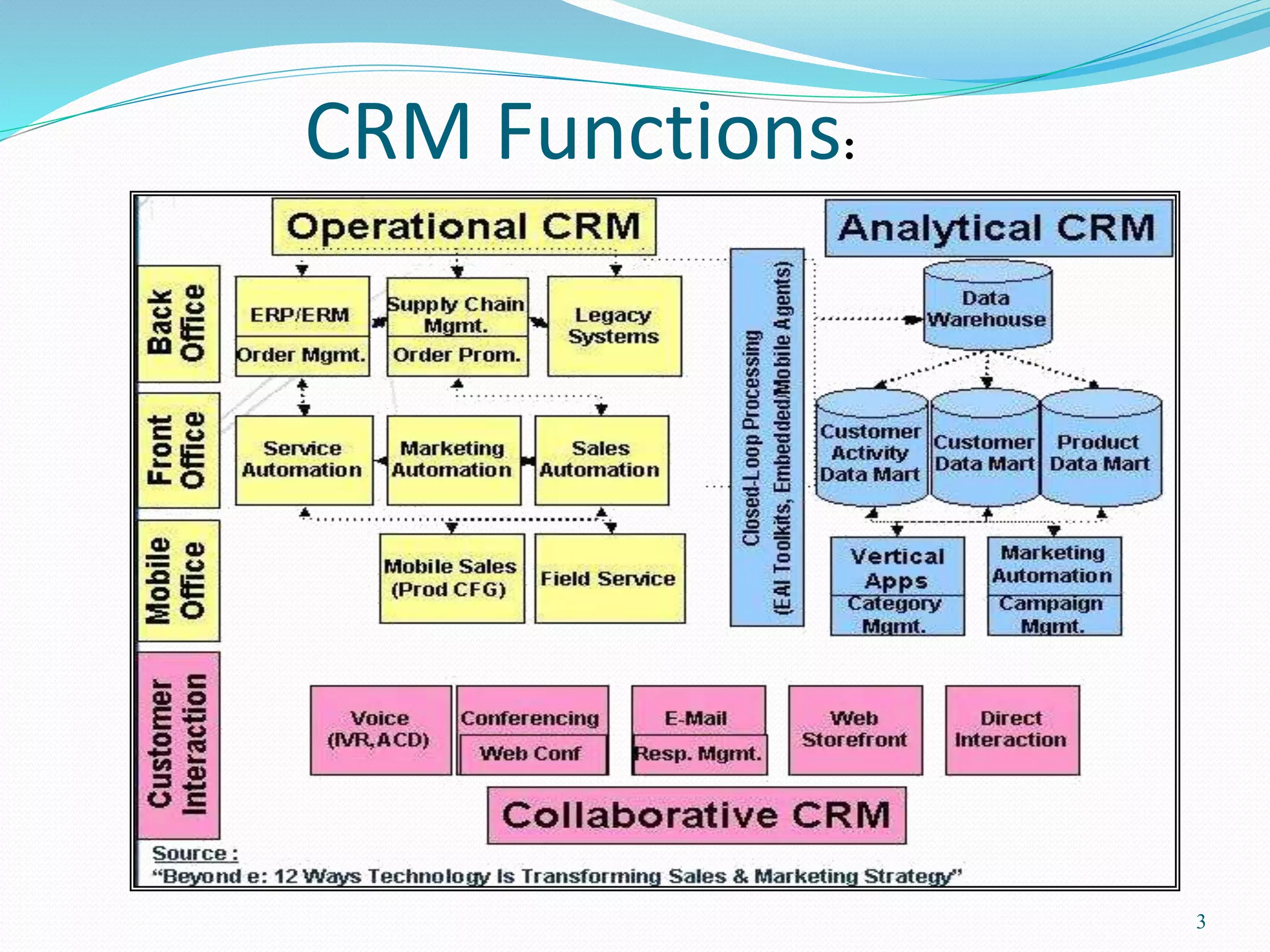
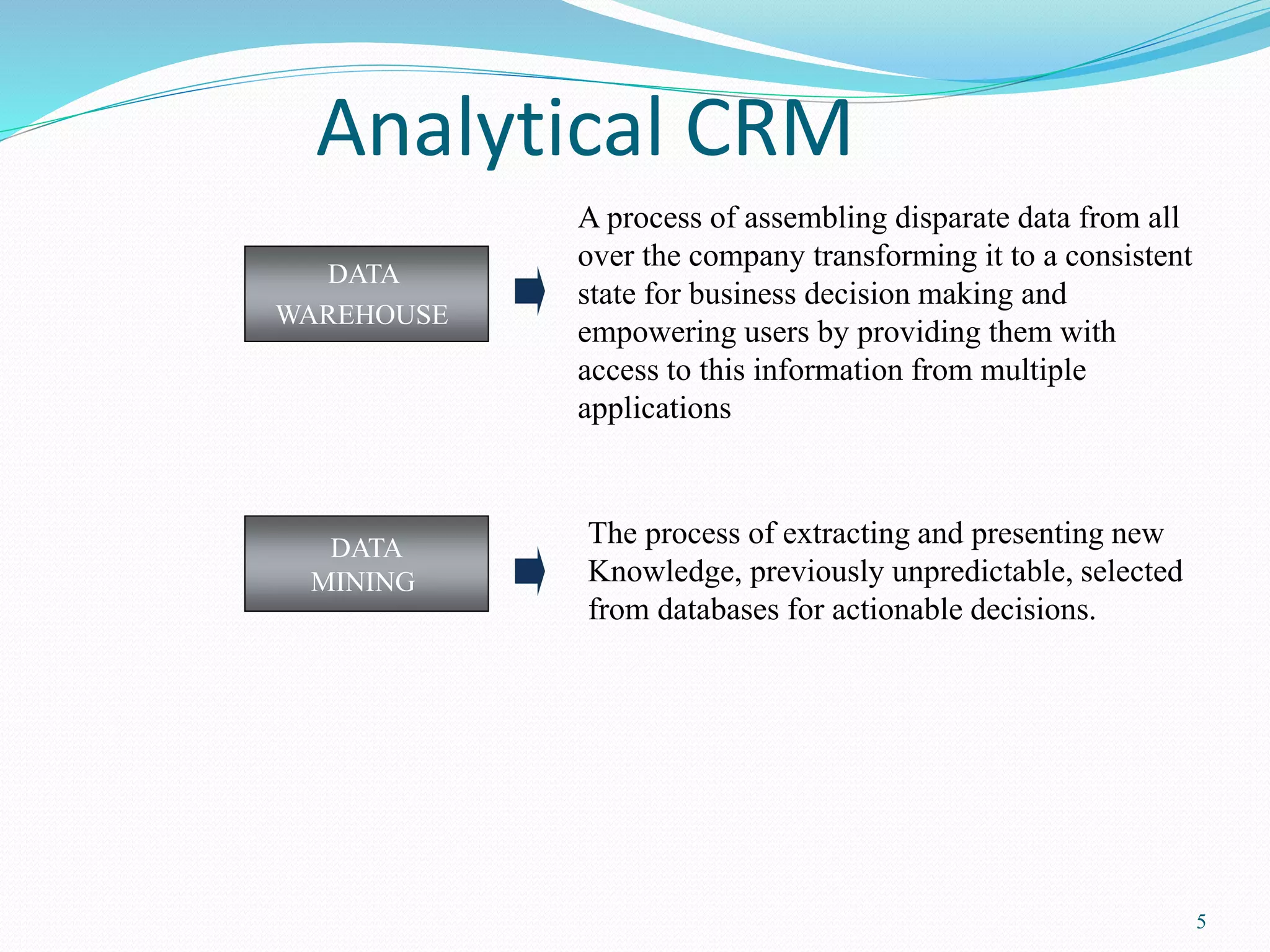
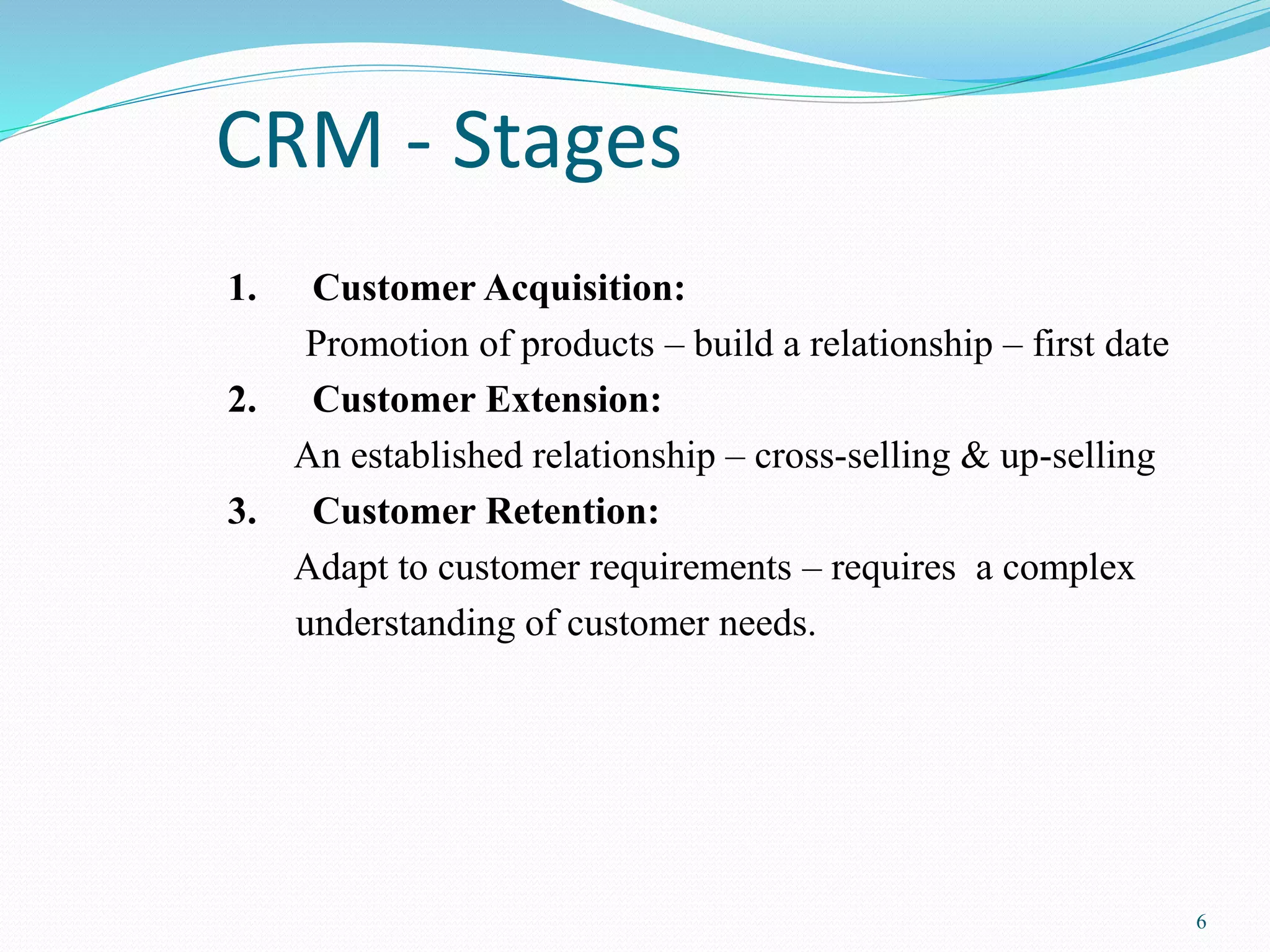
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) involves integrating sales, marketing, and customer service strategies using methodologies and software to efficiently manage customer relationships. CRM functions include operational CRM like marketing automation, sales force automation, and customer service, as well as analytical CRM like data warehousing and data mining. CRM aims to acquire customers, extend relationships through cross-selling and up-selling, and retain customers through understanding their needs. Key challenges are integrating customer information across channels and systems and ensuring end-to-end business process integration between departments like sales and service.