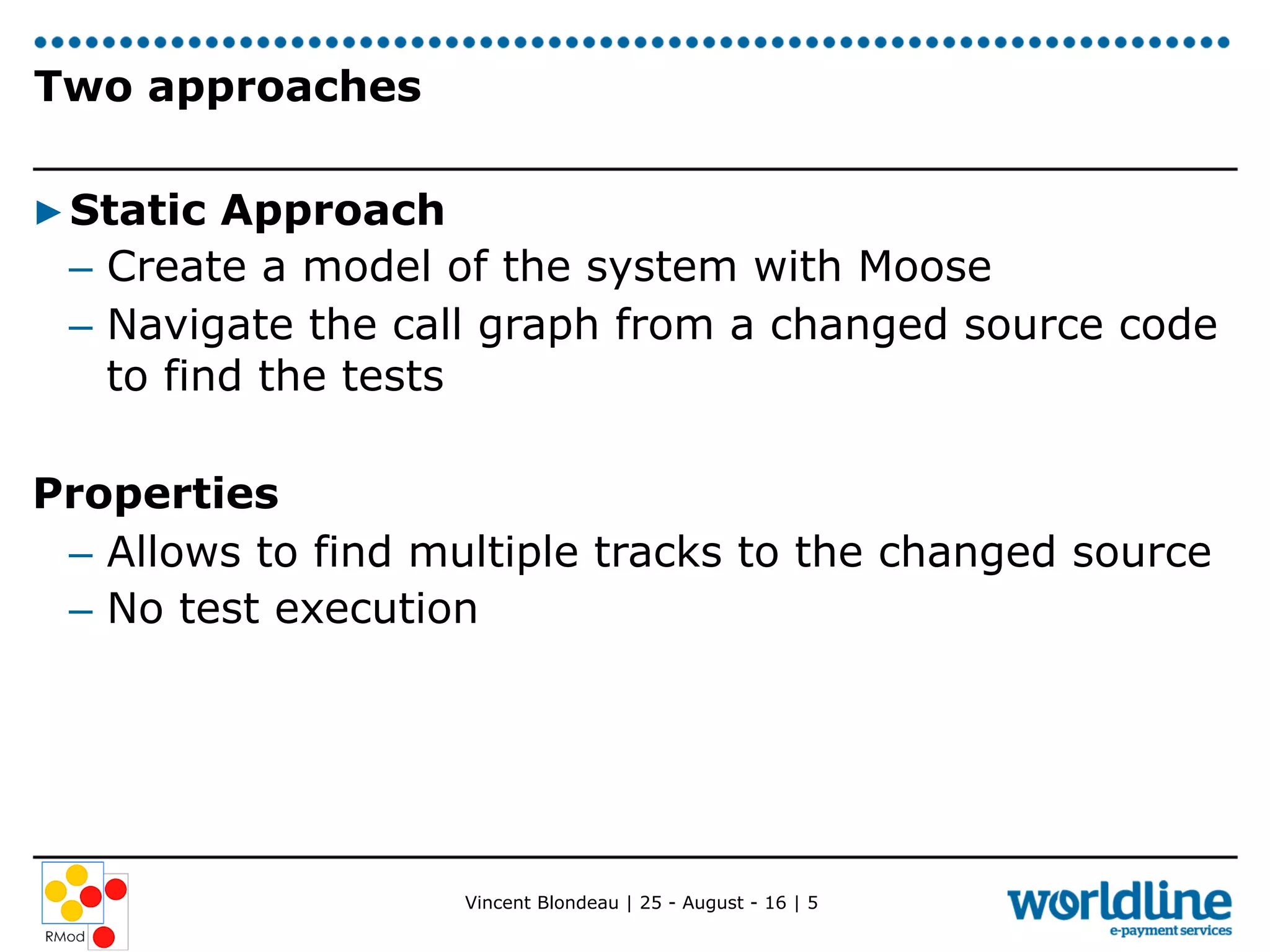
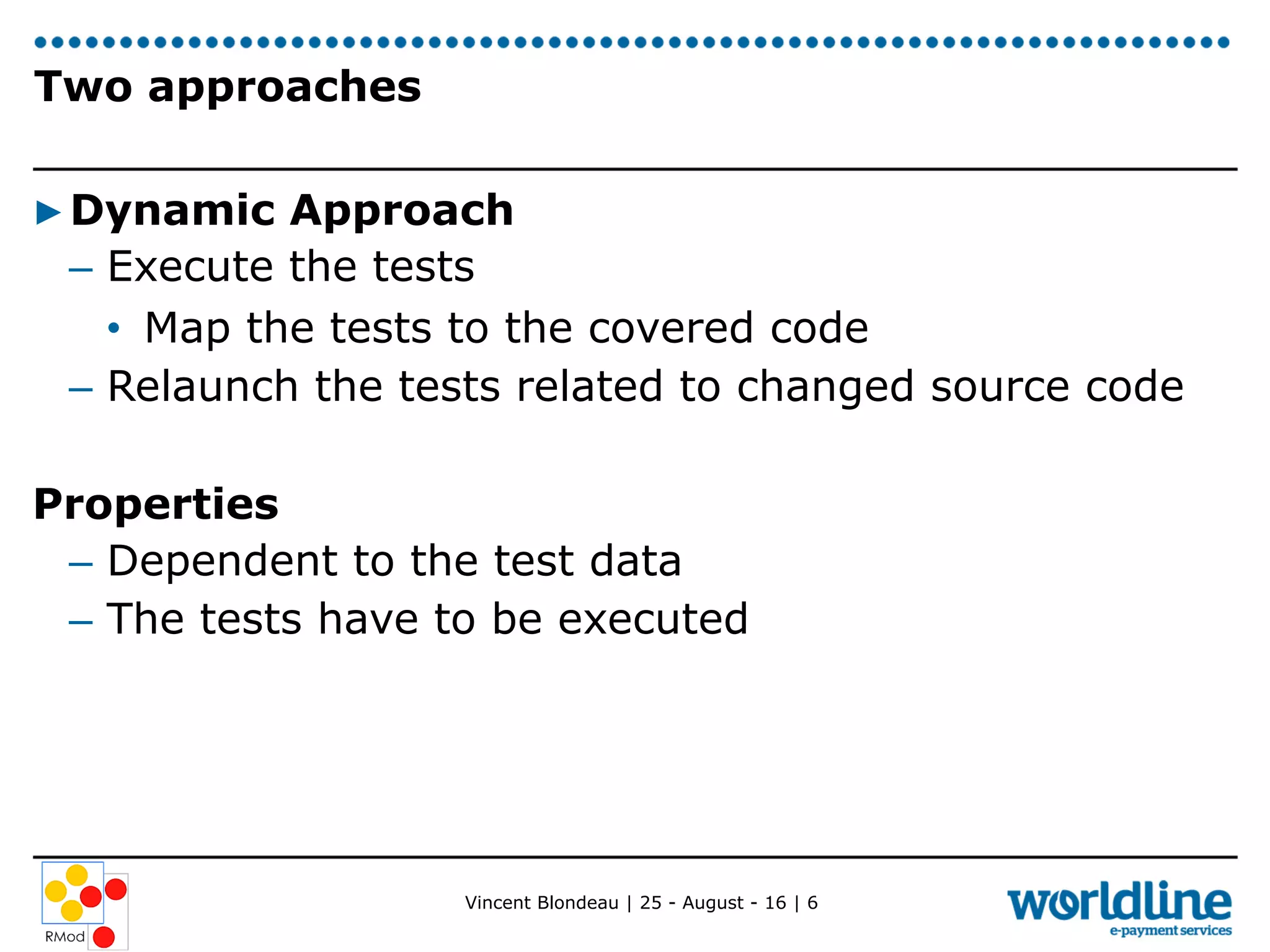
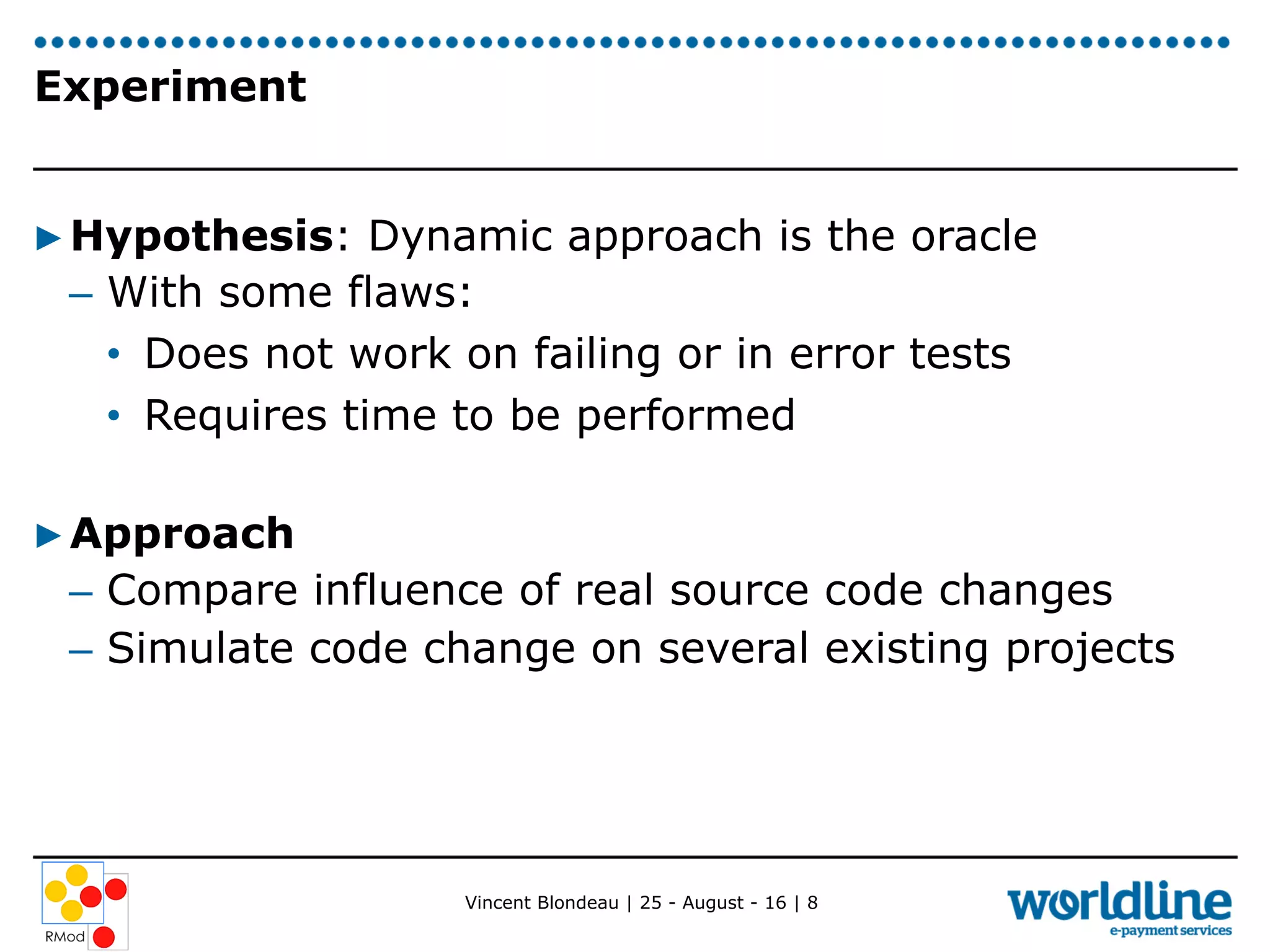
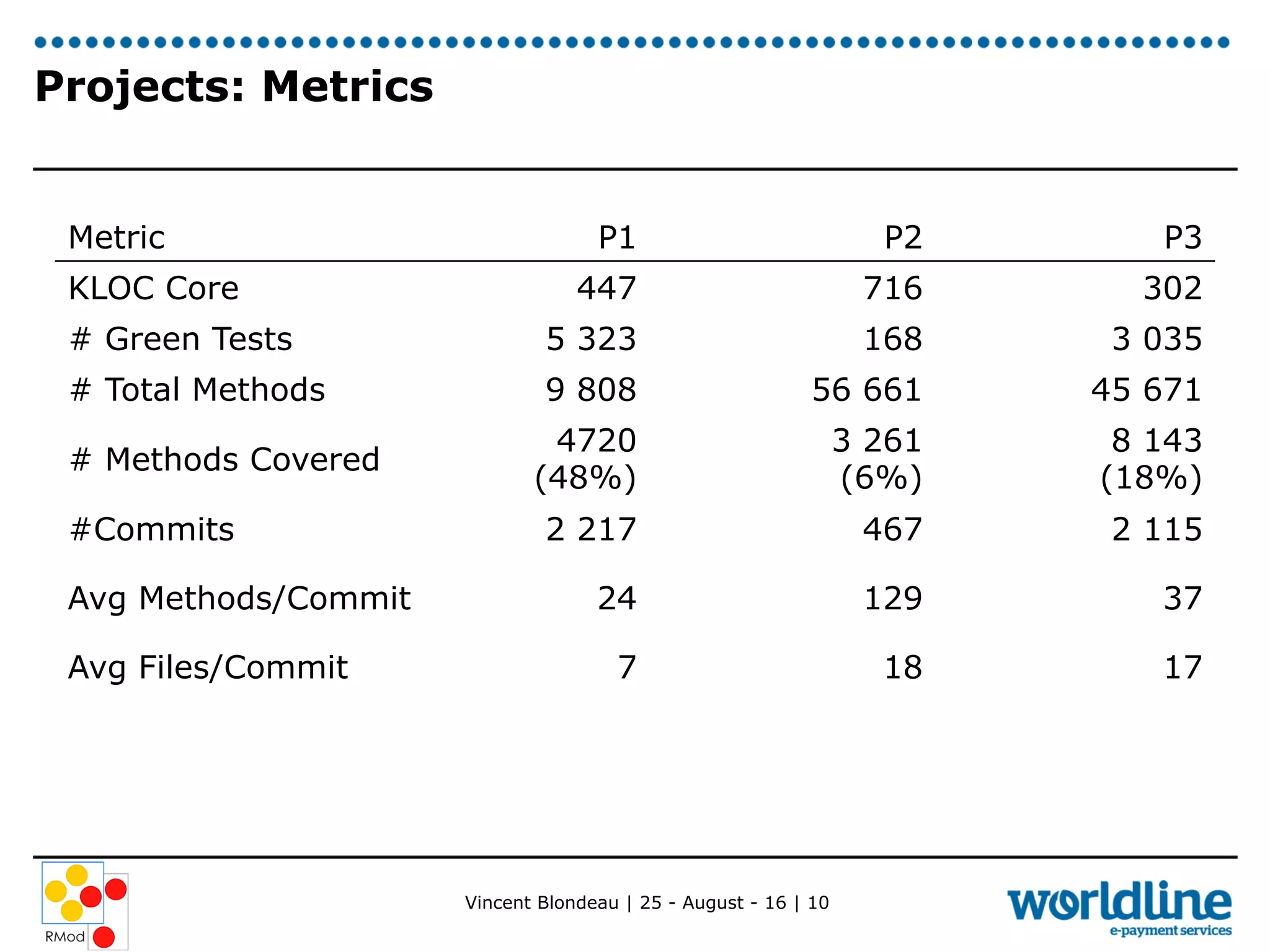
Vincent Blondeau conducted an experiment comparing static and dynamic test selection approaches after code changes. The static approach uses call graph analysis to select tests related to changed code, while the dynamic approach executes tests to map them to covered code. The experiment found that the dynamic approach was more precise and had higher recall, identifying more relevant tests, though it required test execution time. Considering code commits, which group related changes, tended to decrease results for both approaches. The ratios of selected tests to total tests were low, indicating the approaches could still help reduce test suite execution time. Future work includes better understanding how developers use tests and providing a test selection tool.