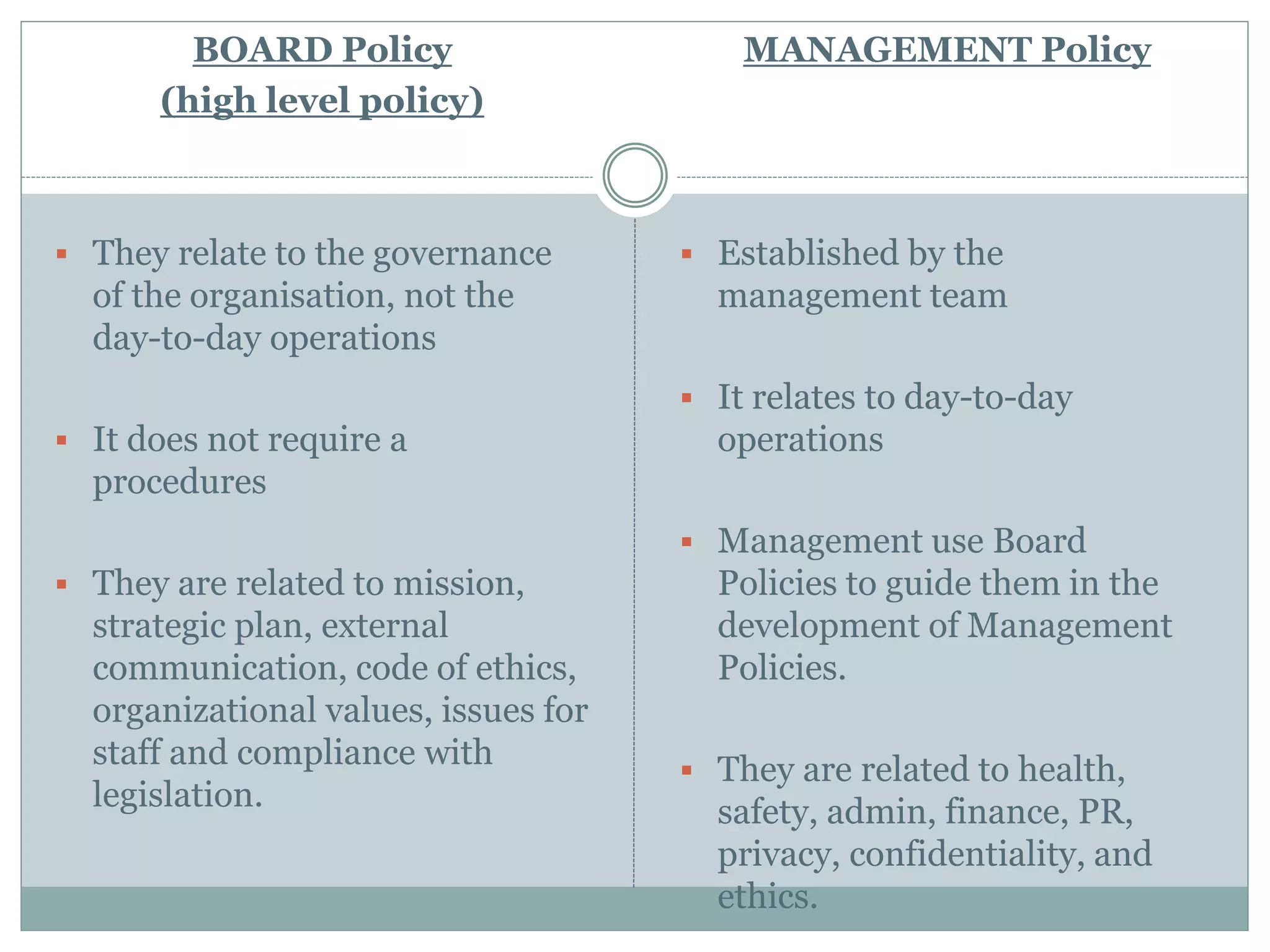
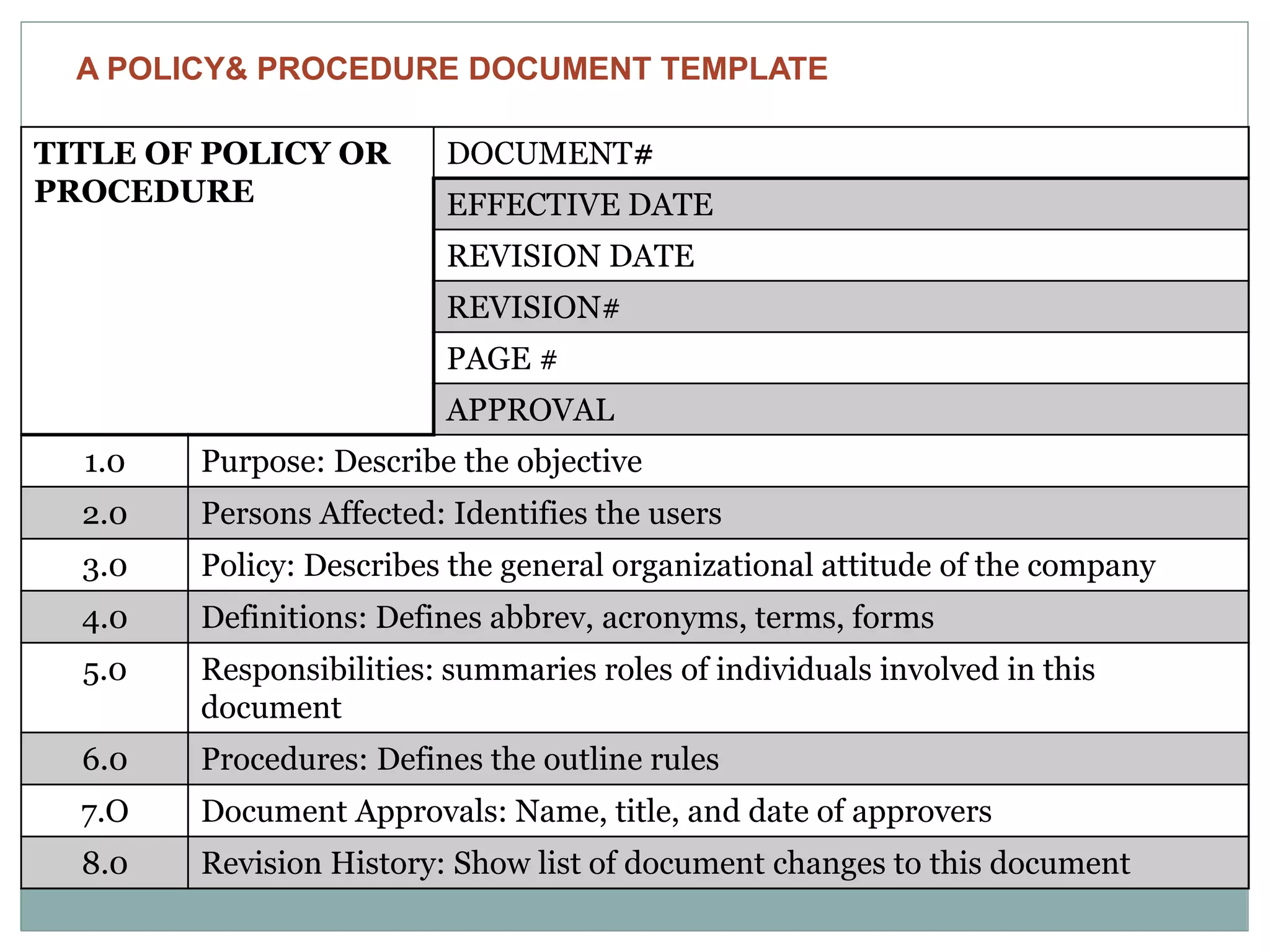
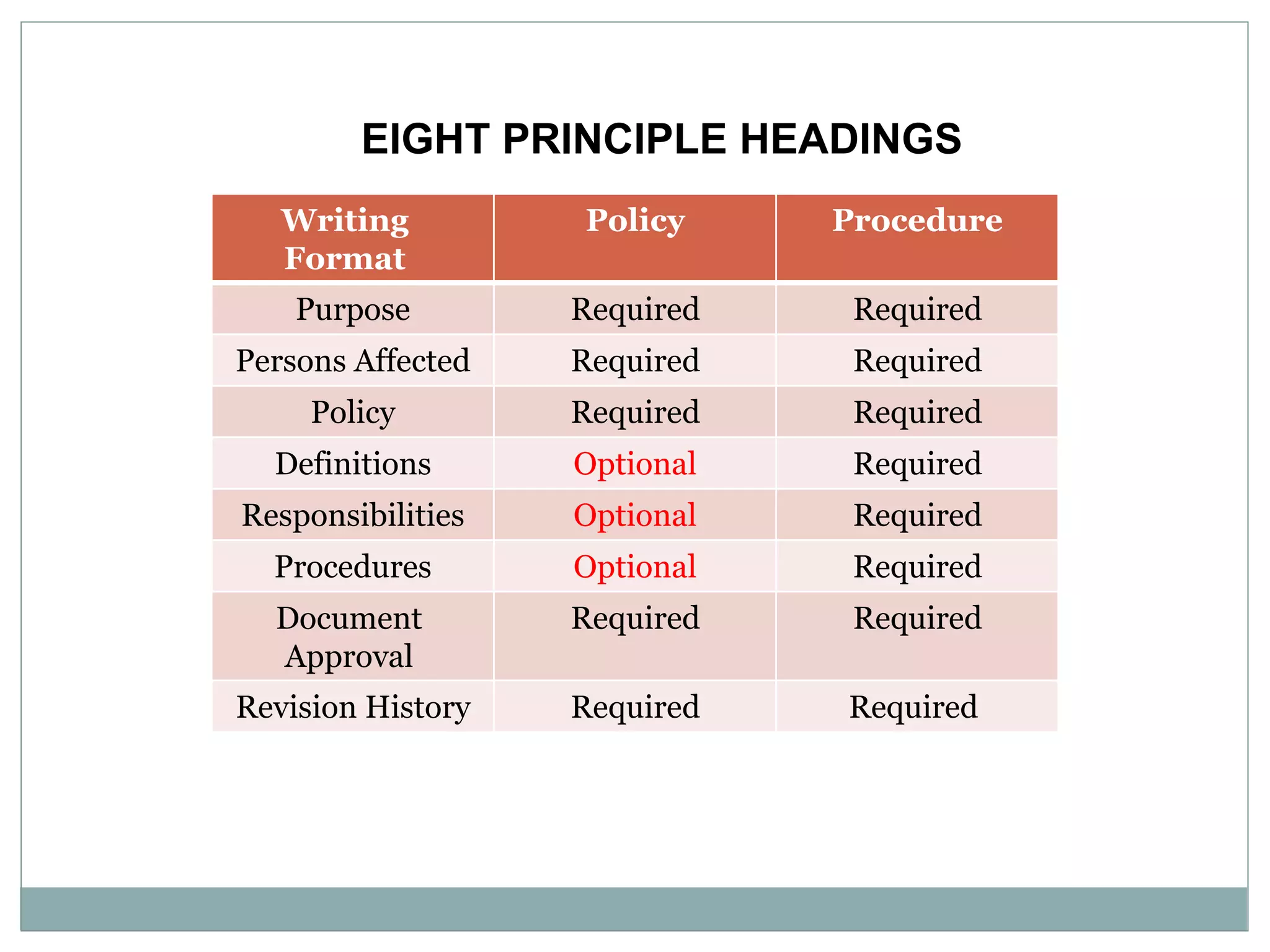
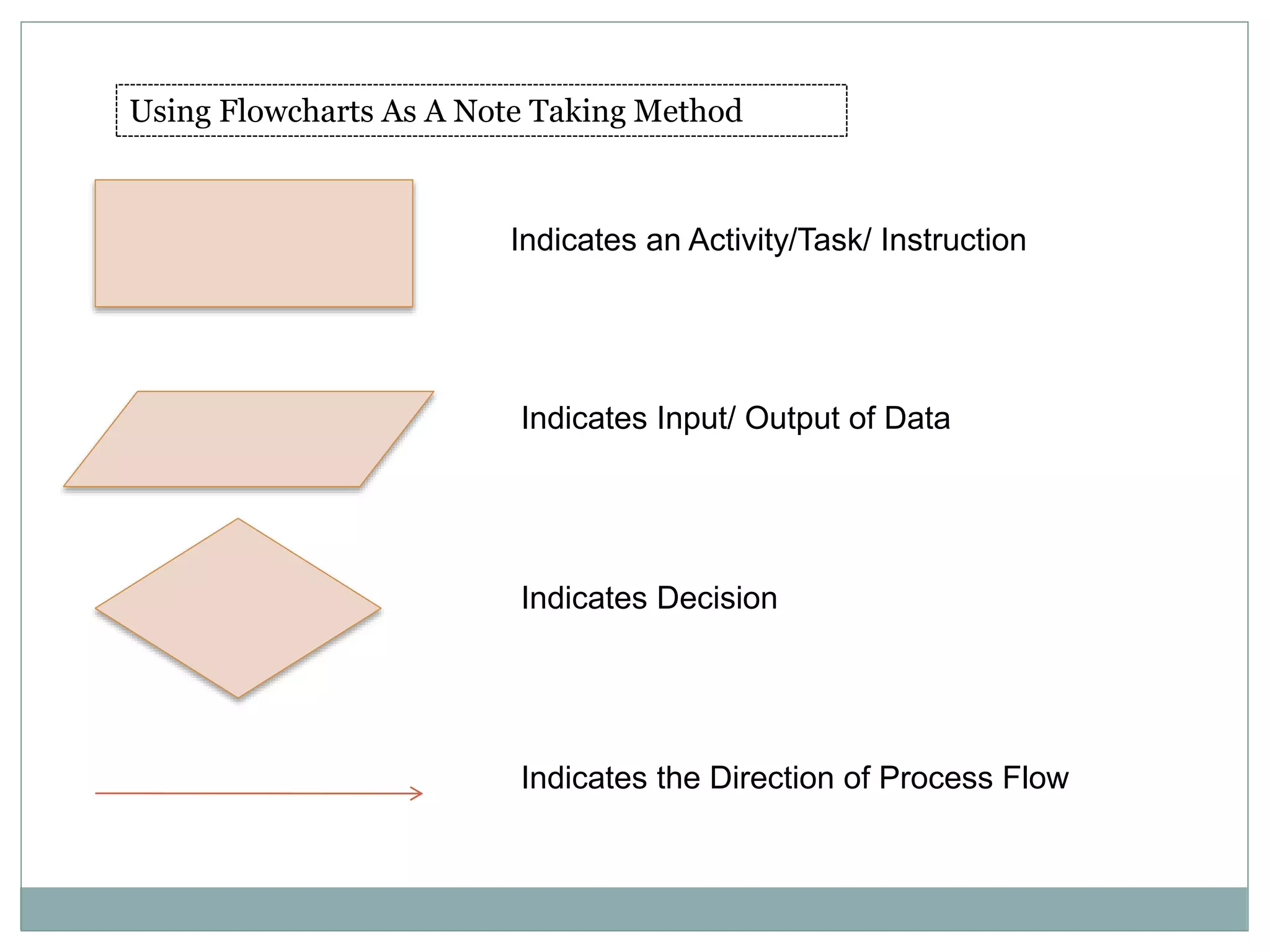
The document discusses how to write effective organizational policies and procedures. It covers identifying the need for policies and procedures, understanding the differences between them, how they link to organizational values, the process for writing them, publishing and implementing them, and revising them. Key aspects include determining what should be a policy versus a procedure, following guidelines for writing them clearly and consistently, involving stakeholders, and effectively communicating the new policies and procedures to employees. The overall process is meant to establish standards and guidelines to help employees understand their roles and responsibilities.