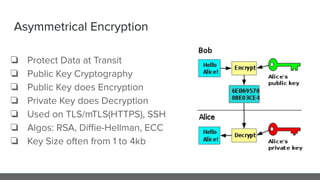
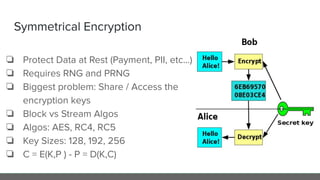
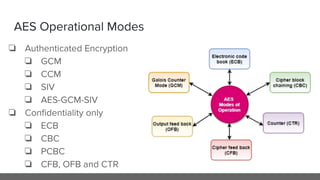
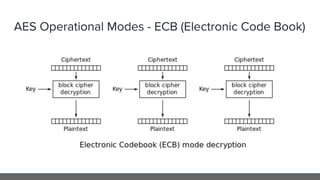
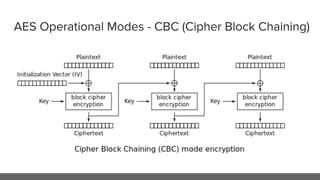
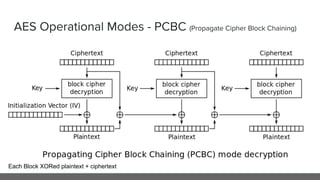
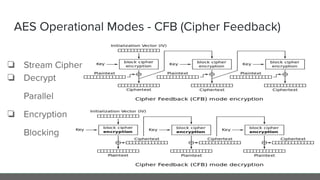
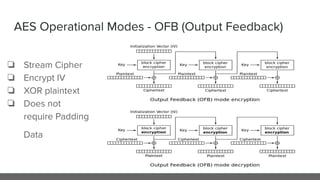
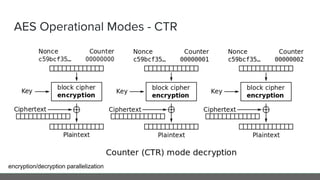
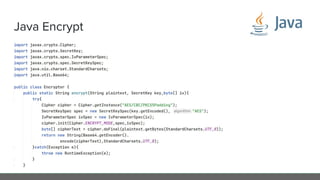
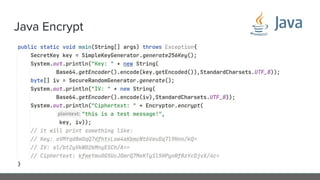
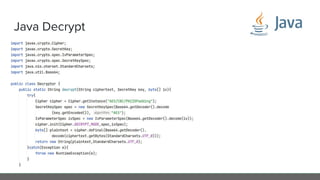
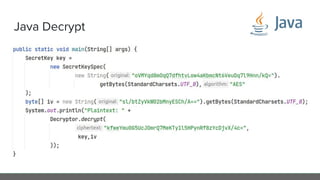
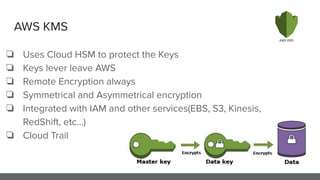
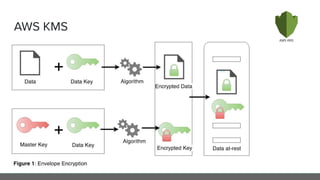
The document provides an in-depth analysis of encryption techniques, focusing on both symmetrical and asymmetrical encryption methods, including key management and operational modes of AES. Key concepts such as randomness, entropy, and the importance of secure key storage are discussed, along with practical implications for application-level encryption. It also touches on industry standards like AWS KMS for key protection and the necessity for engineering discipline in secure practices.