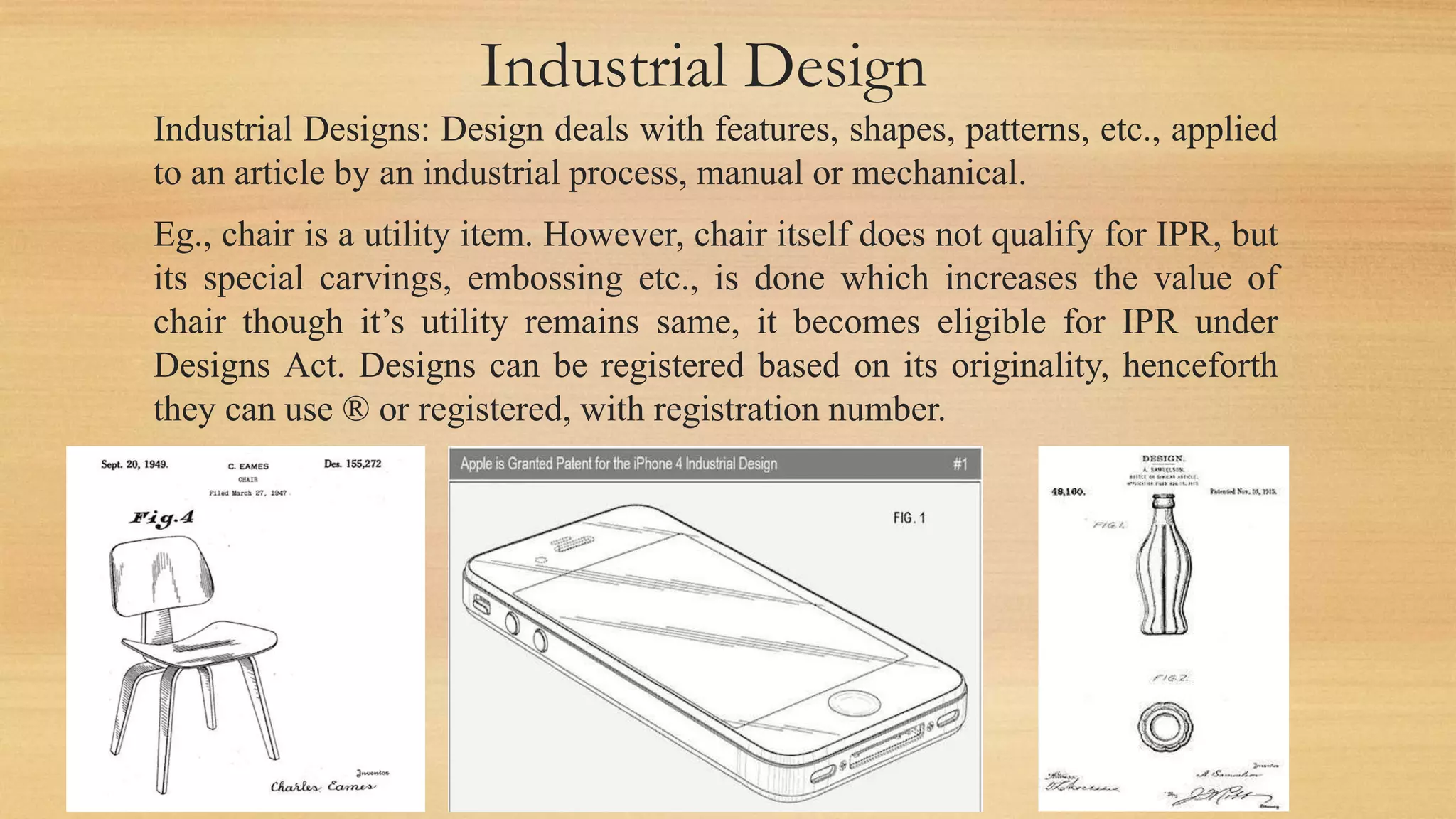
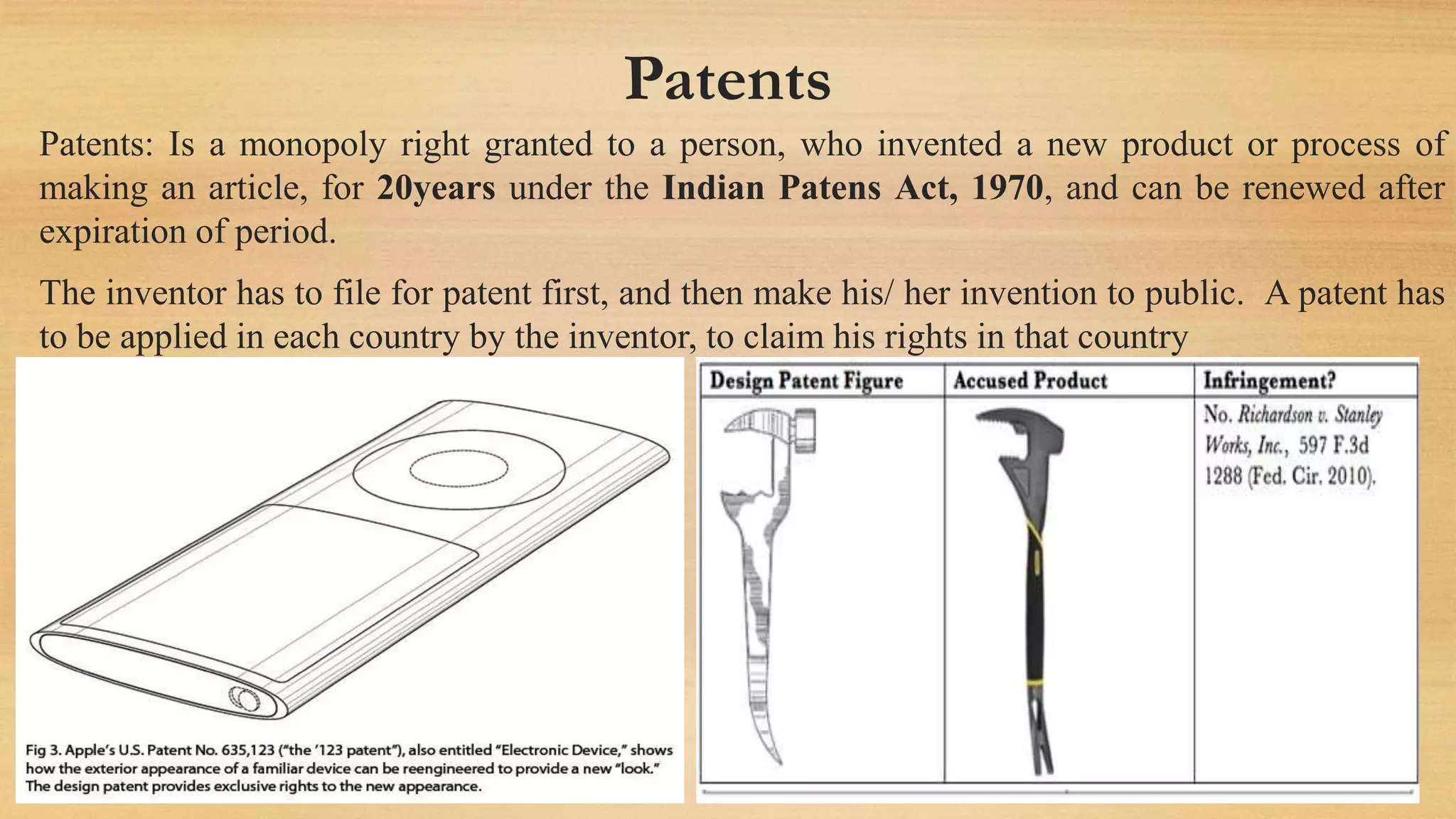
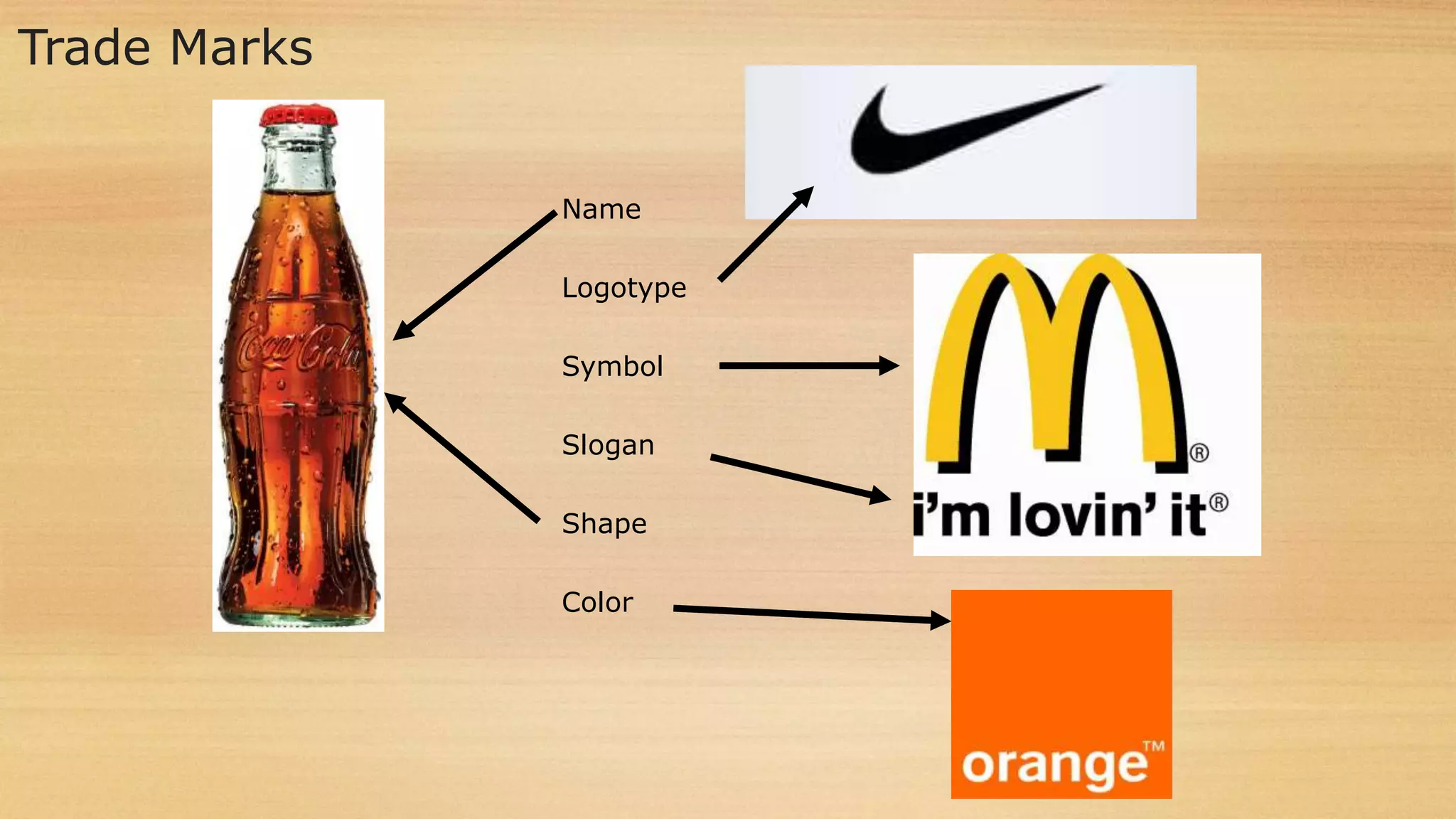
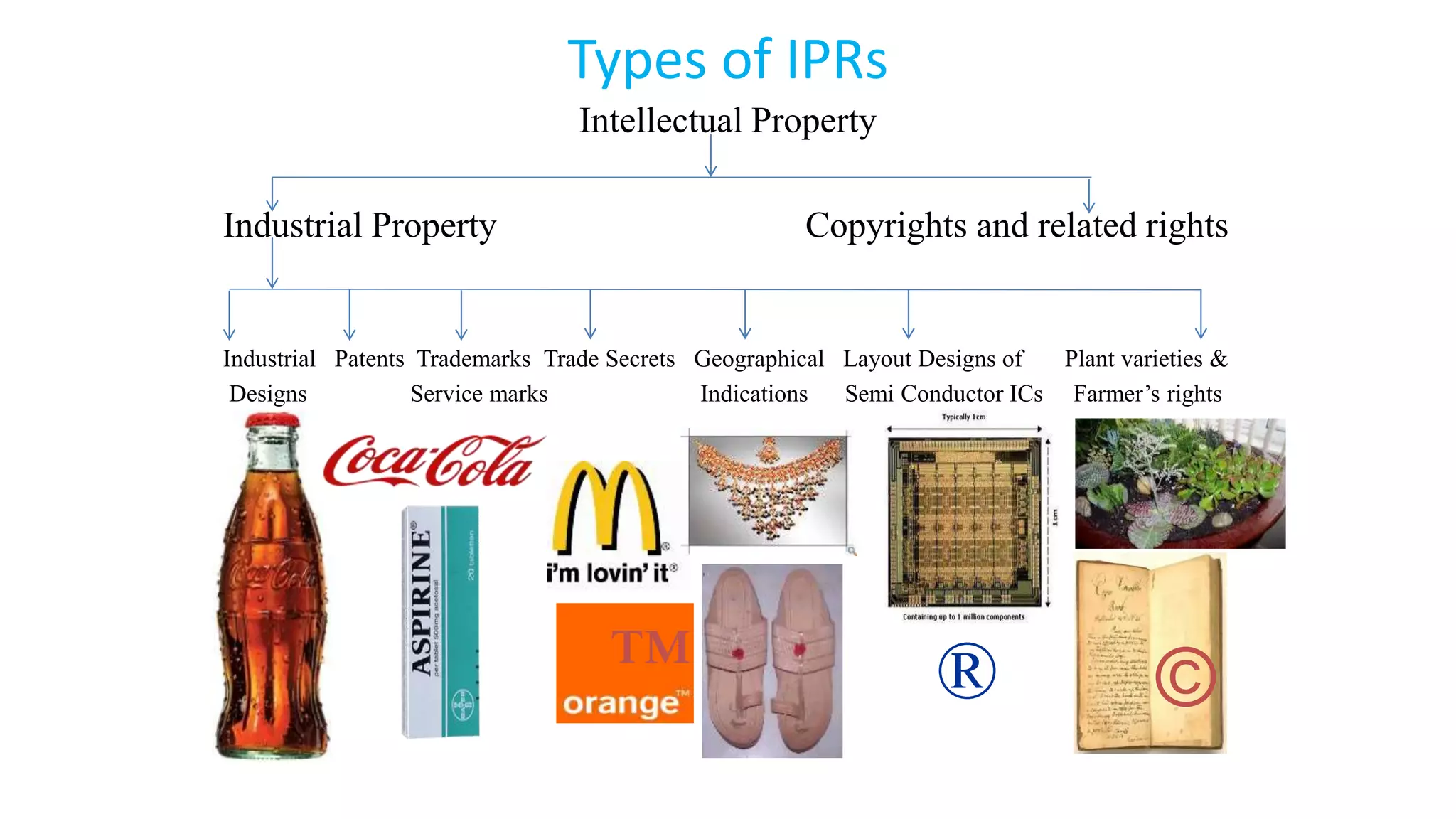
The document discusses the Internet of Things (IoT) as a global network infrastructure with self-configuring capabilities, emphasizing its significant growth, predicted to reach 50 billion connected devices by 2020. It outlines various forms of intellectual property rights (IPR) such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights, and their importance in protecting innovations and designs. Additionally, it touches on product liability and the legal responsibilities of manufacturers and suppliers for product-related injuries.