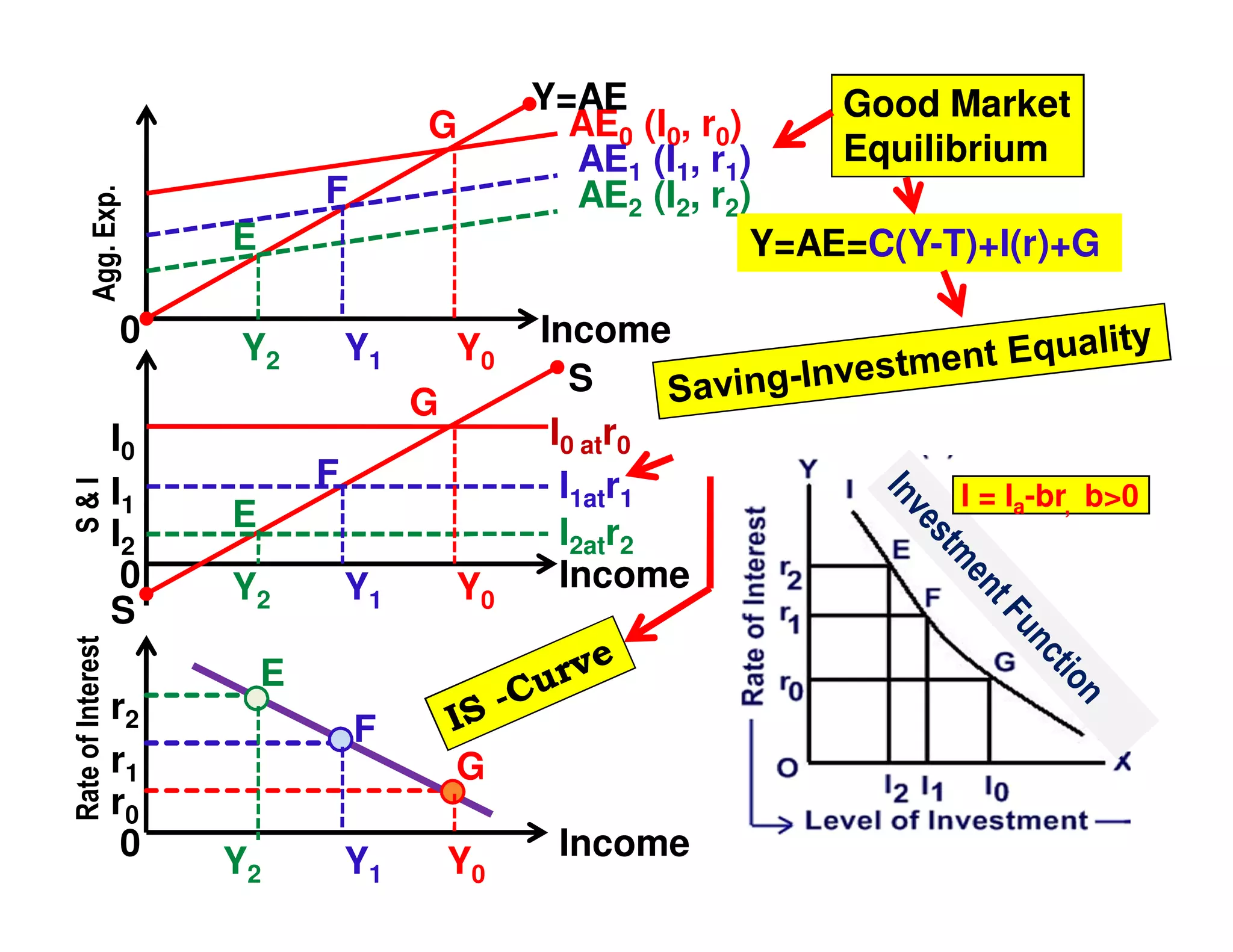
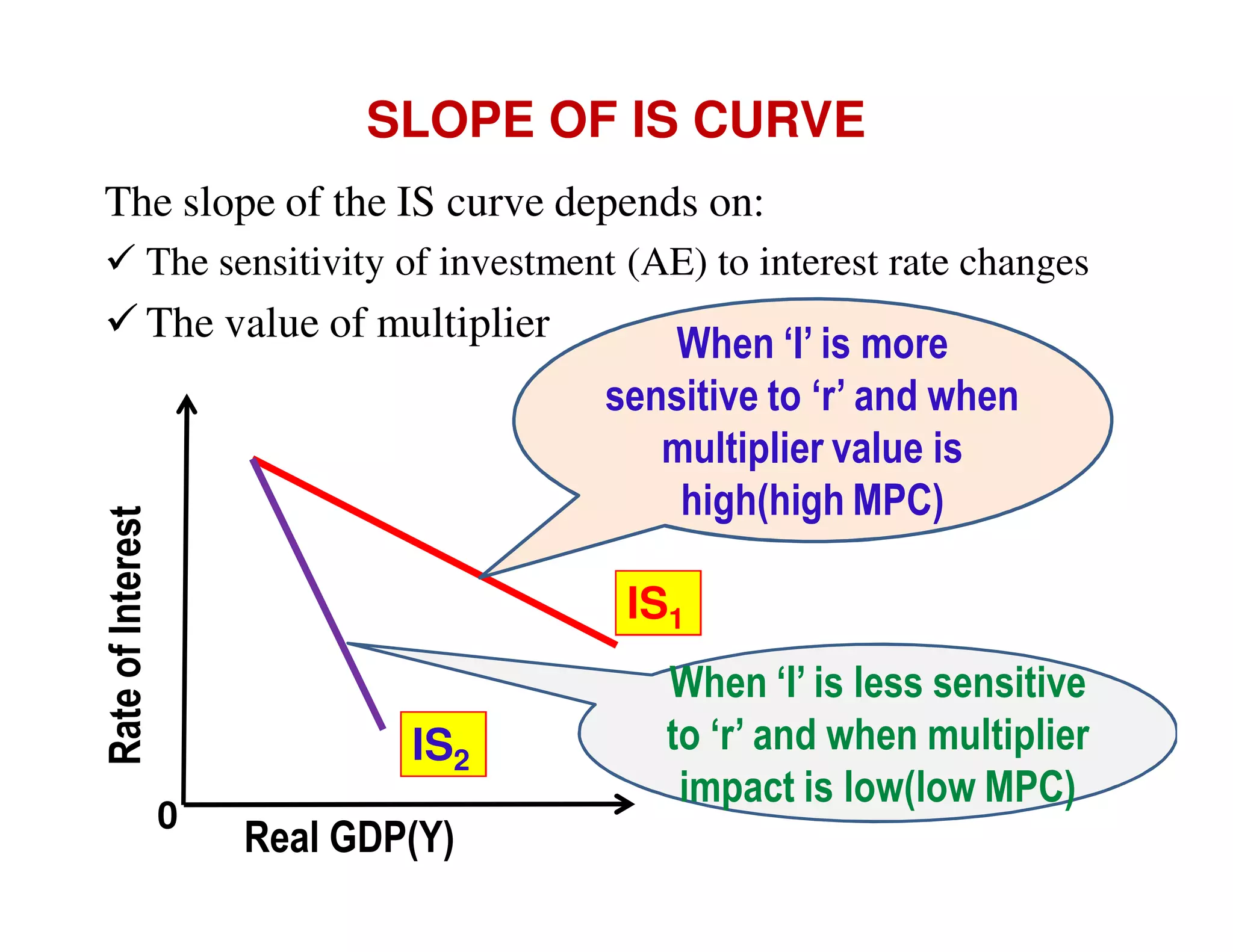
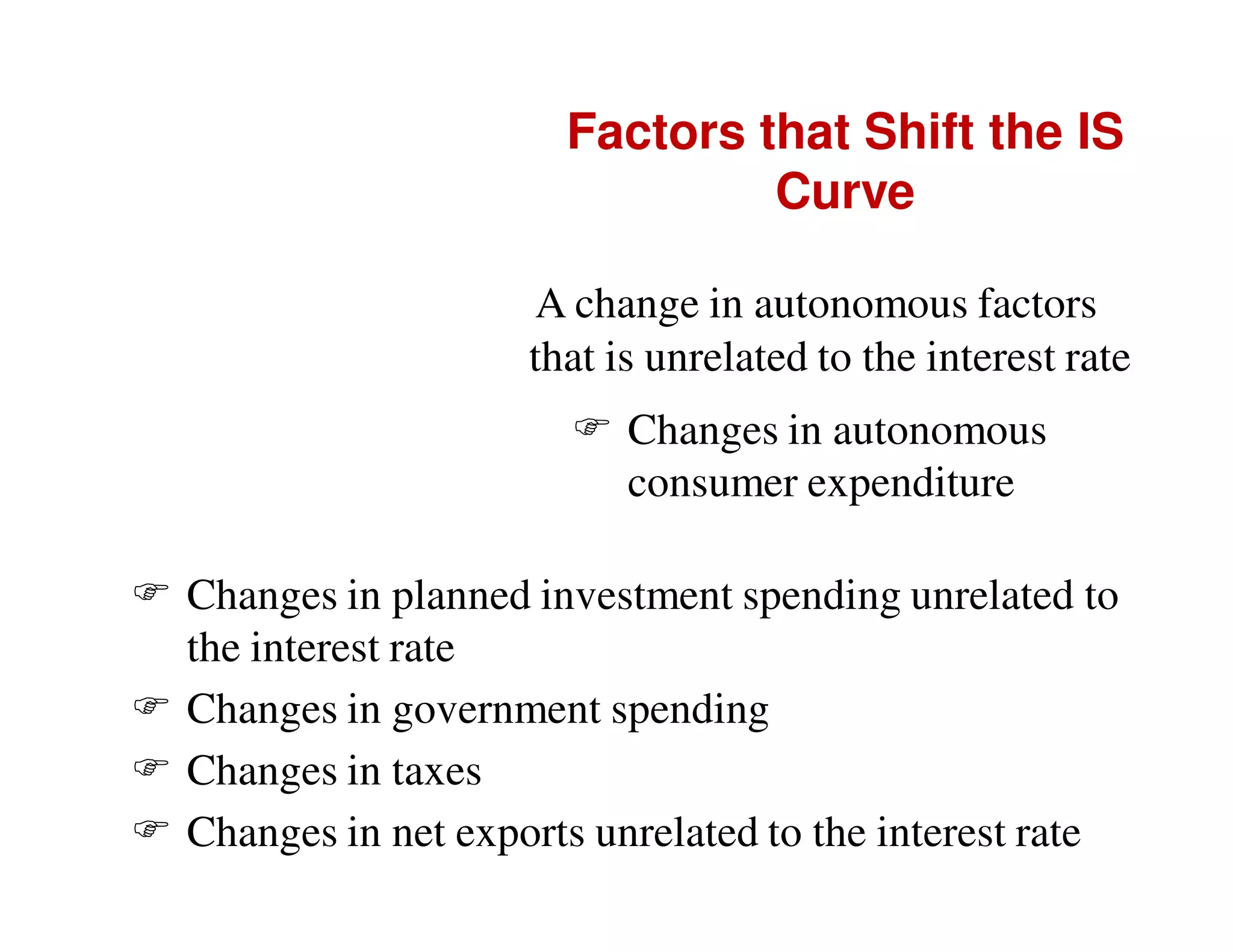
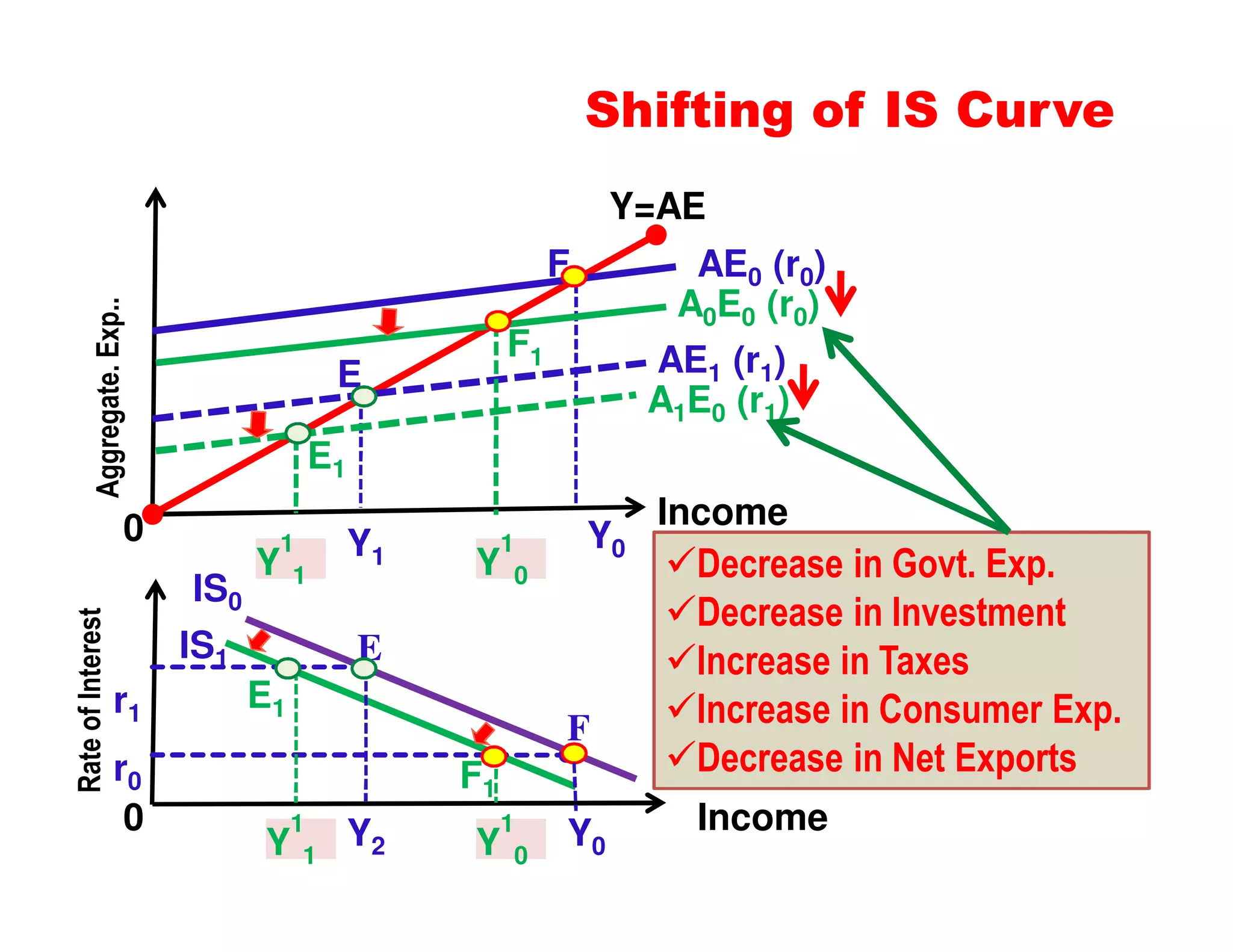
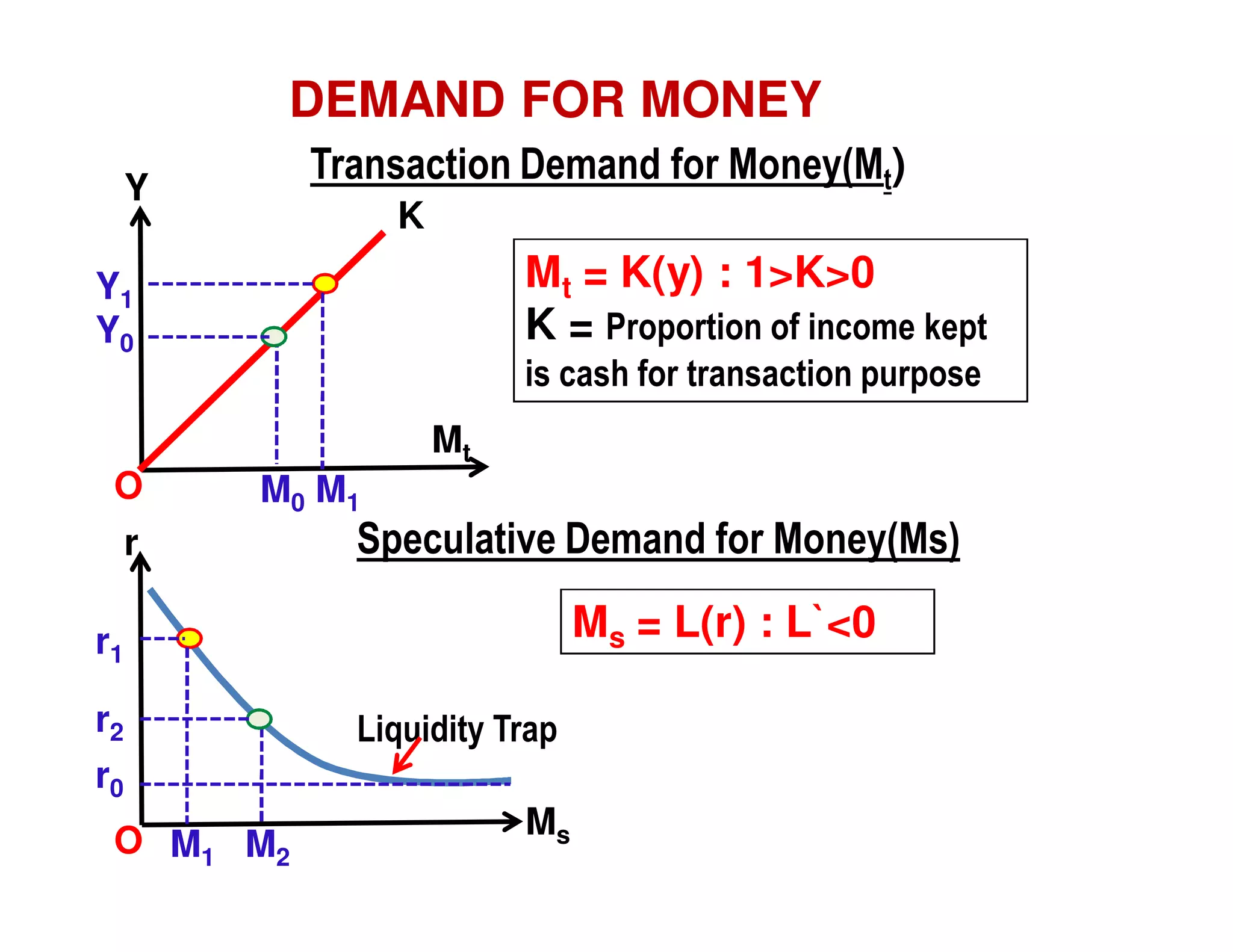
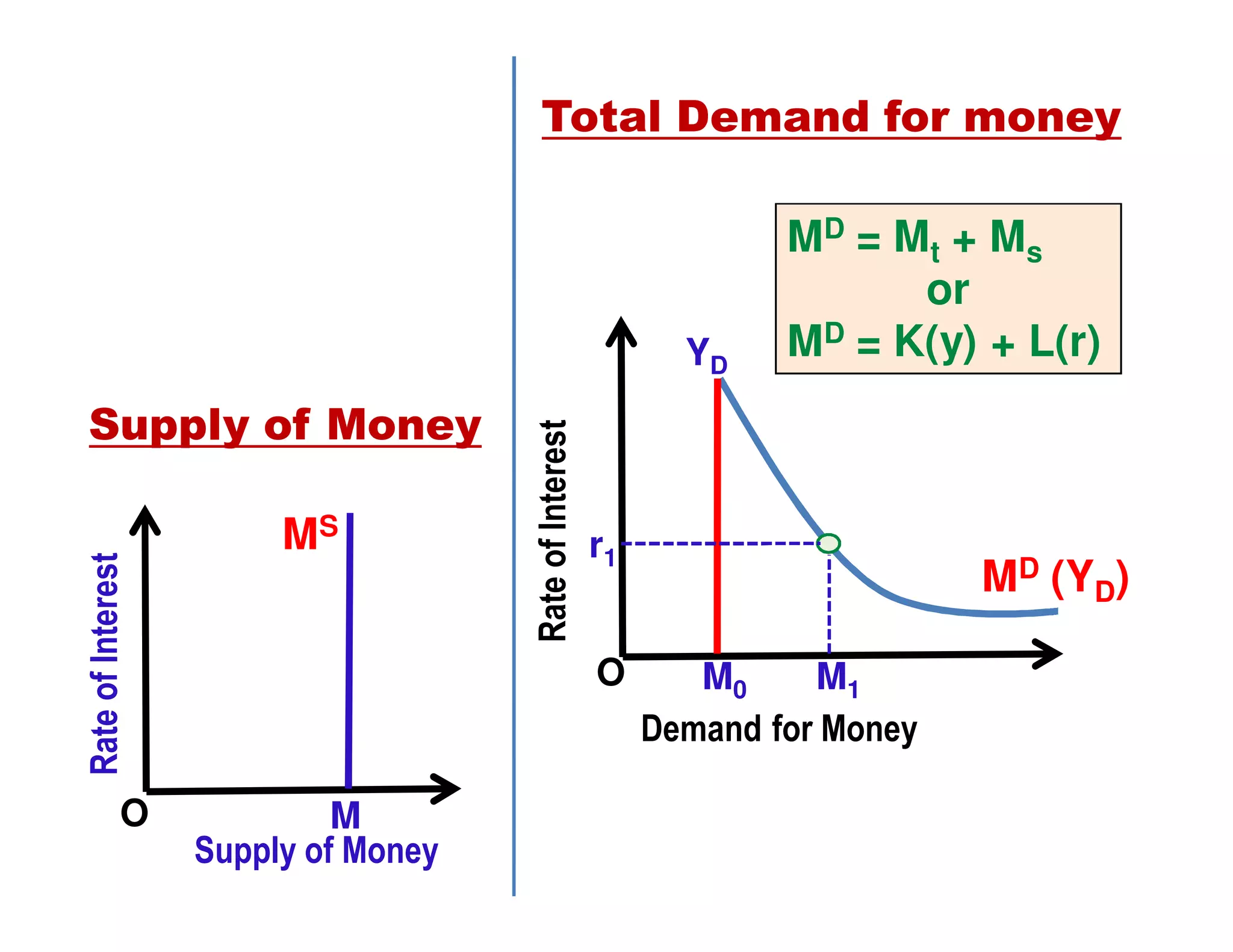
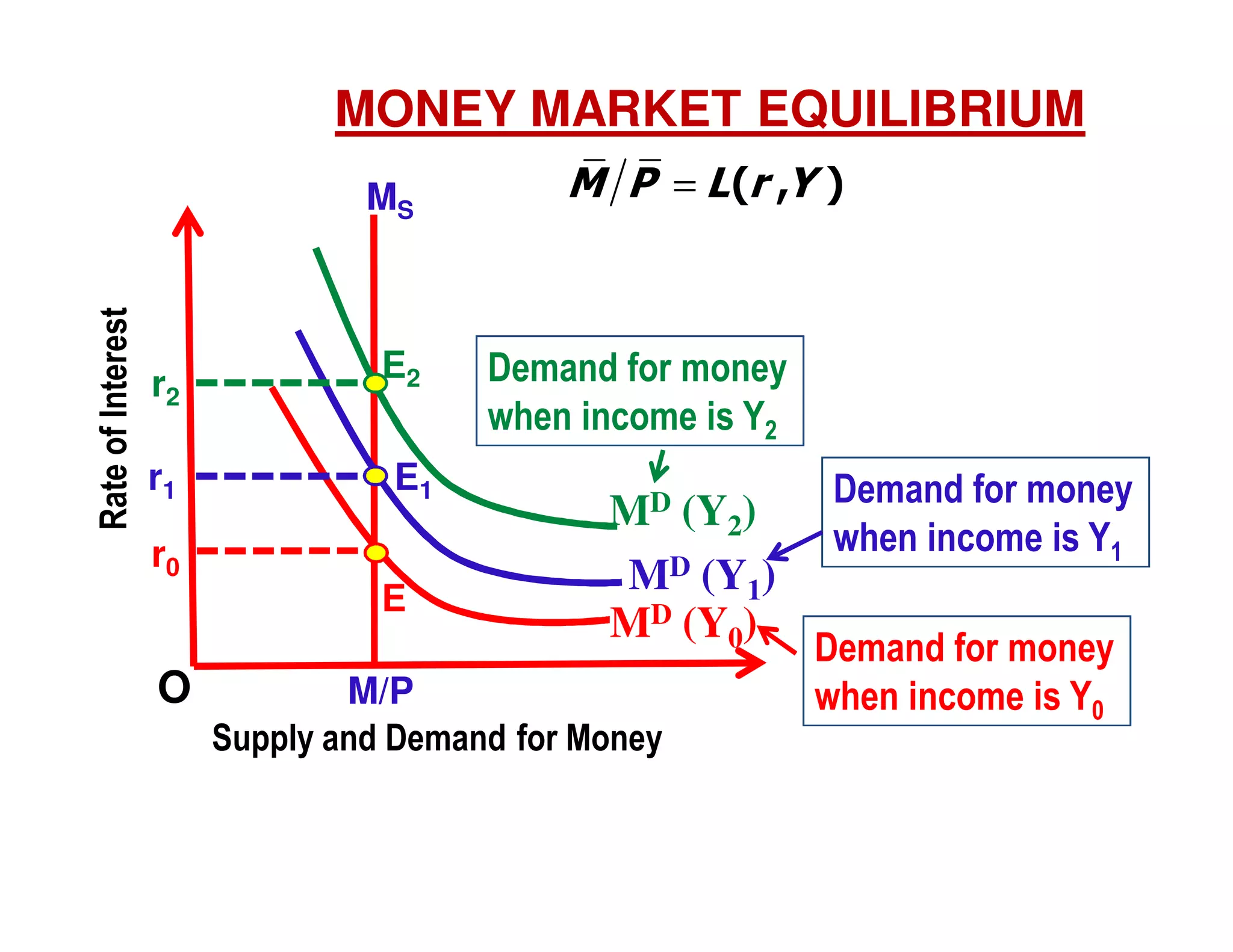
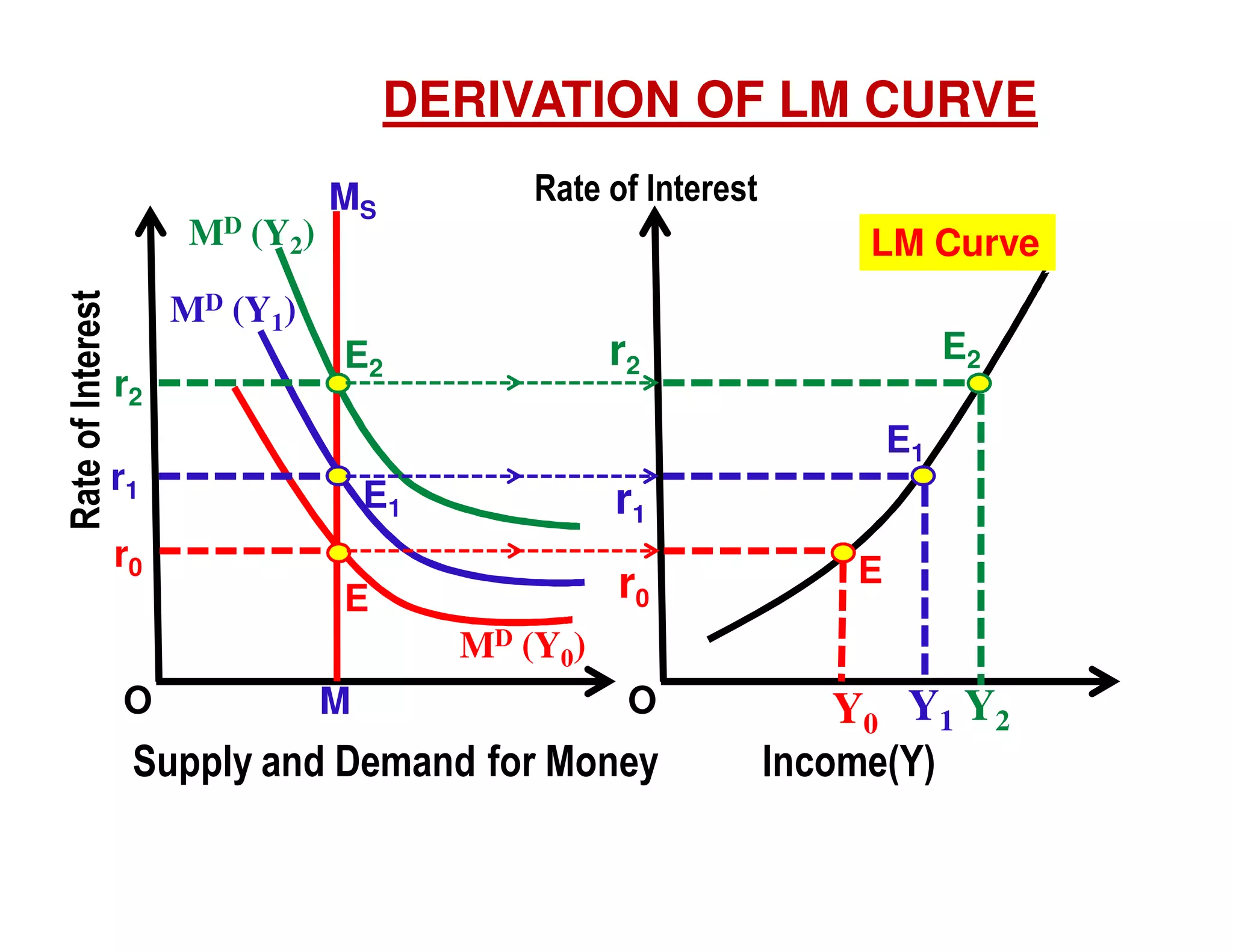
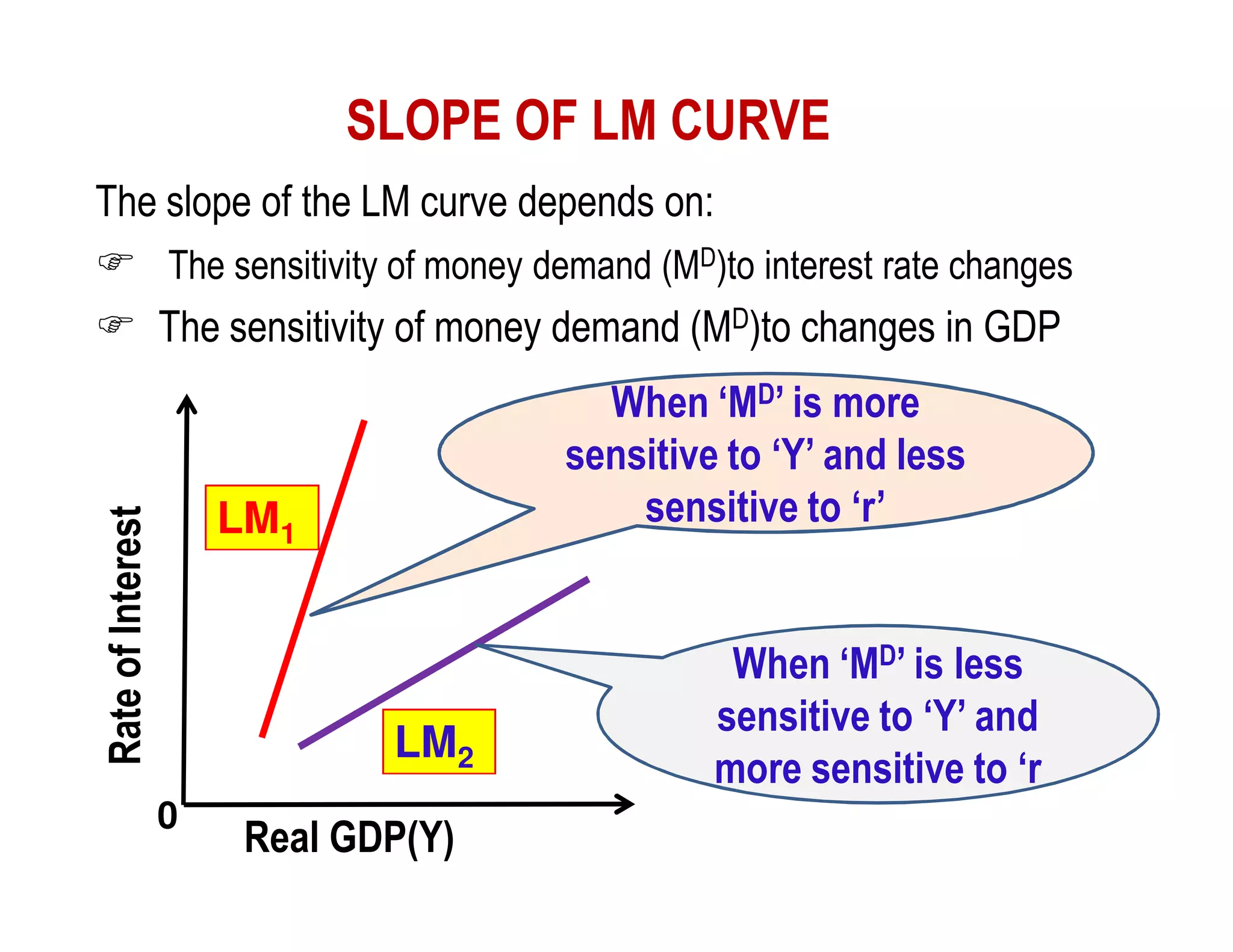
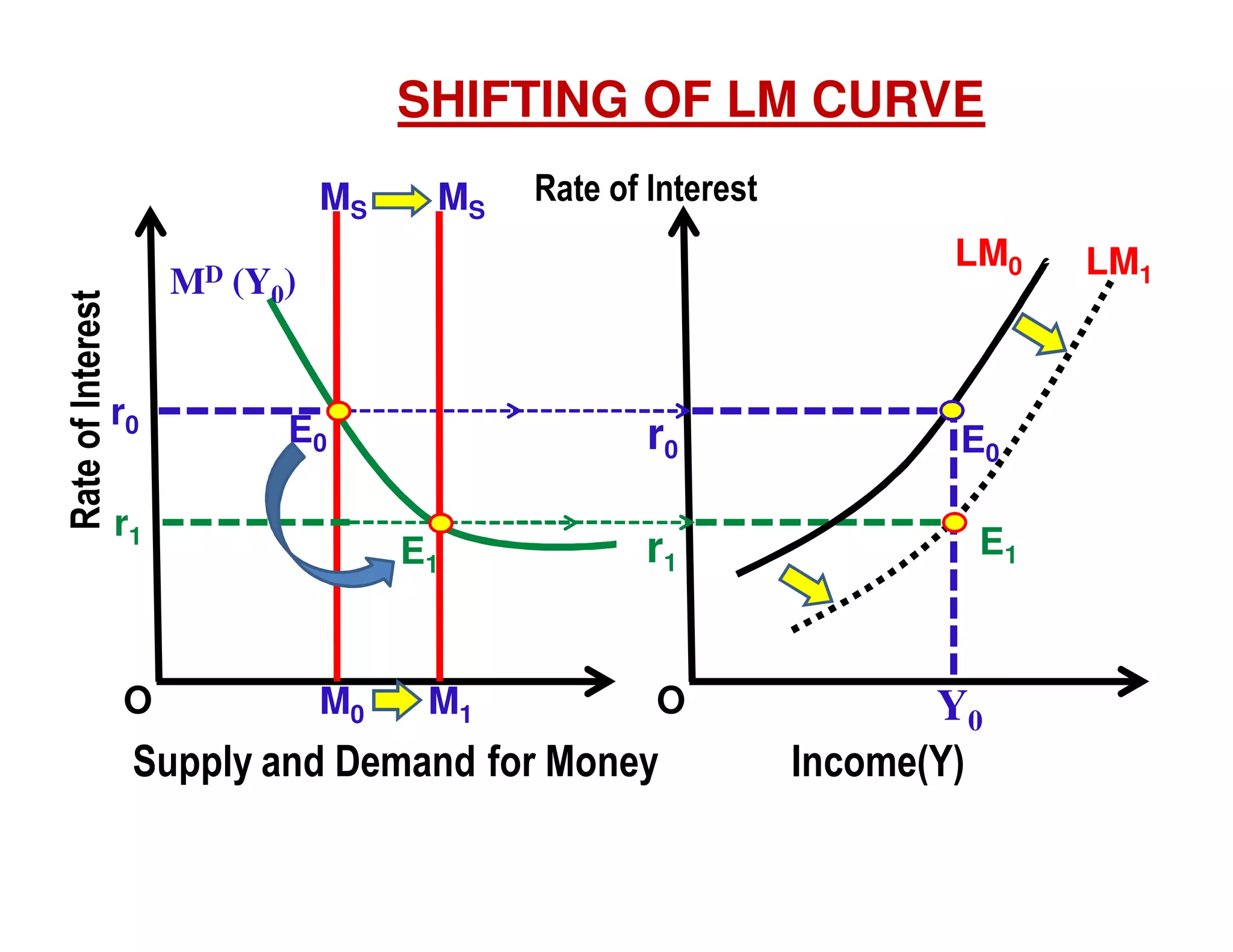
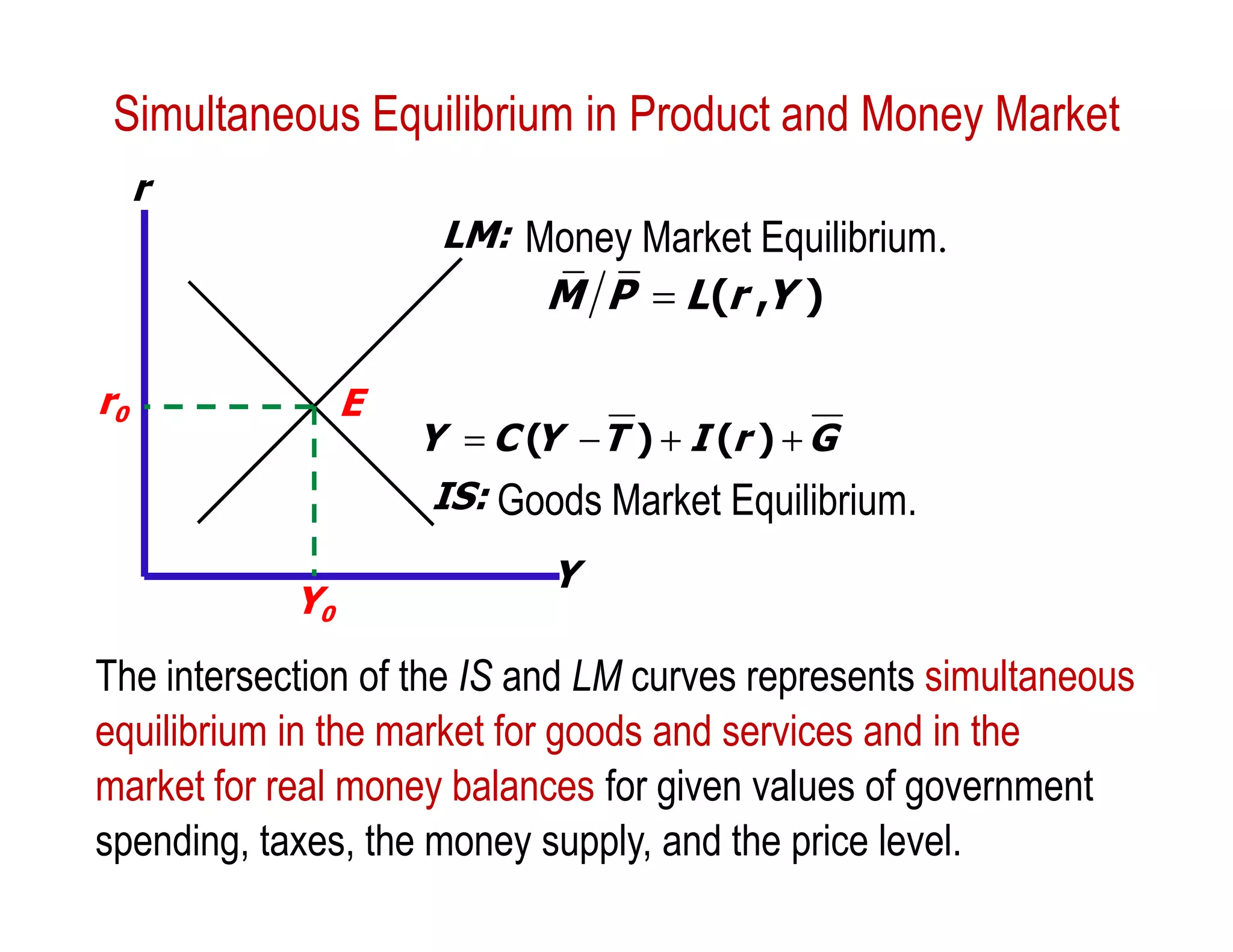
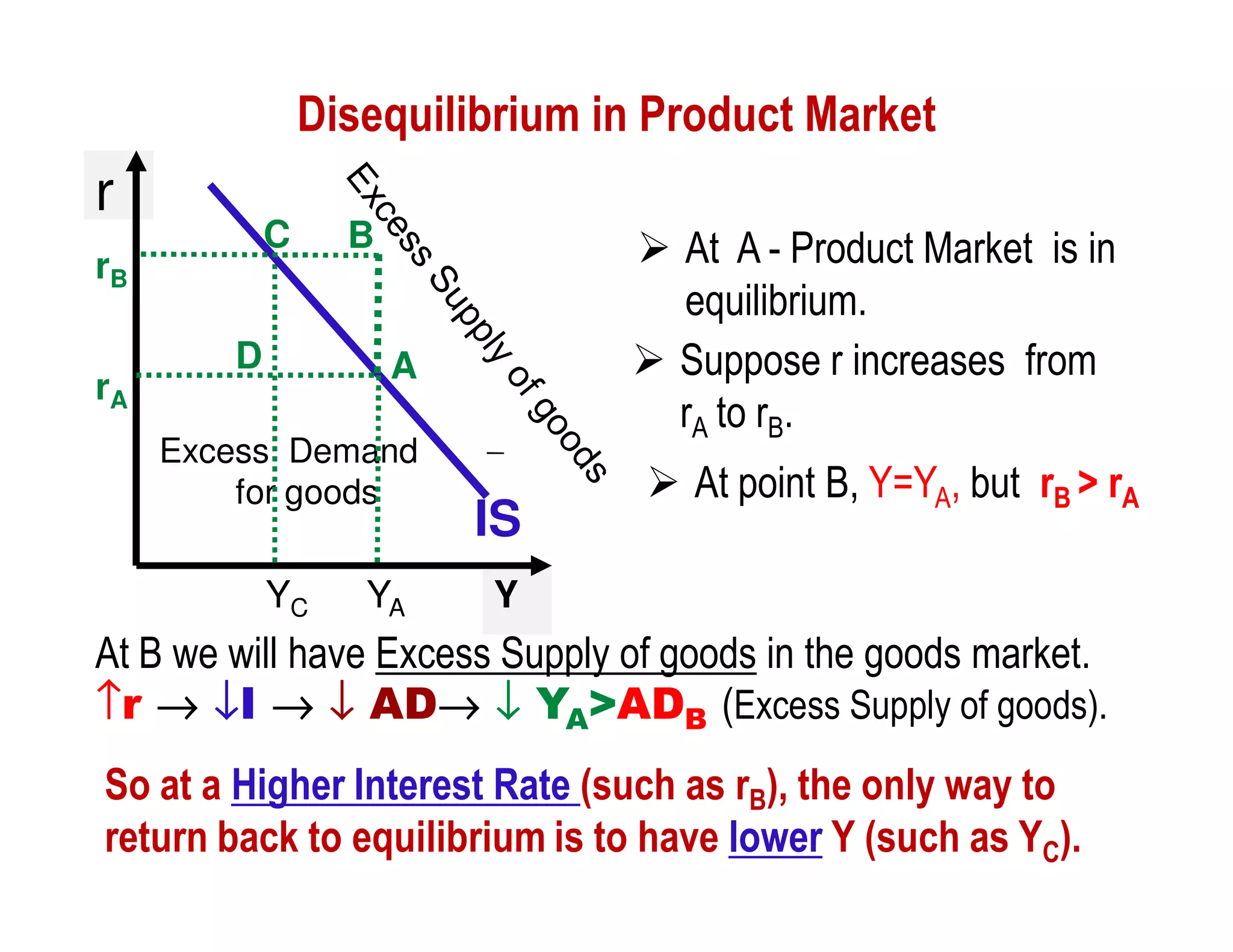
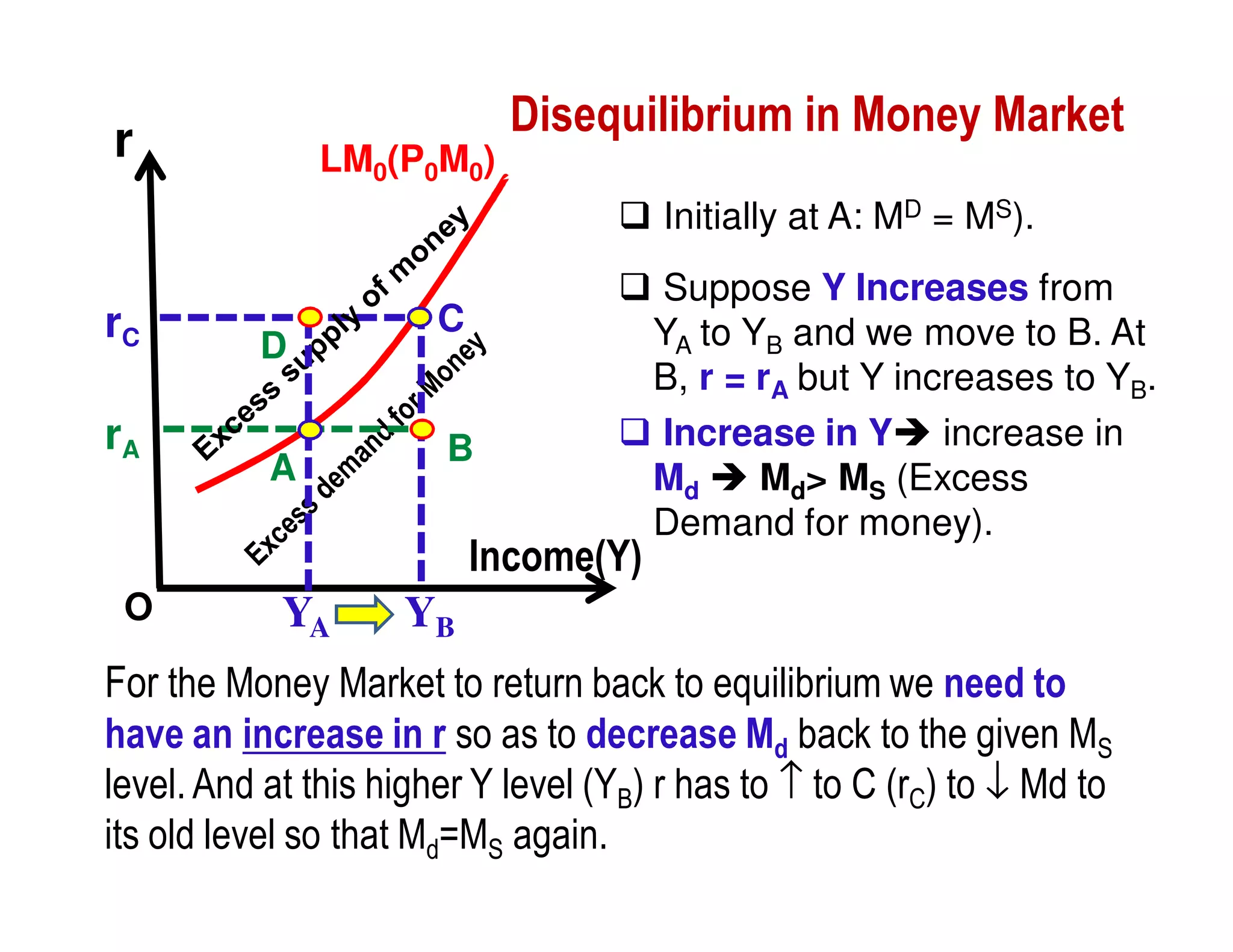
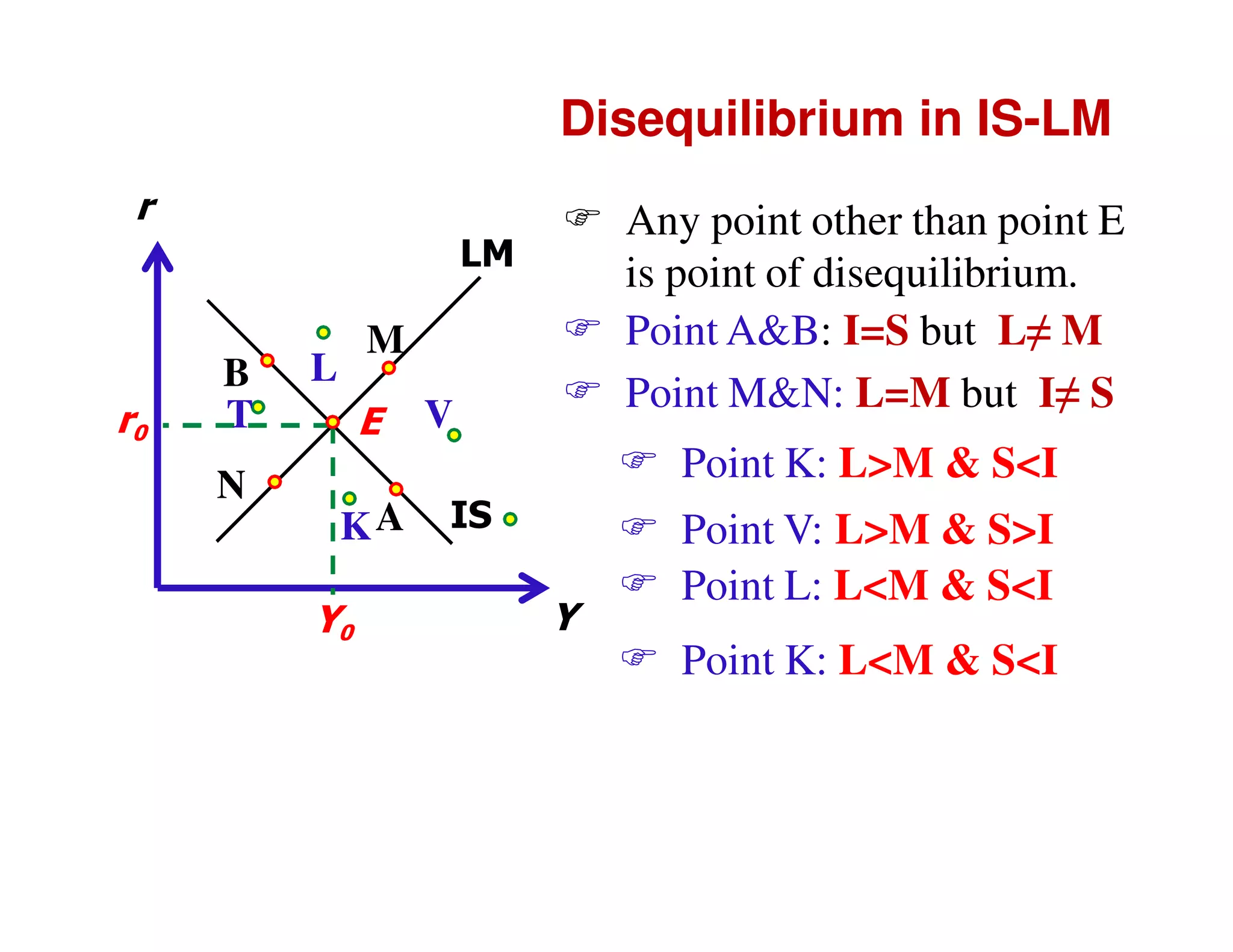
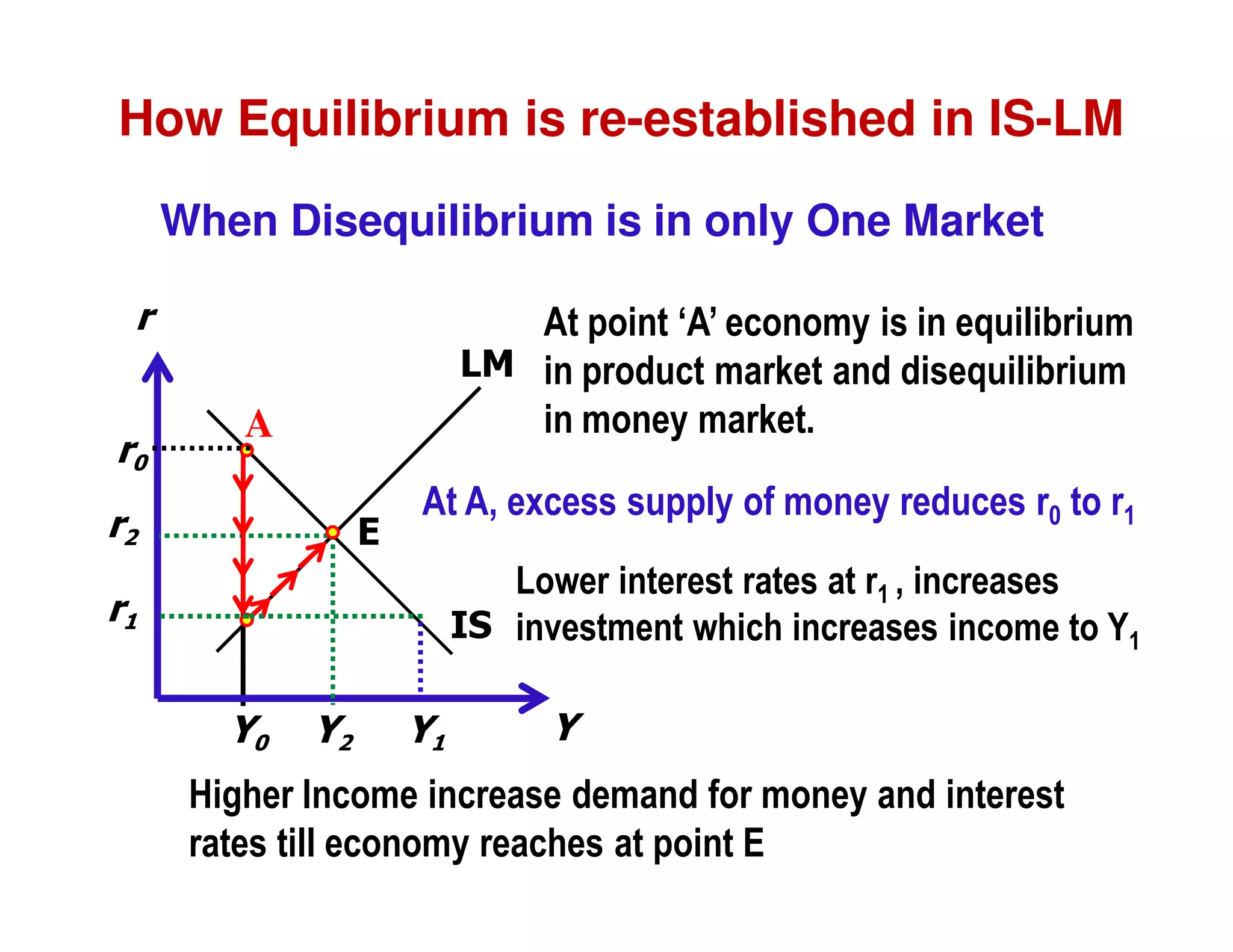
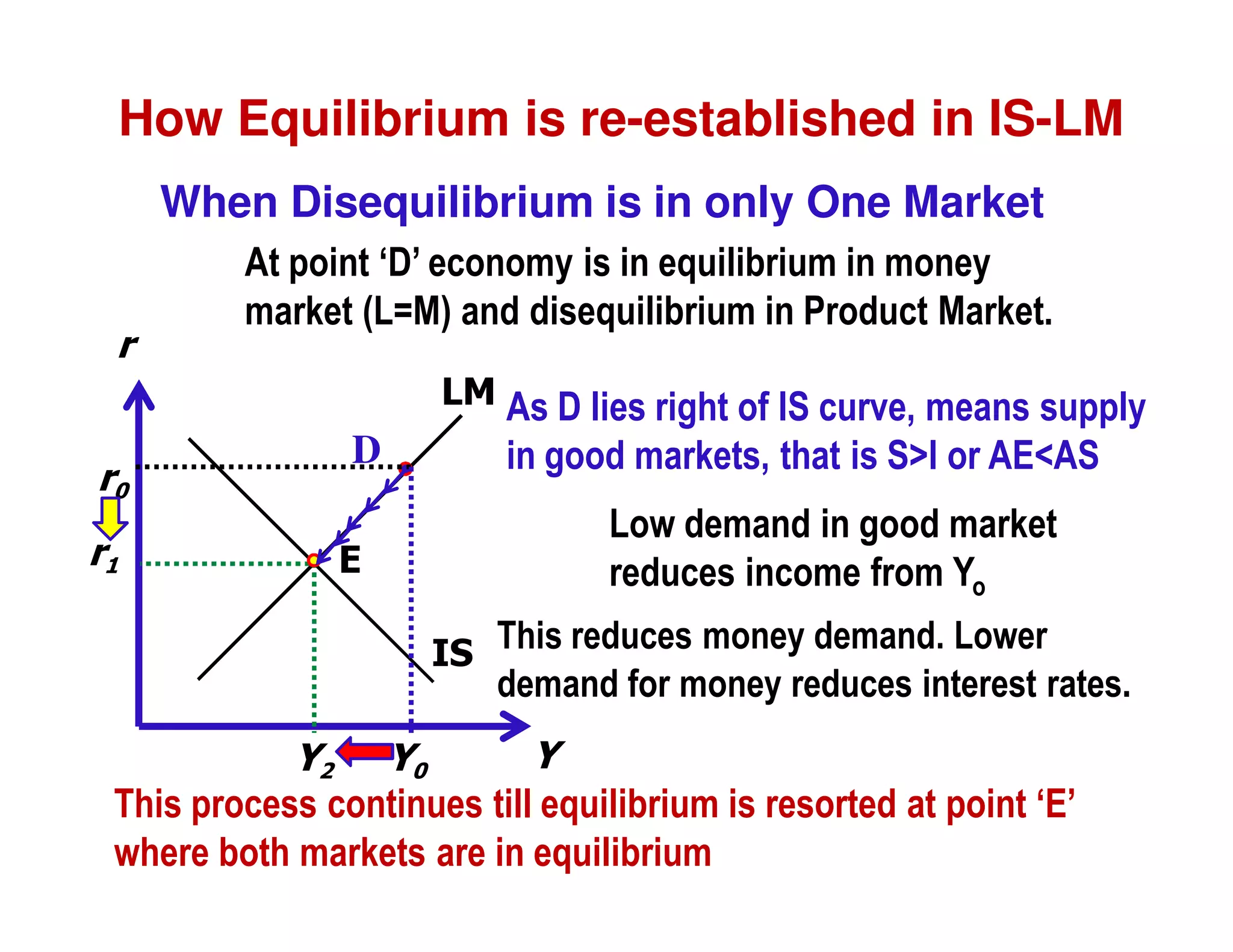
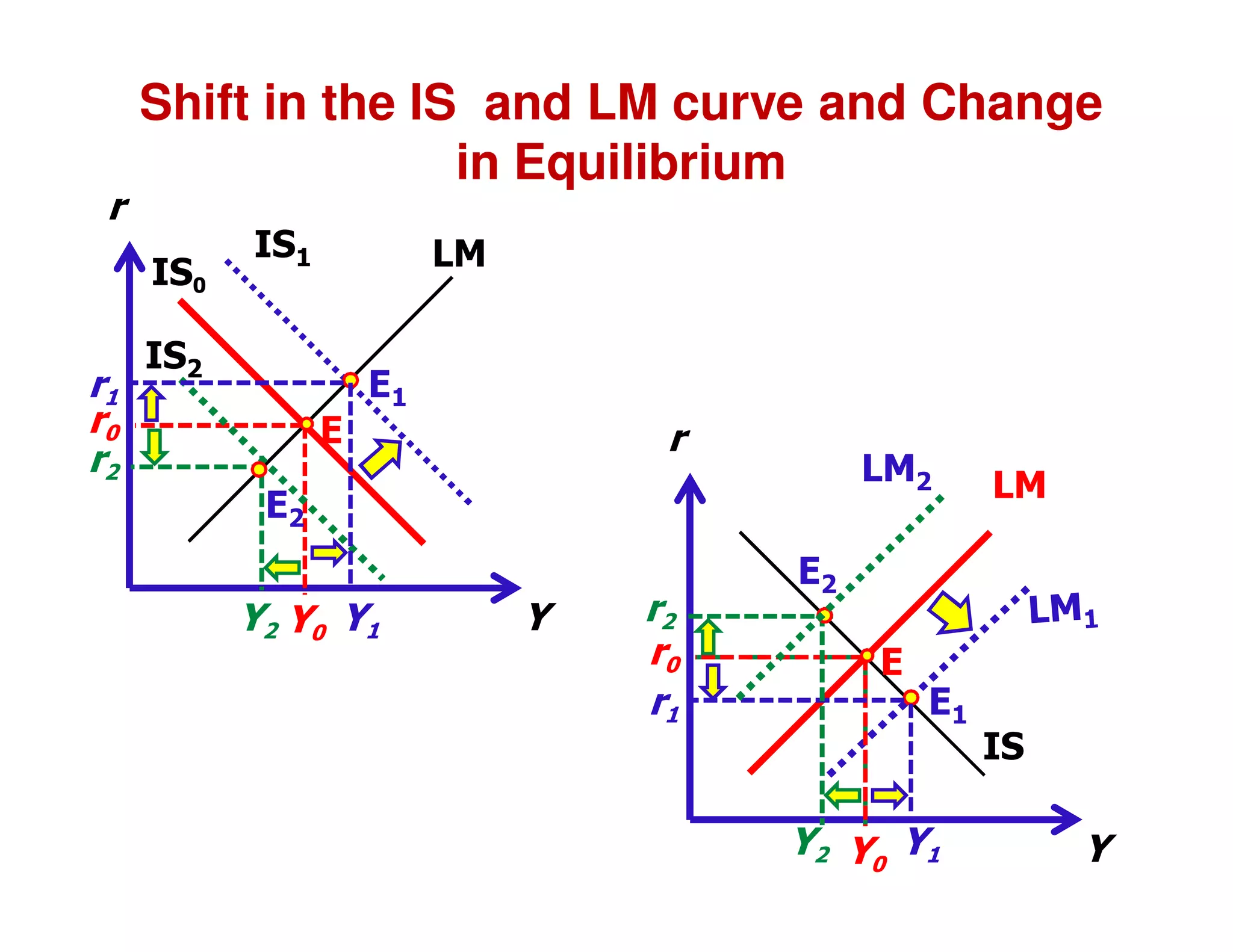
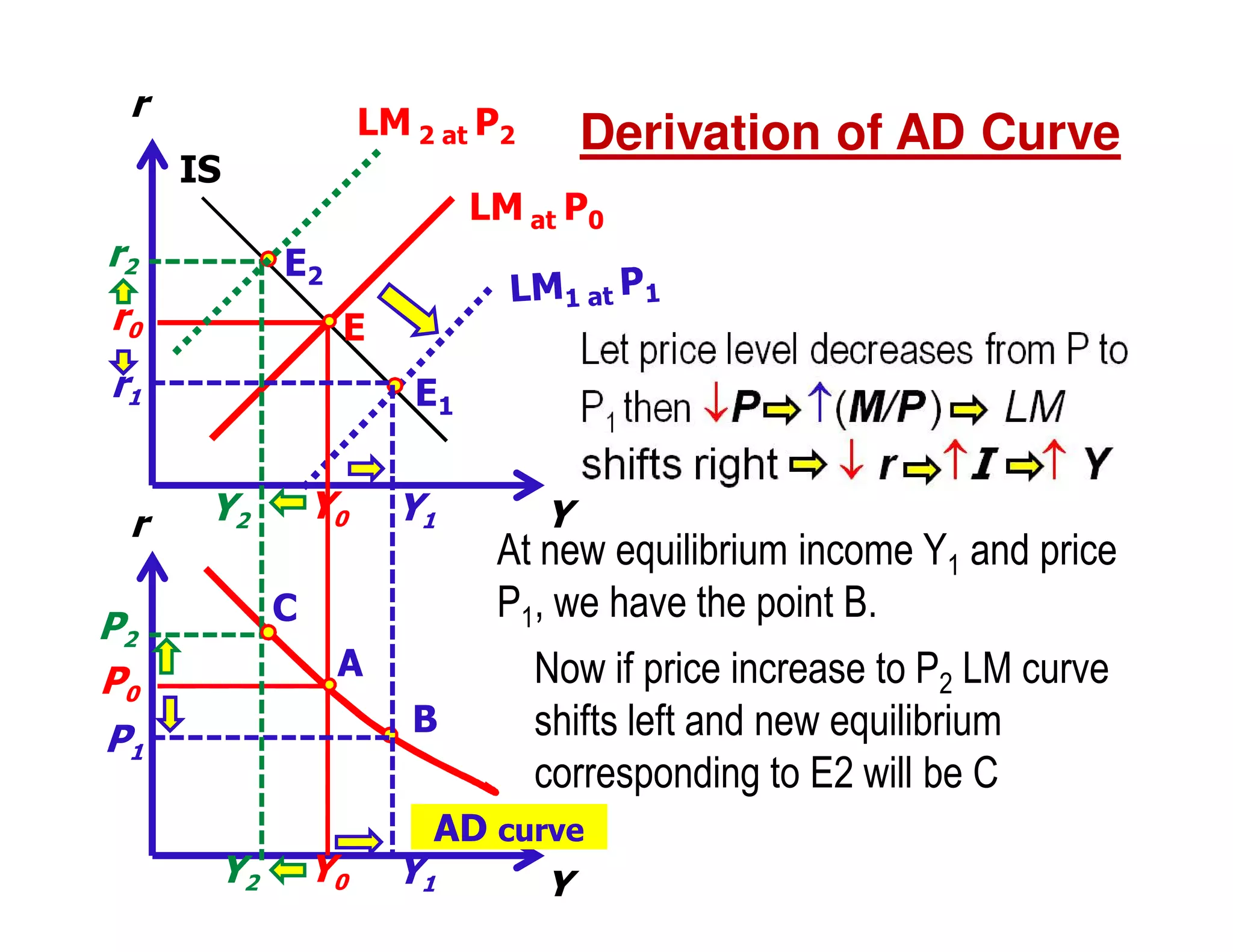
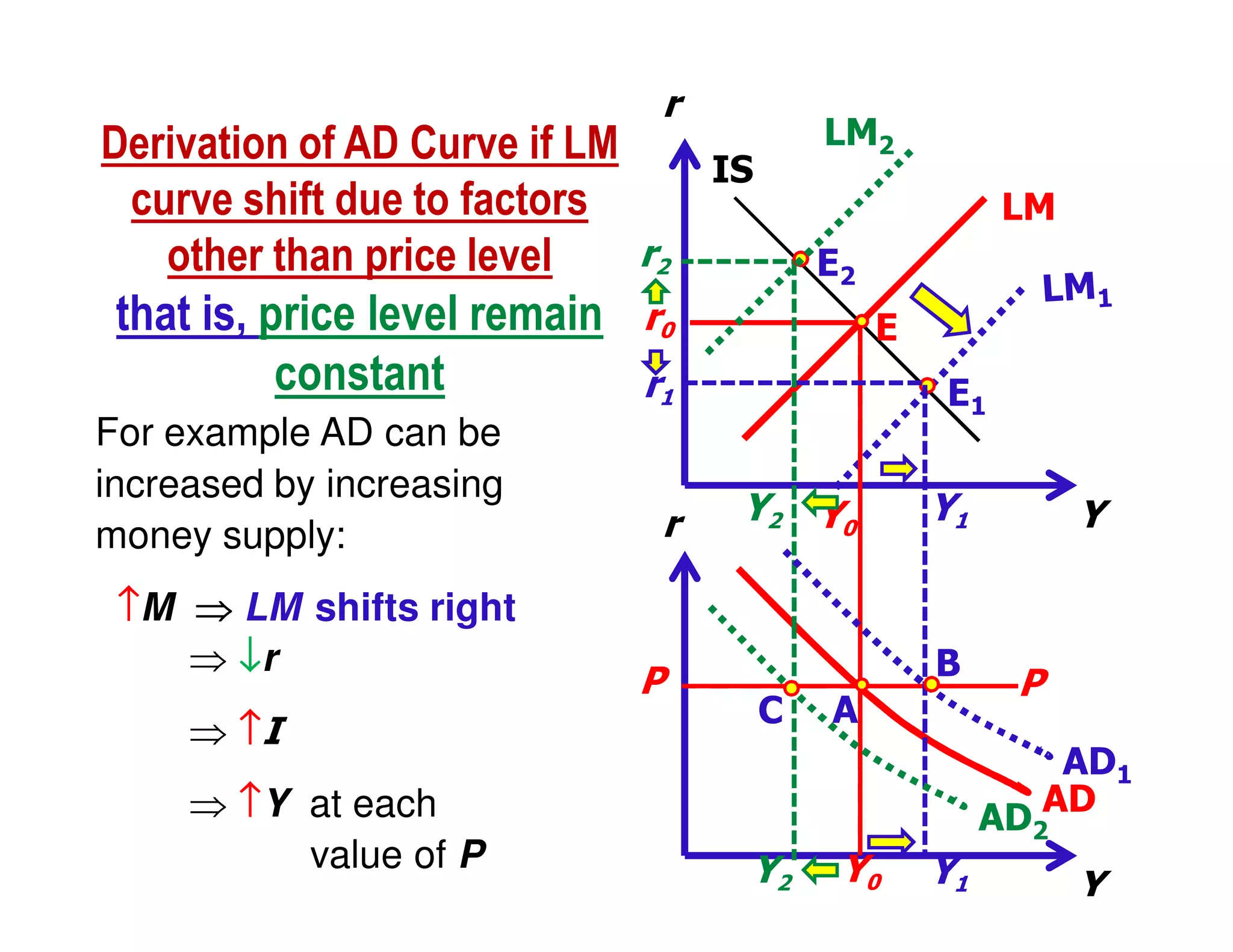
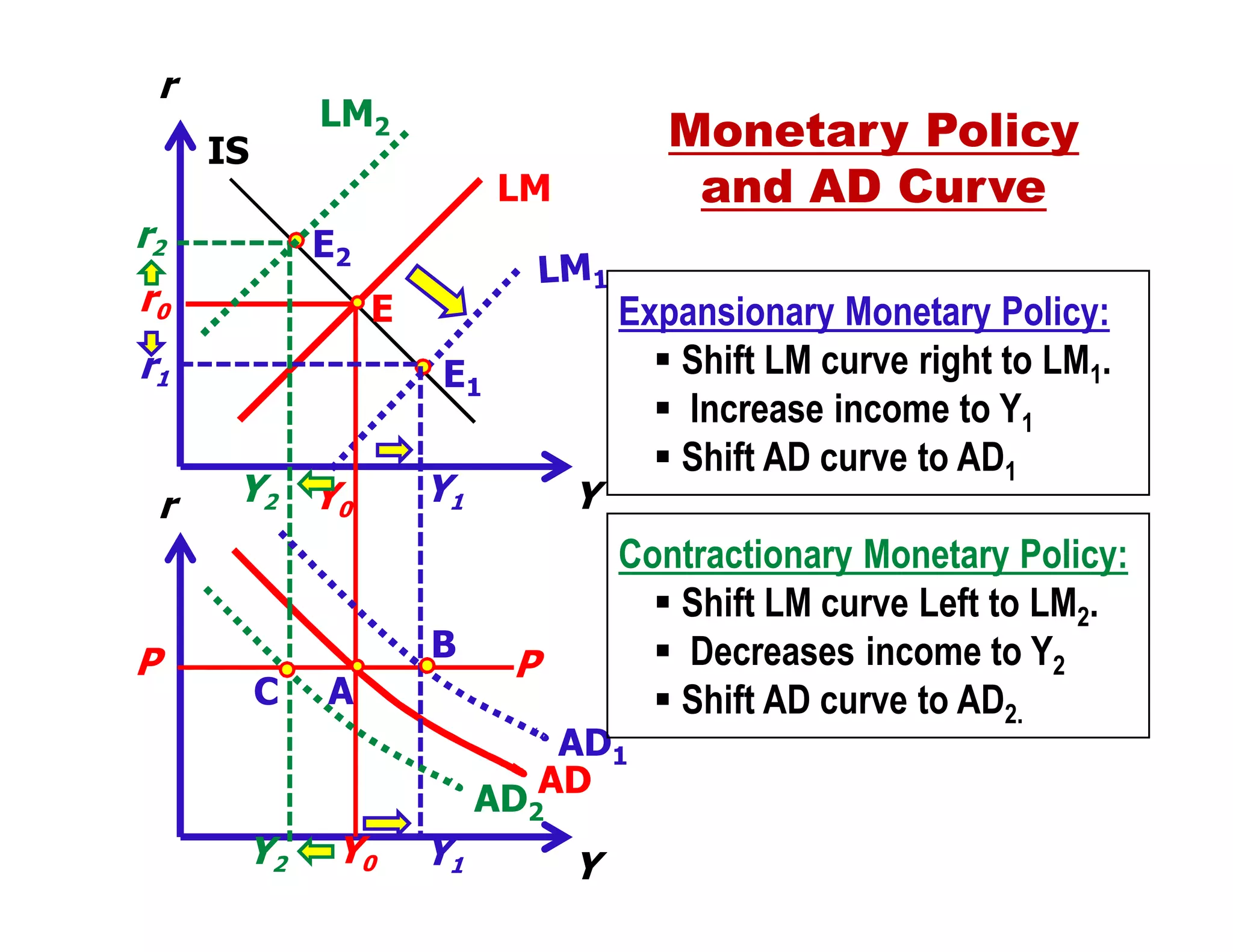
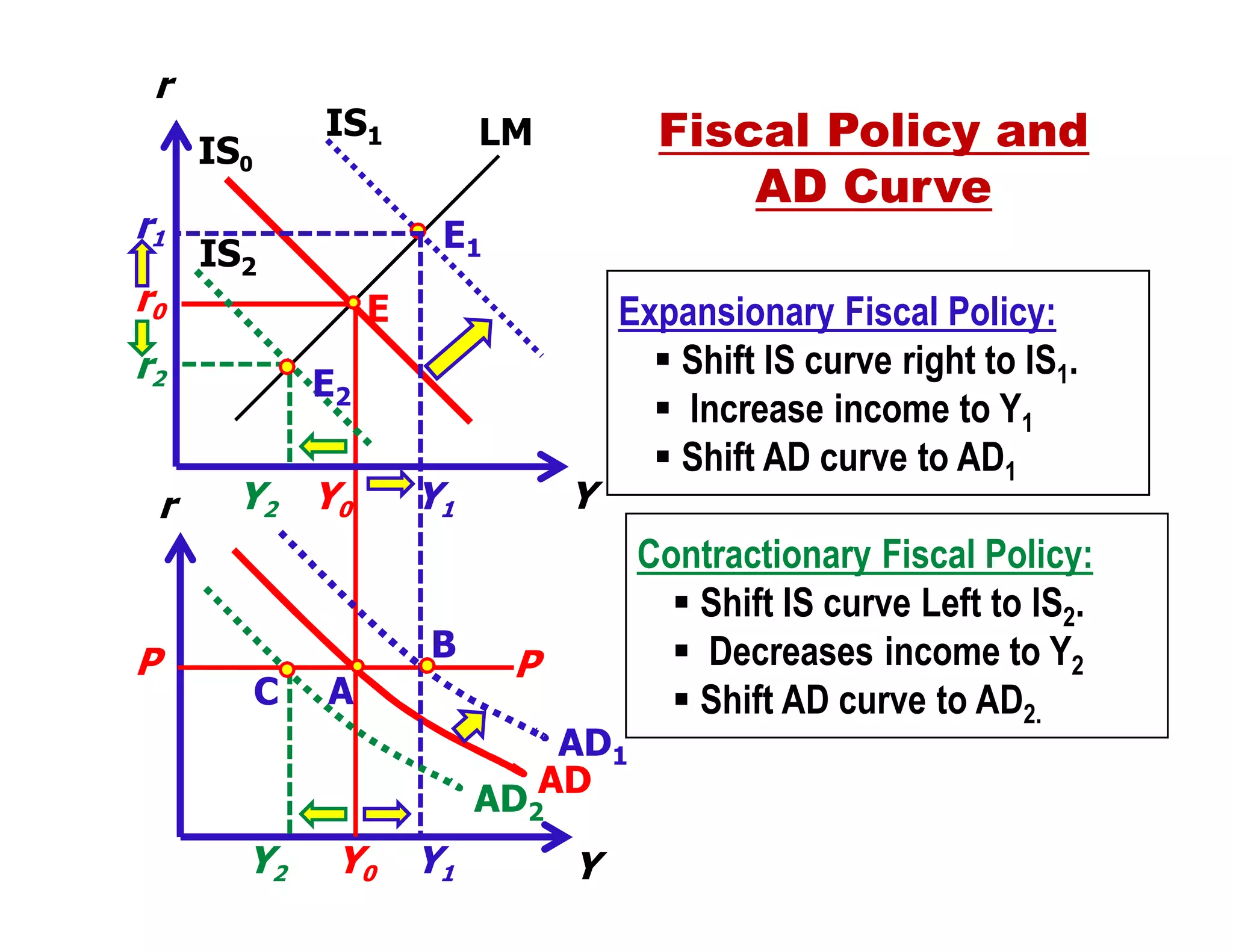
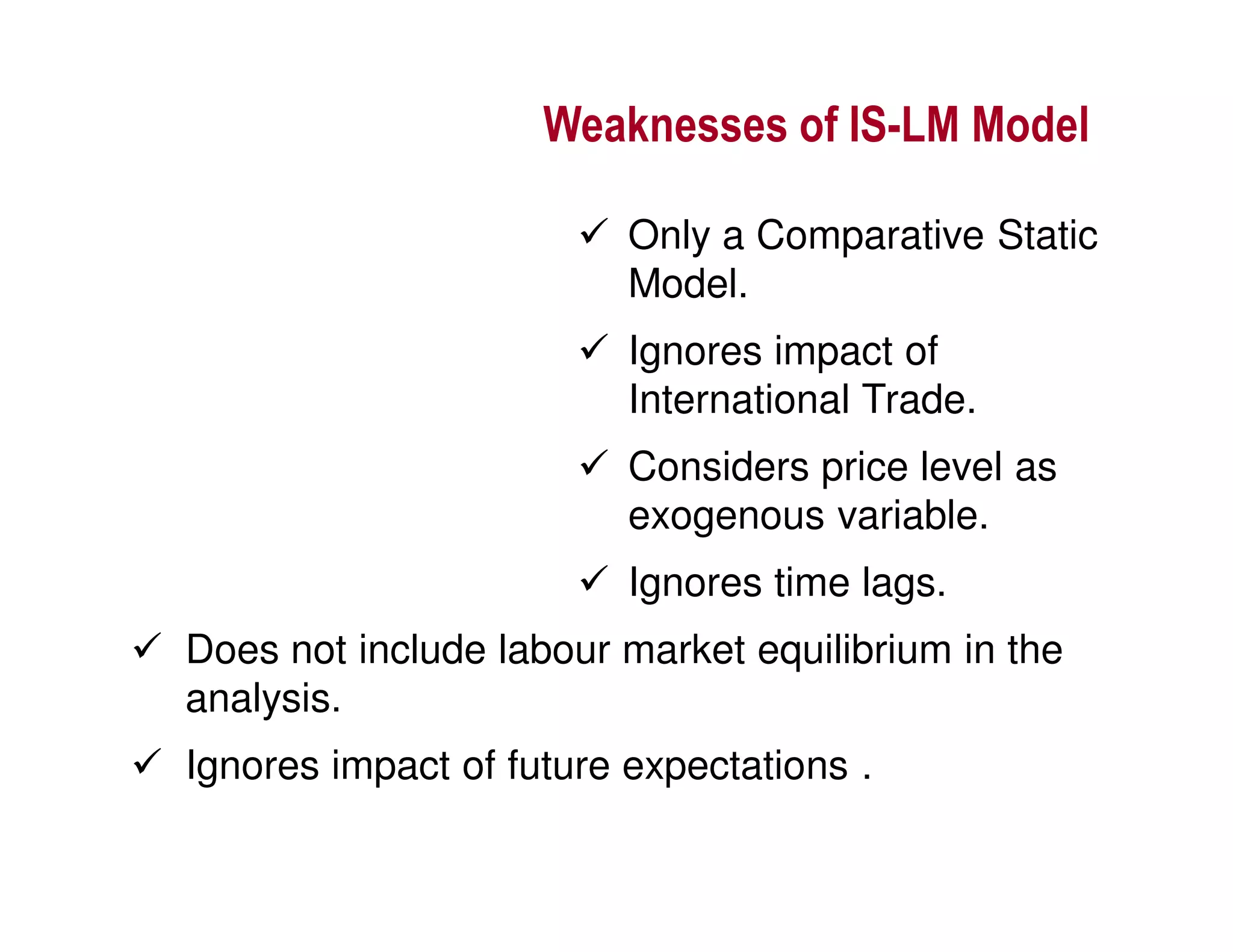
This document provides an outline and explanation of IS-LM analysis and how it can be used to derive the aggregate demand curve. It begins by explaining why IS-LM analysis was developed as a synthesis of classical and Keynesian thought. It then defines the IS curve as representing goods market equilibrium and the LM curve as representing money market equilibrium. It shows how the intersection of the IS and LM curves determines the equilibrium interest rate and level of output. It further explains how shifts in the IS and LM curves affect this equilibrium and can be used to trace the aggregate demand curve. Fiscal and monetary policy shifts are also discussed through their impacts on the IS and LM curves.