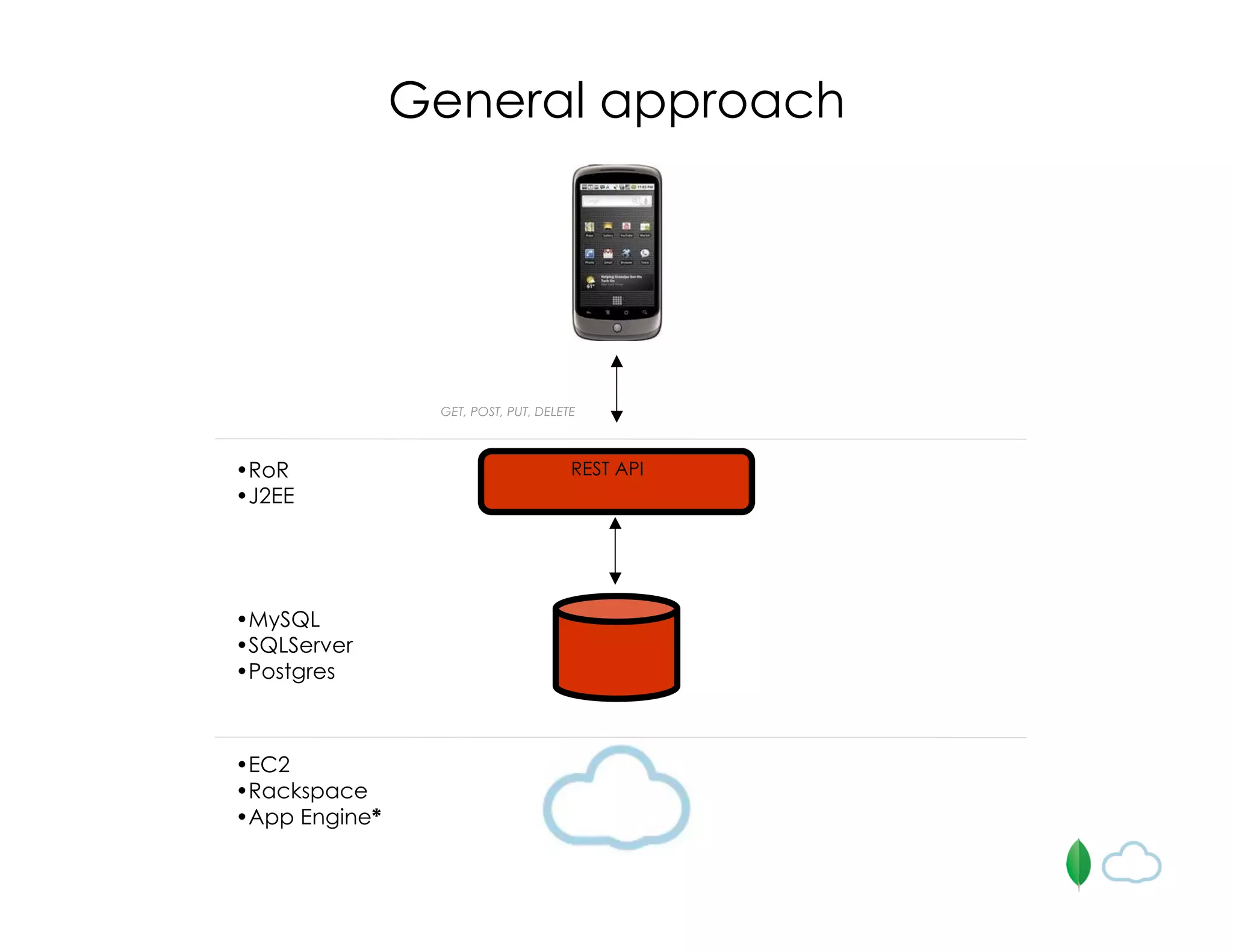
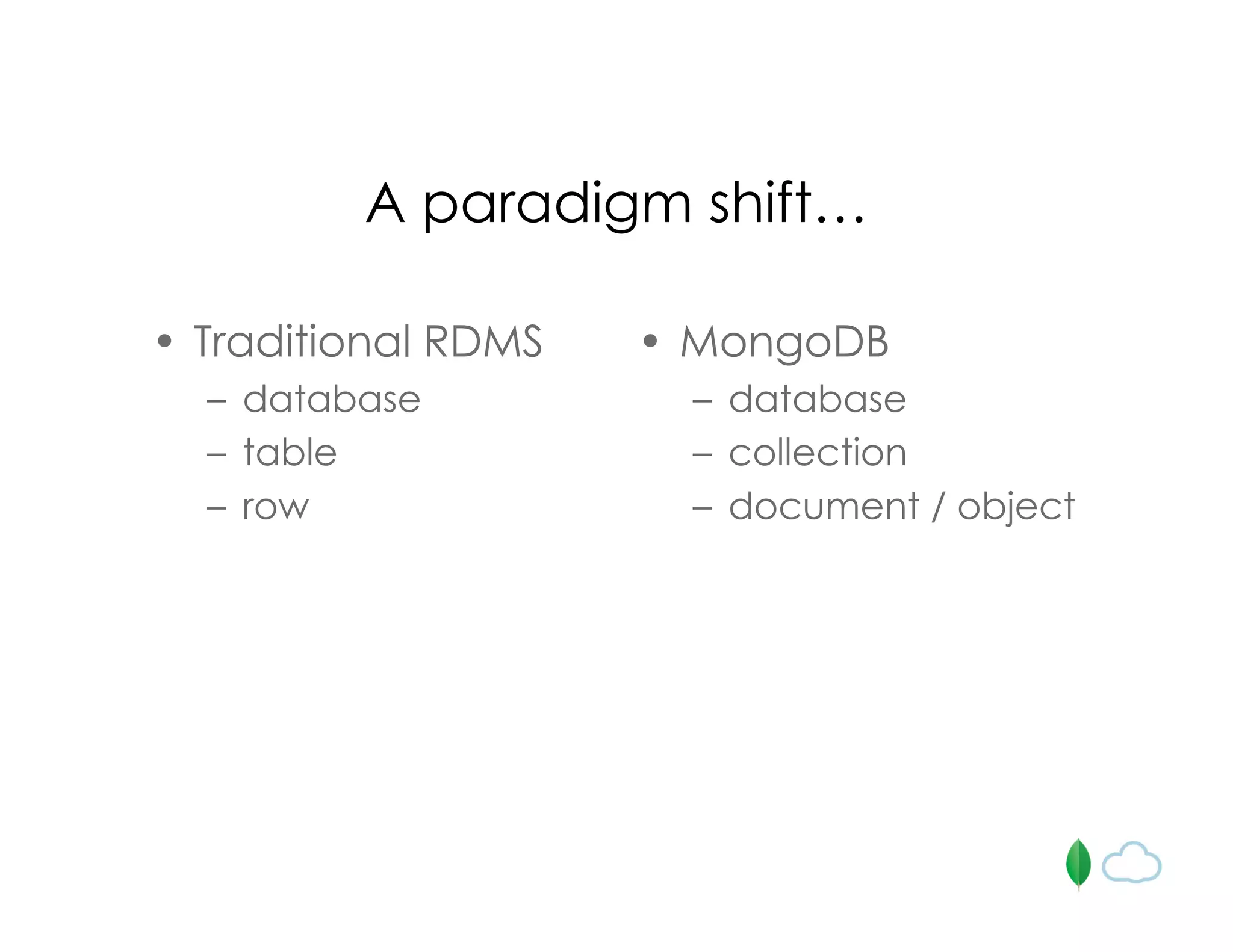
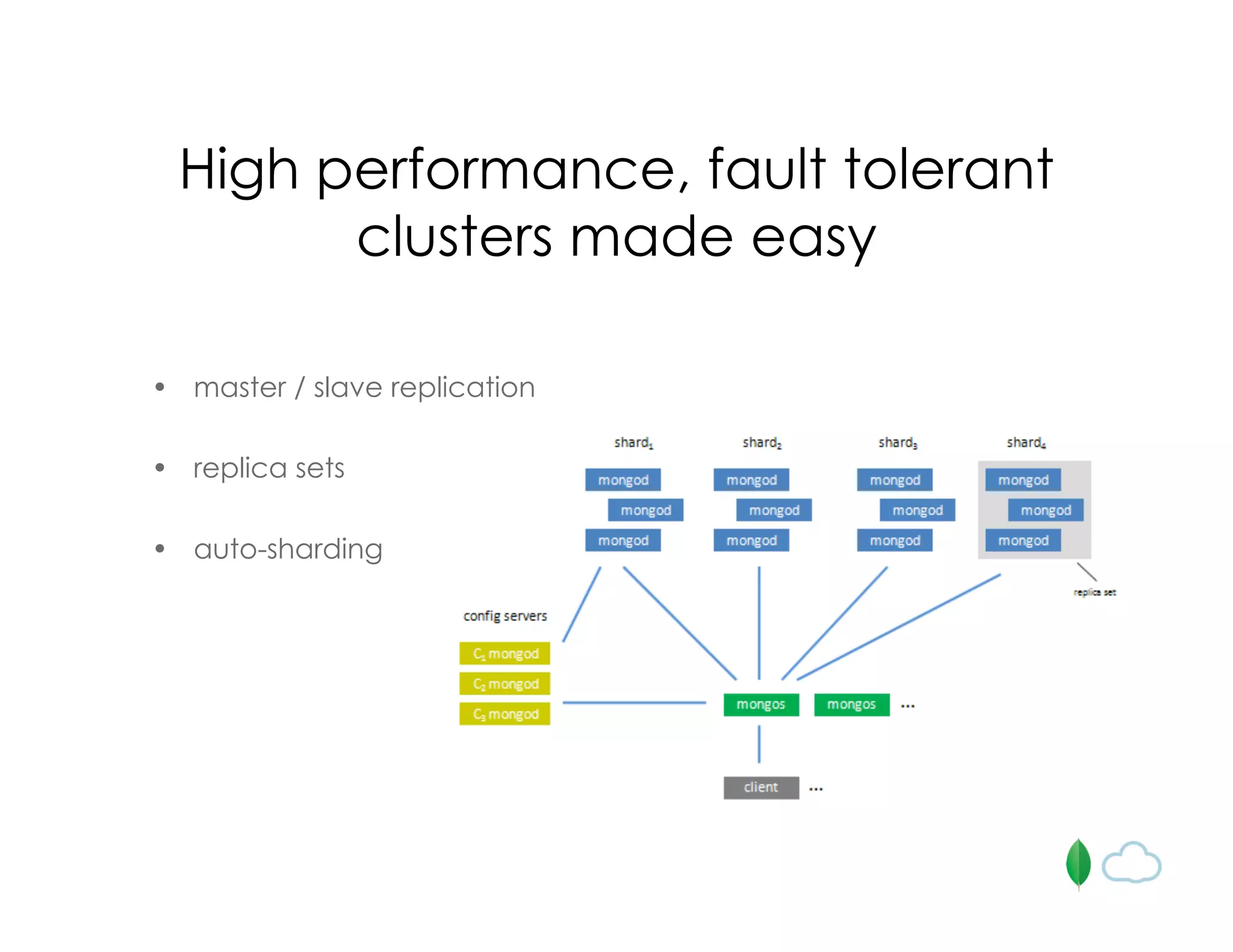
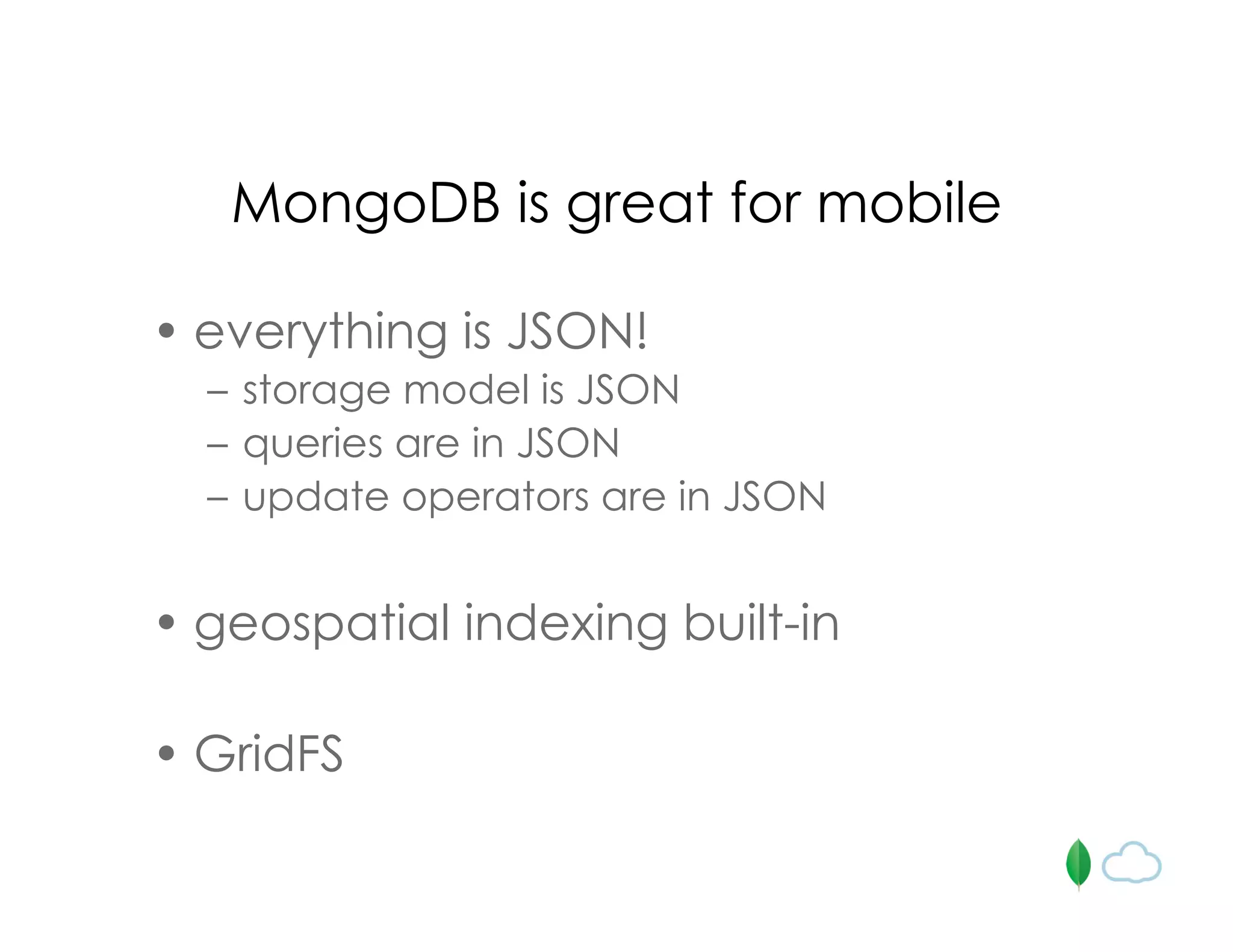
The document discusses the use of MongoDB for mobile app backends, highlighting its advantages such as scalability, high performance, and flexible data storage through a JSON-like structure. It provides insights into how MongoDB addresses common database challenges, including object-relational impedance mismatch and the need for horizontal scalability. Additionally, it mentions use cases, including geospatial indexing and a cloud-hosted MongoDB solution via Mongolab, while also noting limitations in performing complex transactions.







![Documents (a.k.a. Objects)
{
_id: 1234,
author: { name: “Bob Jones”, email: “b@b.com” },
post: “In these troubled times I like to …“,
date: { $date: “2010-07-12 13:23UTC” },
location: [ -121.2322, 42.1223222 ],
rating: 2.2,
comments: [
{ user: “jgs32@hotmail.com”,
upVotes: 22,
downVotes: 14,
text: “Great point! I agree” },
{ user: “holly.davidson@gmail.com”,
upVotes: 421,
downVotes: 22,
text: “You are a moron” }
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/android-talk2-101029140439-phpapp02/75/Learn-Learn-how-to-build-your-mobile-back-end-with-MongoDB-11-2048.jpg)
![{
_id: 1234,
author: { name: “Bob Jones”, email: “b@b.com” },
post: “In these troubled times I like to …“,
date: { $date: “2010-07-12 13:23UTC” },
location: [ -121.2322, 42.1223222 ],
rating: 2.2,
comments: [
{ user: “jgs32@hotmail.com”,
upVotes: 22,
downVotes: 14,
text: “Great point! I agree” },
{ user: “holly.davidson@gmail.com”,
upVotes: 421,
downVotes: 22,
text: “You are a moron” }
],
tags: [ “politics”, “Virginia” ]
}
Flexible “schemas”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/android-talk2-101029140439-phpapp02/75/Learn-Learn-how-to-build-your-mobile-back-end-with-MongoDB-12-2048.jpg)


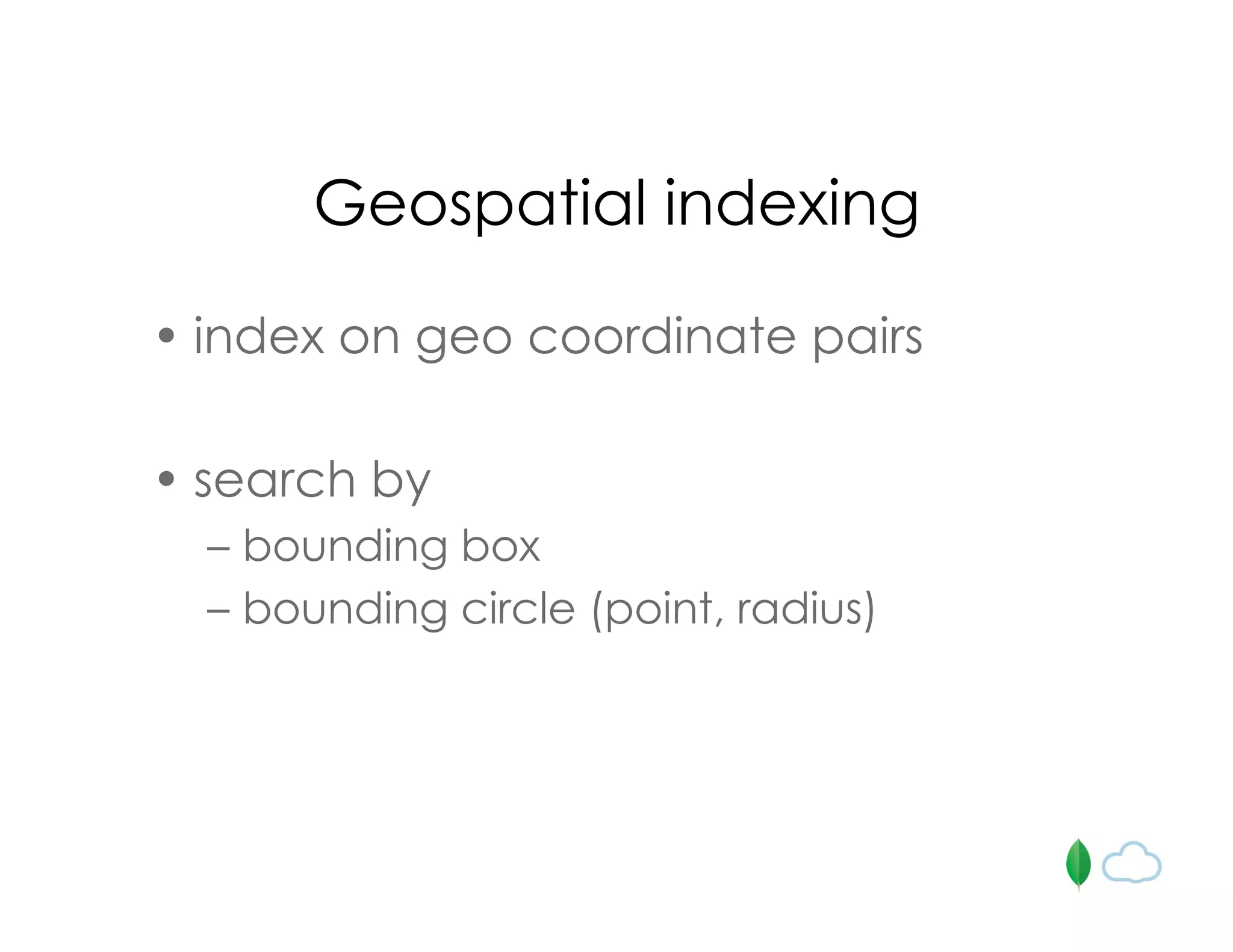
![Geospatial indexing
db.places.ensureIndex( { loc: “2d” } )
db.places.find({ loc: { $near : [50, 50] } }).limit(10)
db.places.find({loc: {$within : {$box : [[40,40],[60,60]]}}})
db.places.find({loc: {$within : {$center : [[40,40],10]}}})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/android-talk2-101029140439-phpapp02/75/Learn-Learn-how-to-build-your-mobile-back-end-with-MongoDB-21-2048.jpg)




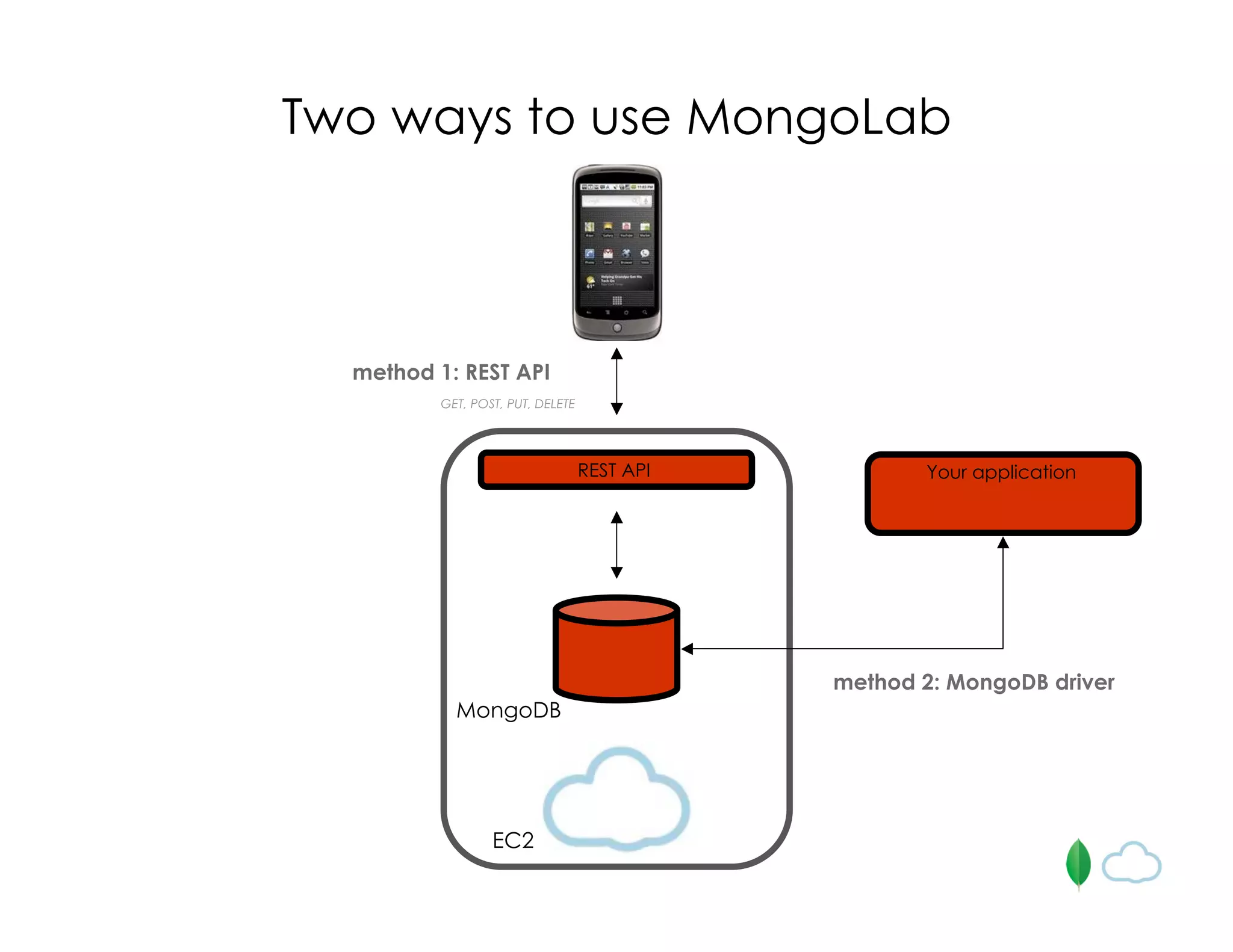
![/databases/<d>/collections
GET
/databases/<d>/collections/<c>
GET
POST
/databases/<d>/collections/<c>/<_id>
GET
PUT
DELETE
/databases/<d>/collections/<c>?[q=<query>]
[&f=<fields>]
[&s=<order>]
[&sk=<skip>]
[&l=<limit>]
GET
MongoLab API](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/android-talk2-101029140439-phpapp02/75/Learn-Learn-how-to-build-your-mobile-back-end-with-MongoDB-29-2048.jpg)