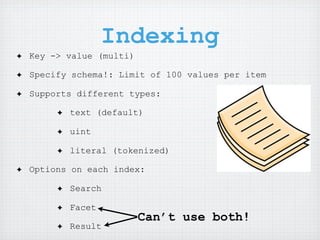
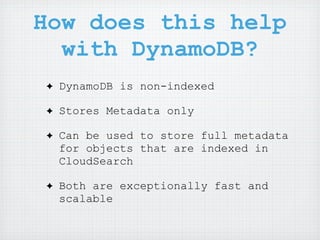
Chris Moyer, VP of Technology at Newstex, introduced Amazon CloudSearch, a fully managed search service. CloudSearch is powered by the same search engine used on Amazon.com and provides search domains, indexing of documents and metadata, and APIs to search and return results and facets without AWS credentials. It can help with indexing and searching when used alongside DynamoDB for metadata storage. CloudSearch is an expensive but powerful service that saves development time by providing features that would otherwise need to be built.