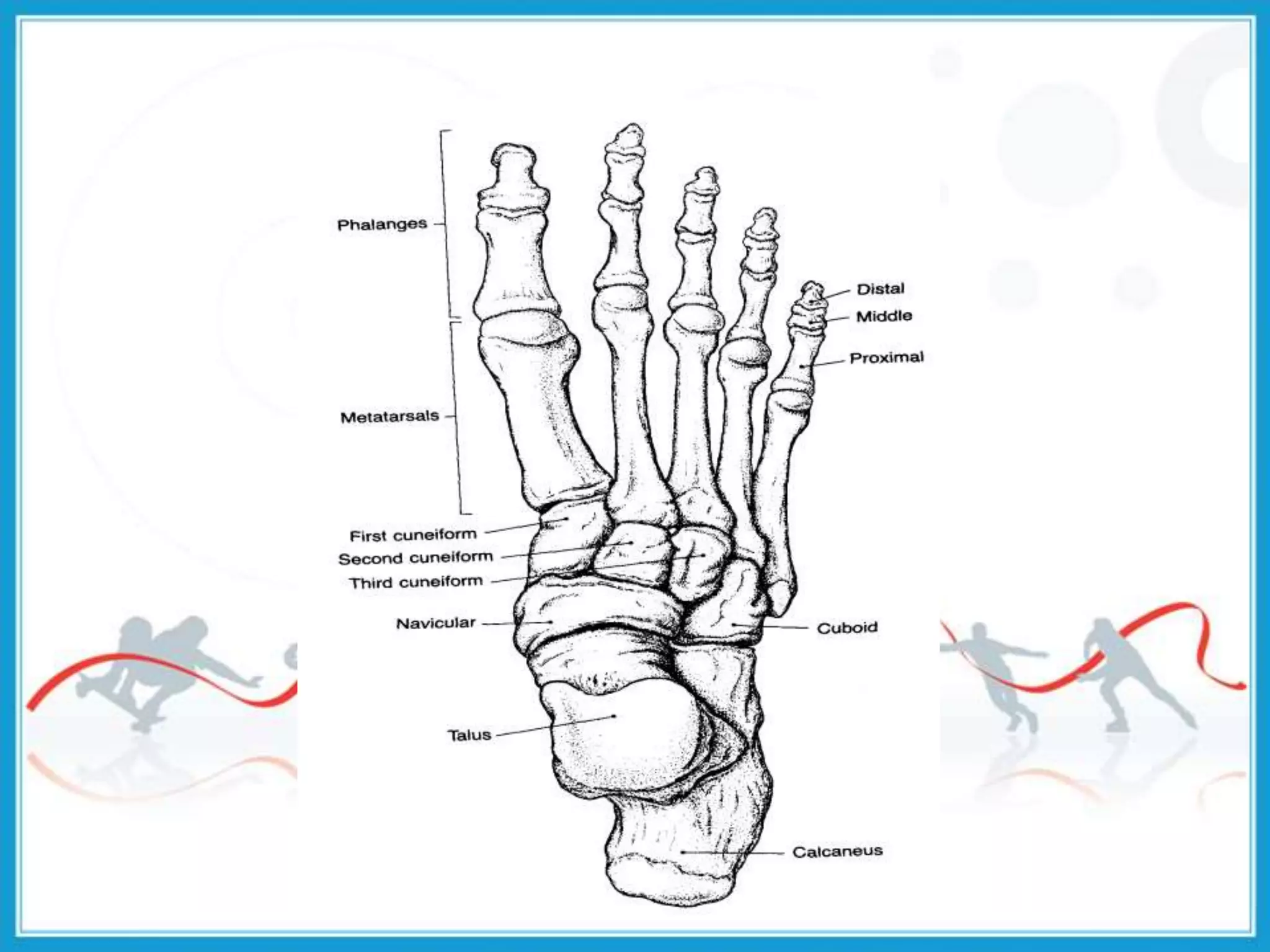
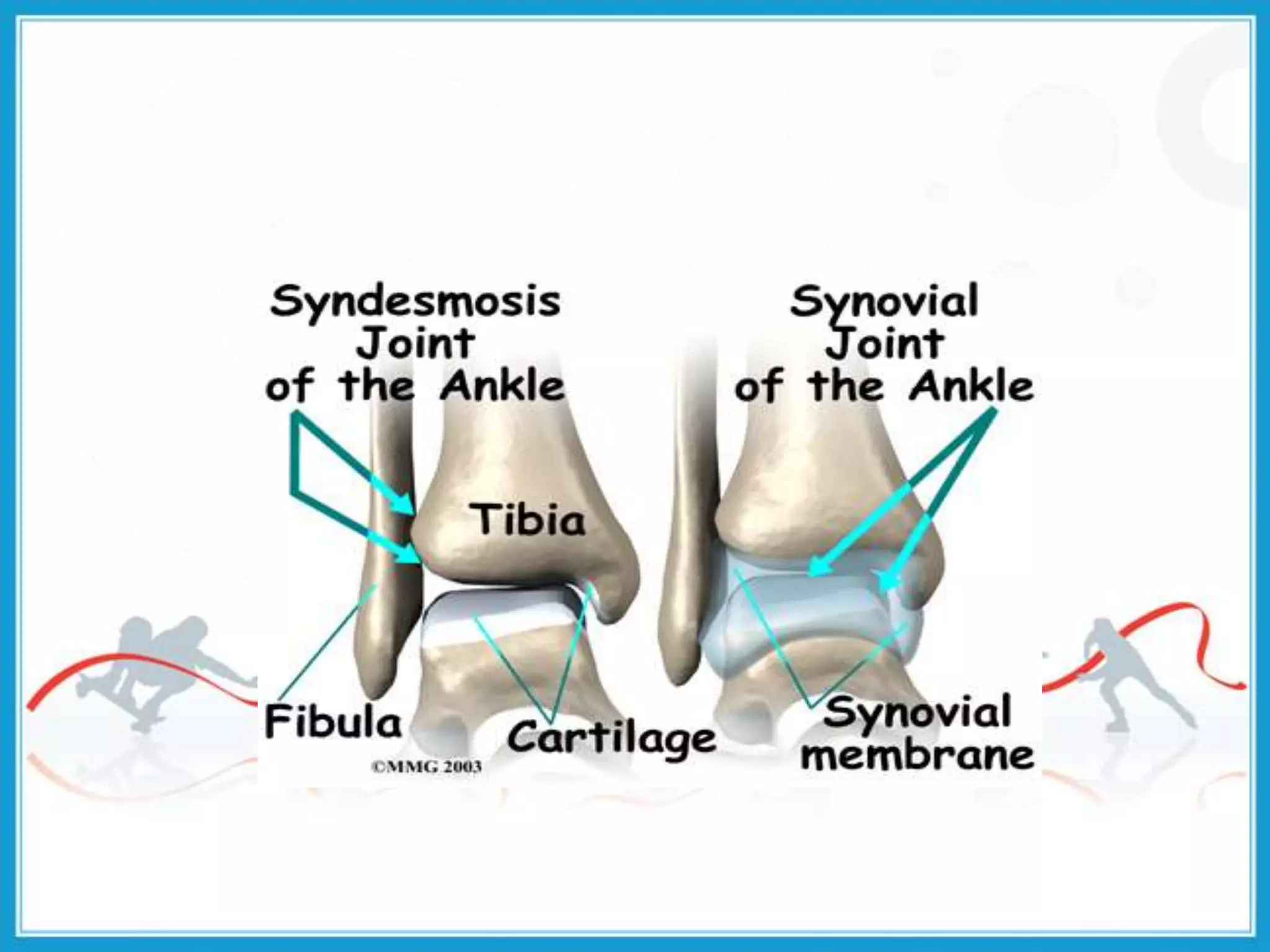
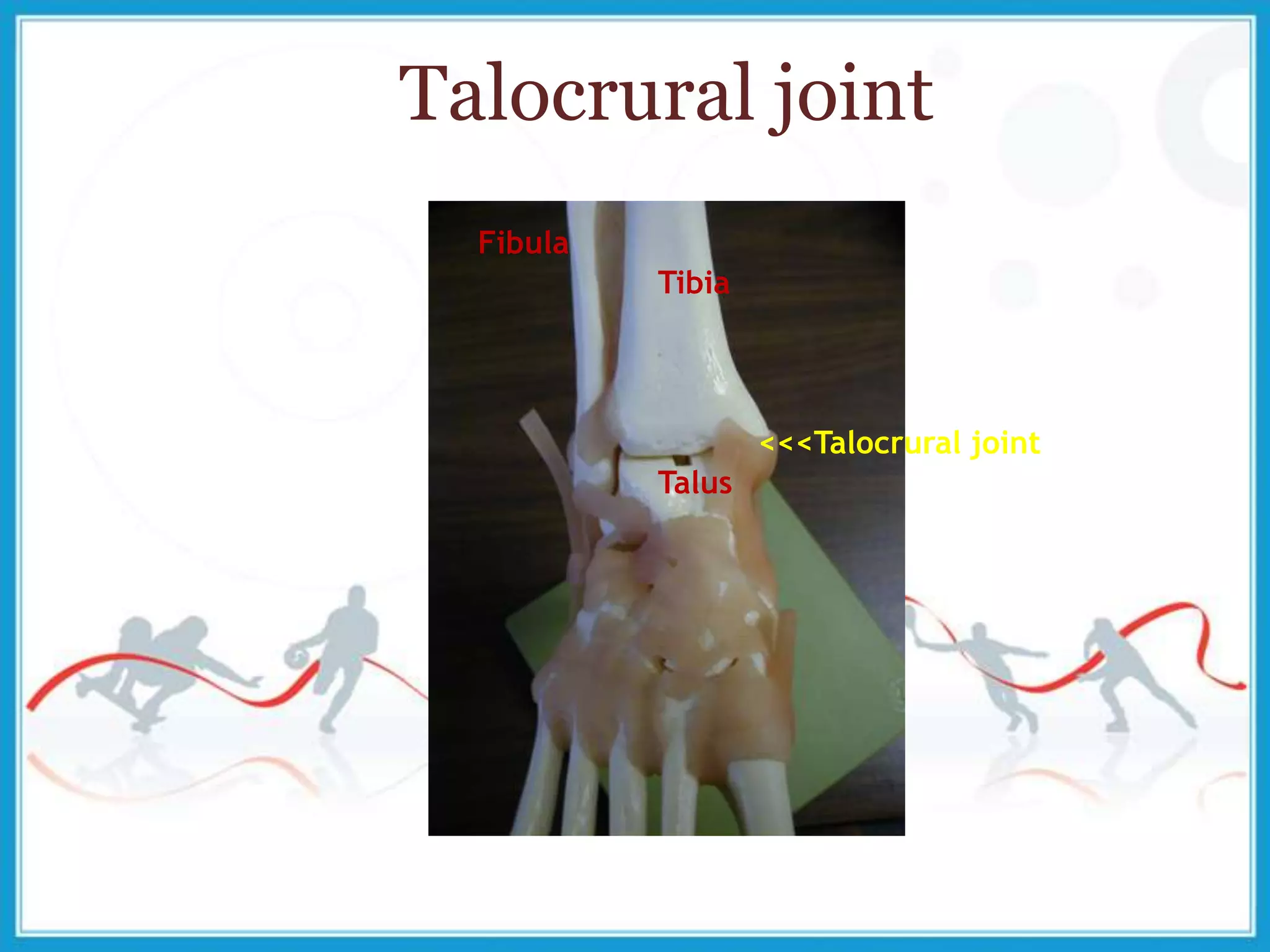
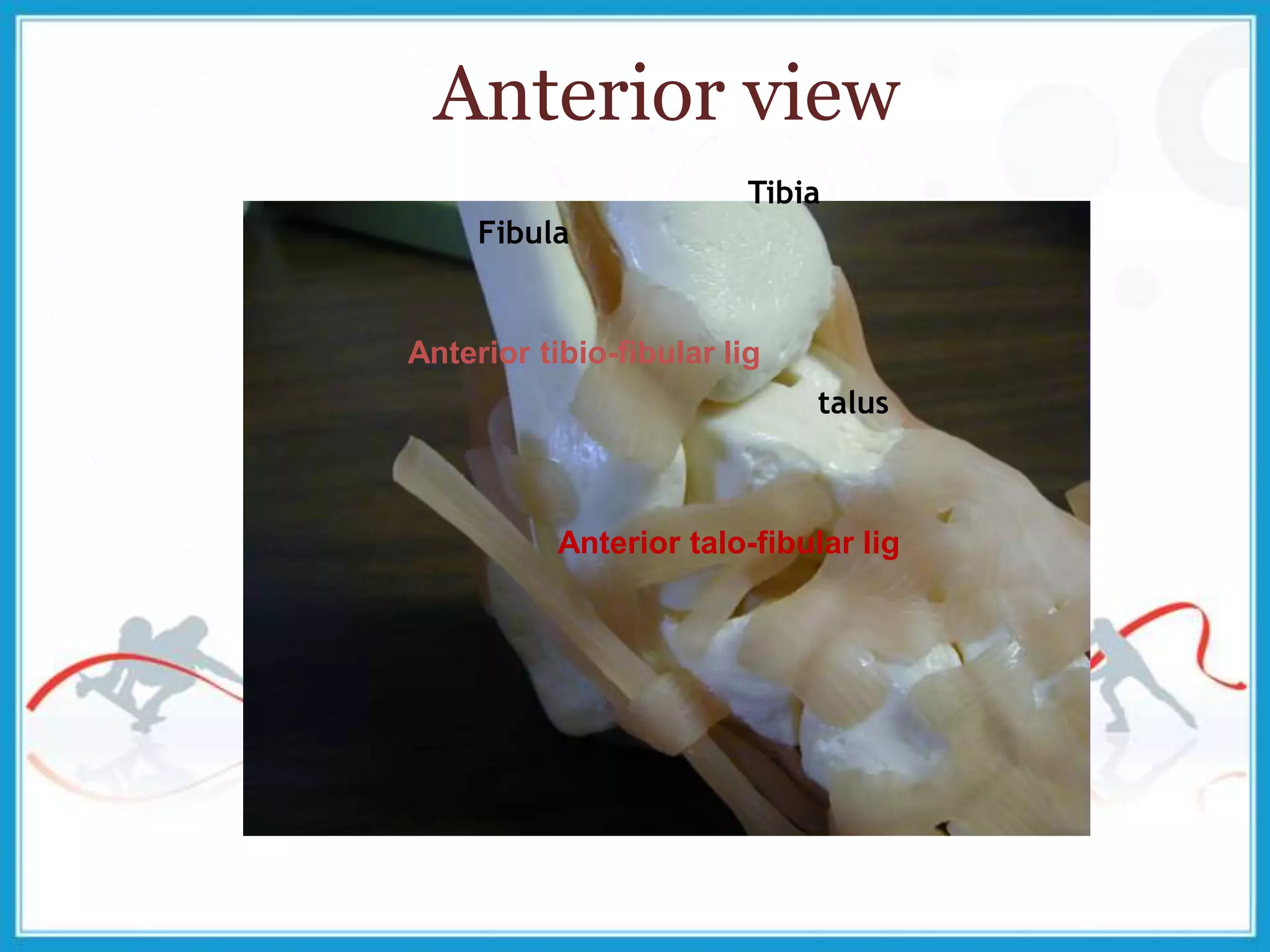
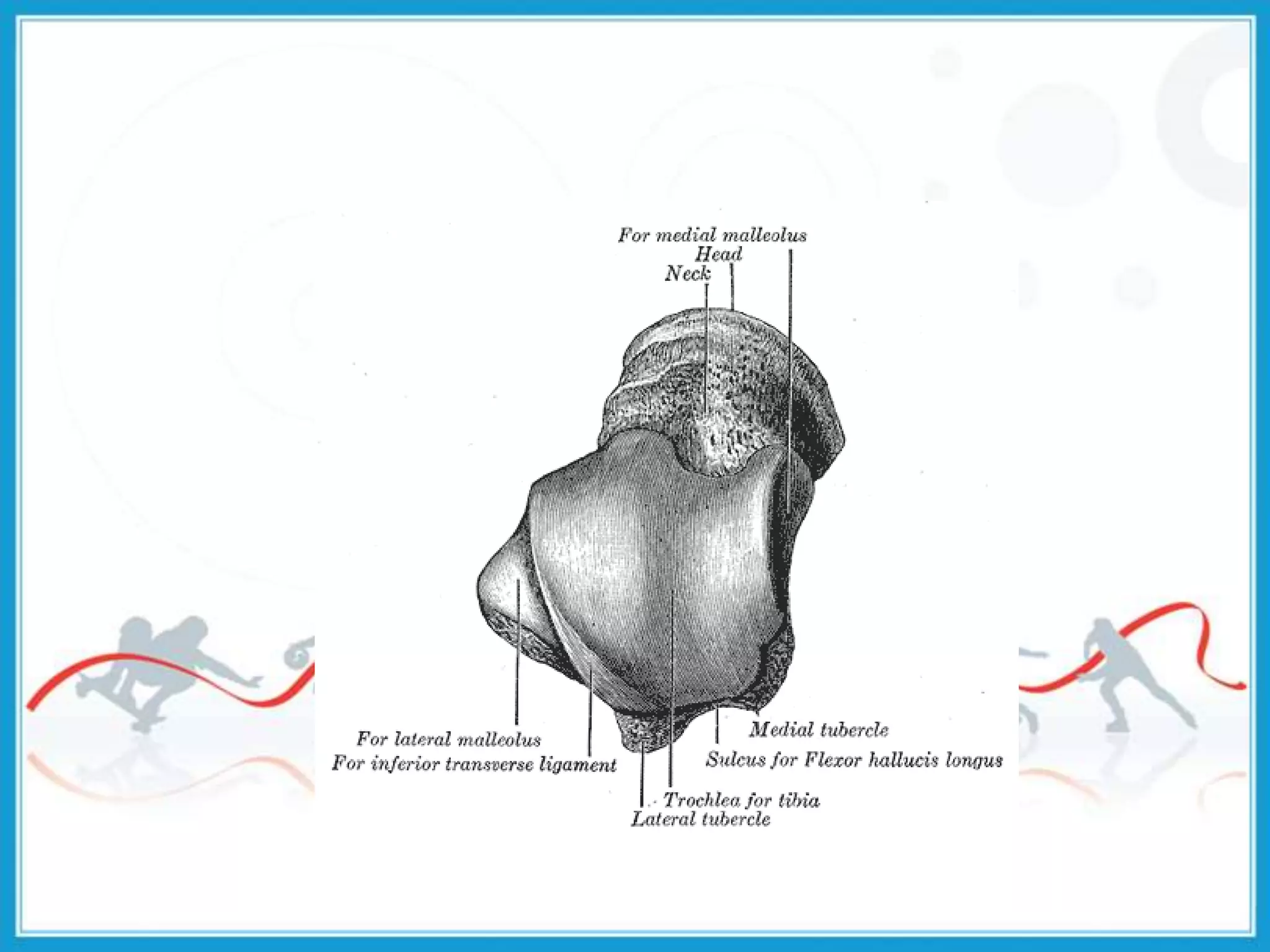
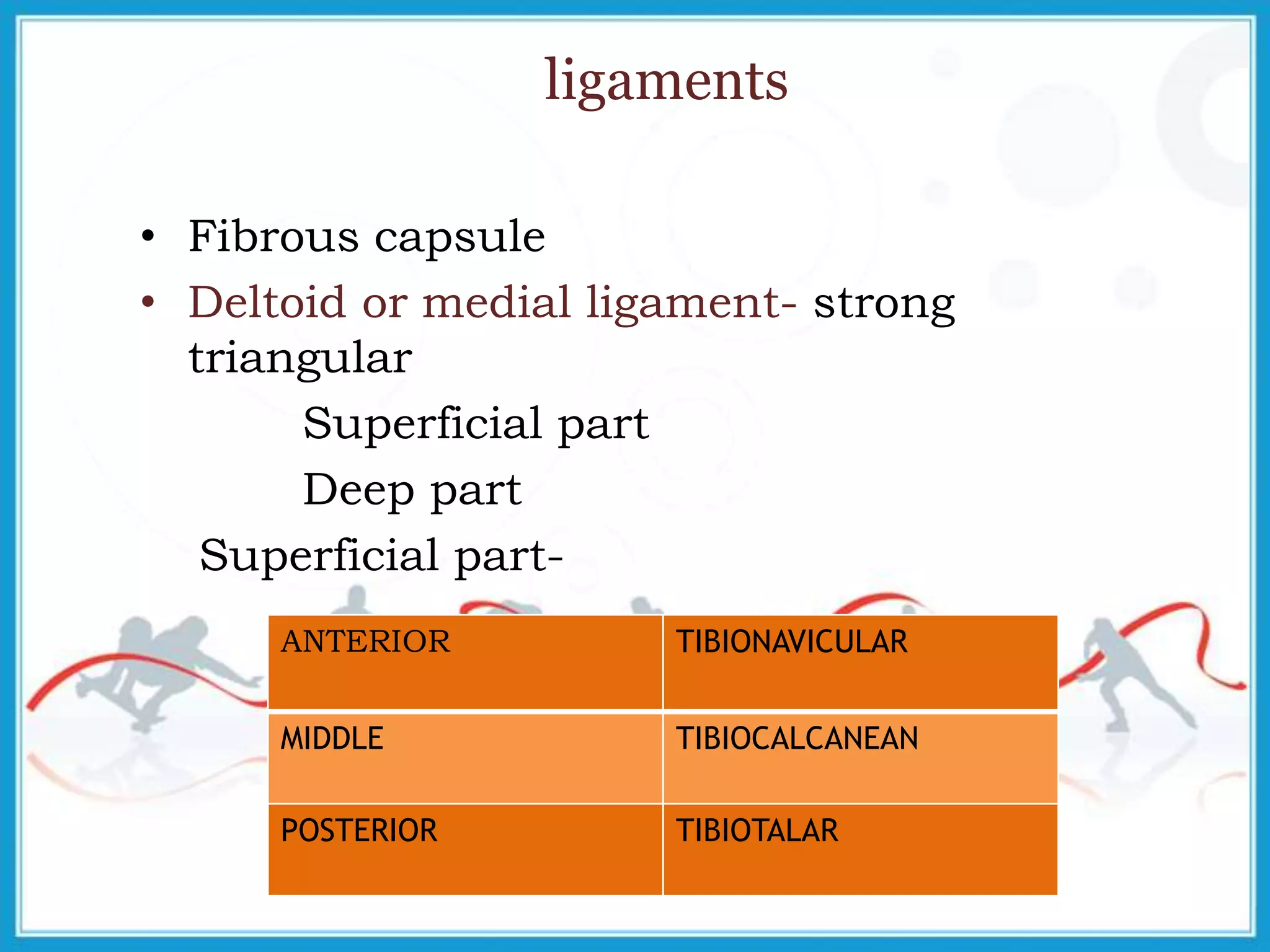
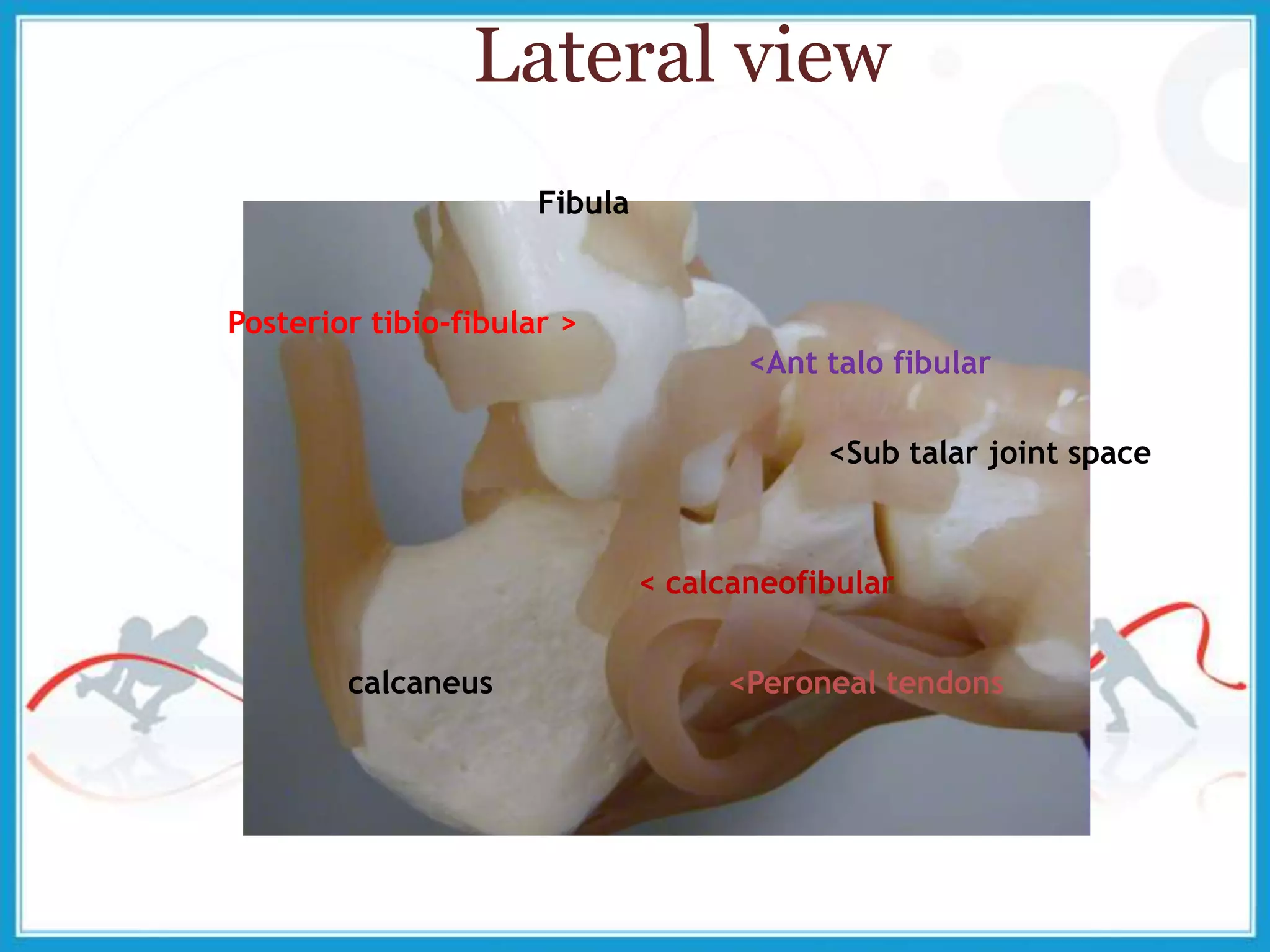
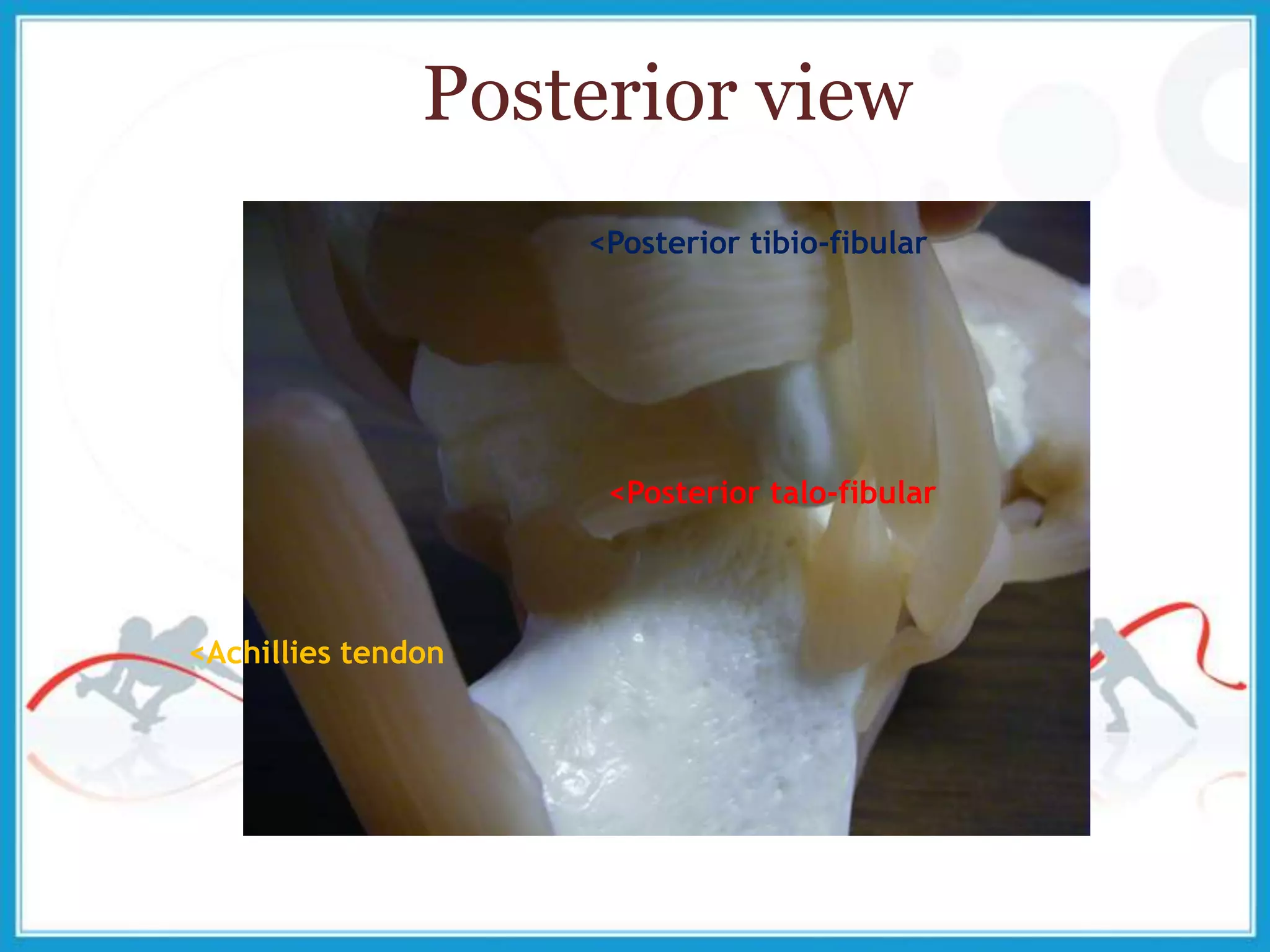
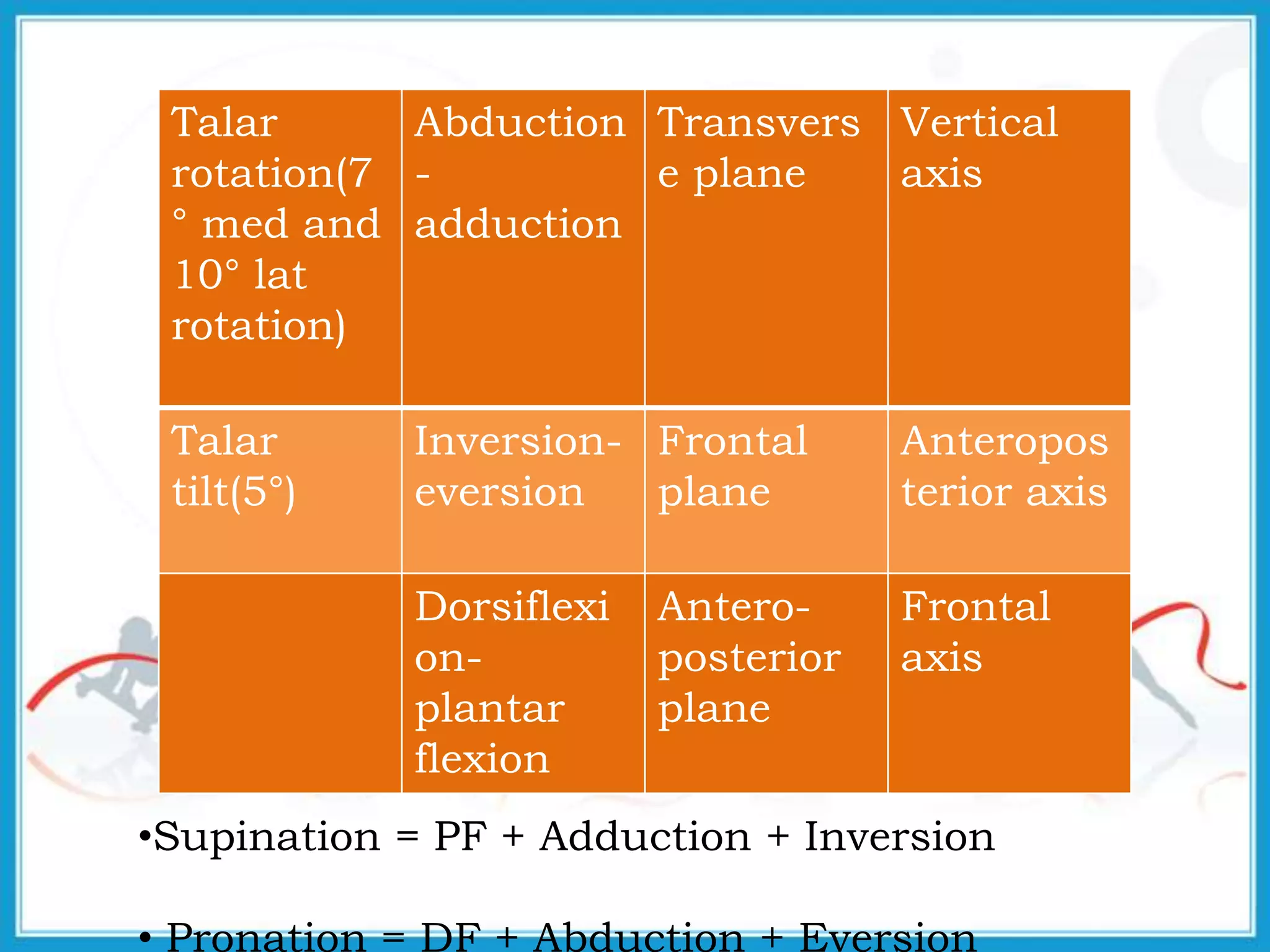
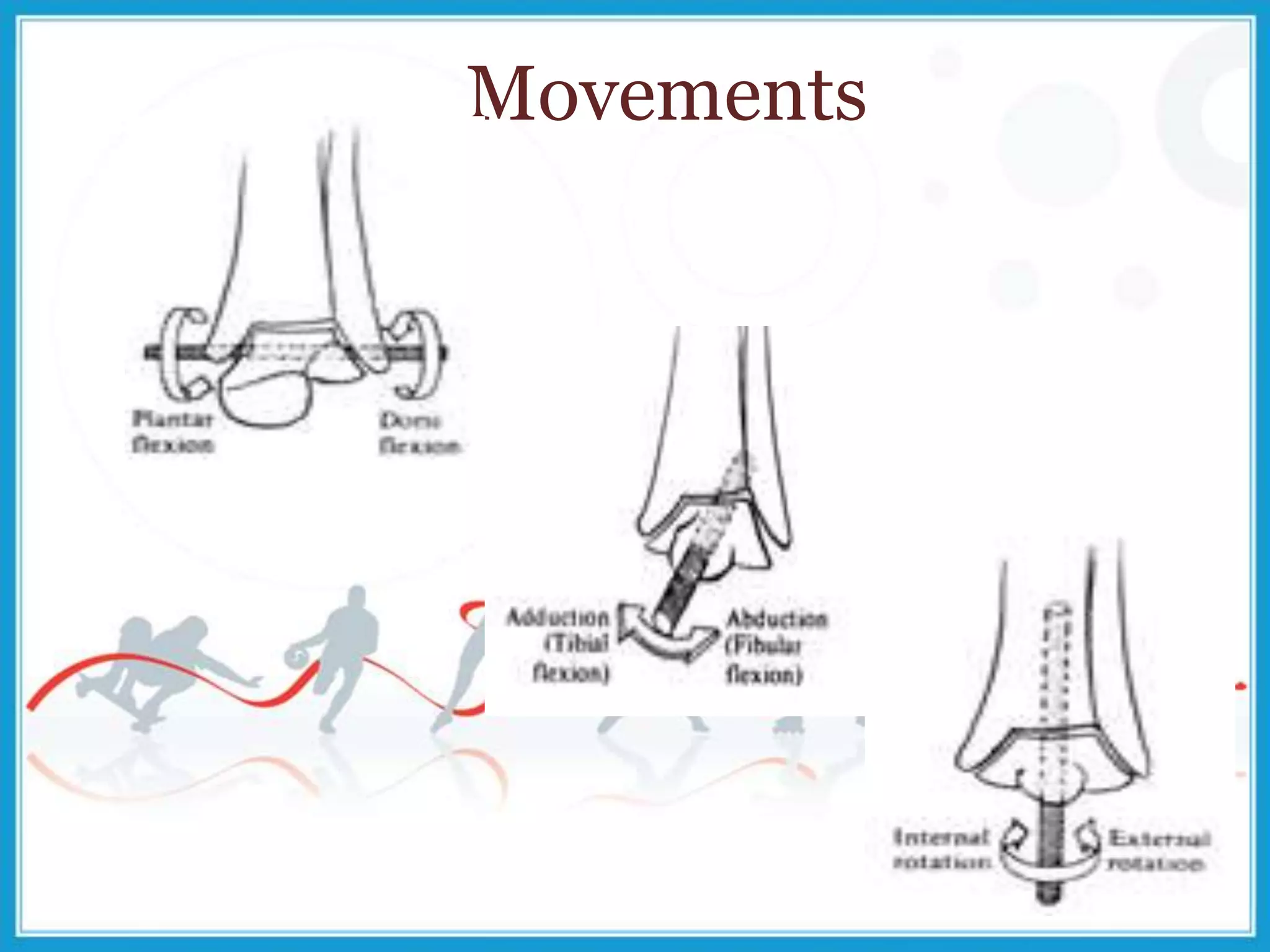
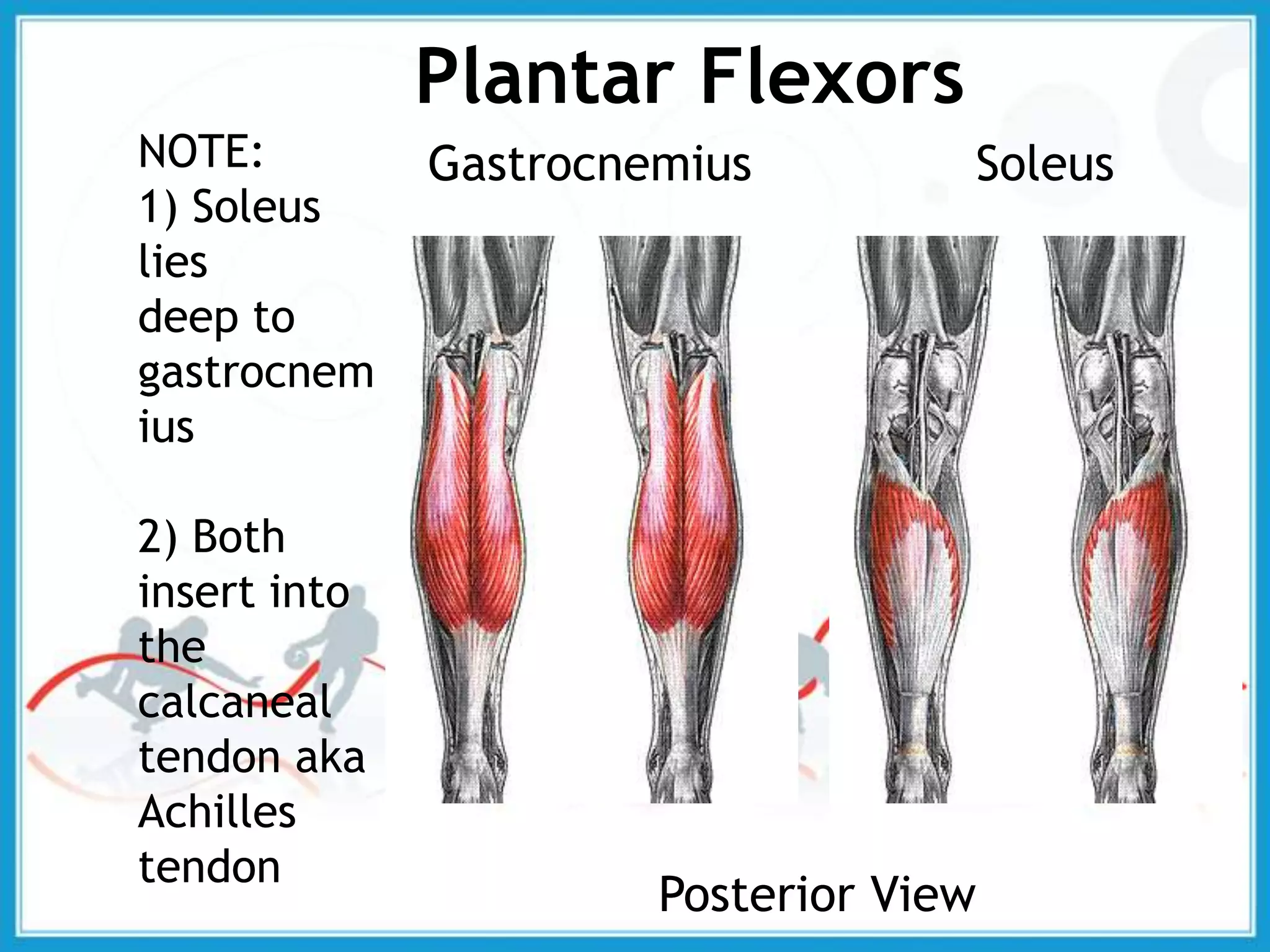
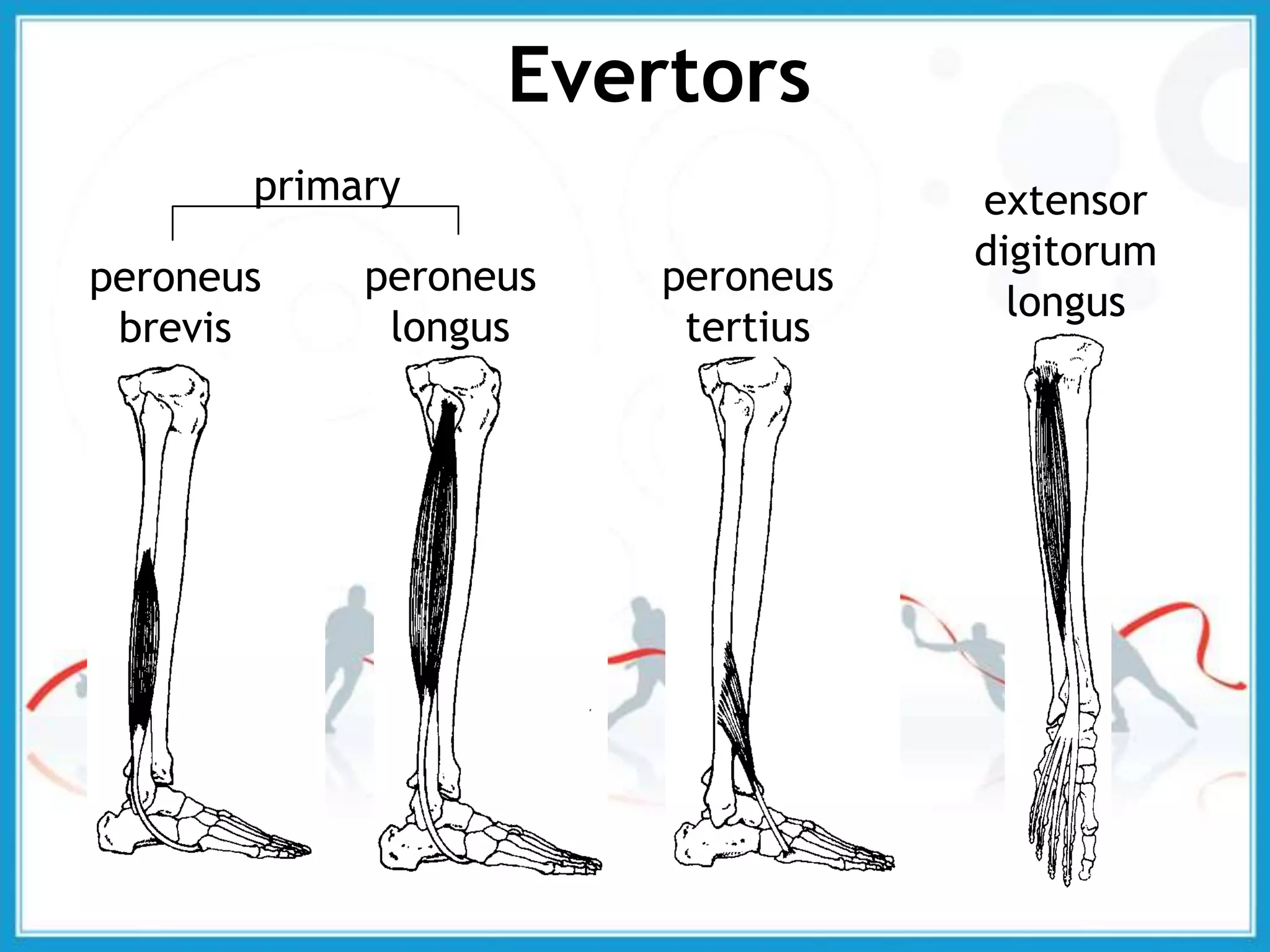
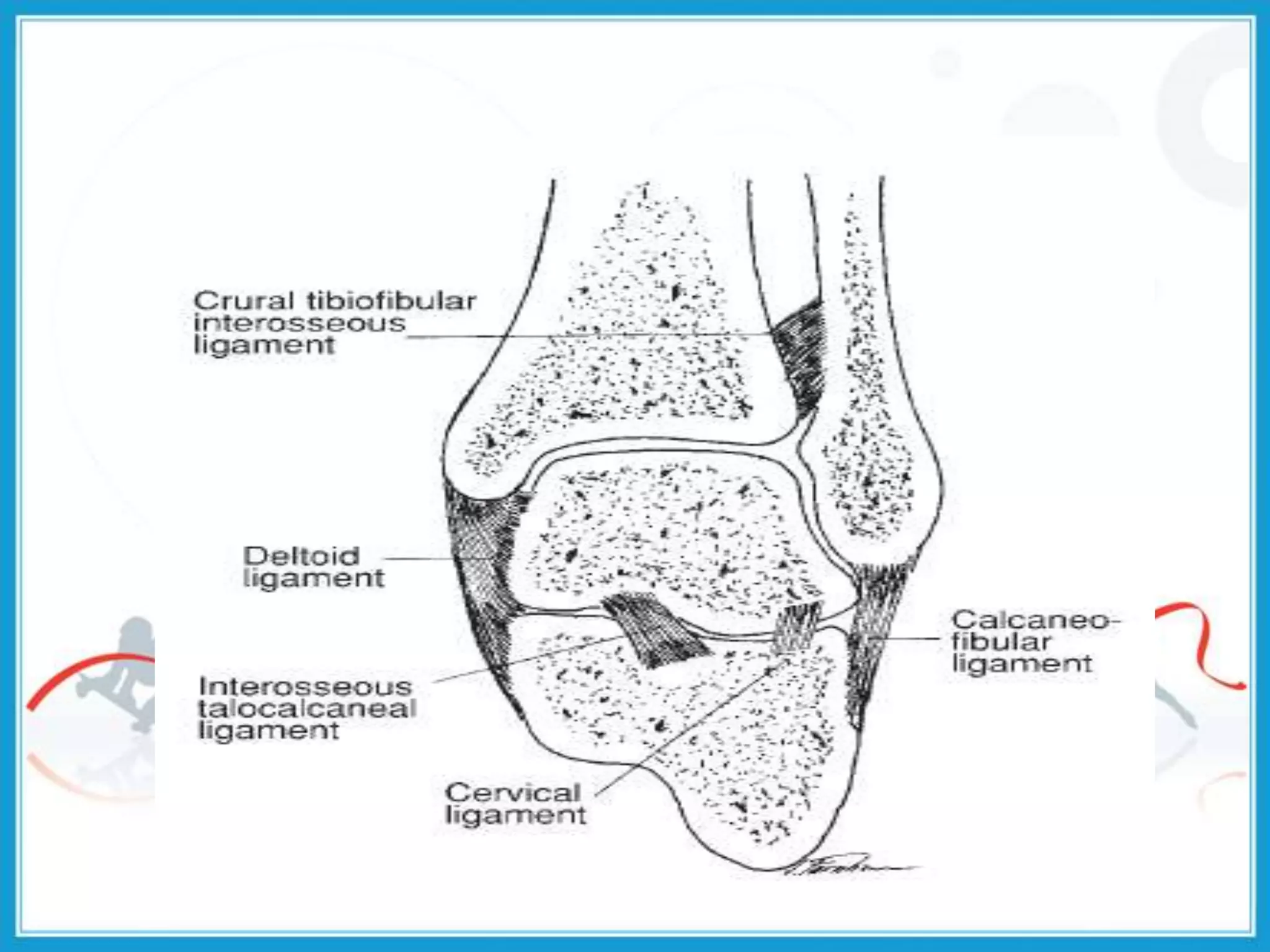
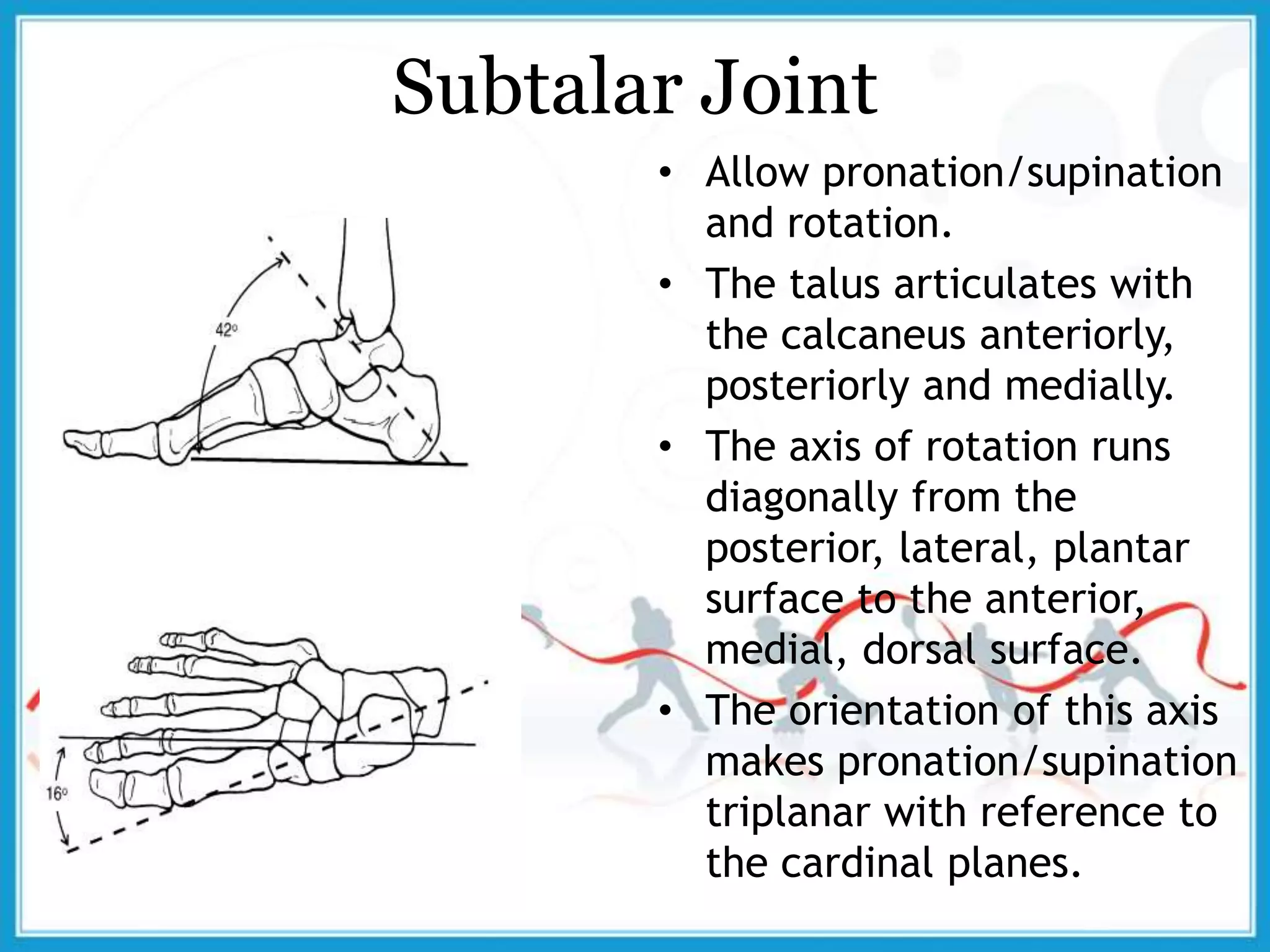
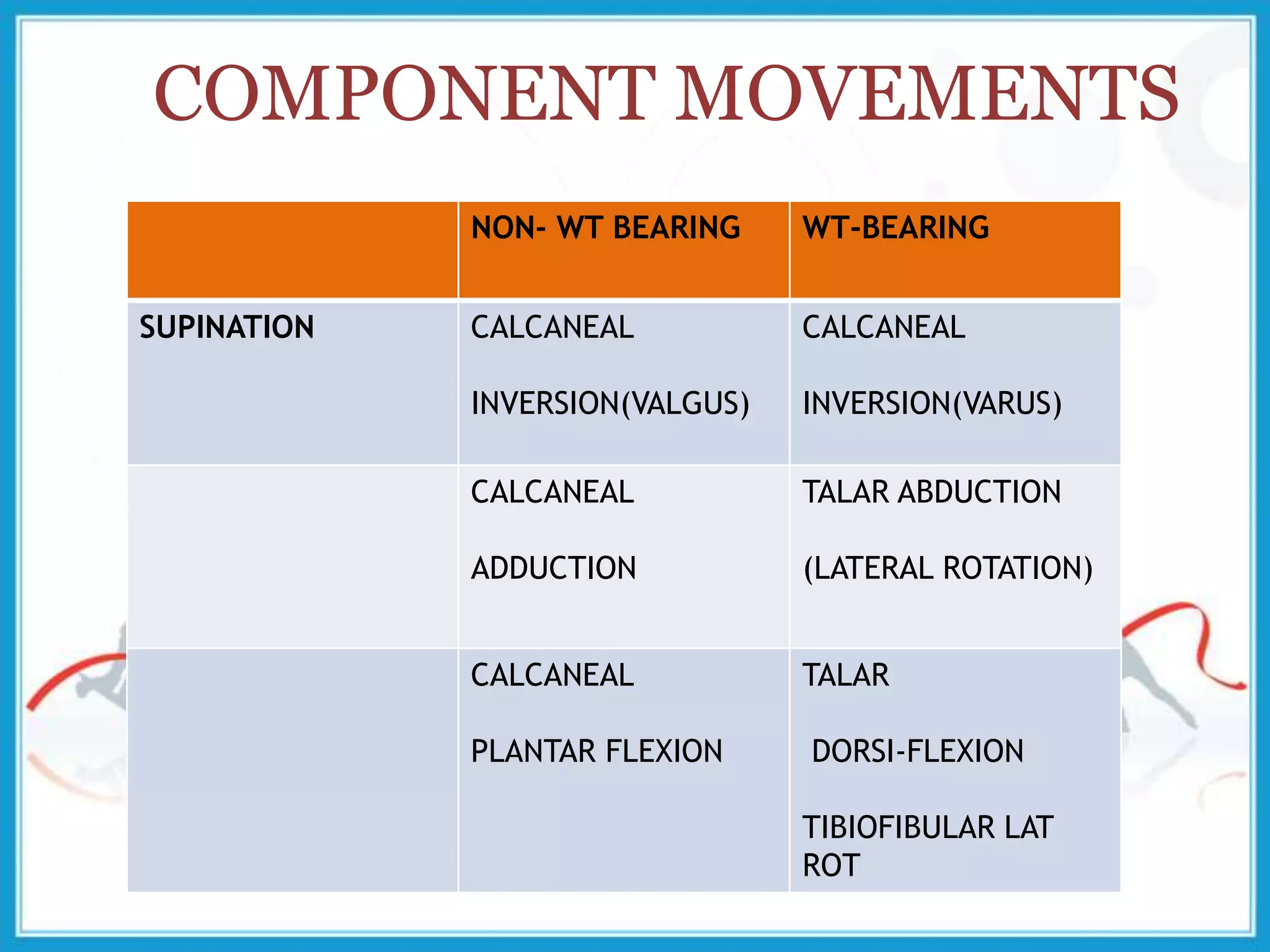
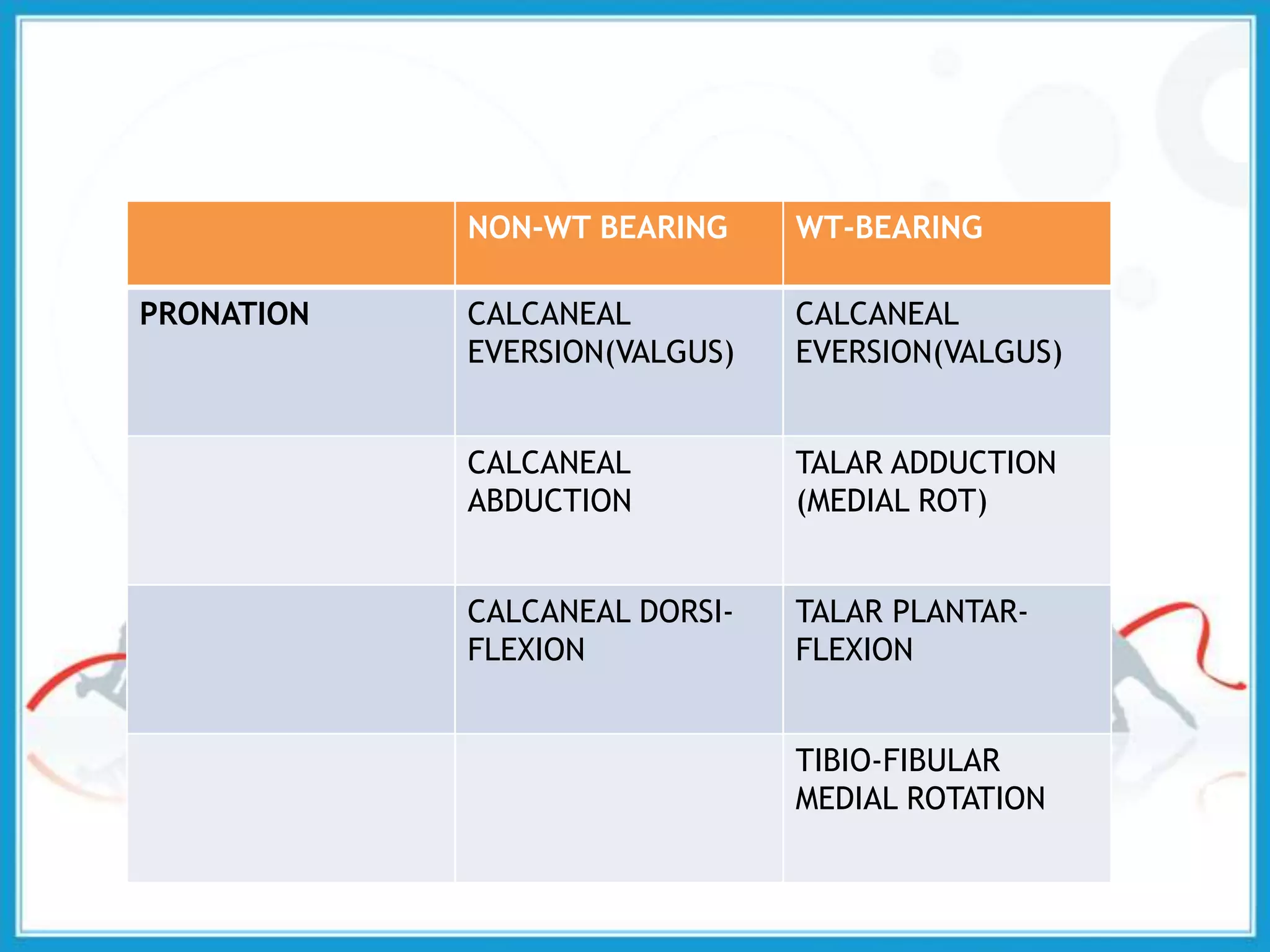
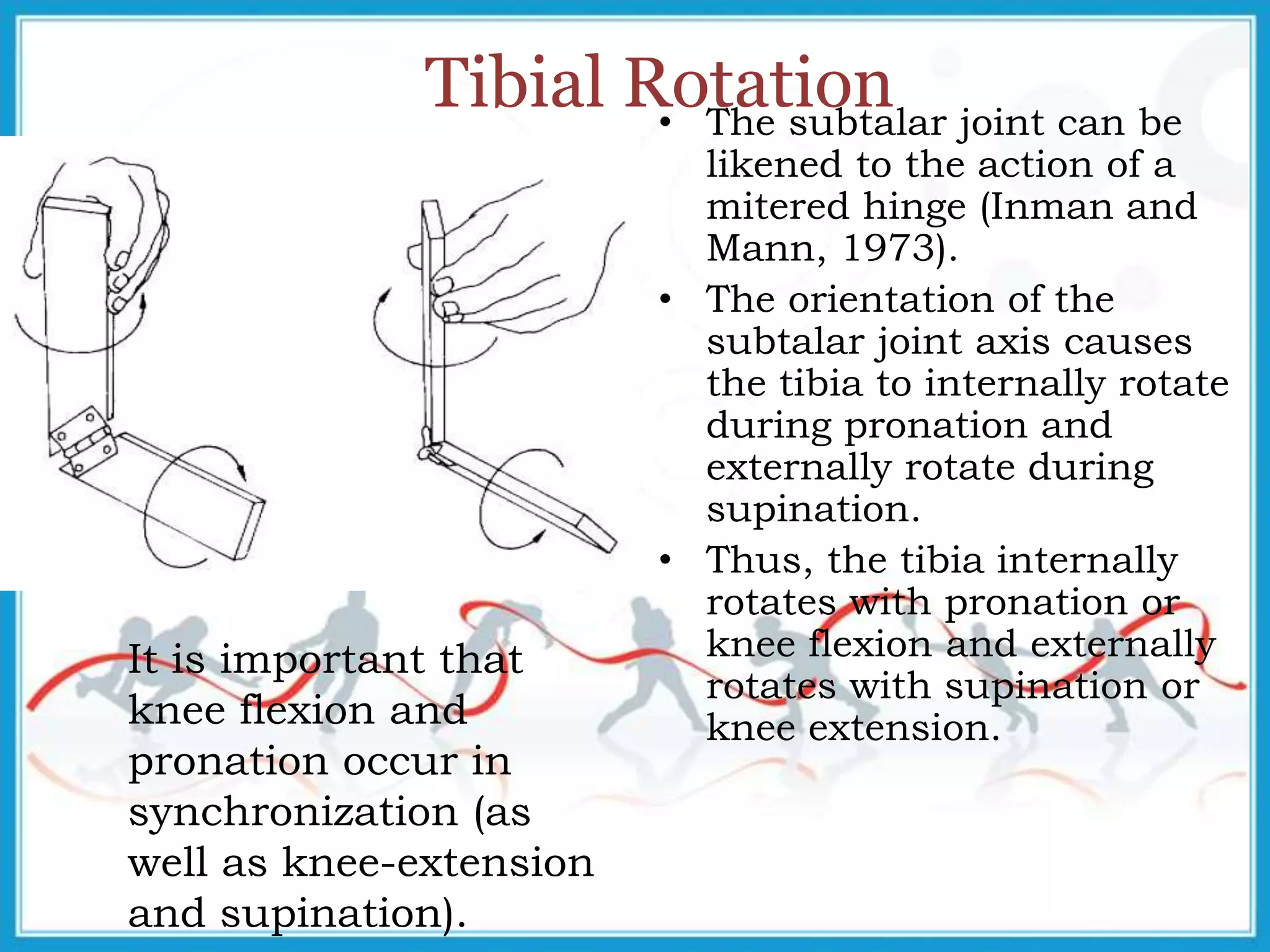
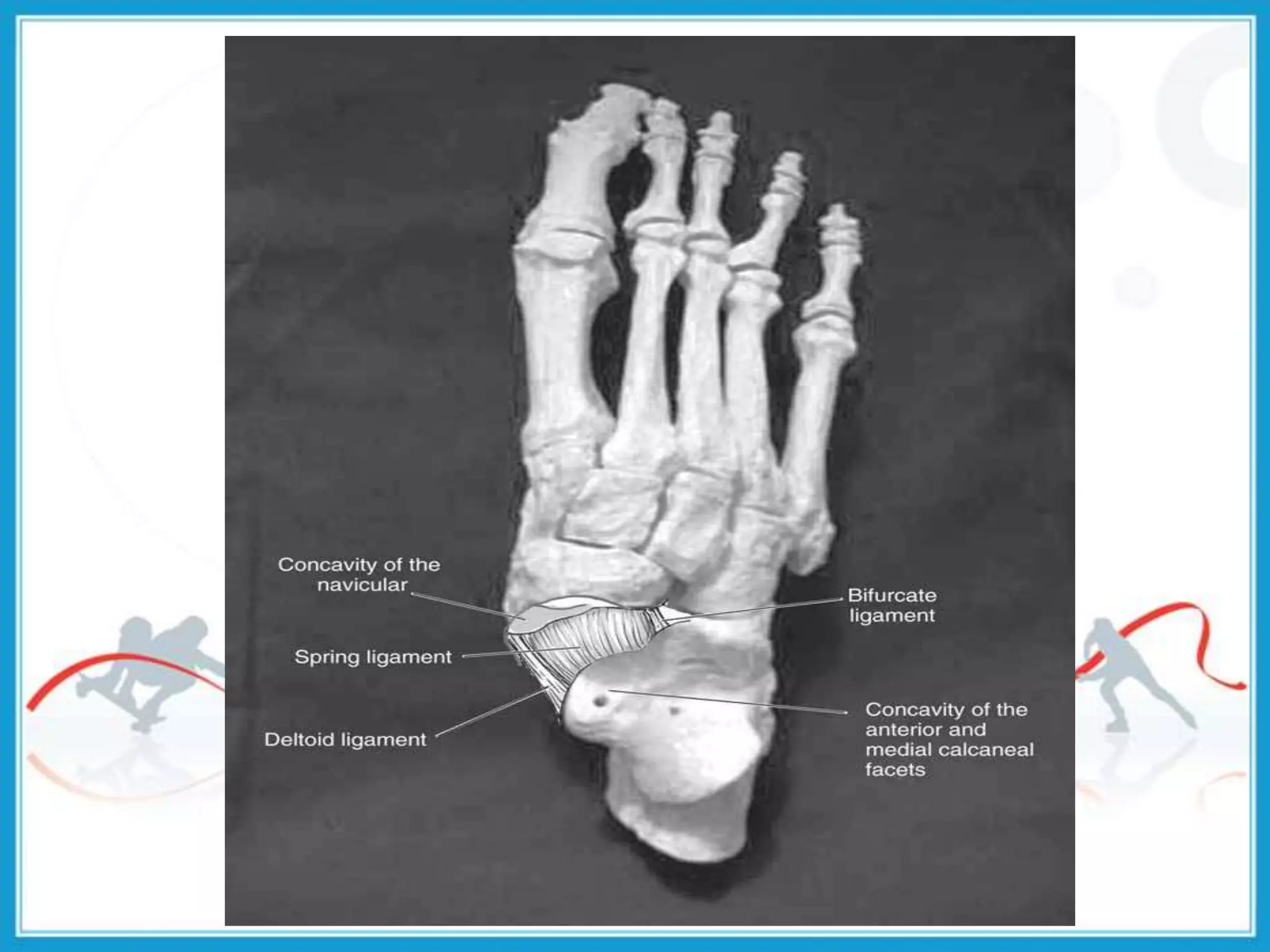
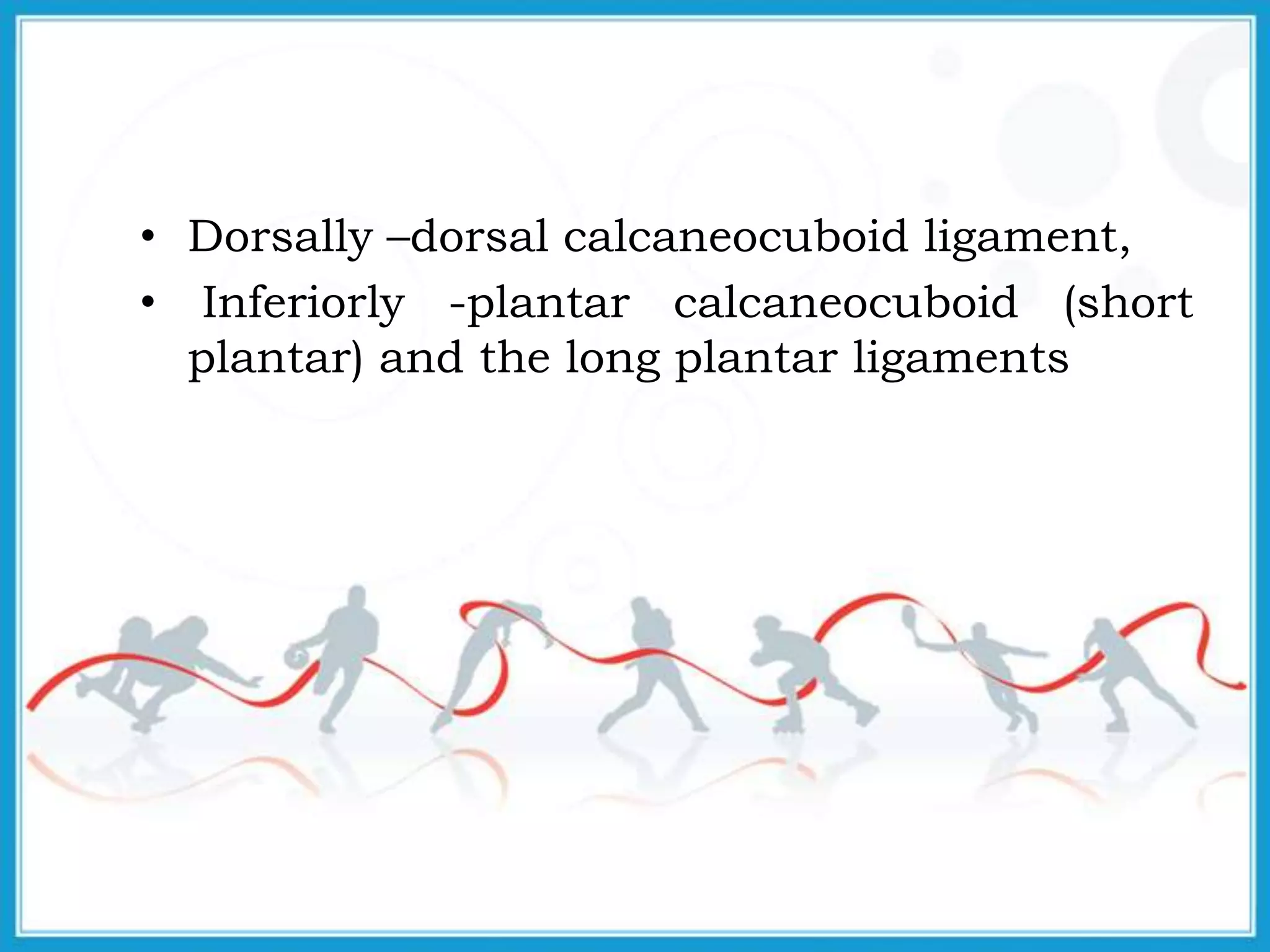
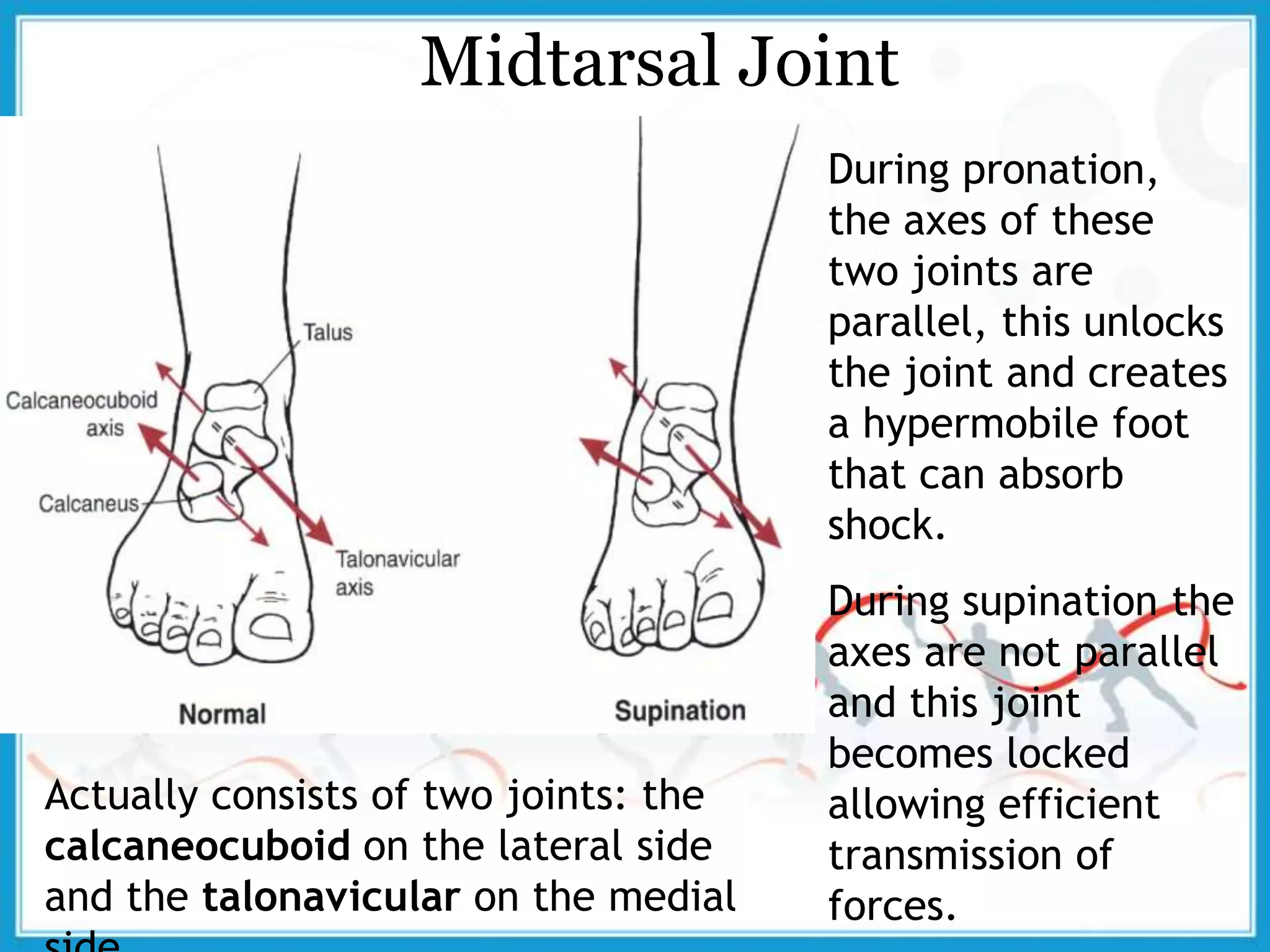
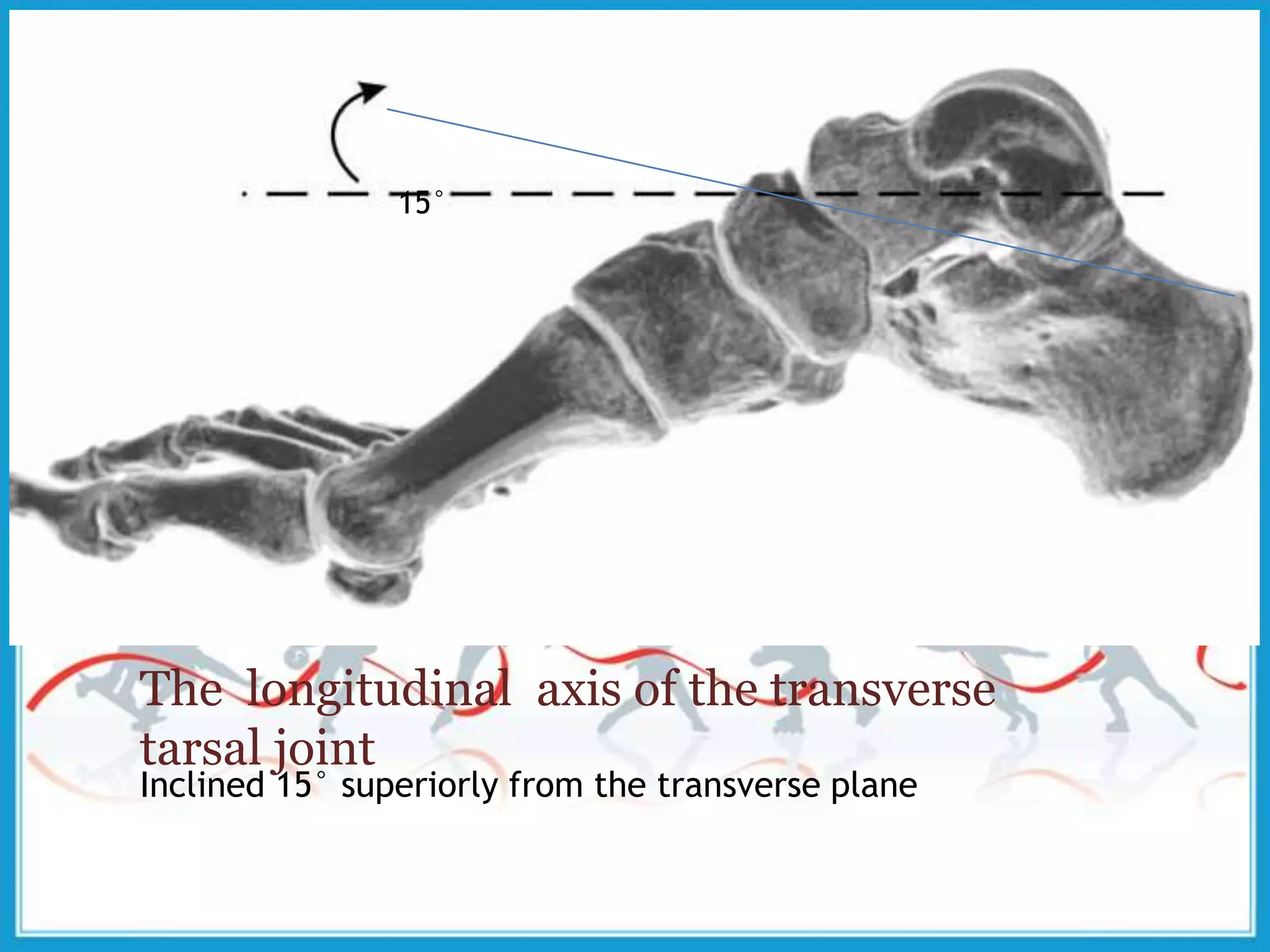
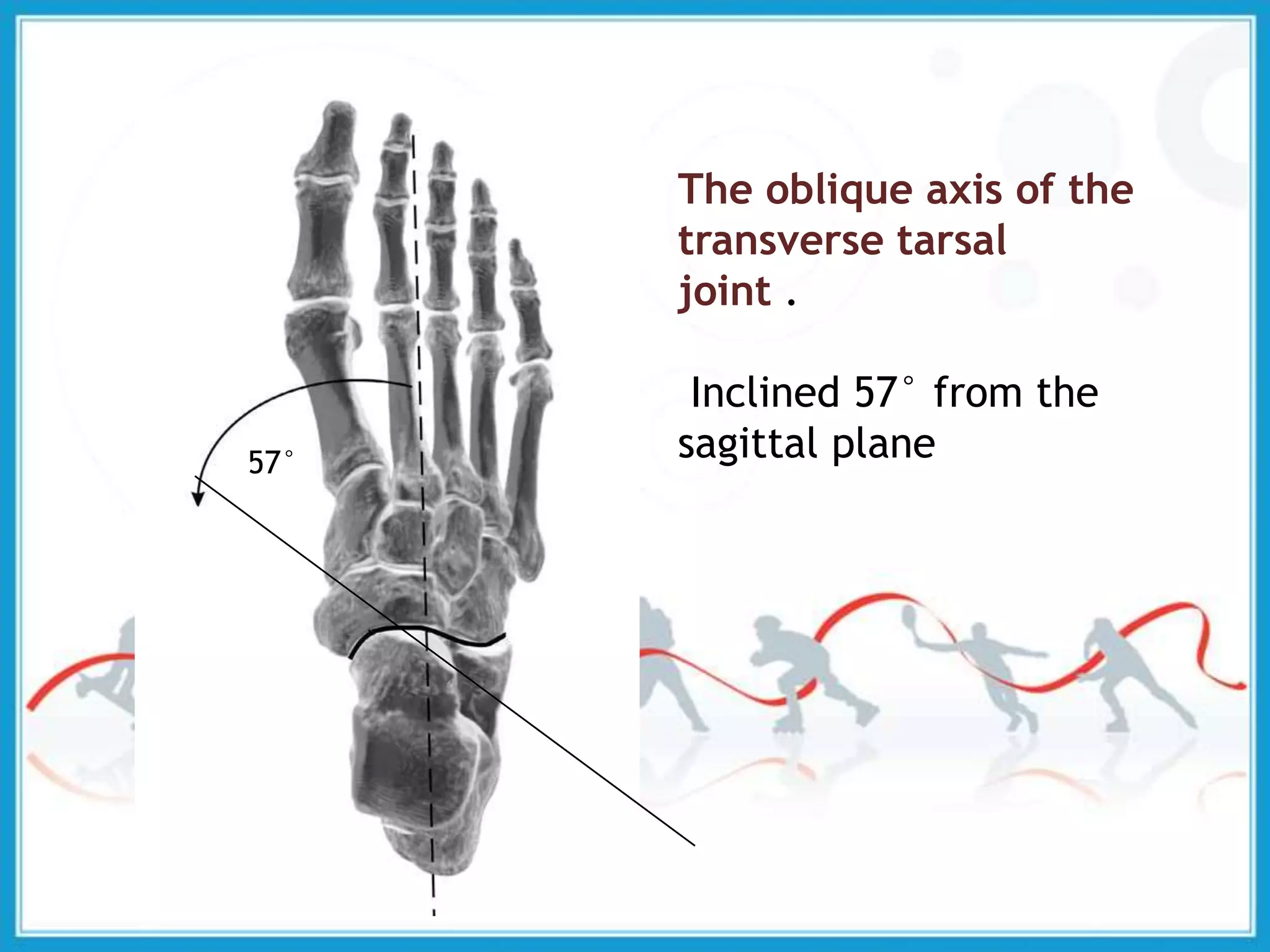
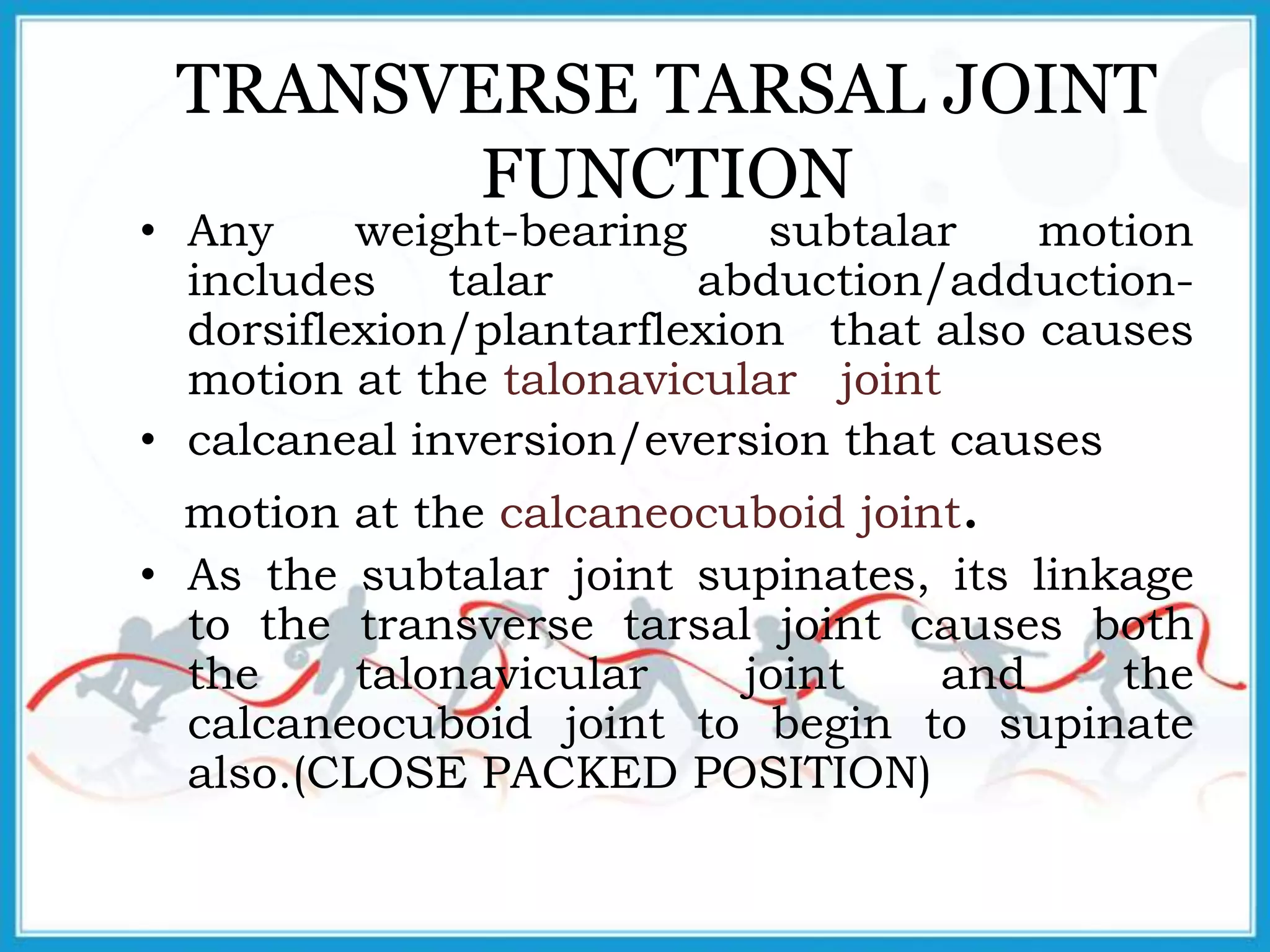
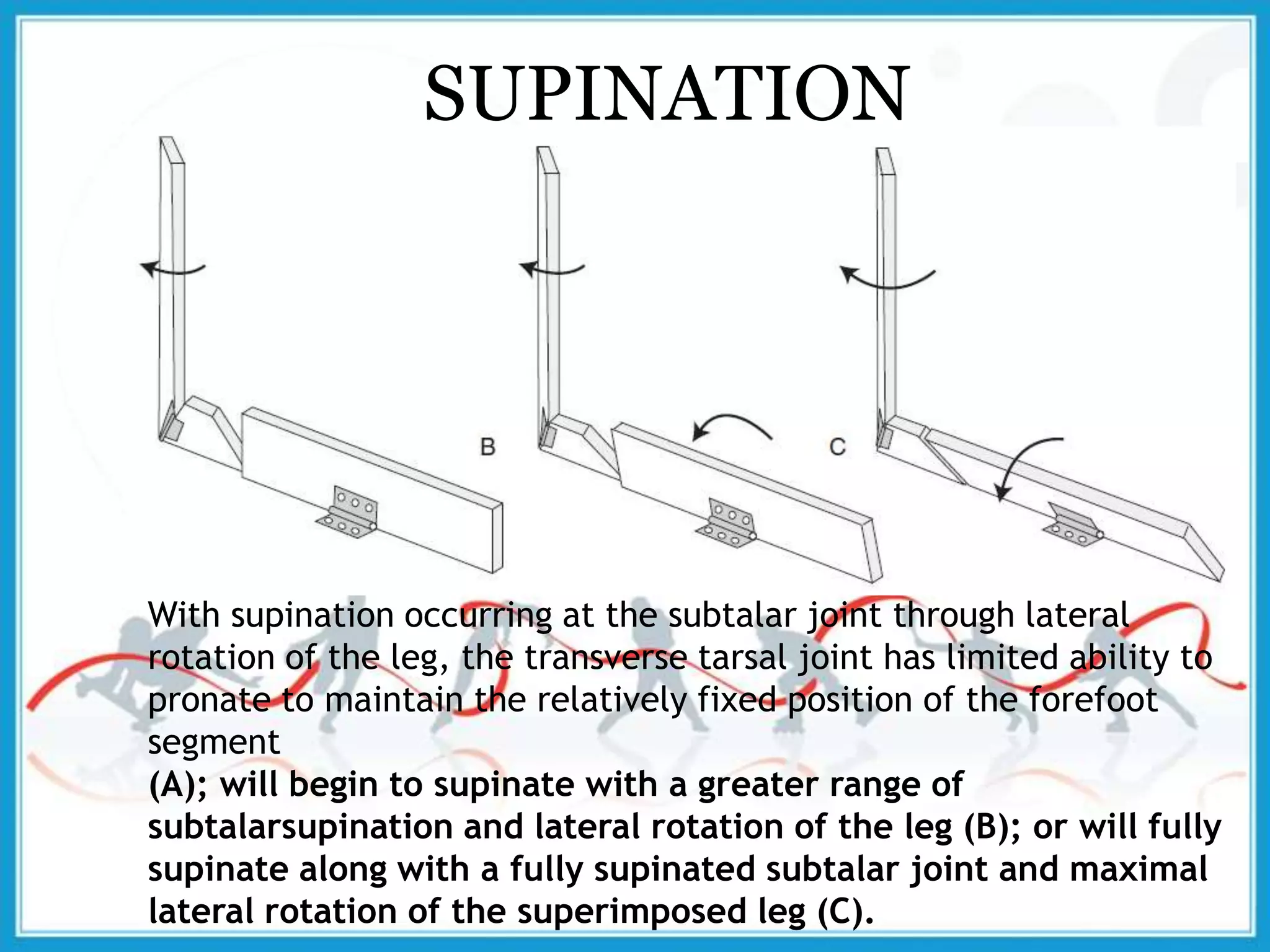
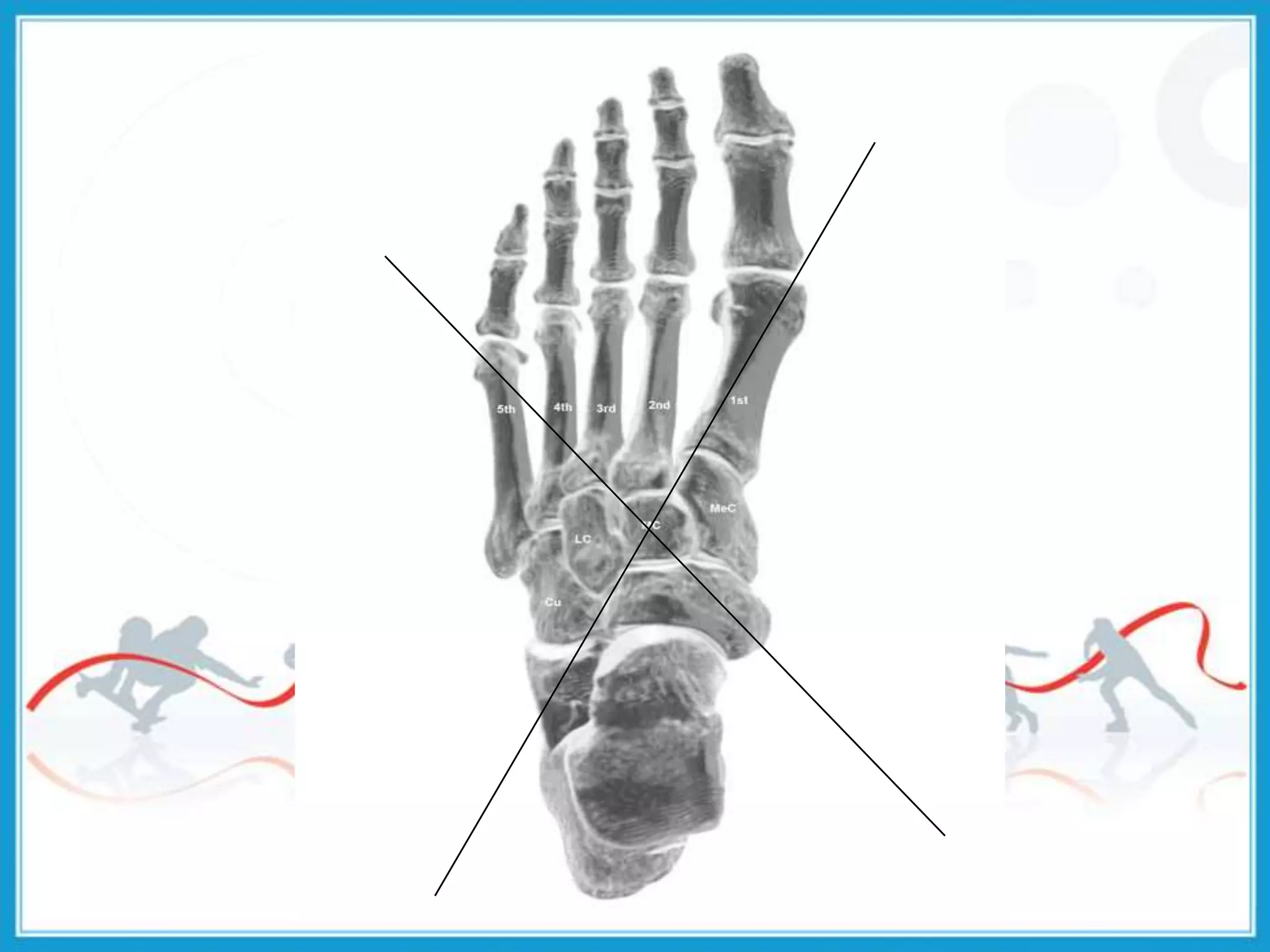
The document summarizes the biomechanics of the ankle joint complex. It describes the anatomy and function of the talocrural joint (ankle joint), subtalar joint, and transverse tarsal joint. The ankle-foot complex consists of 28 bones and 25 joints that allow the foot to meet stability and mobility demands through dorsiflexion, plantarflexion, pronation, and supination movements. Key bones include the talus, tibia, and fibula. Ligaments such as the deltoid and tibiofibular ligaments provide stability to the ankle mortise.