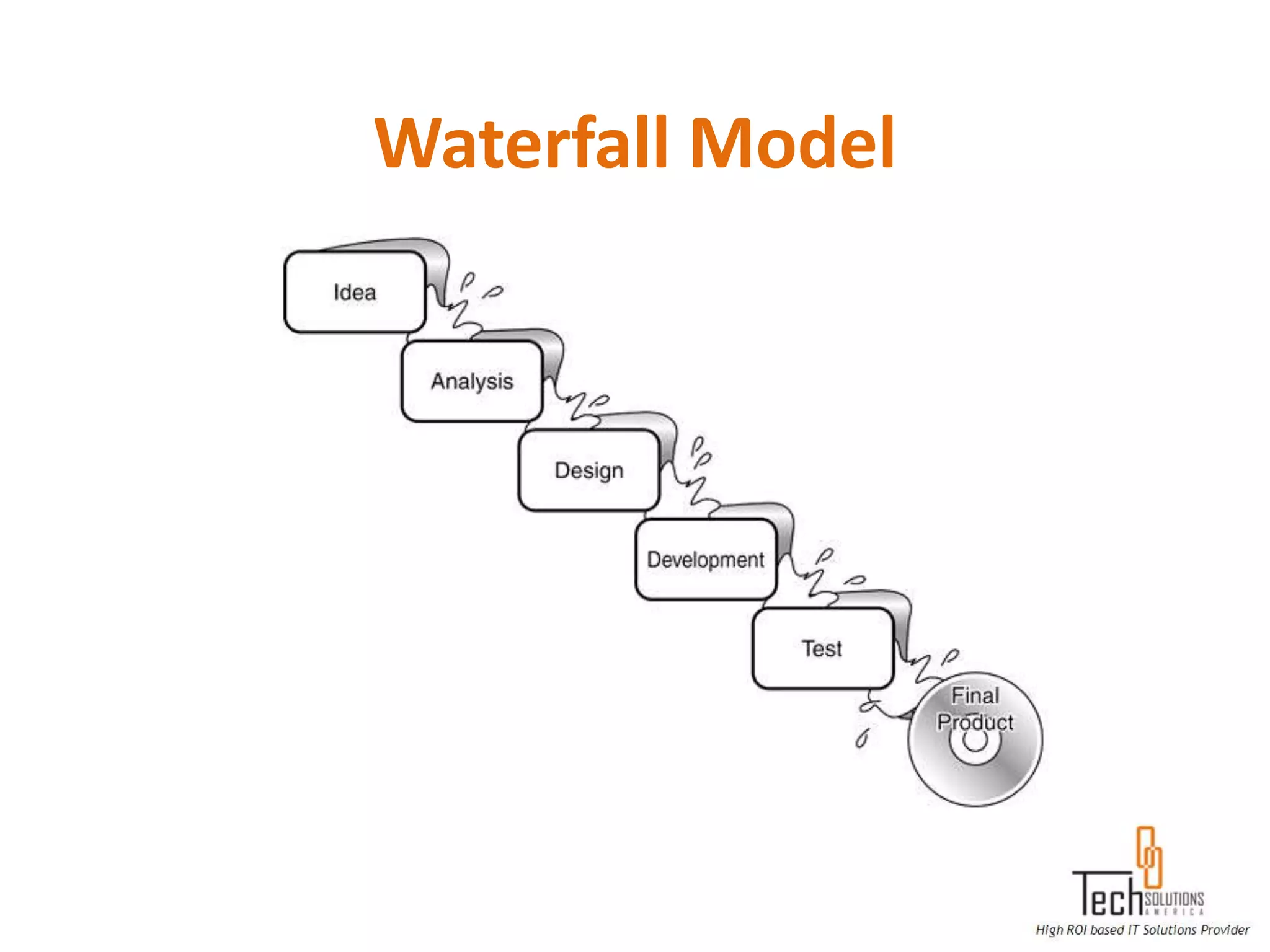
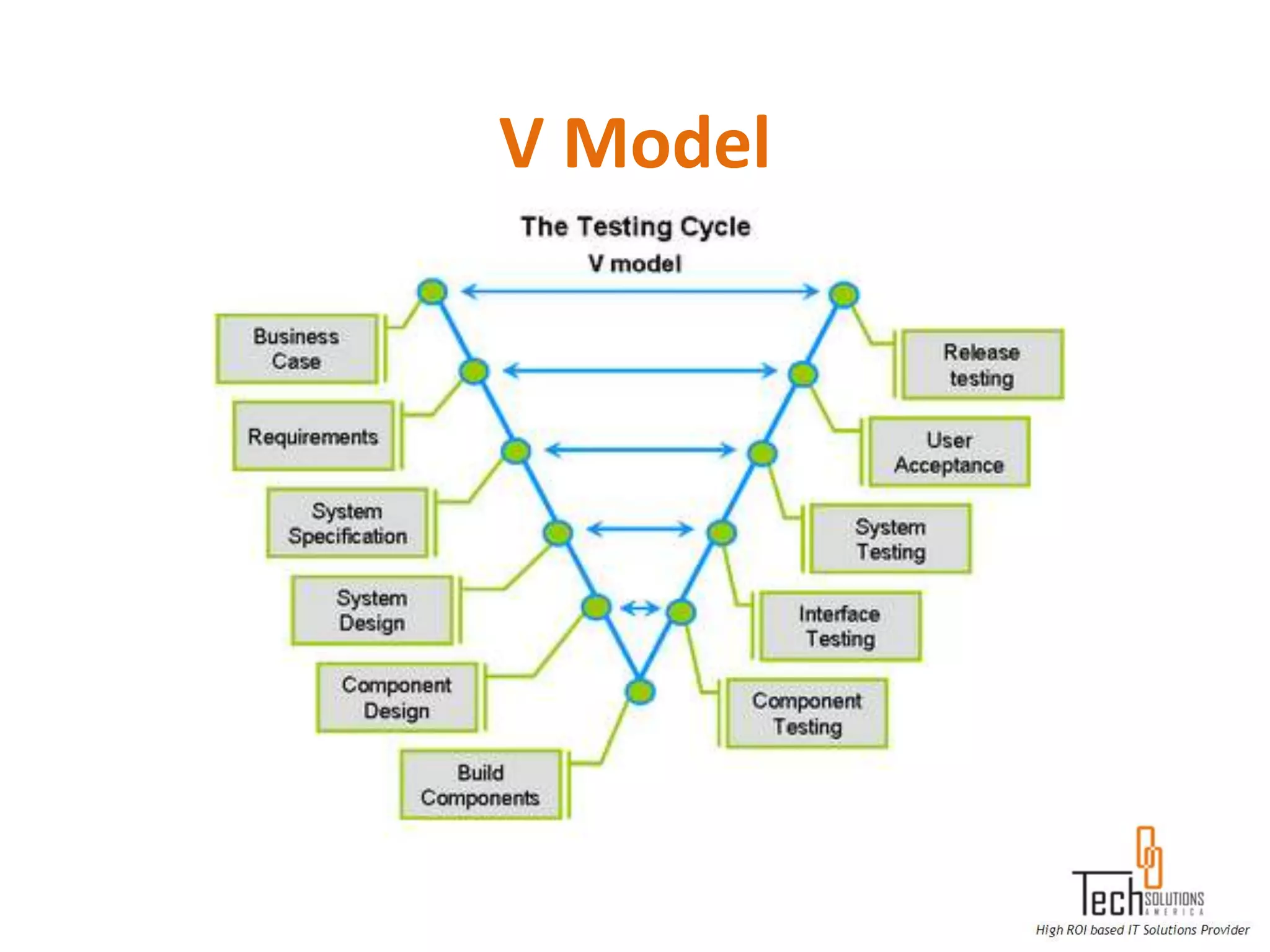
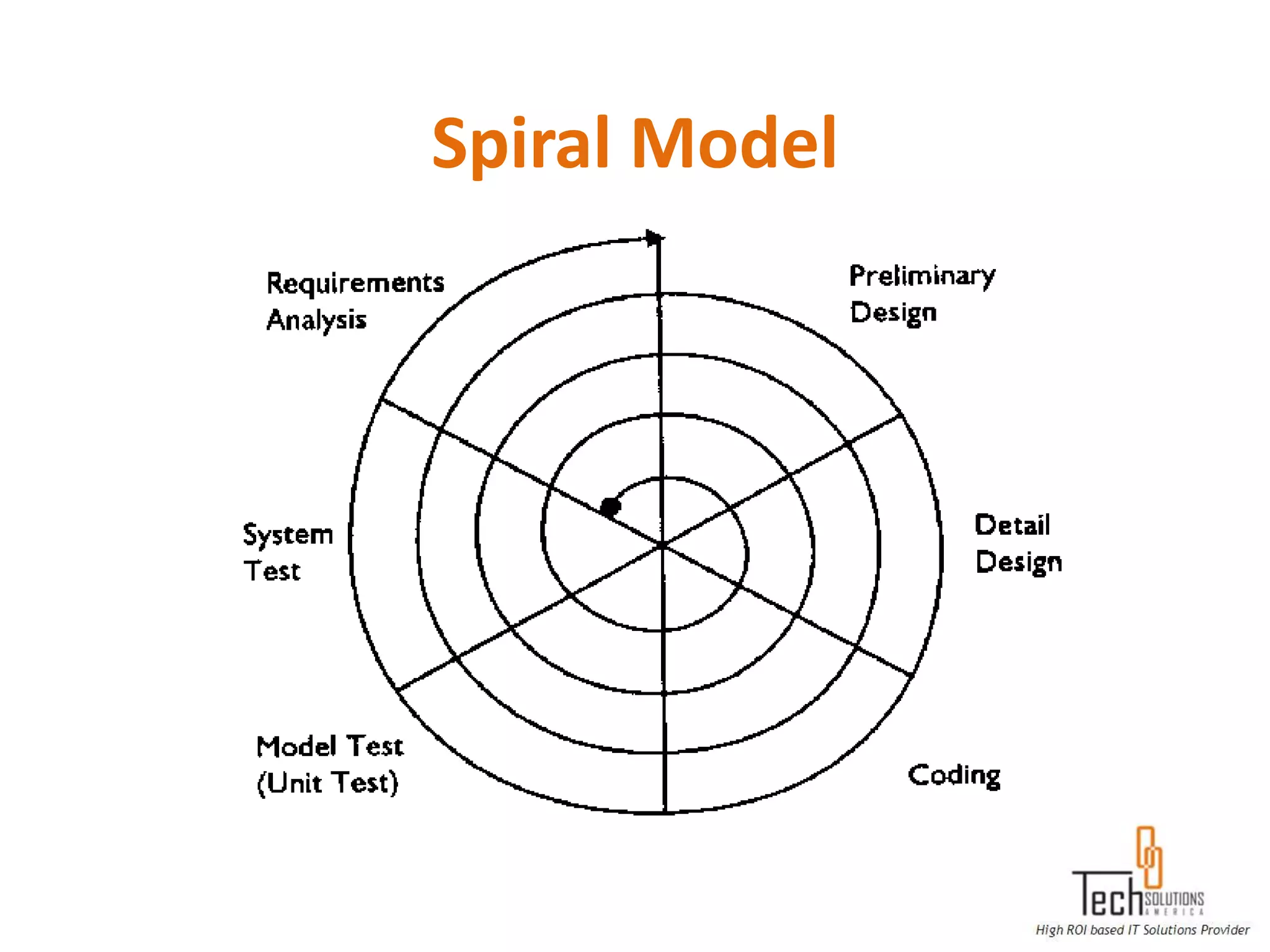
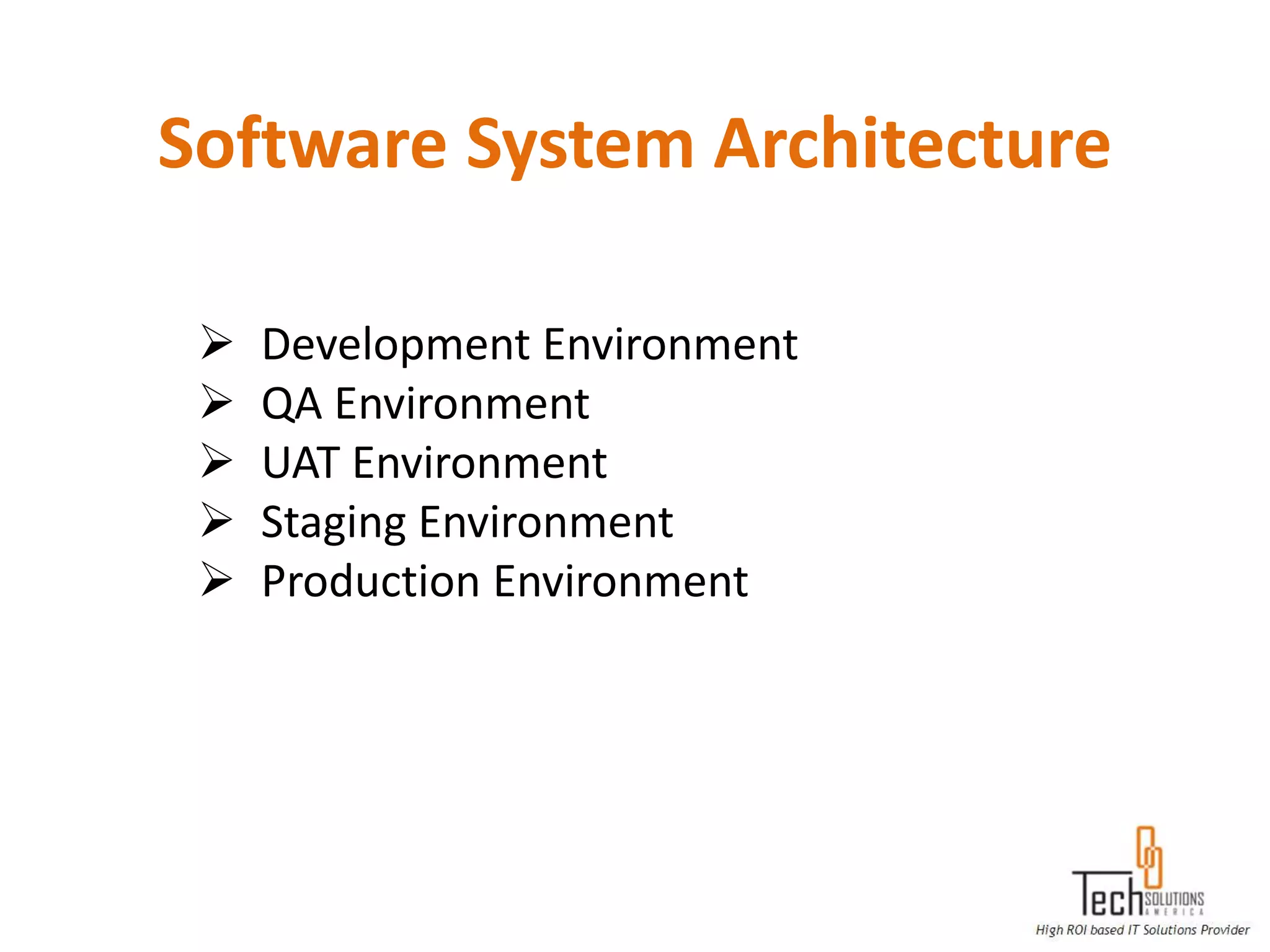
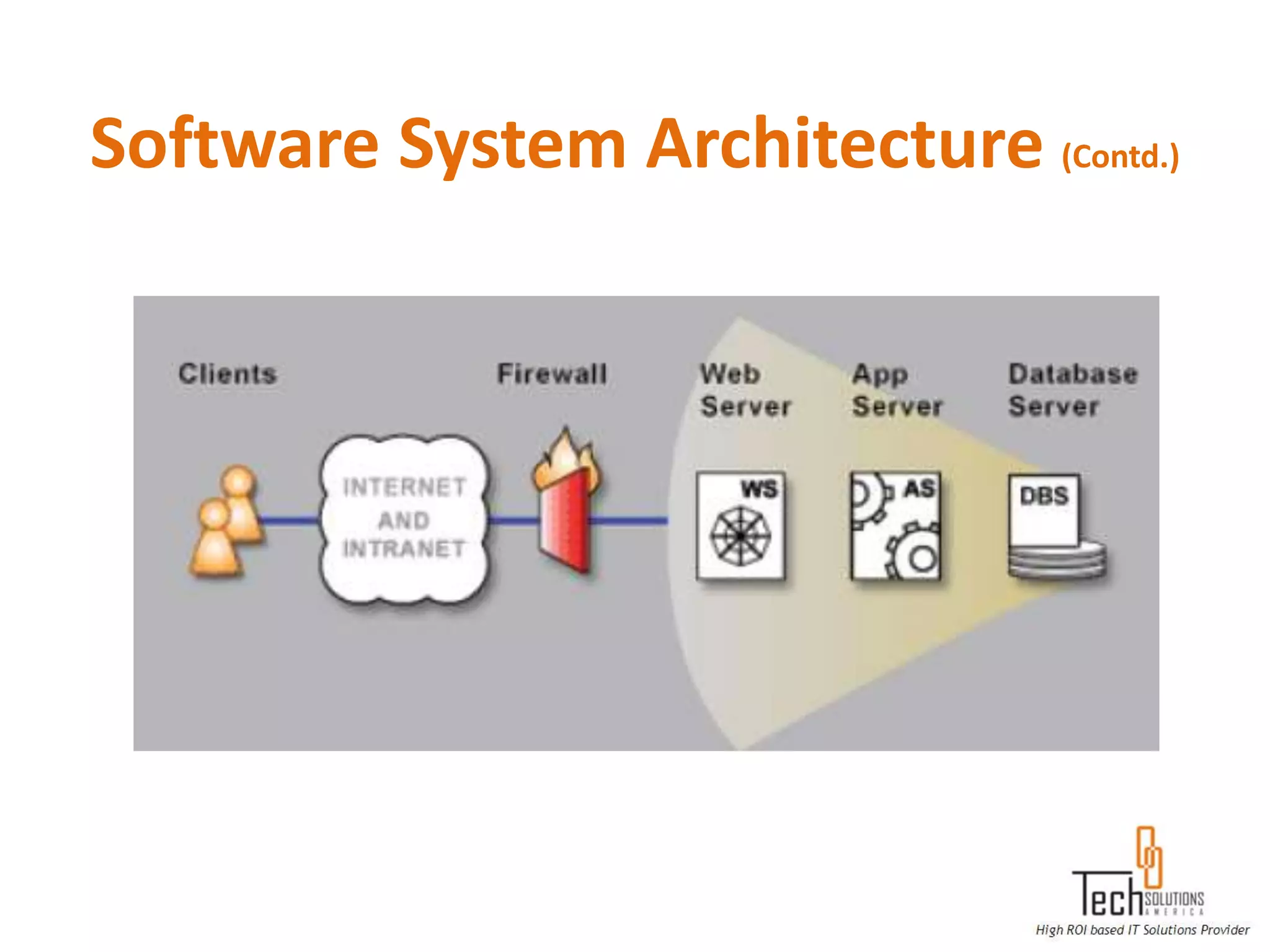
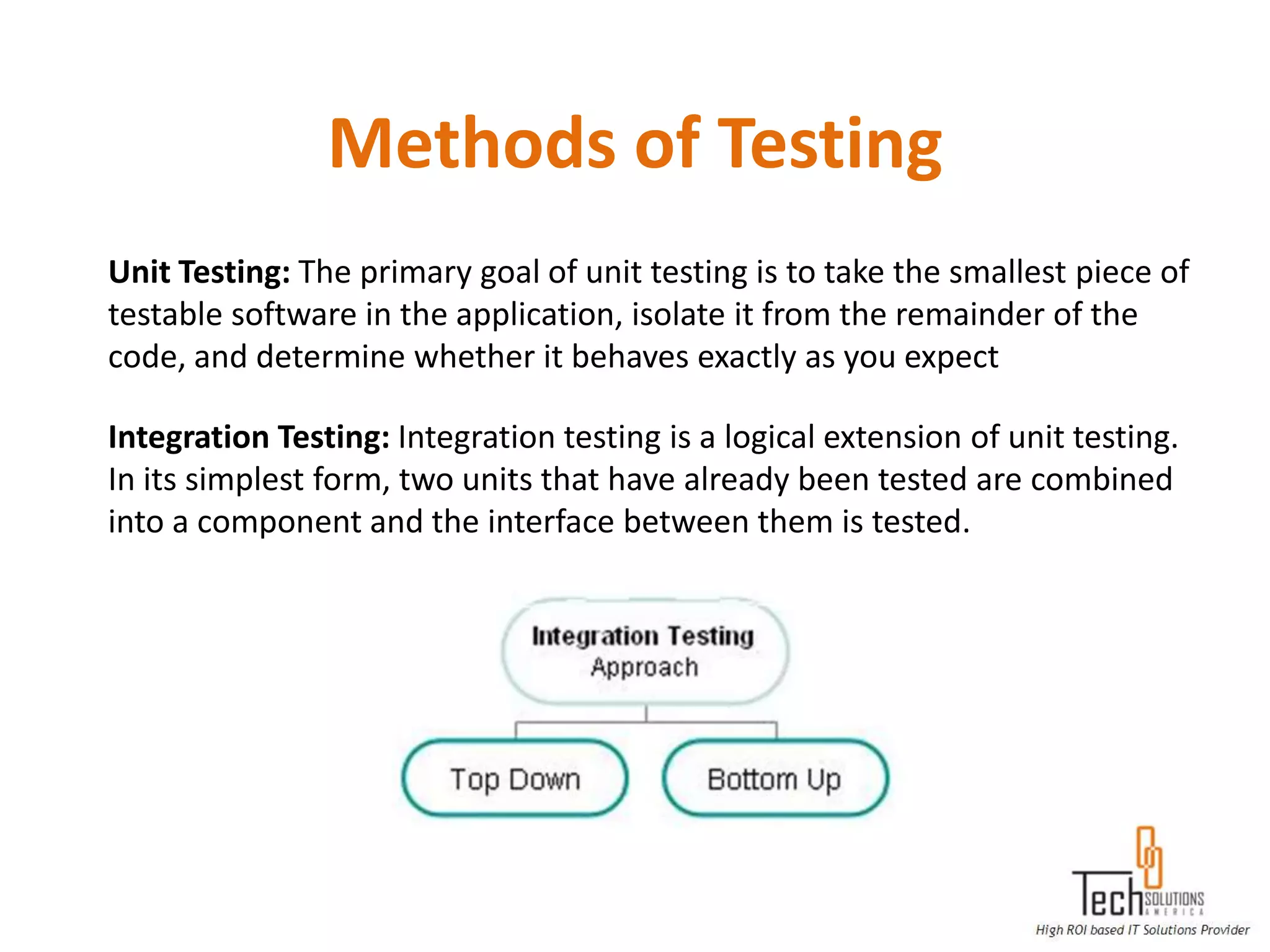
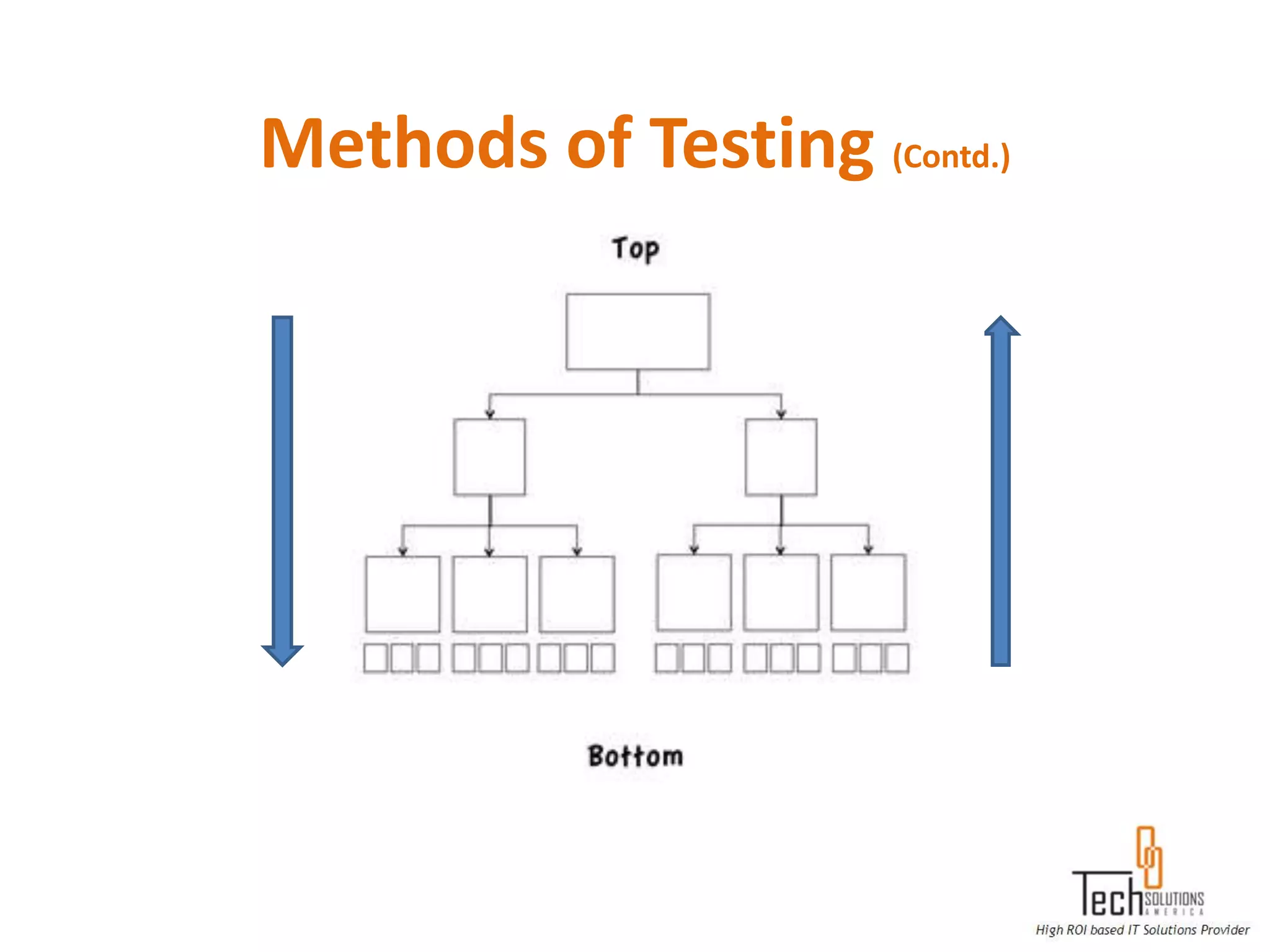
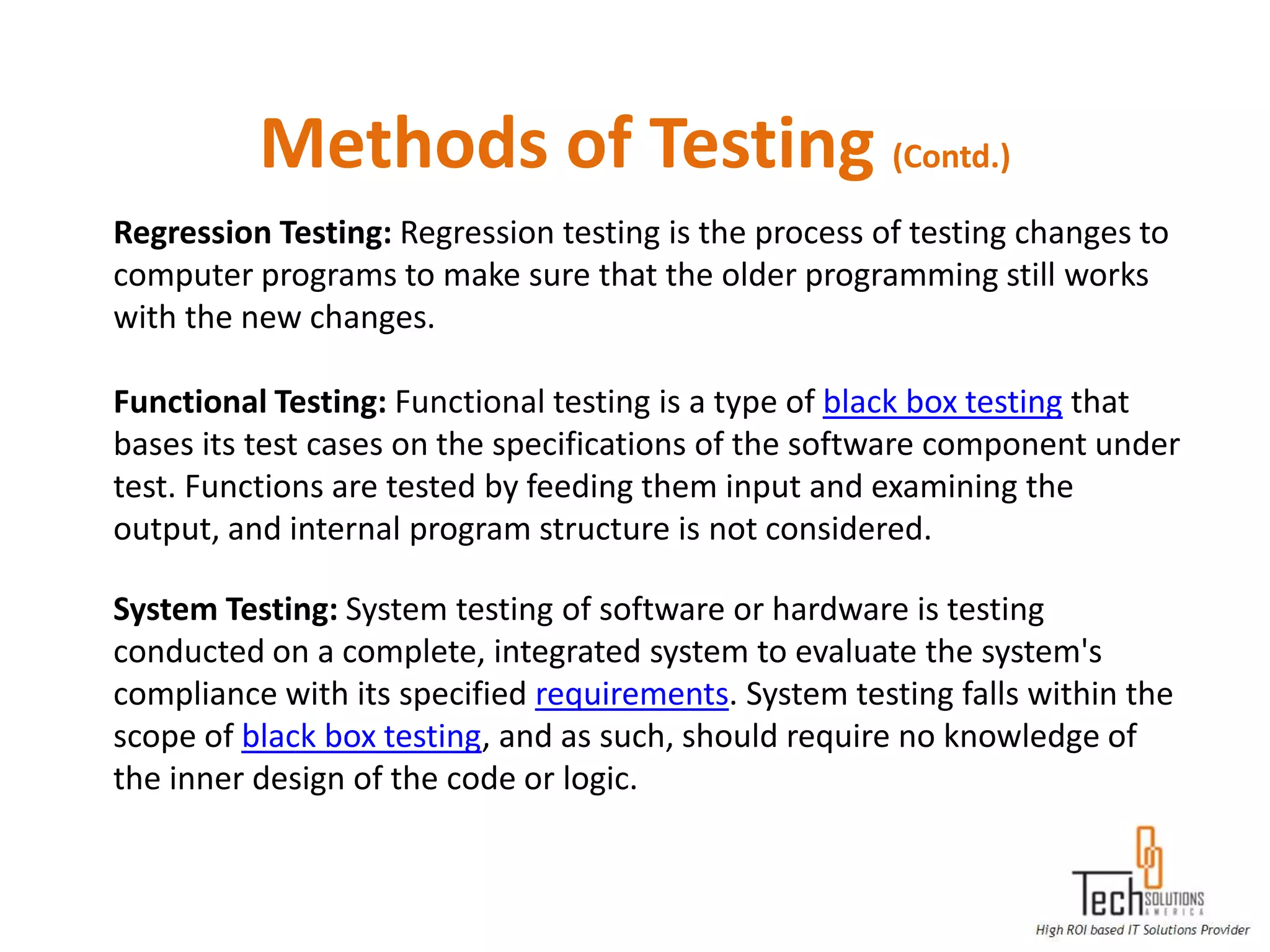
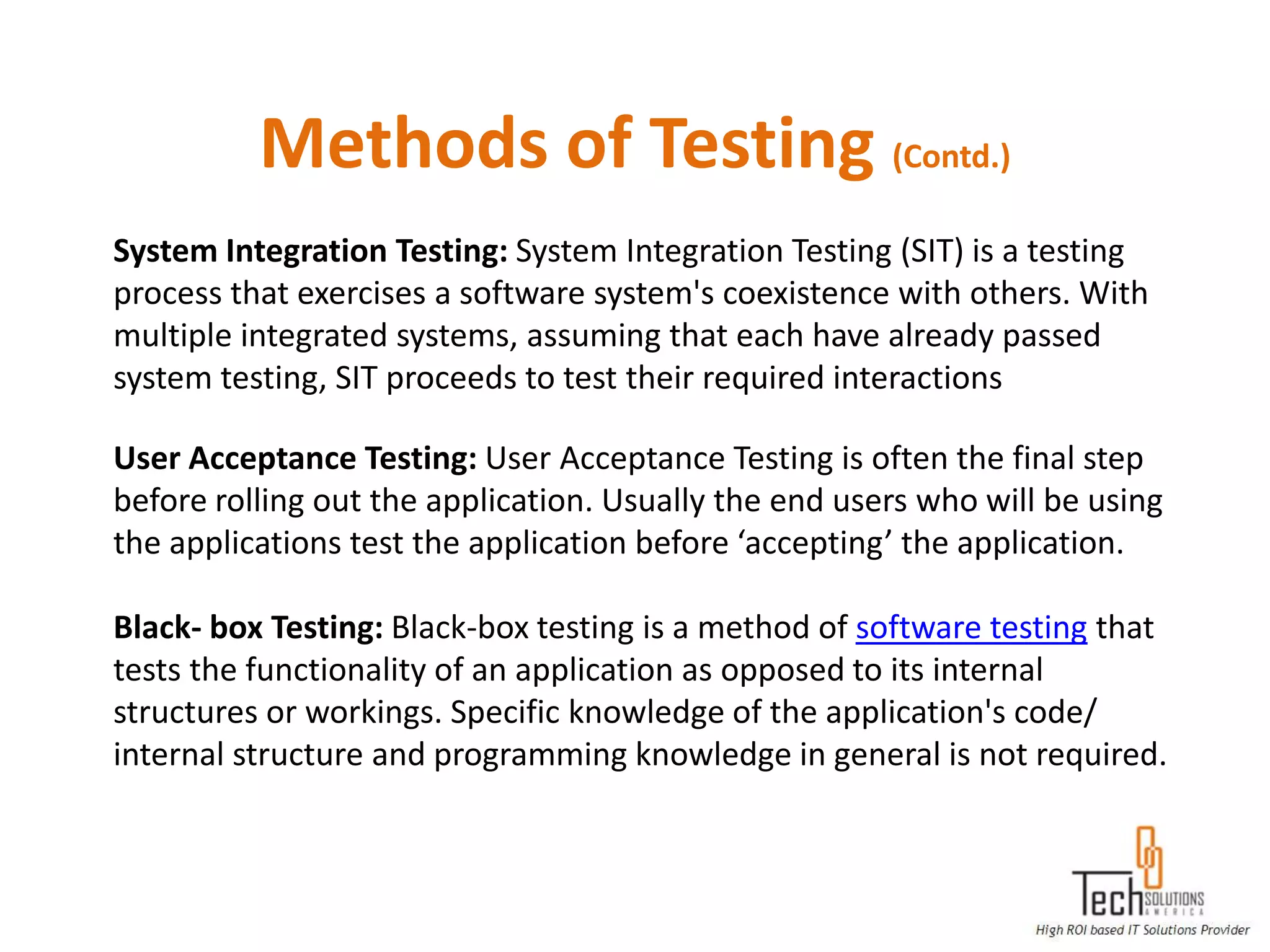
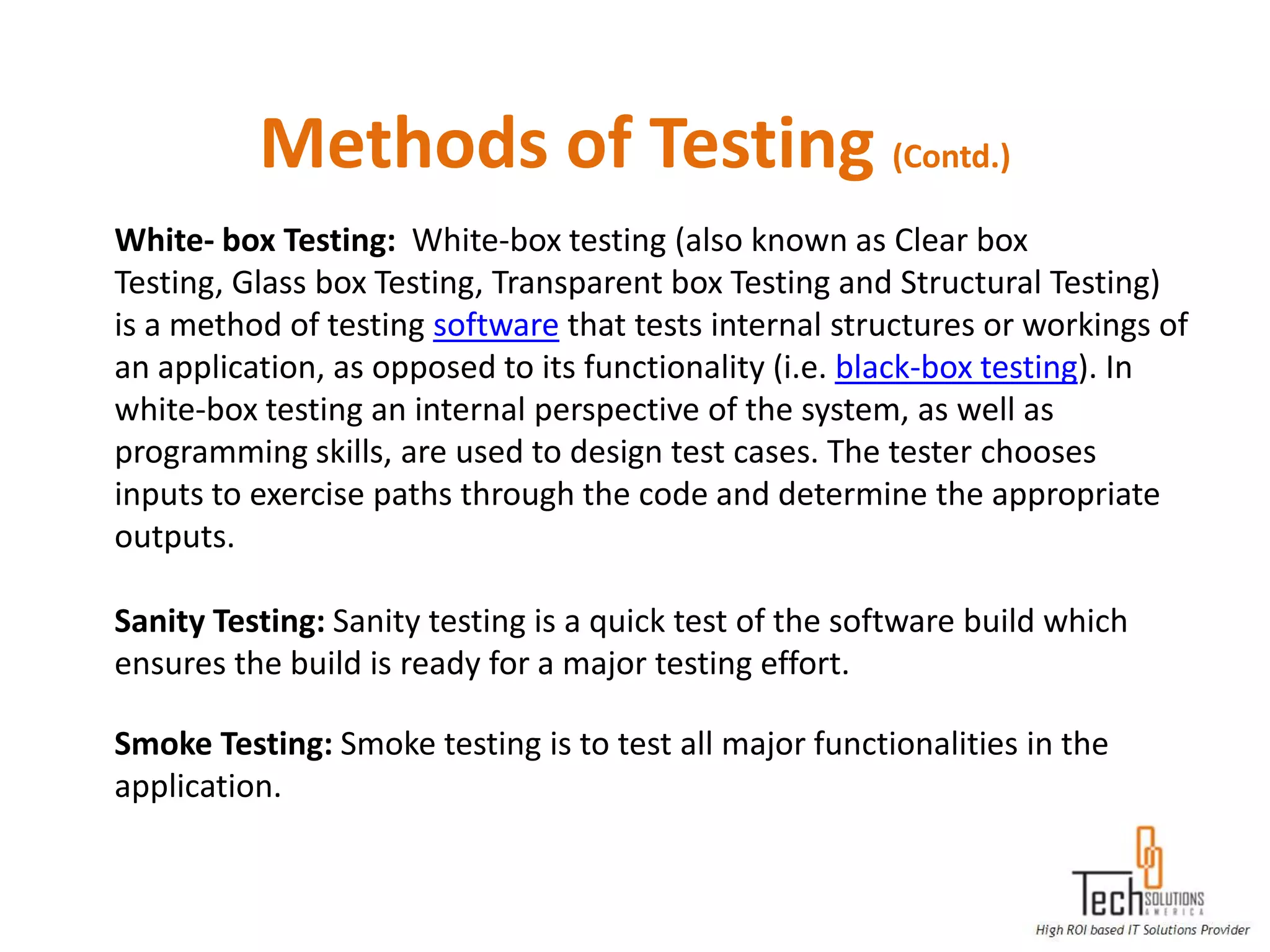
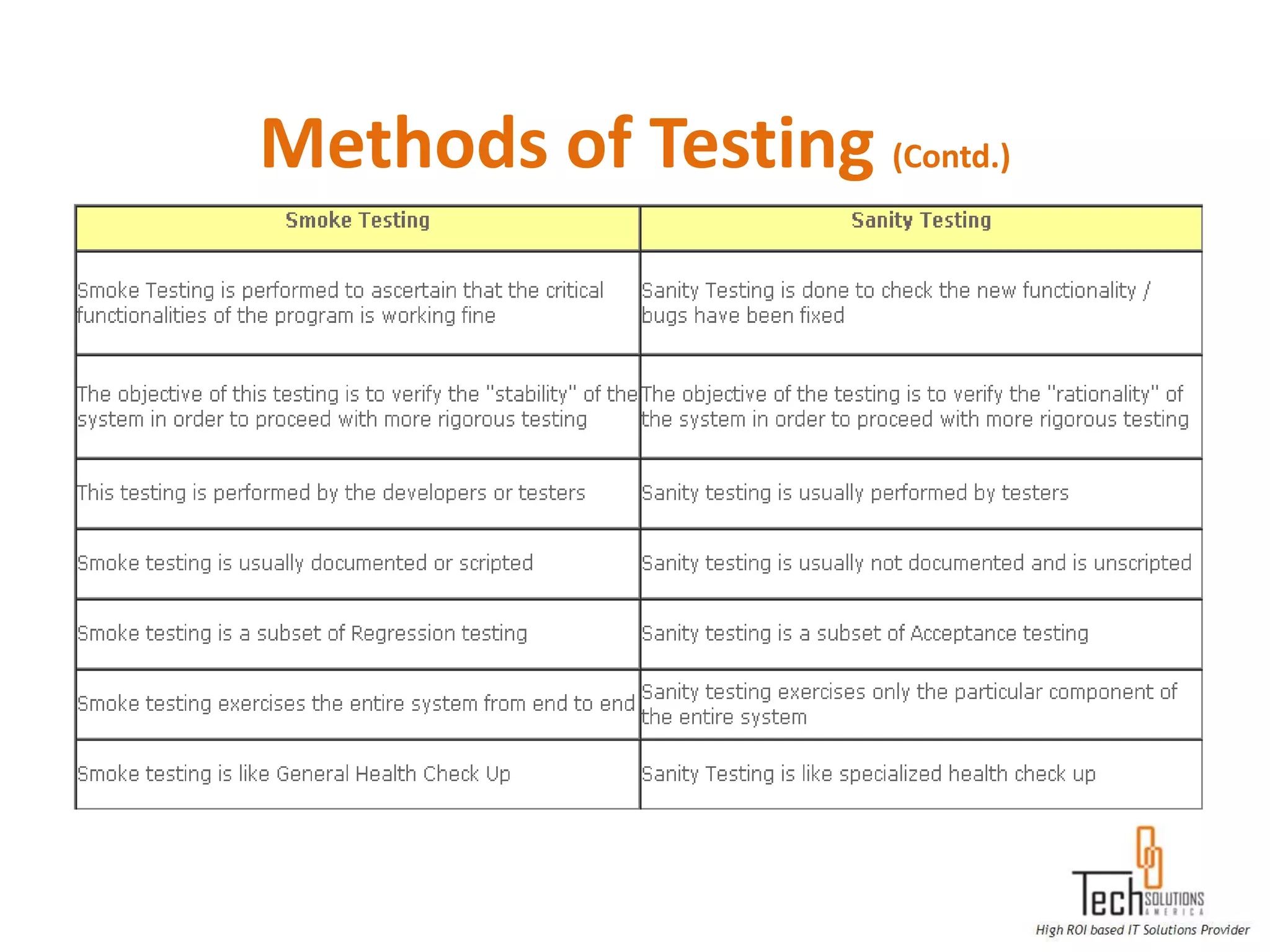
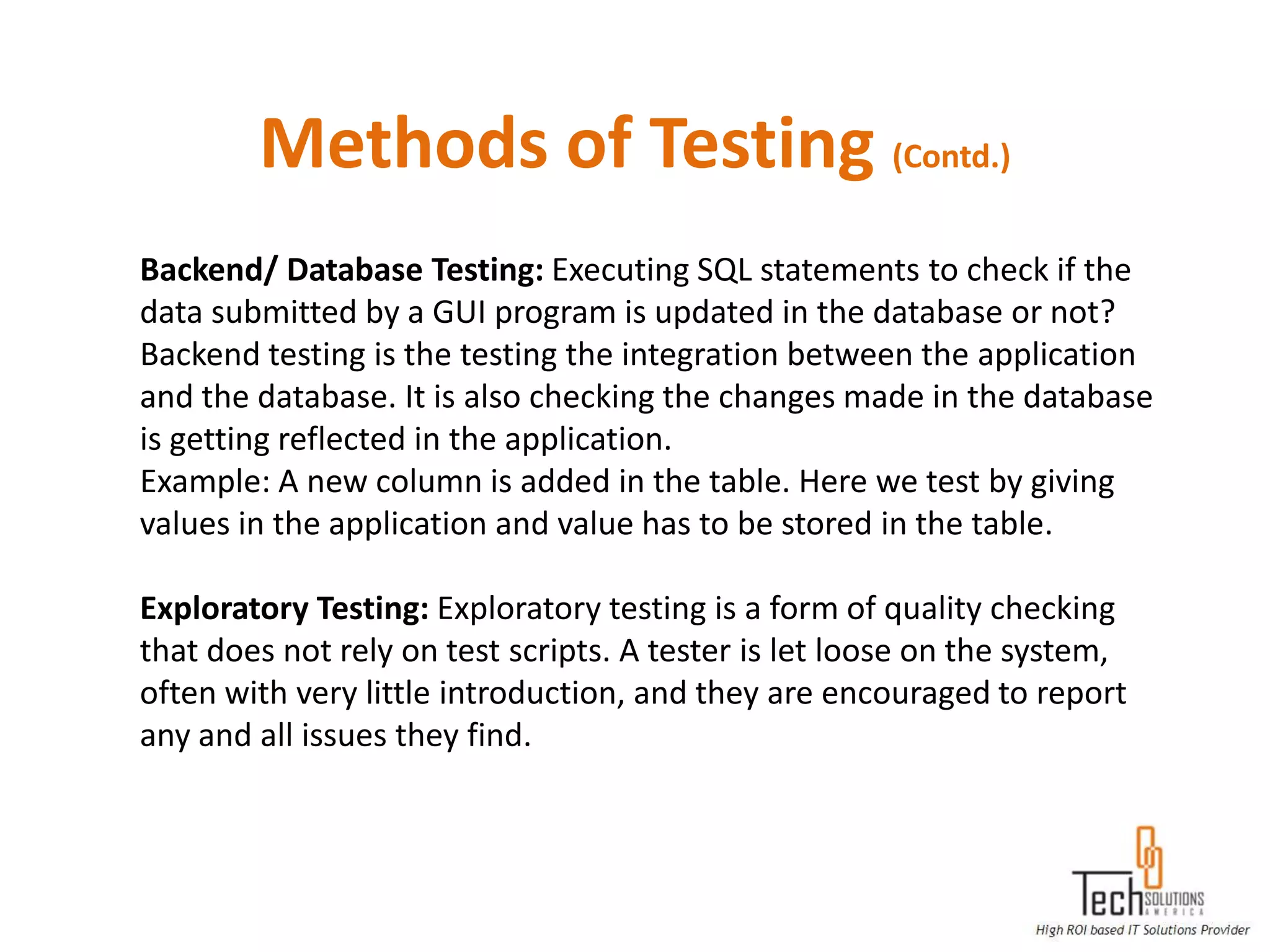
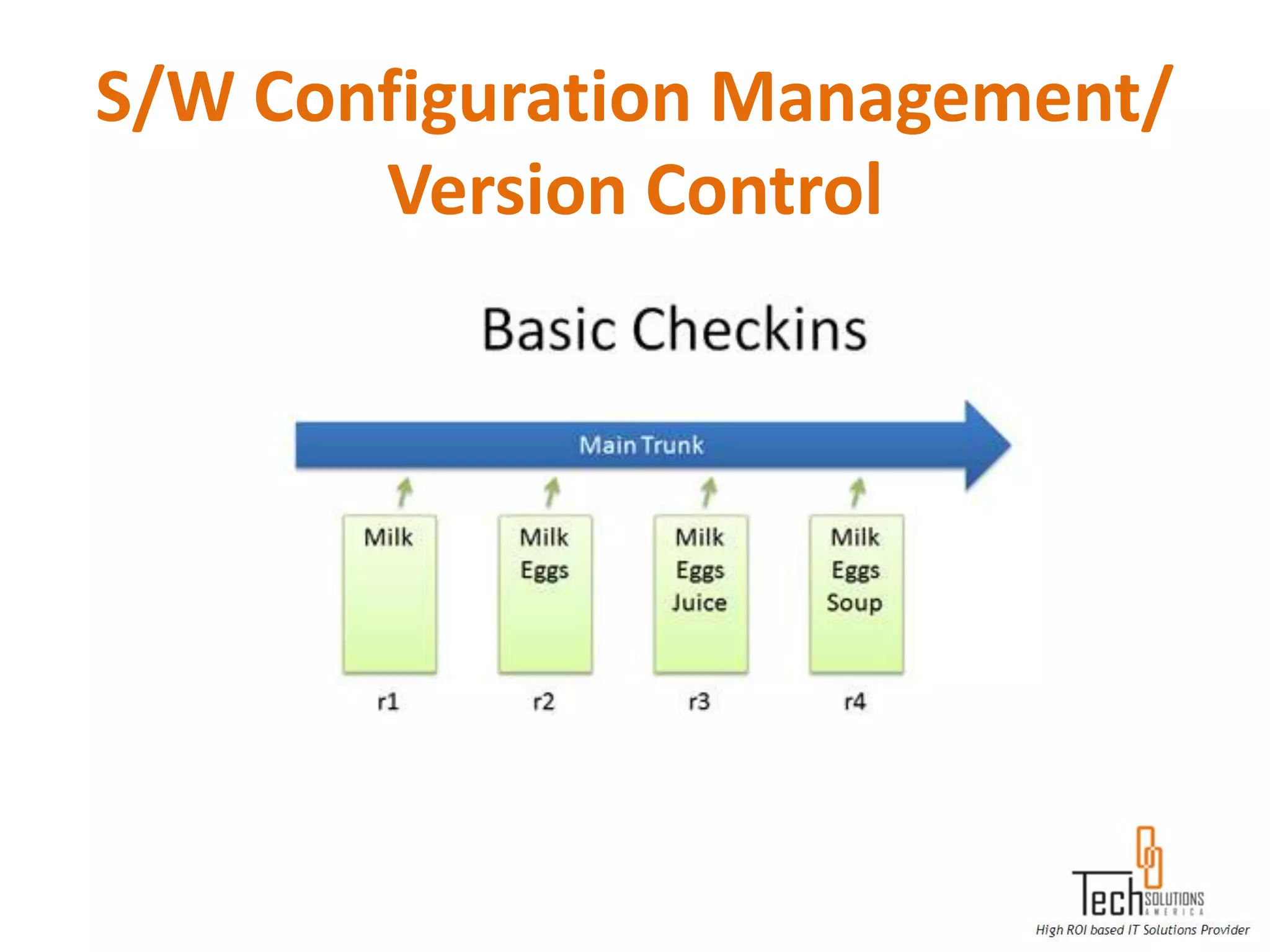
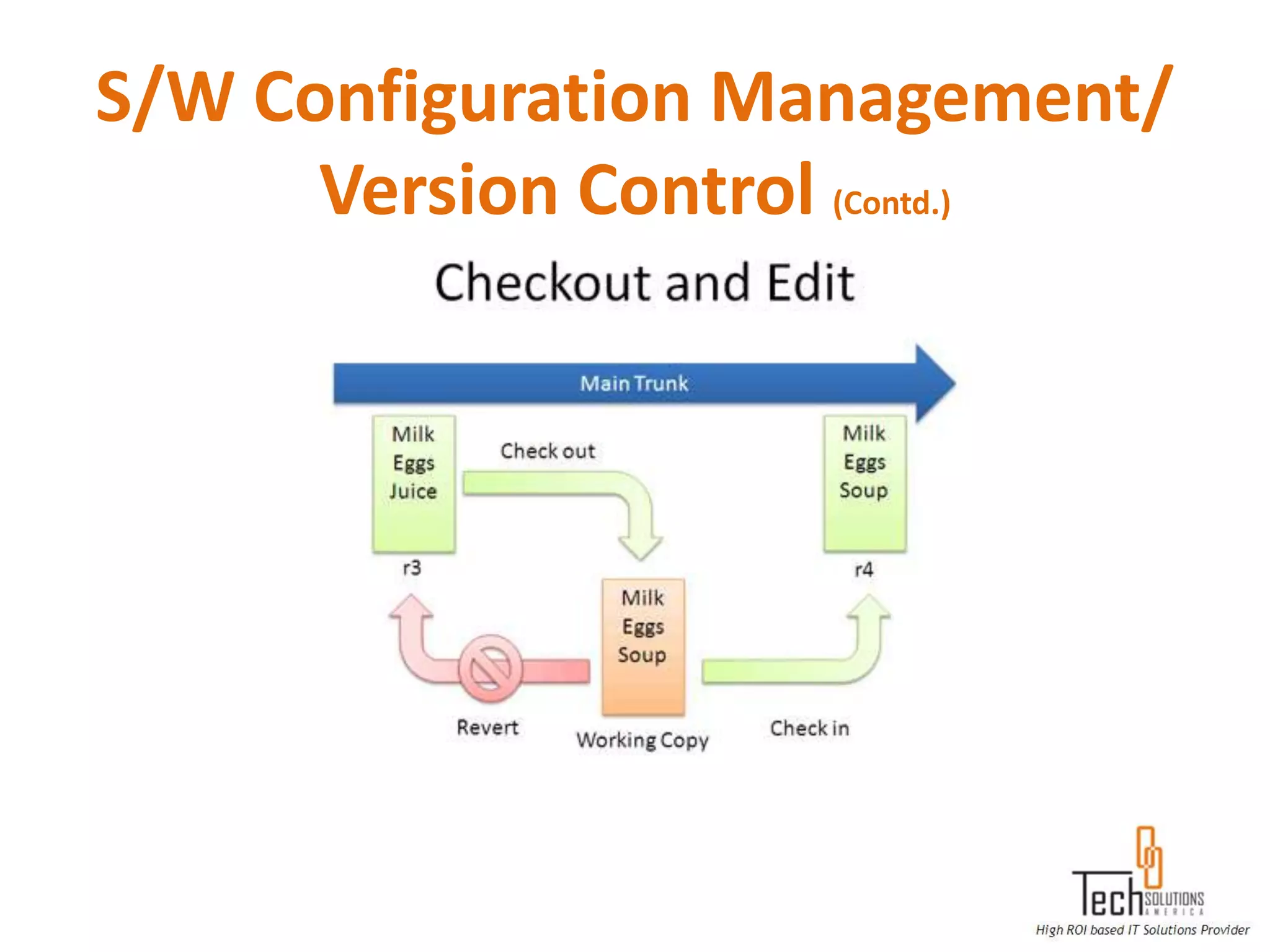
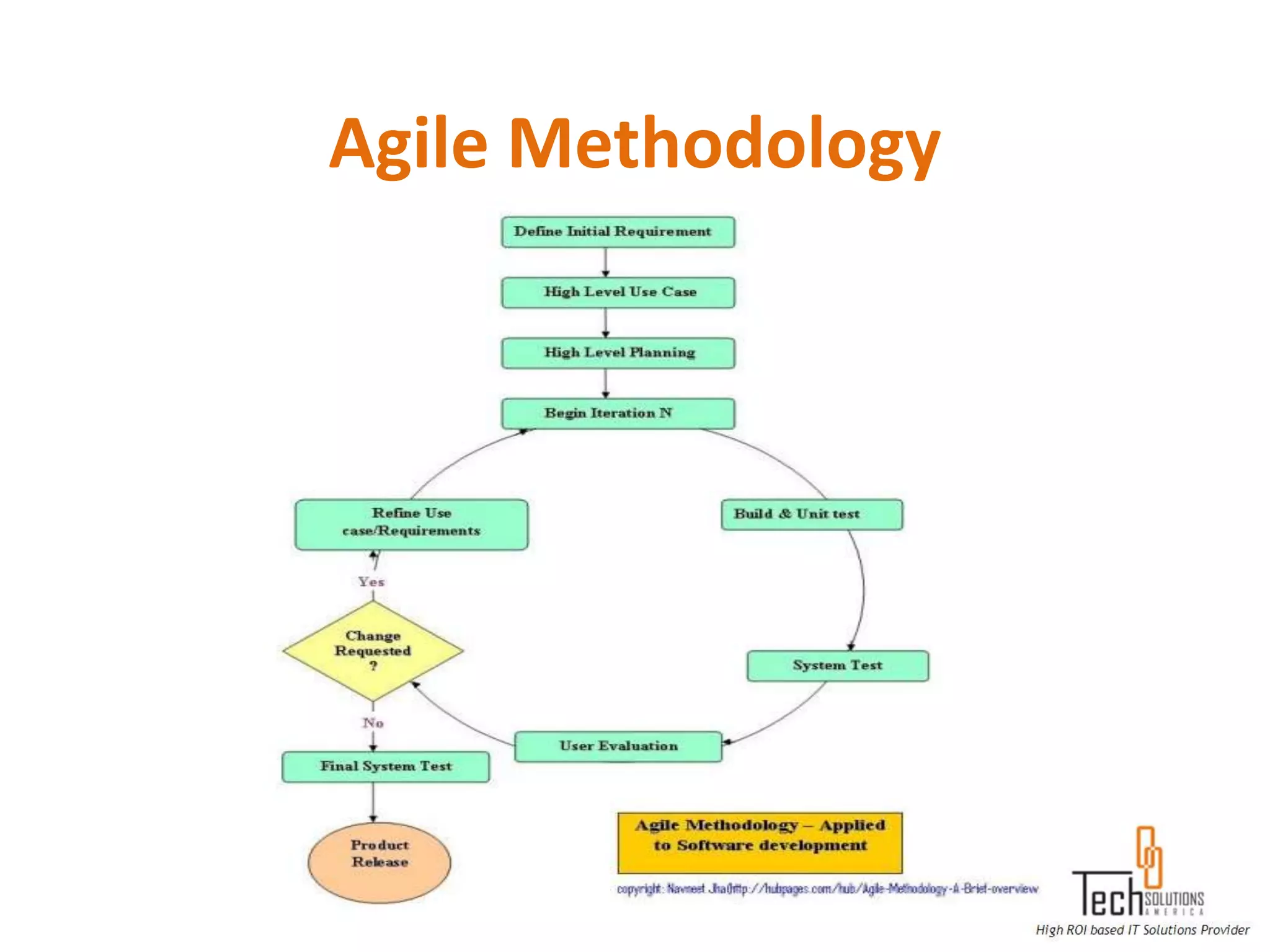
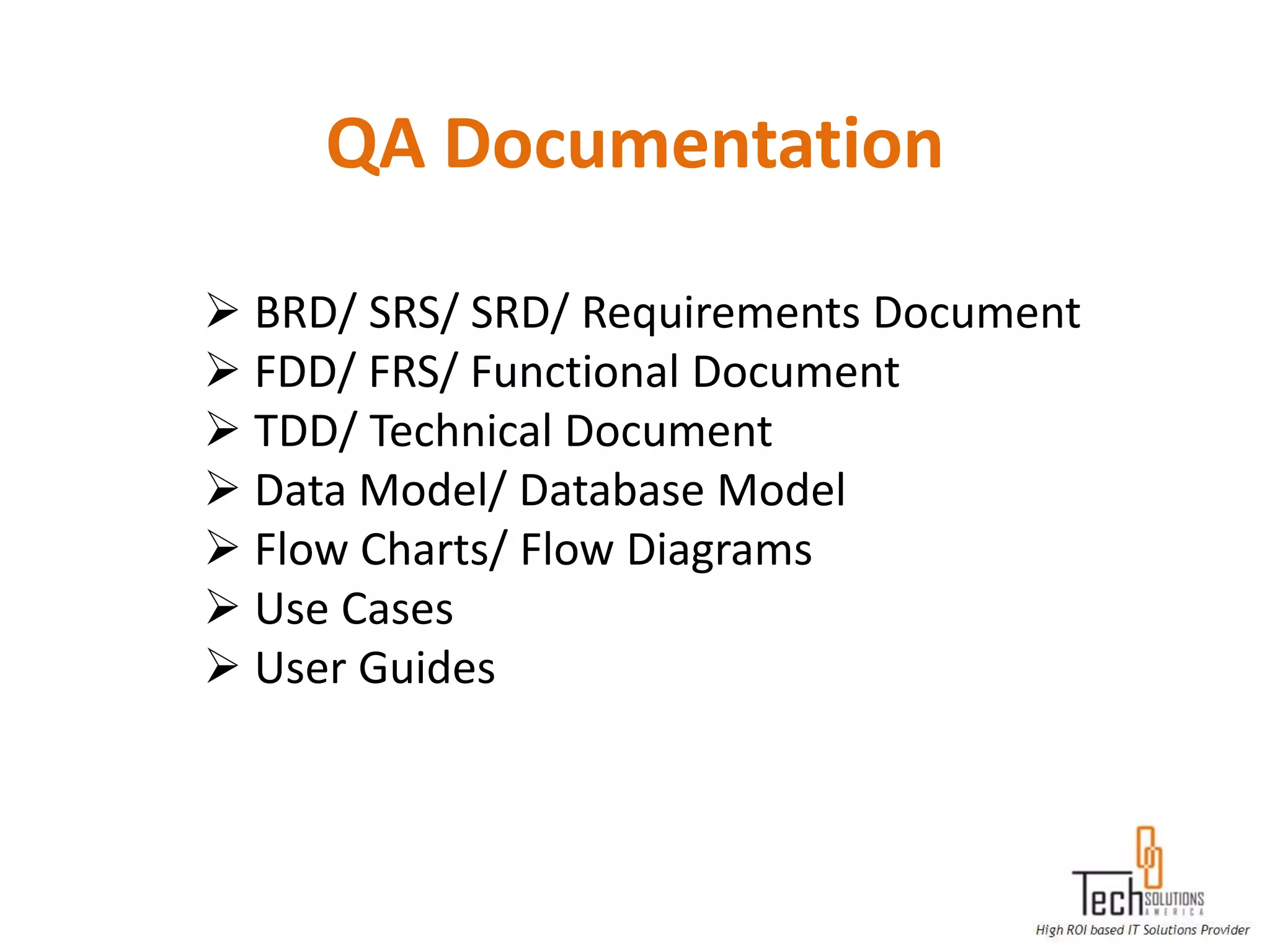
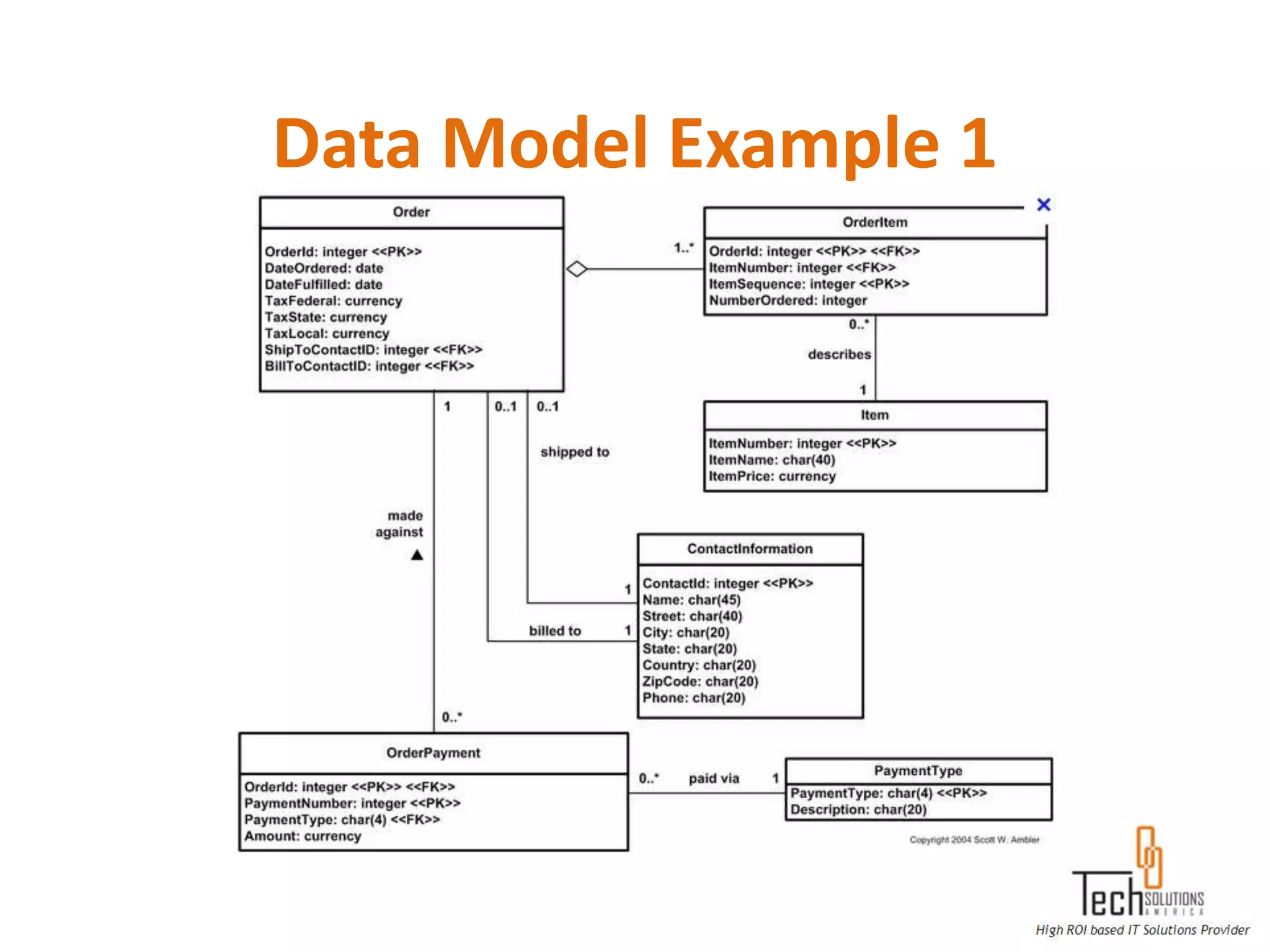
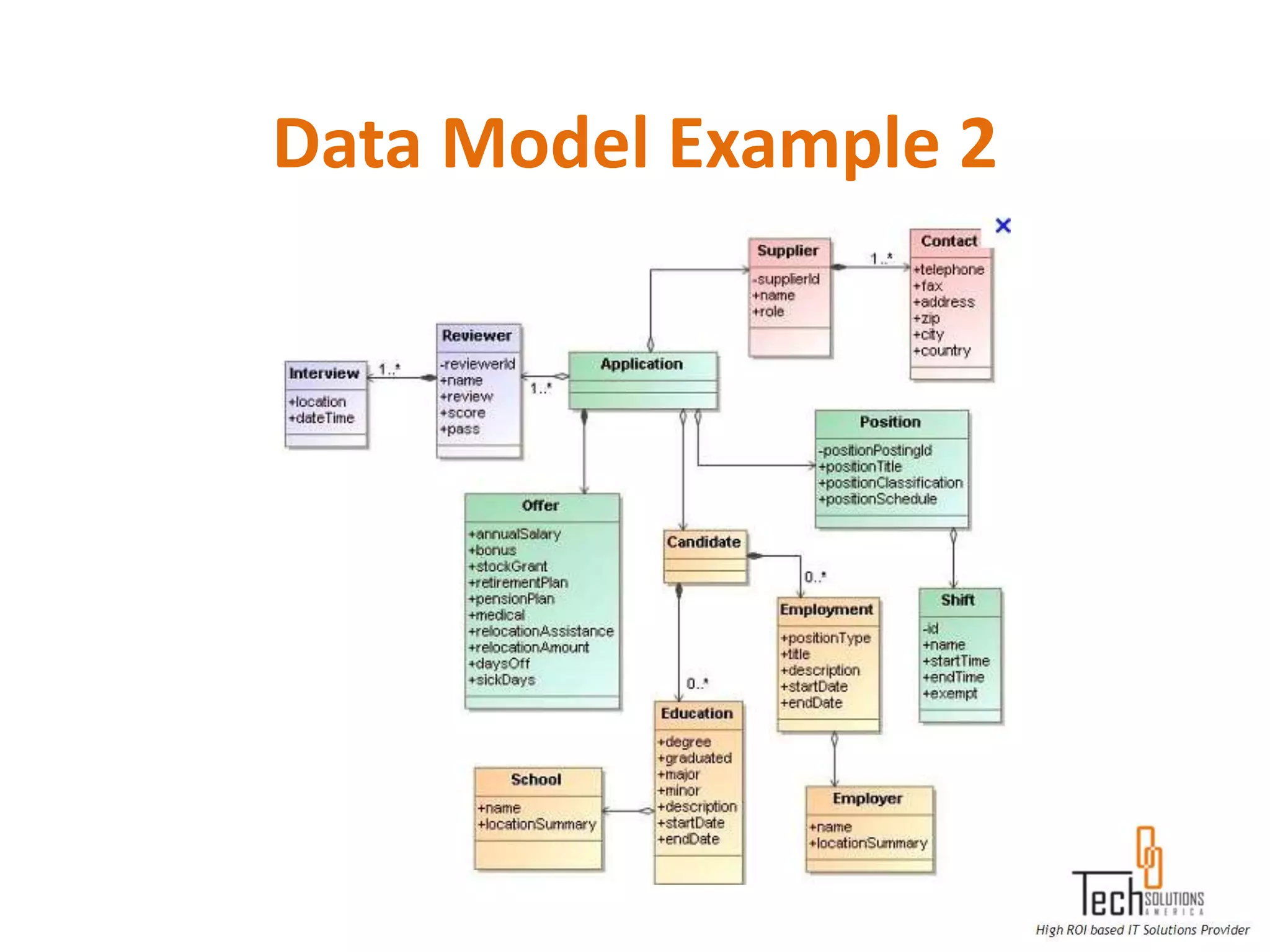
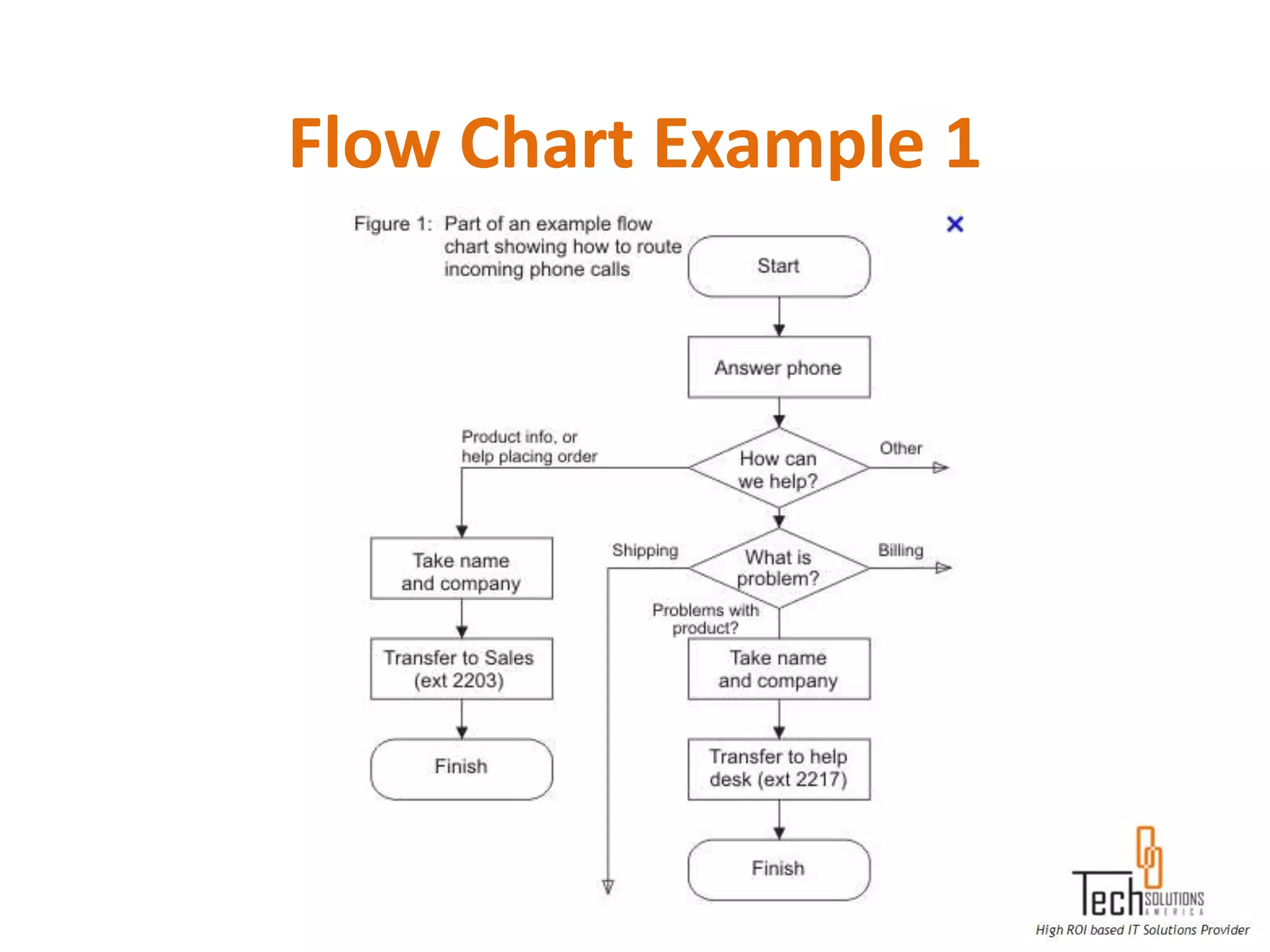
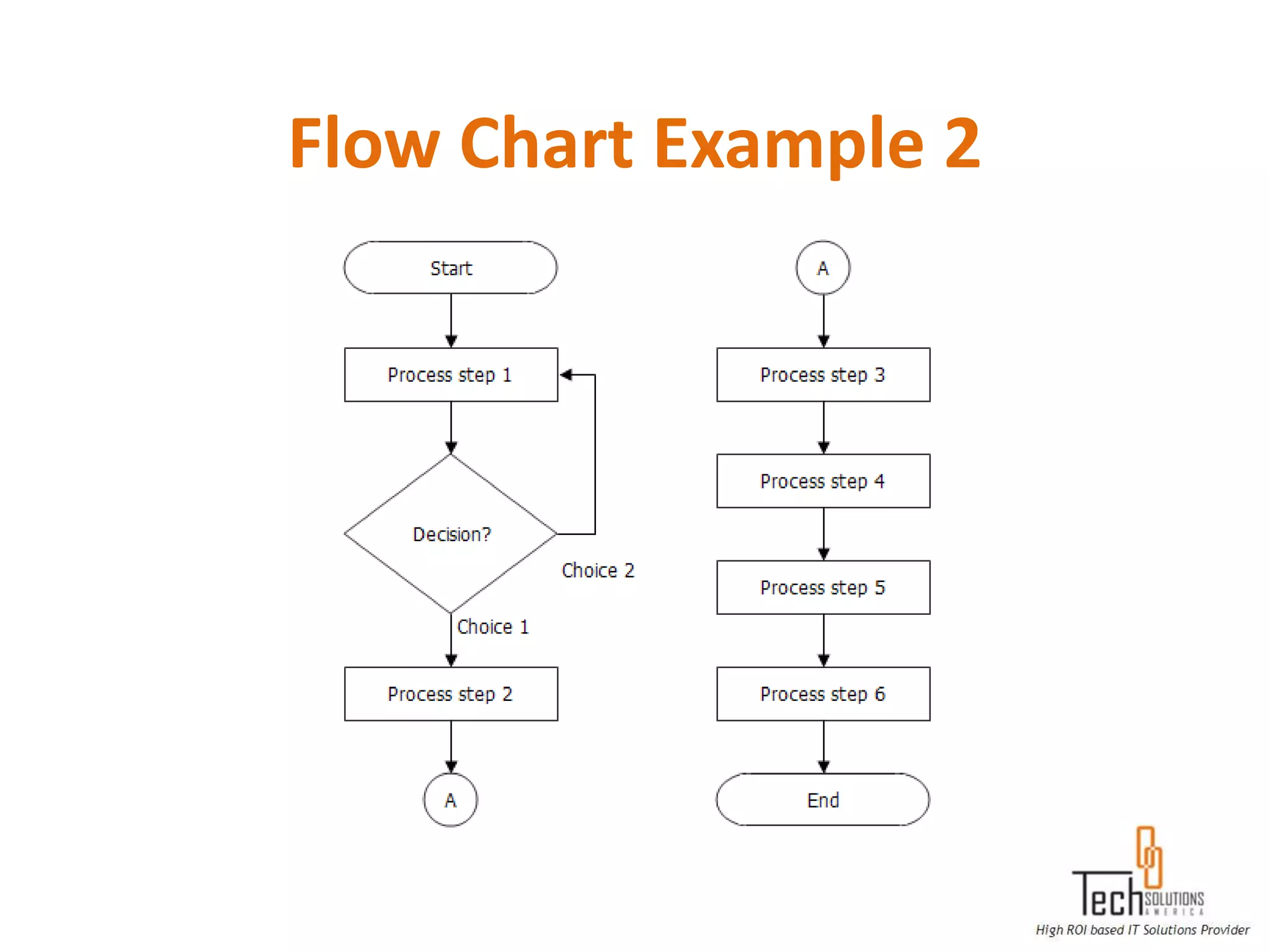
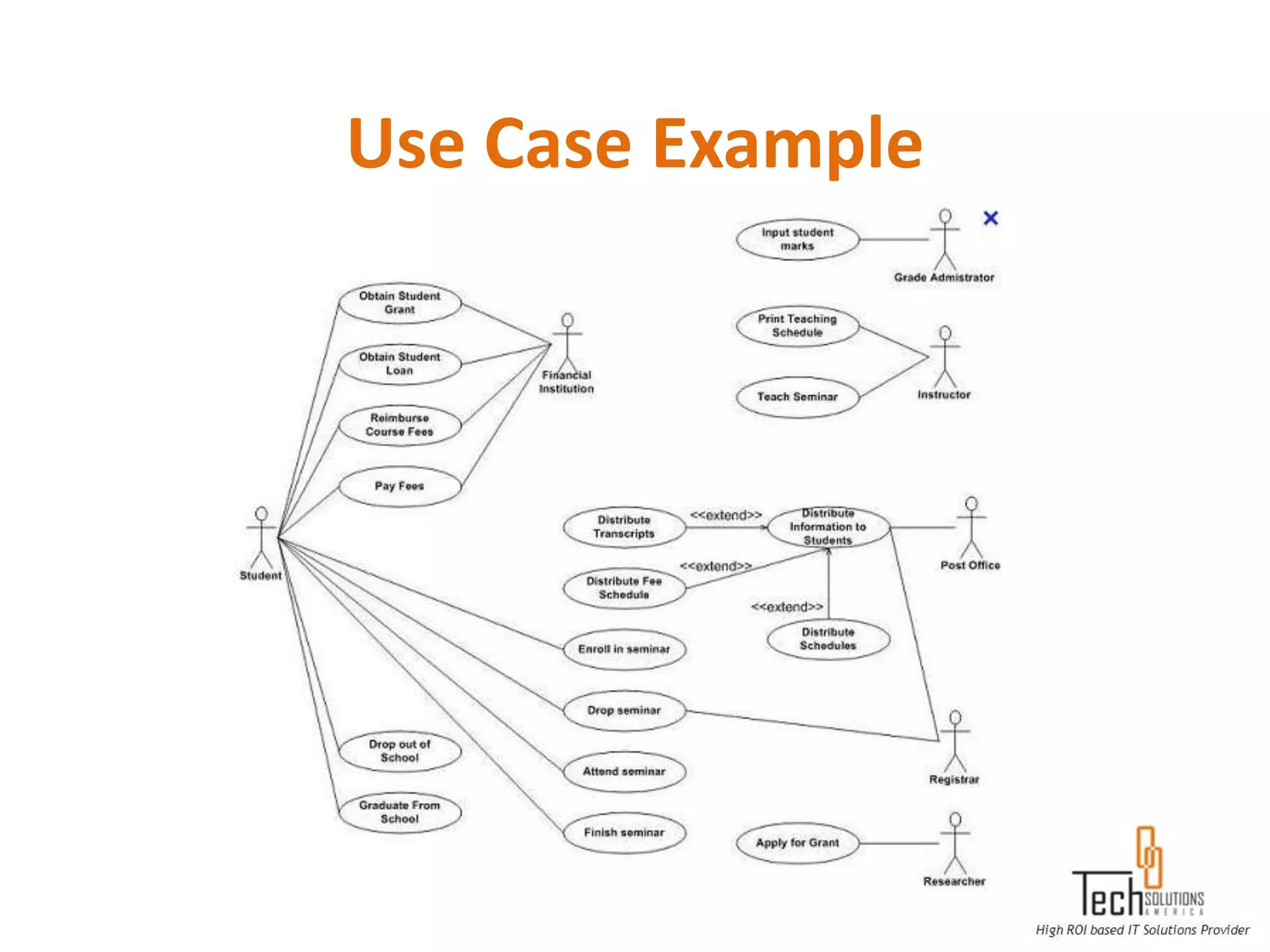
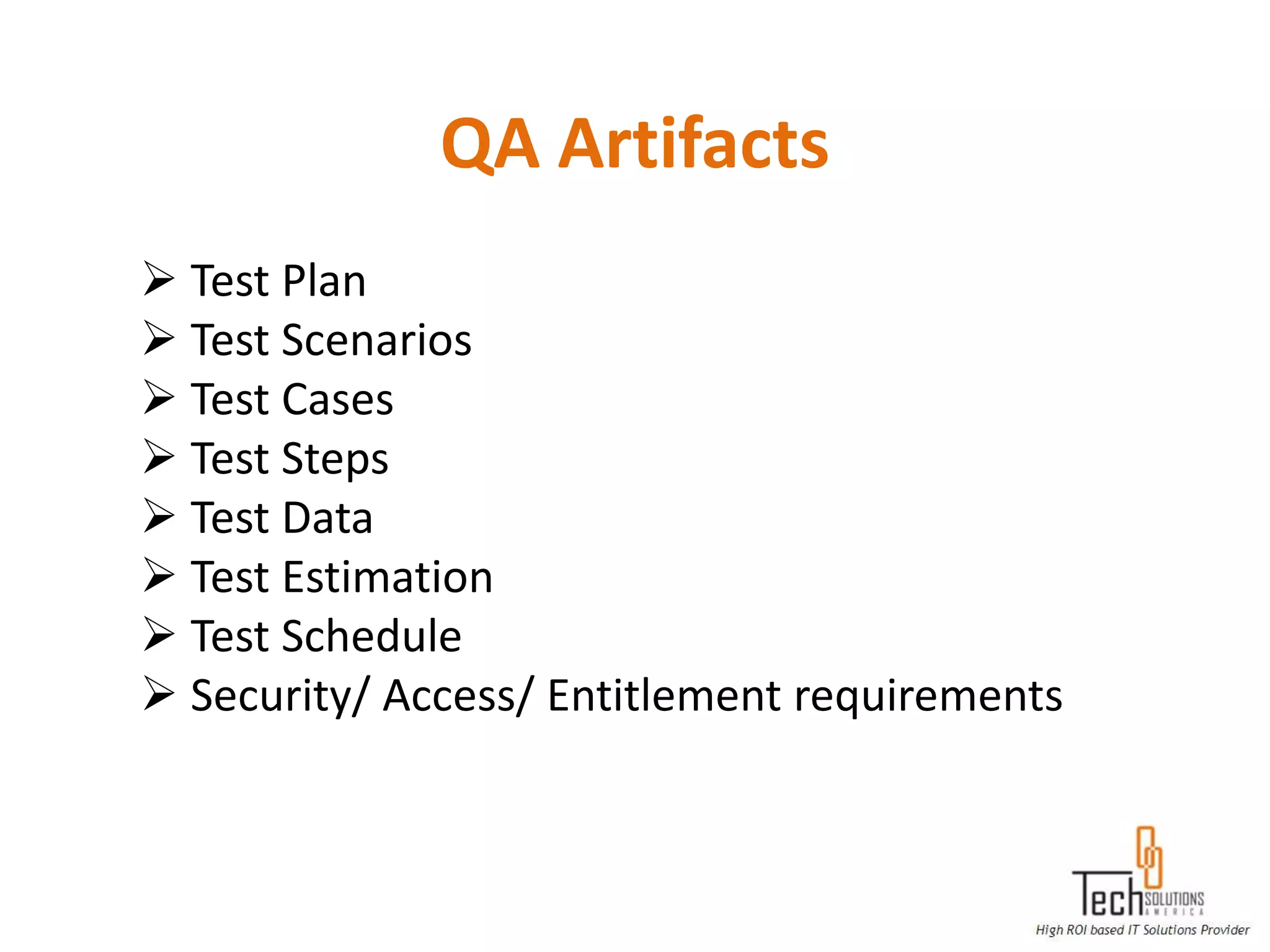
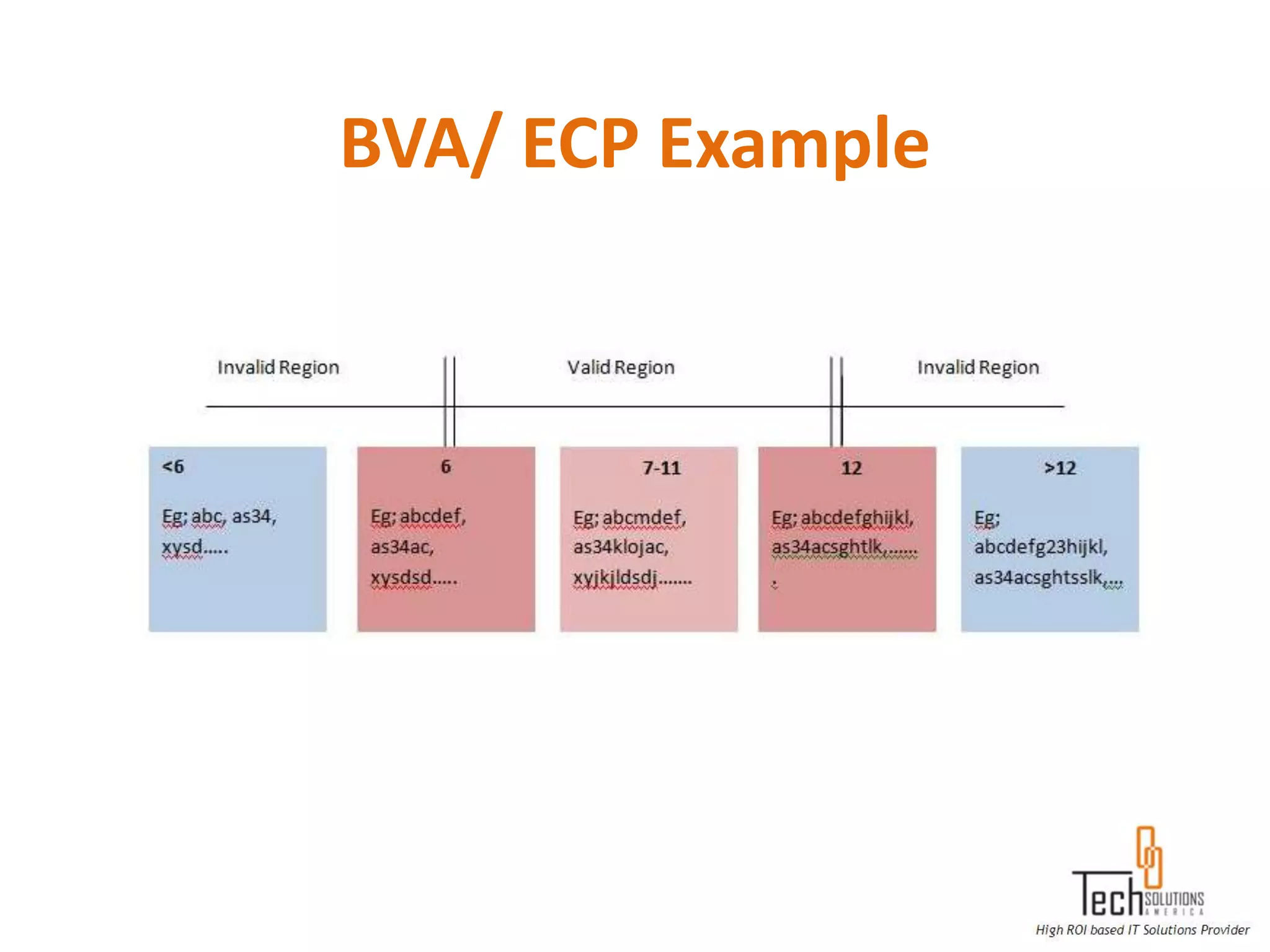
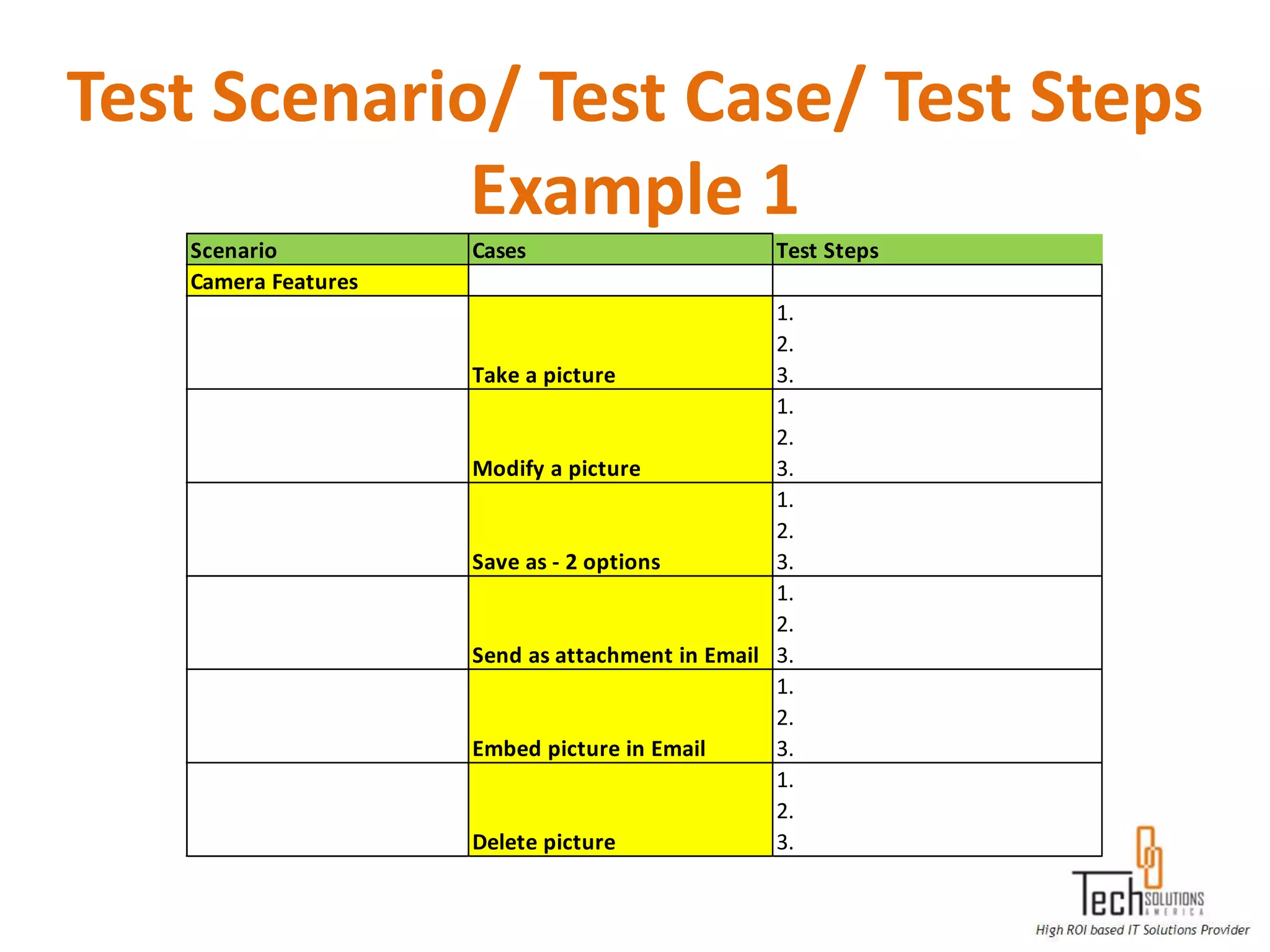
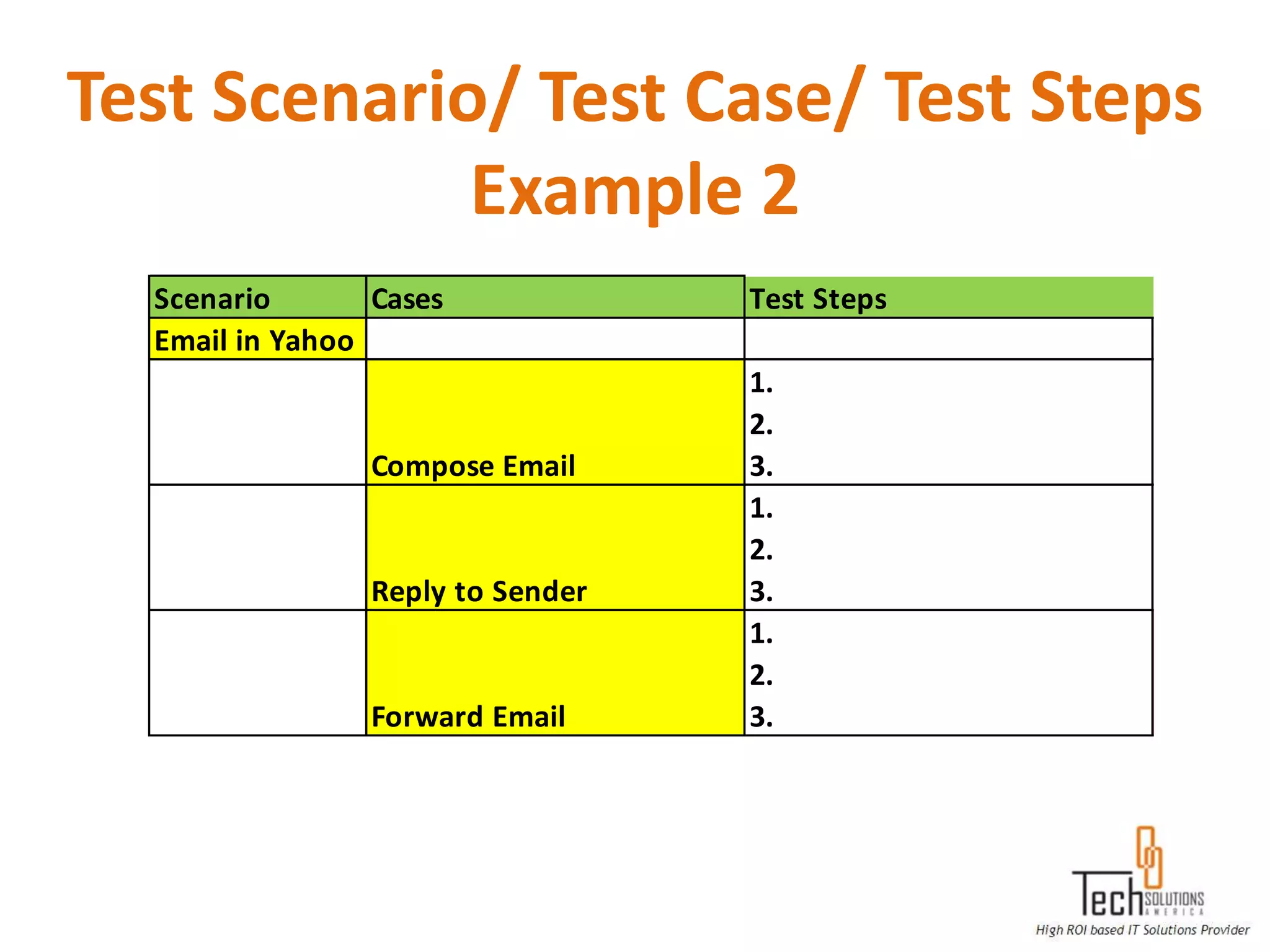
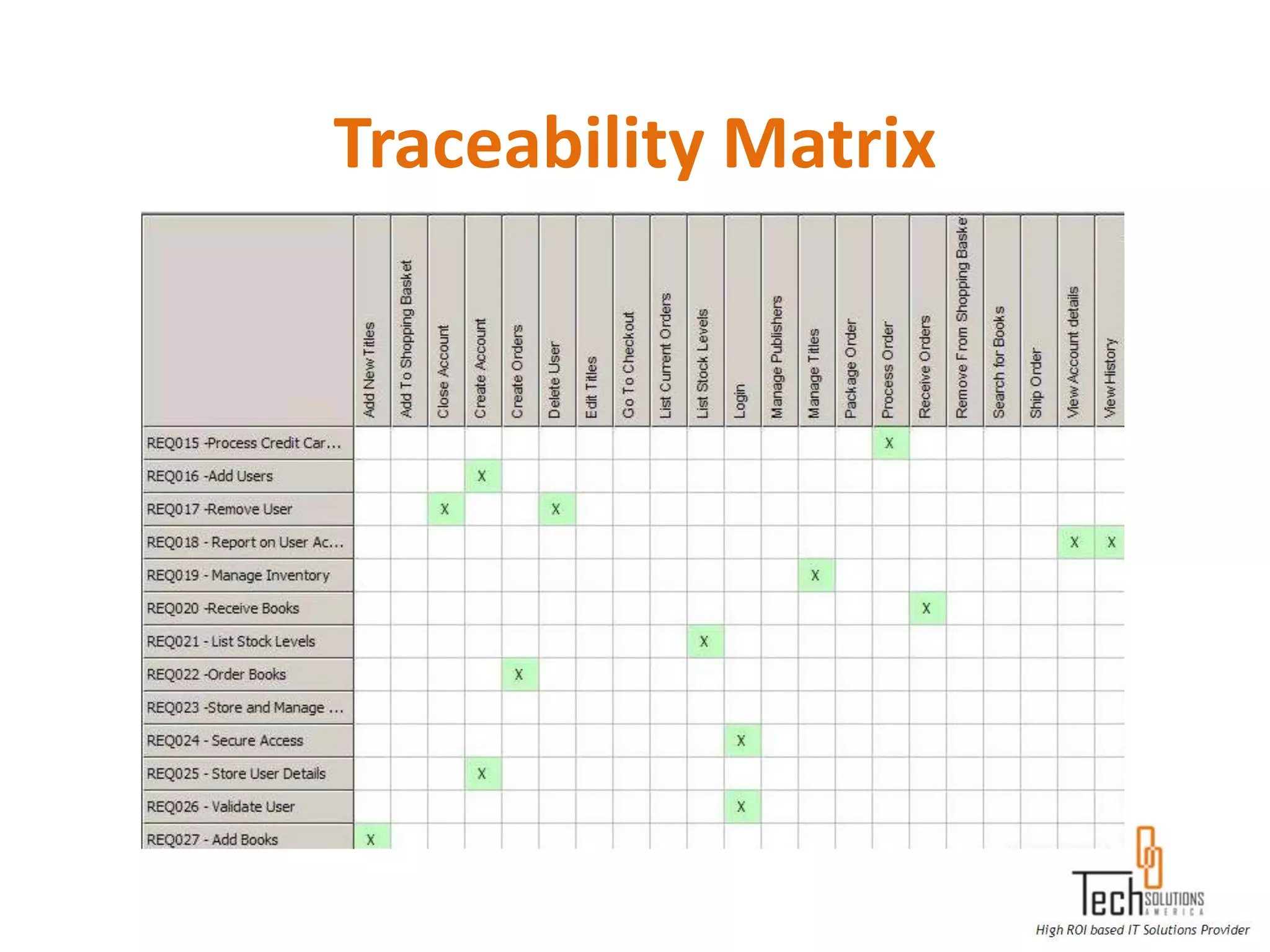
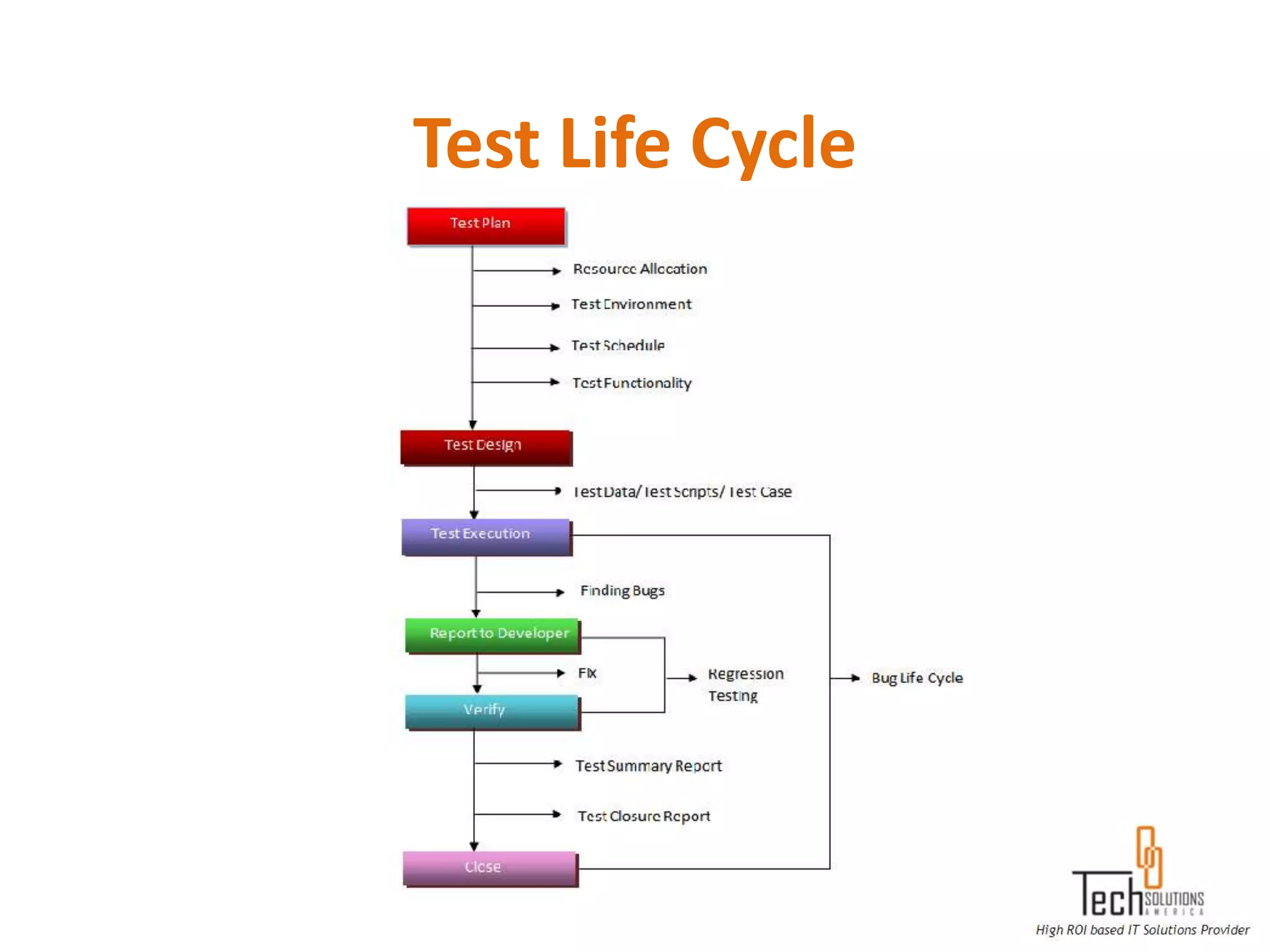
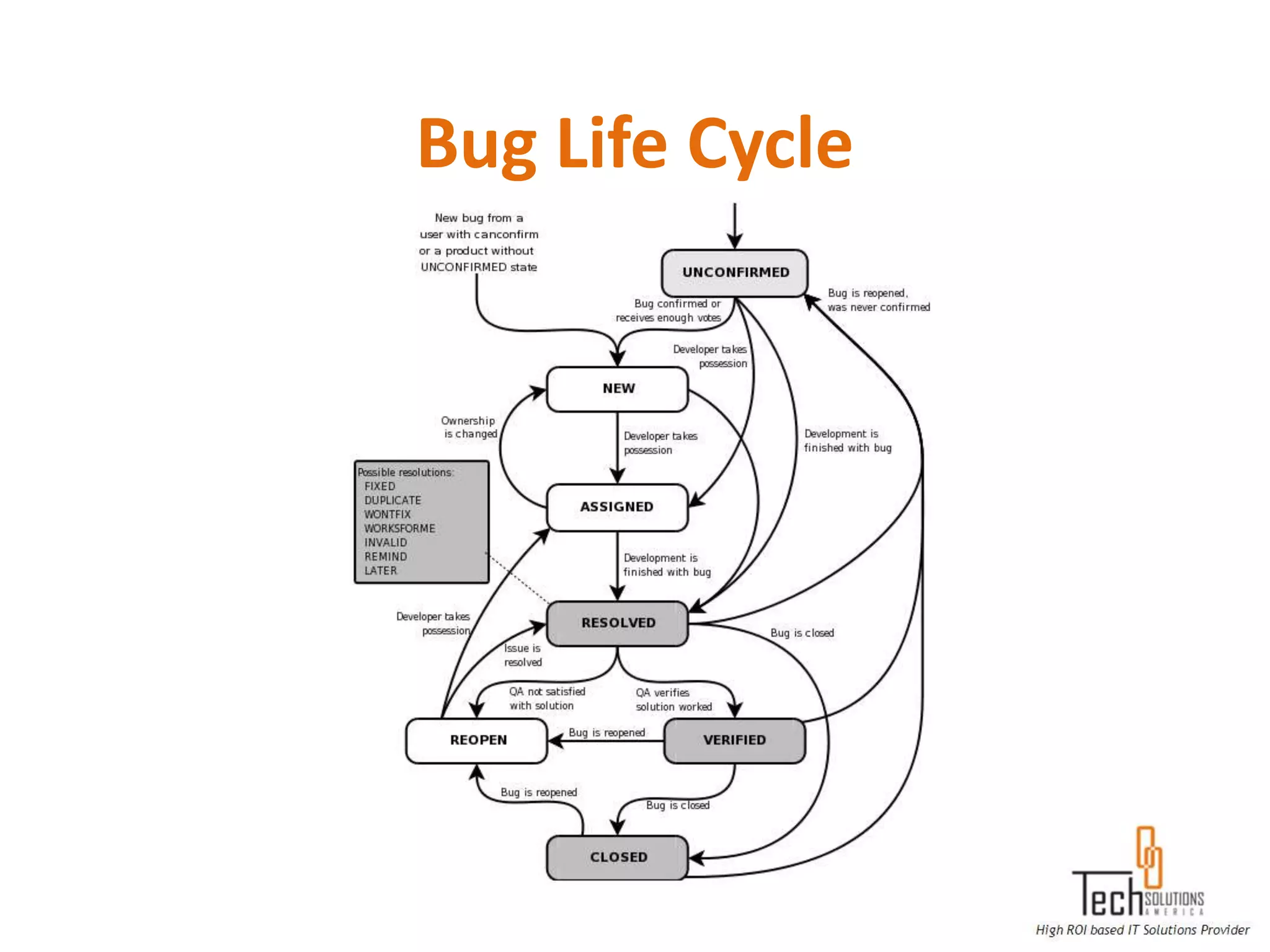
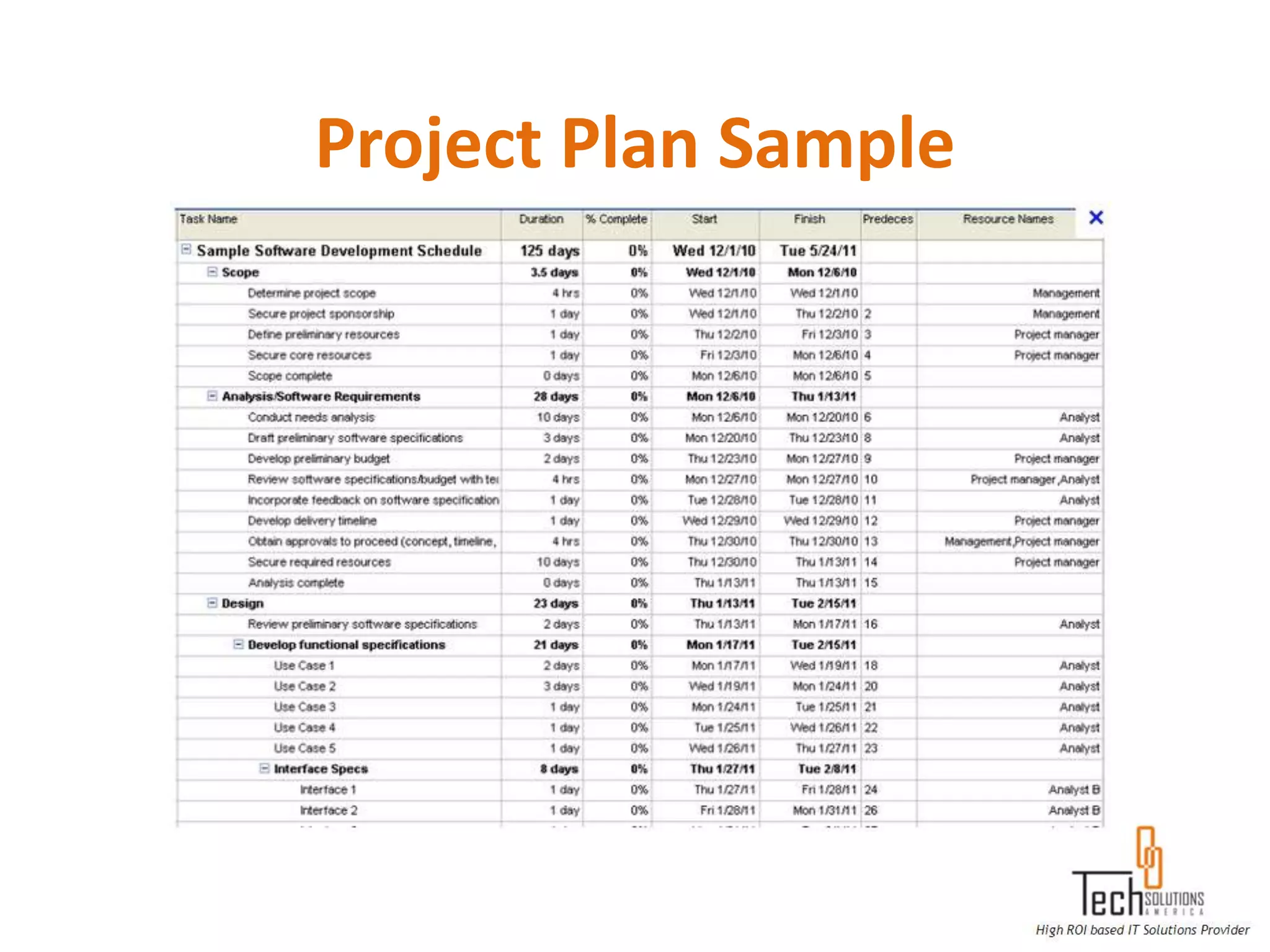
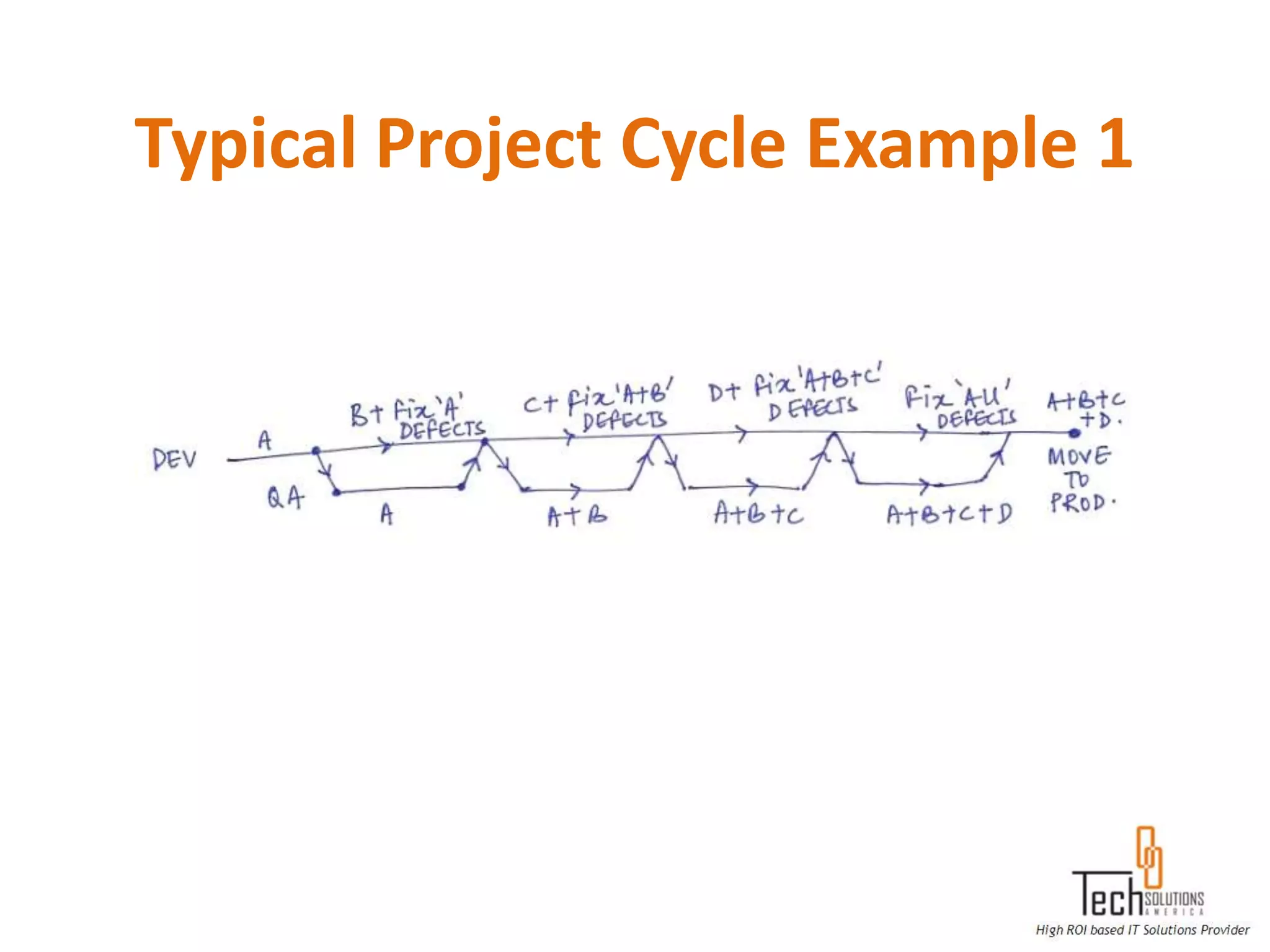
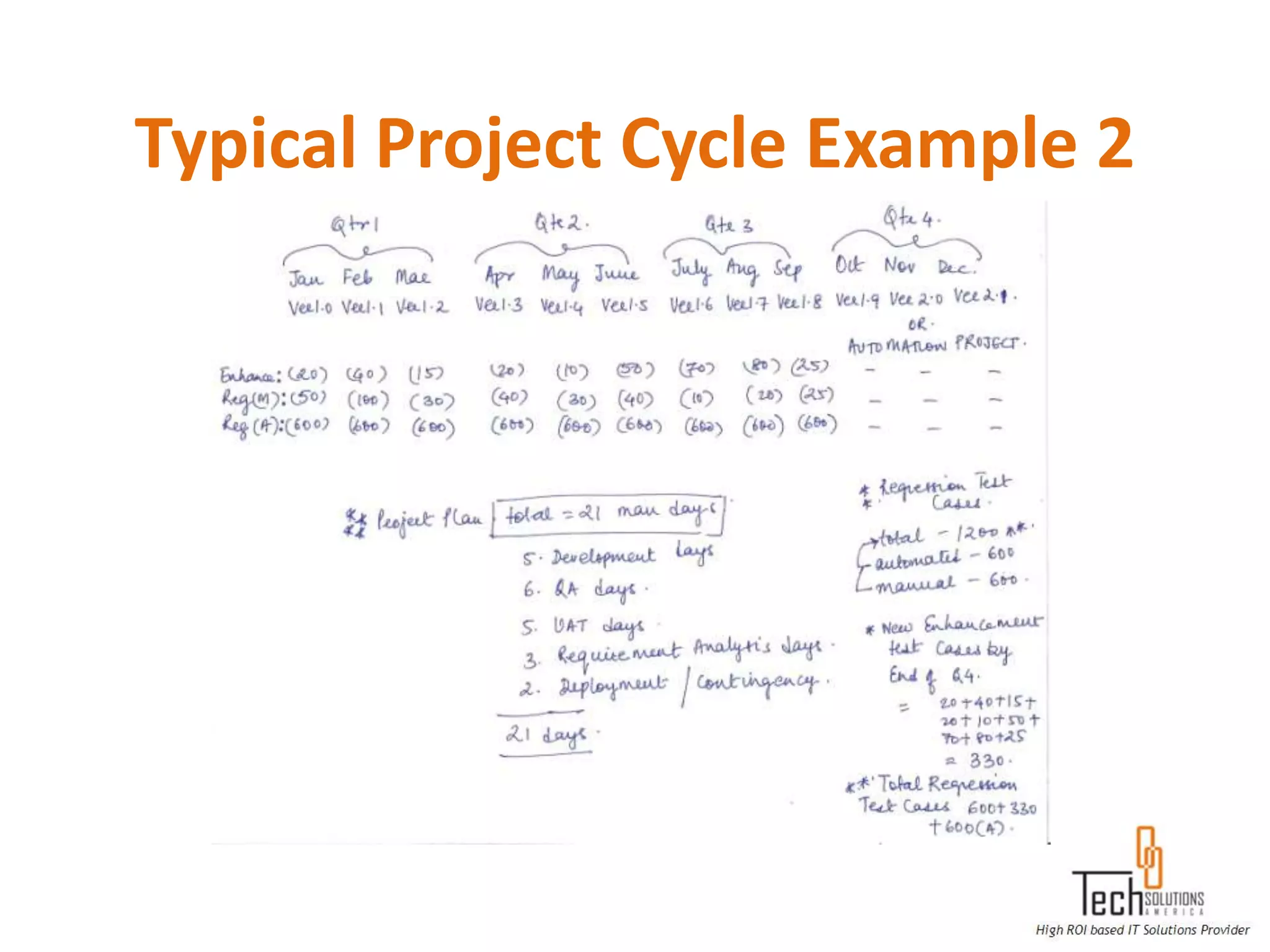
The document provides an overview of quality assurance and software testing processes. It describes key concepts like requirements gathering, test planning, test case development, defect reporting, retesting and sign off. It also covers quality standards, software development life cycles, testing methodologies, documentation artifacts, and project management structures.