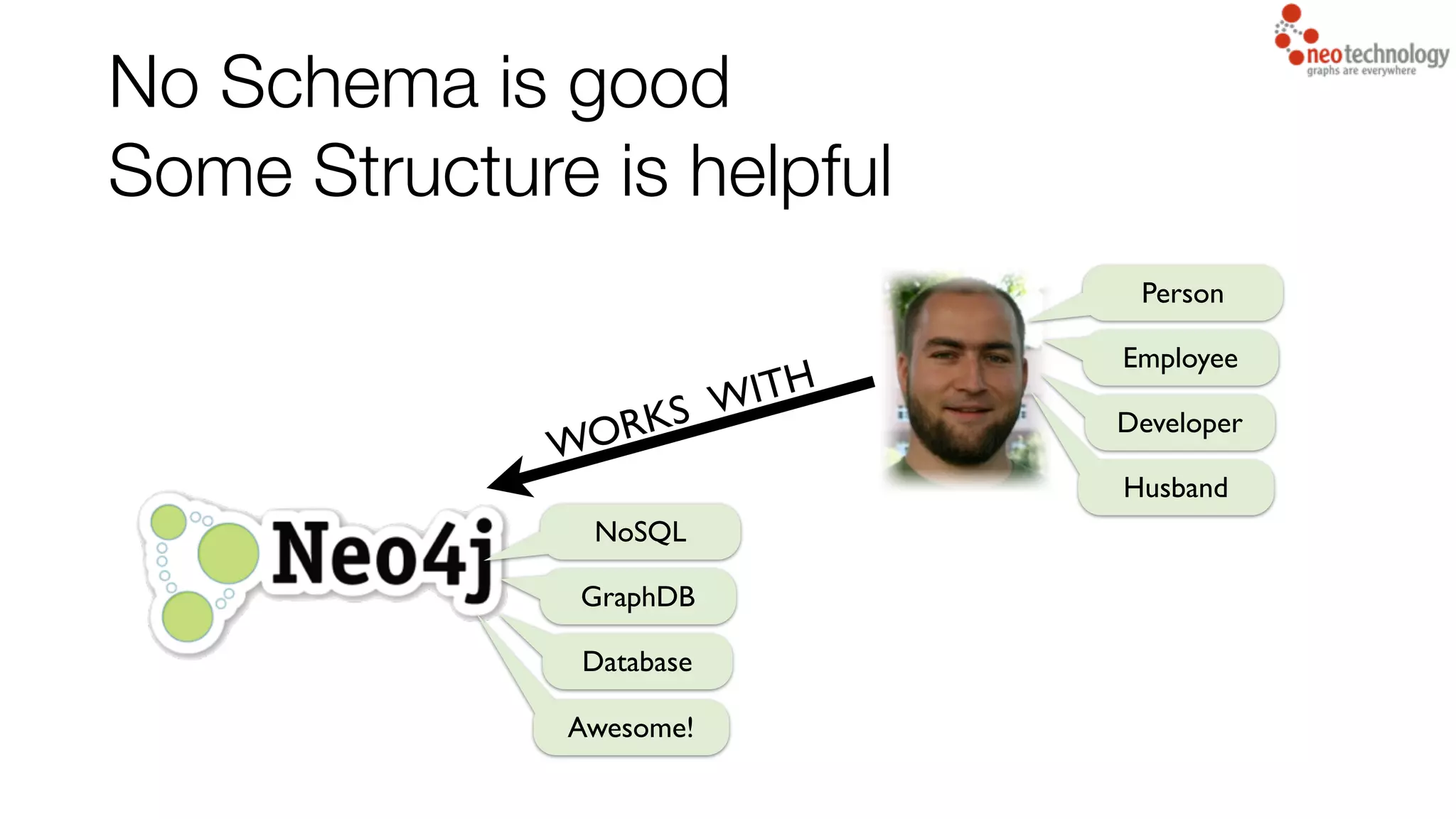
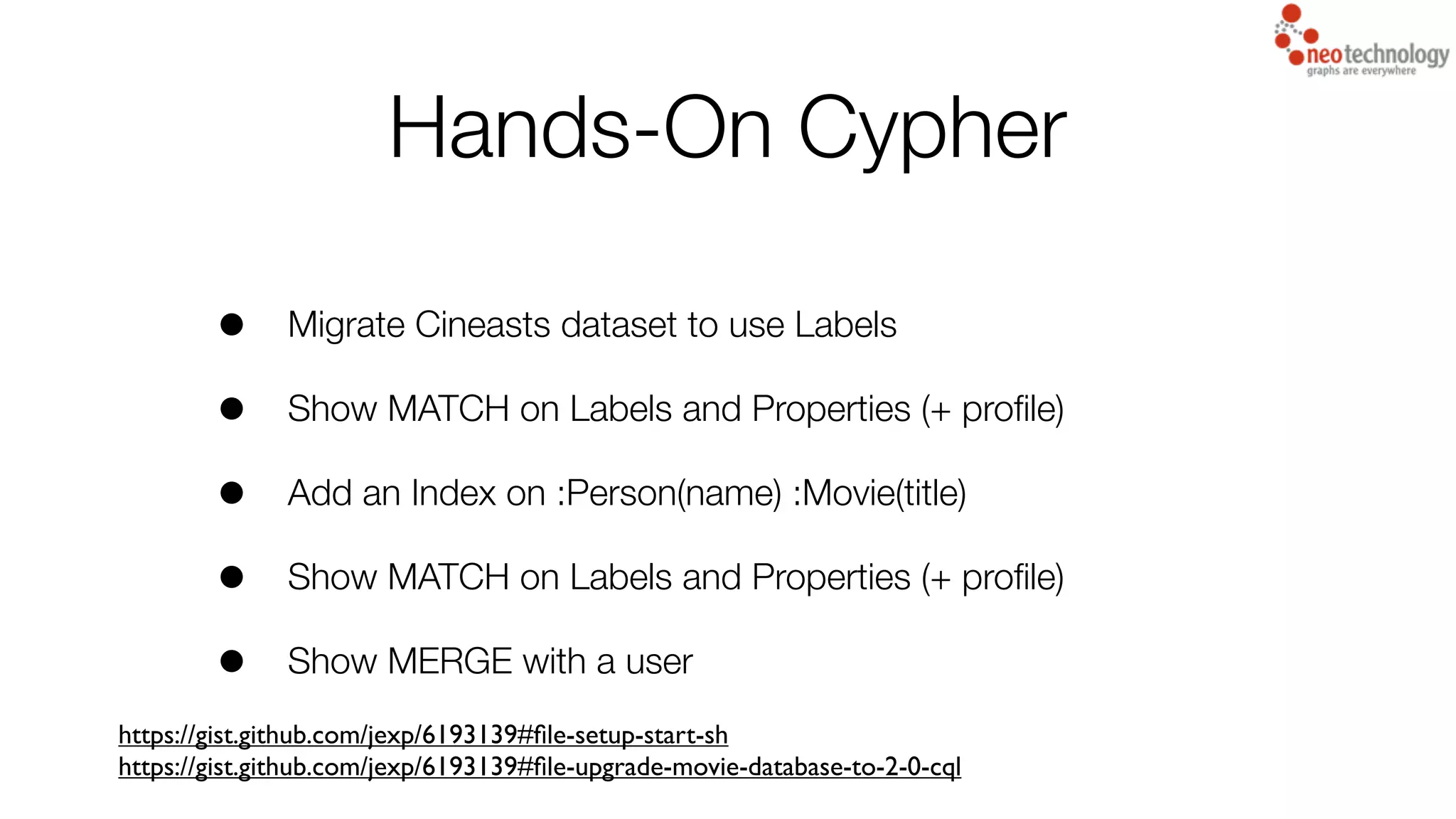
This document summarizes the key new features in Neo4j 2.0 including:
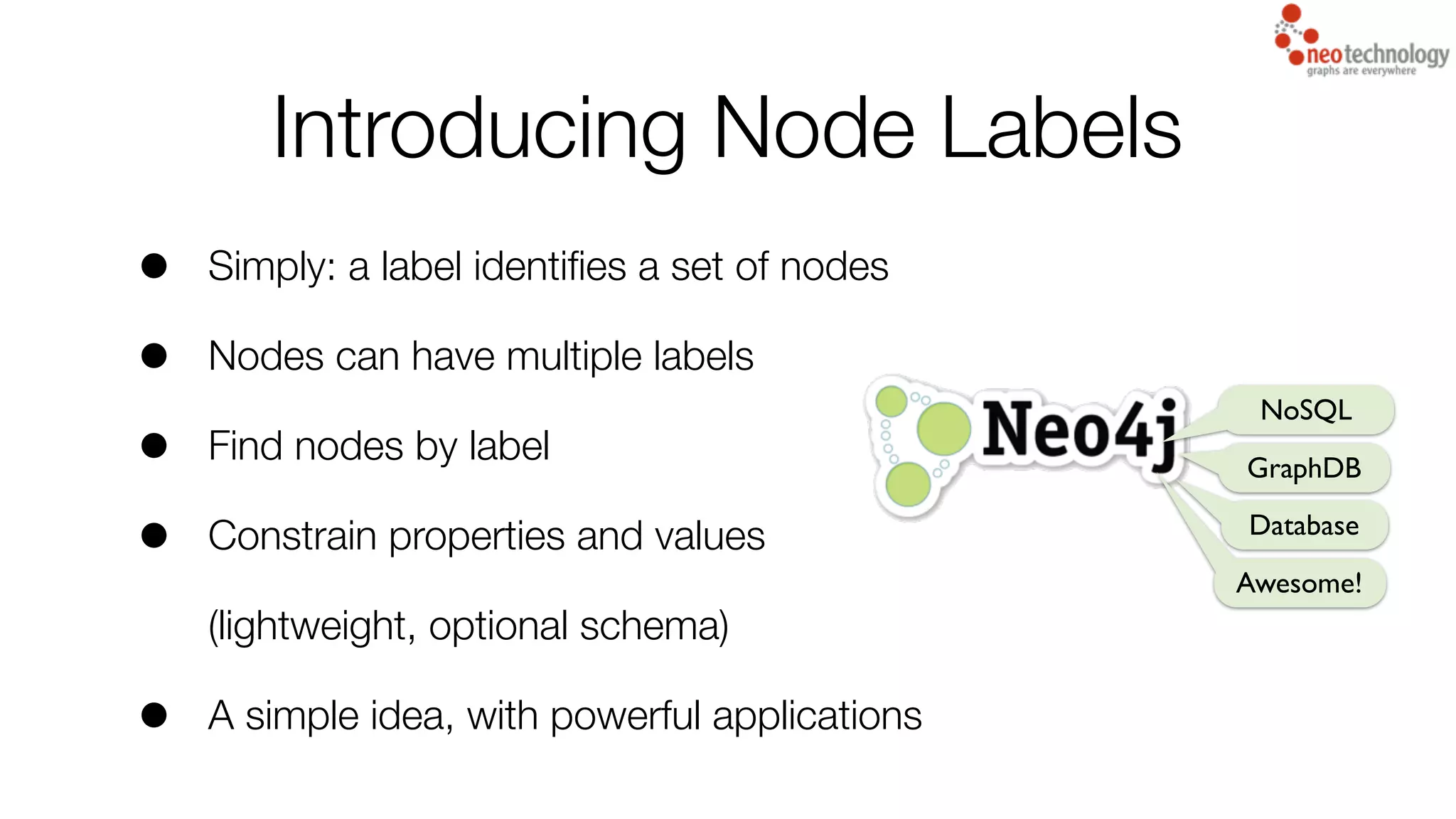
1) The introduction of node labels which allow nodes to have multiple labels to identify and categorize nodes and improve query performance.
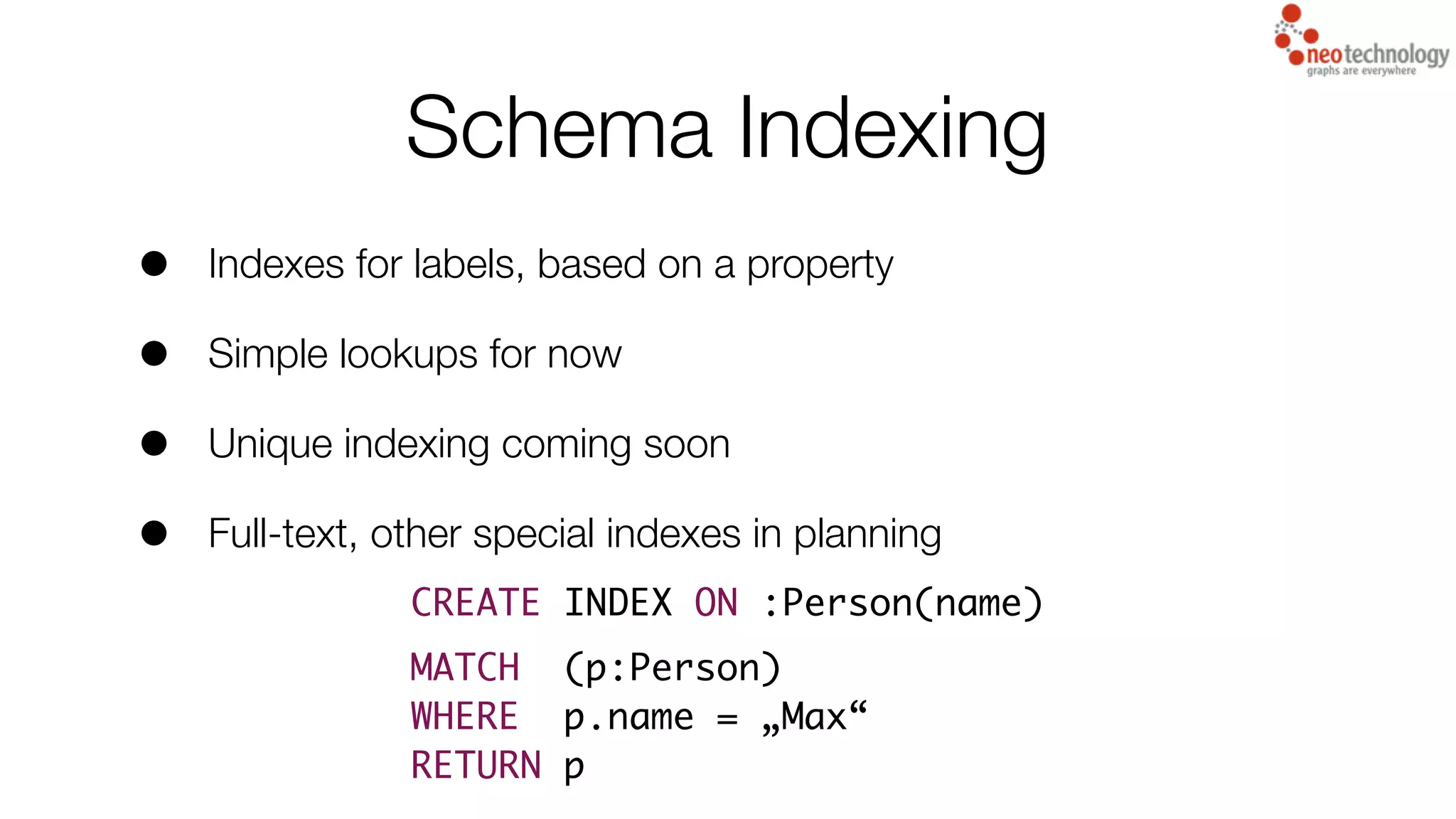
2) Schema indexing which allows indexes to be created for labels based on a property for simple lookups.
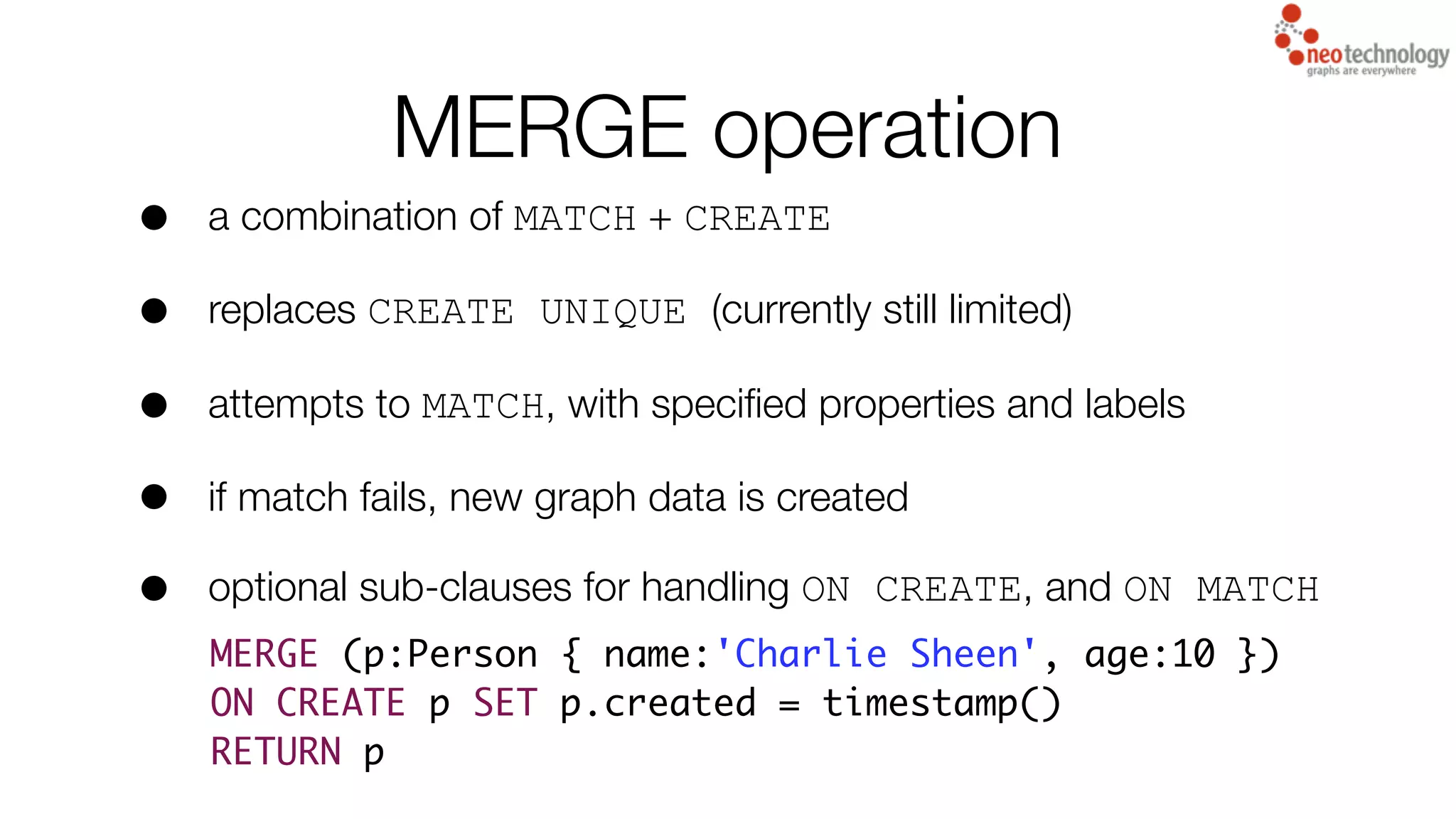
3) The MERGE operation which combines MATCH and CREATE to either match existing graph data or create new data if no match is found.
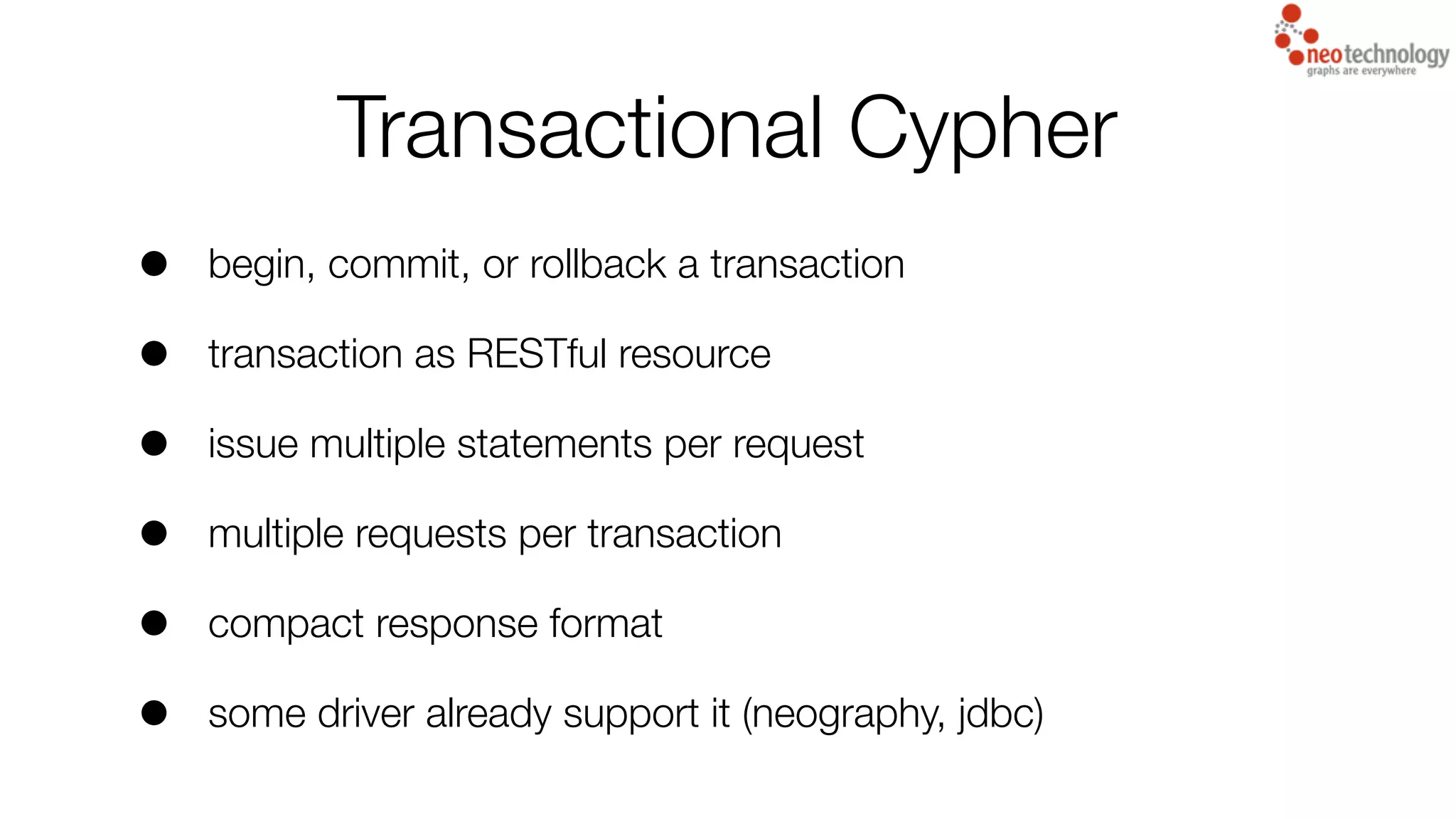
4) Transactions now being mandatory for all database interactions to improve consistency and isolation.
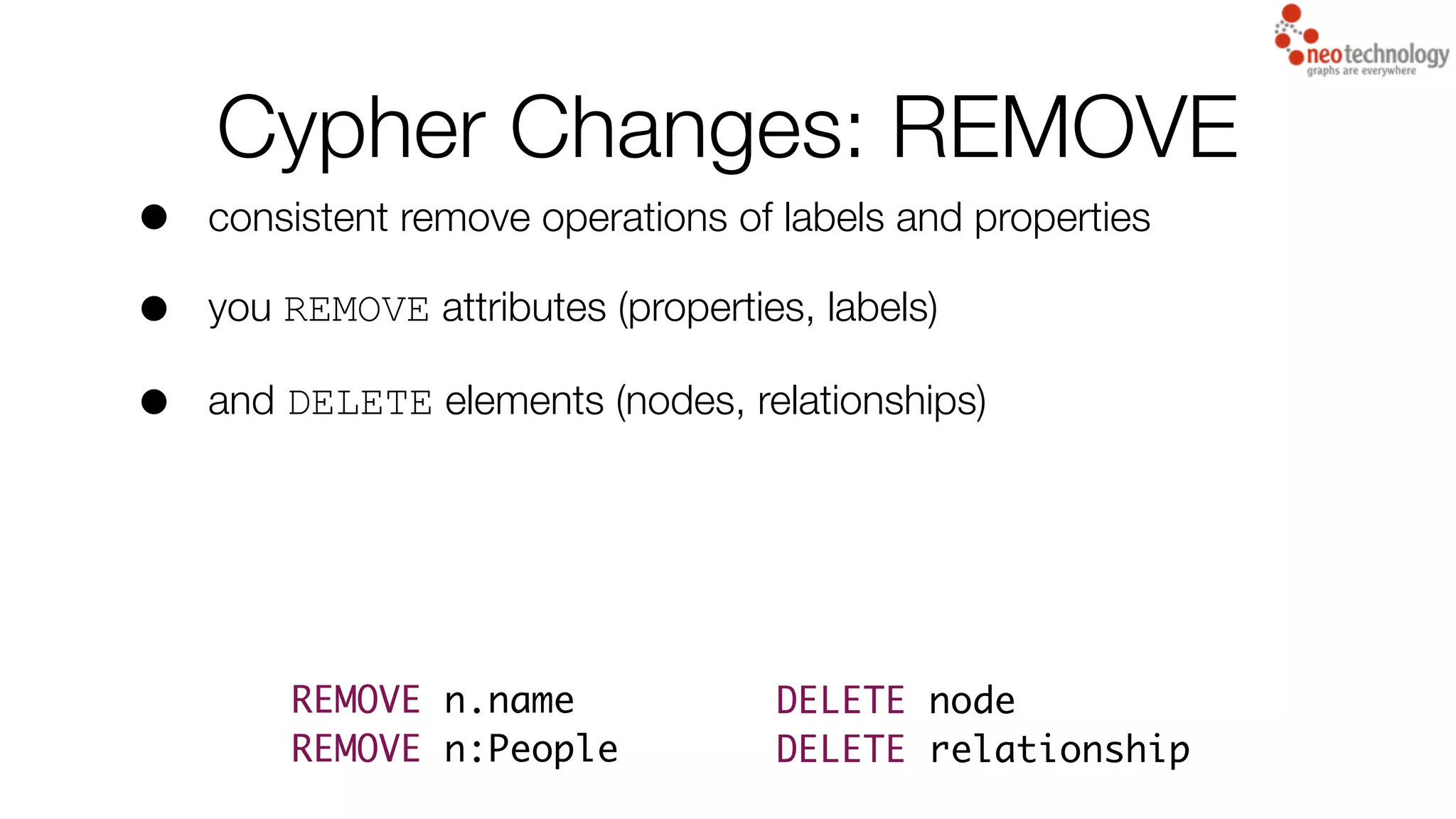
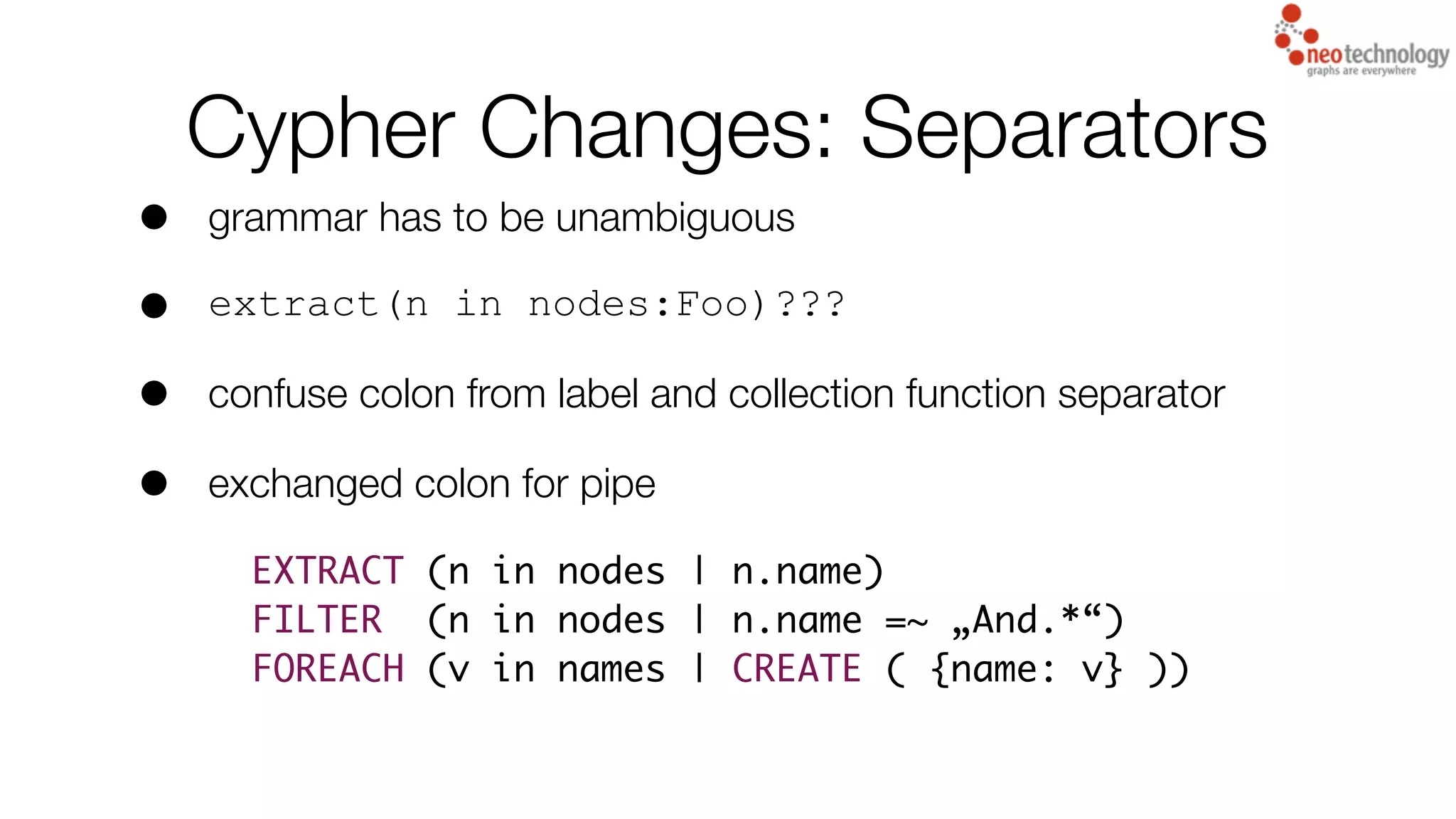
5) Various Cypher query language changes and improvements focused on making queries easier to write and read.












![Find friends who like cheese
MATCH (p:Person)-[:FRIENDS]->(friend:Person),
(friend) -[:LIKE]-> (thing:Thing)
WHERE p.name = "Max De Marzi"
AND thing:Food AND thing.name = "Cheese"
RETURN thing, labels(thing);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newin2-130809071932-phpapp02/75/Webinar-What-s-new-in-Neo4j-2-0-15-2048.jpg)







![Thanks :)
MATCH (you)-[:HAVE]->(q:Question)
RETURN q.text
@neo4j or @mesirii to keep in touch](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newin2-130809071932-phpapp02/75/Webinar-What-s-new-in-Neo4j-2-0-29-2048.jpg)