1. The document provides definitions and guidelines for effectively explaining things, including being clear, using reasons and details, foreshadowing the explanation, and using logical connectors to link ideas.
2. It emphasizes giving details, using nouns rather than pronouns, and descriptive verbs to provide clarity. Explanations should also include reasons to help the listener understand why something occurred.
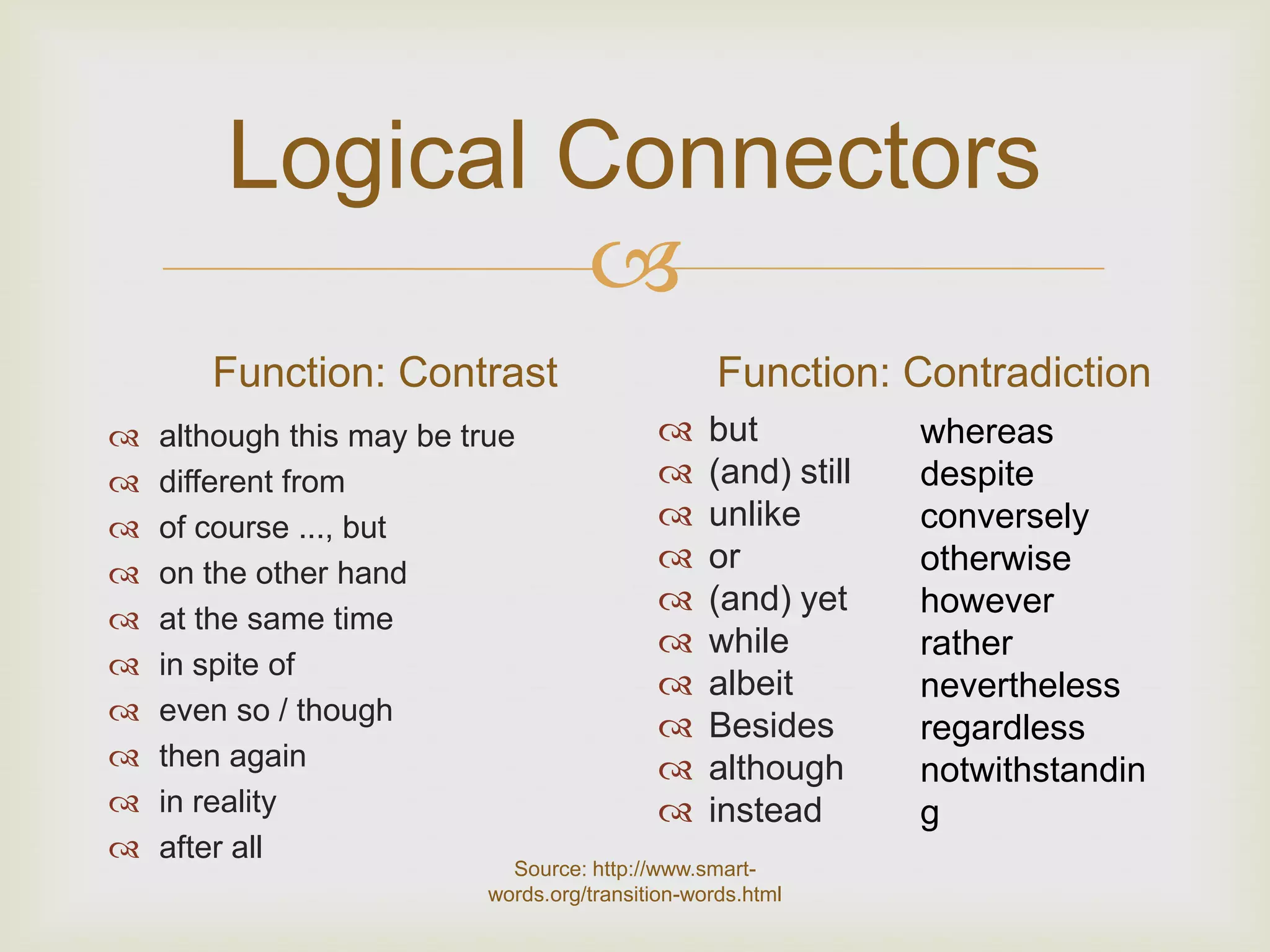
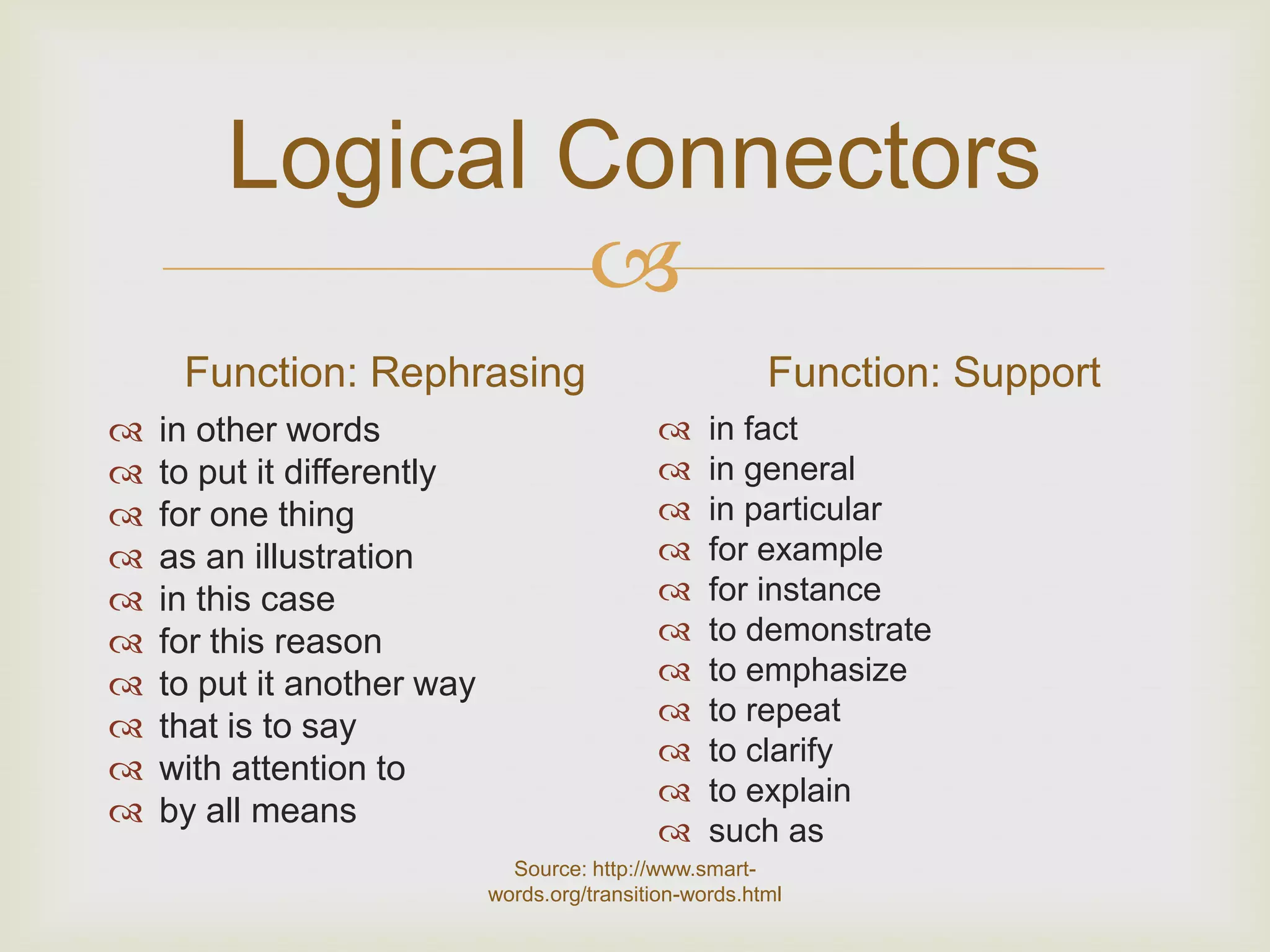
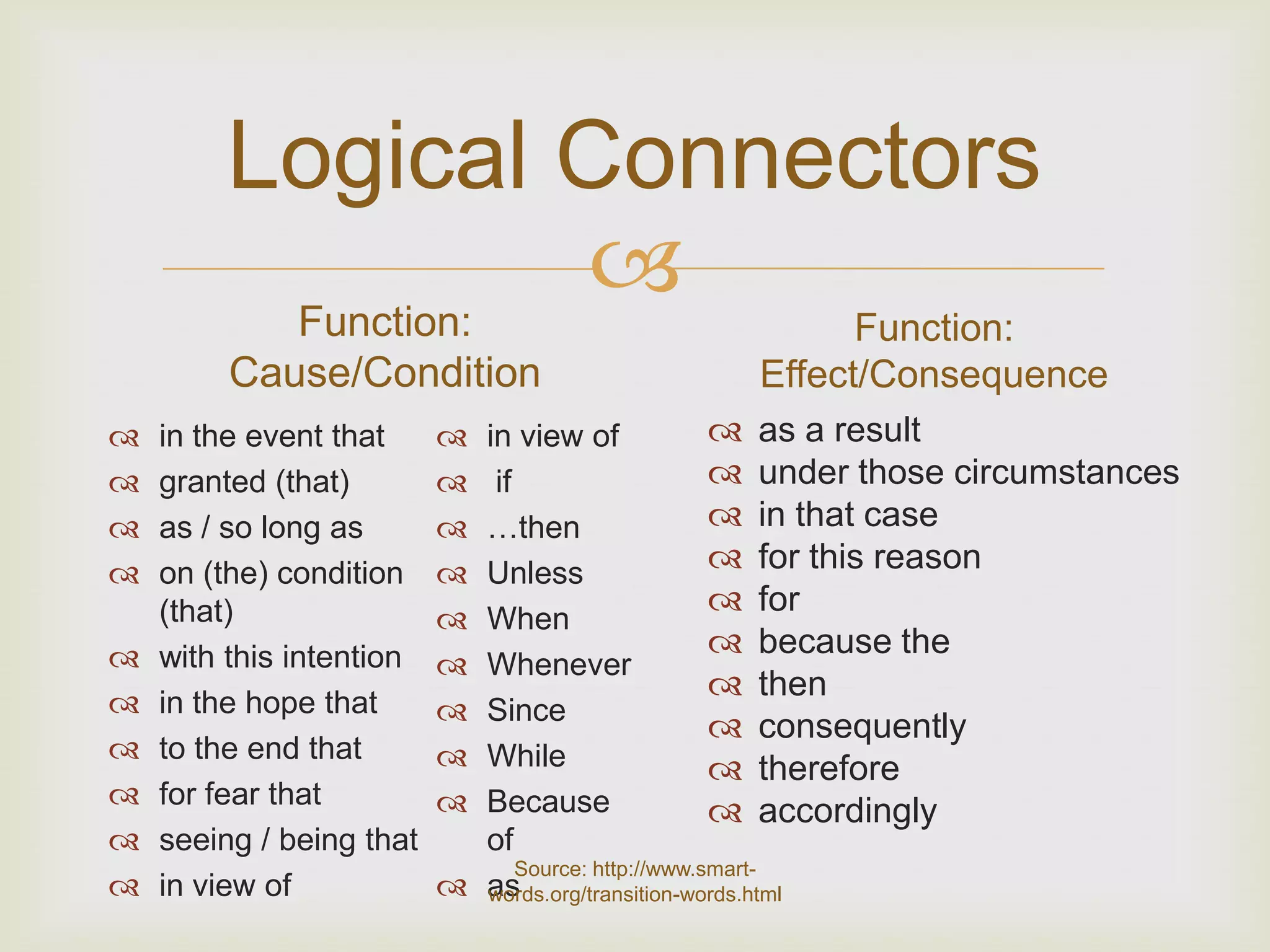
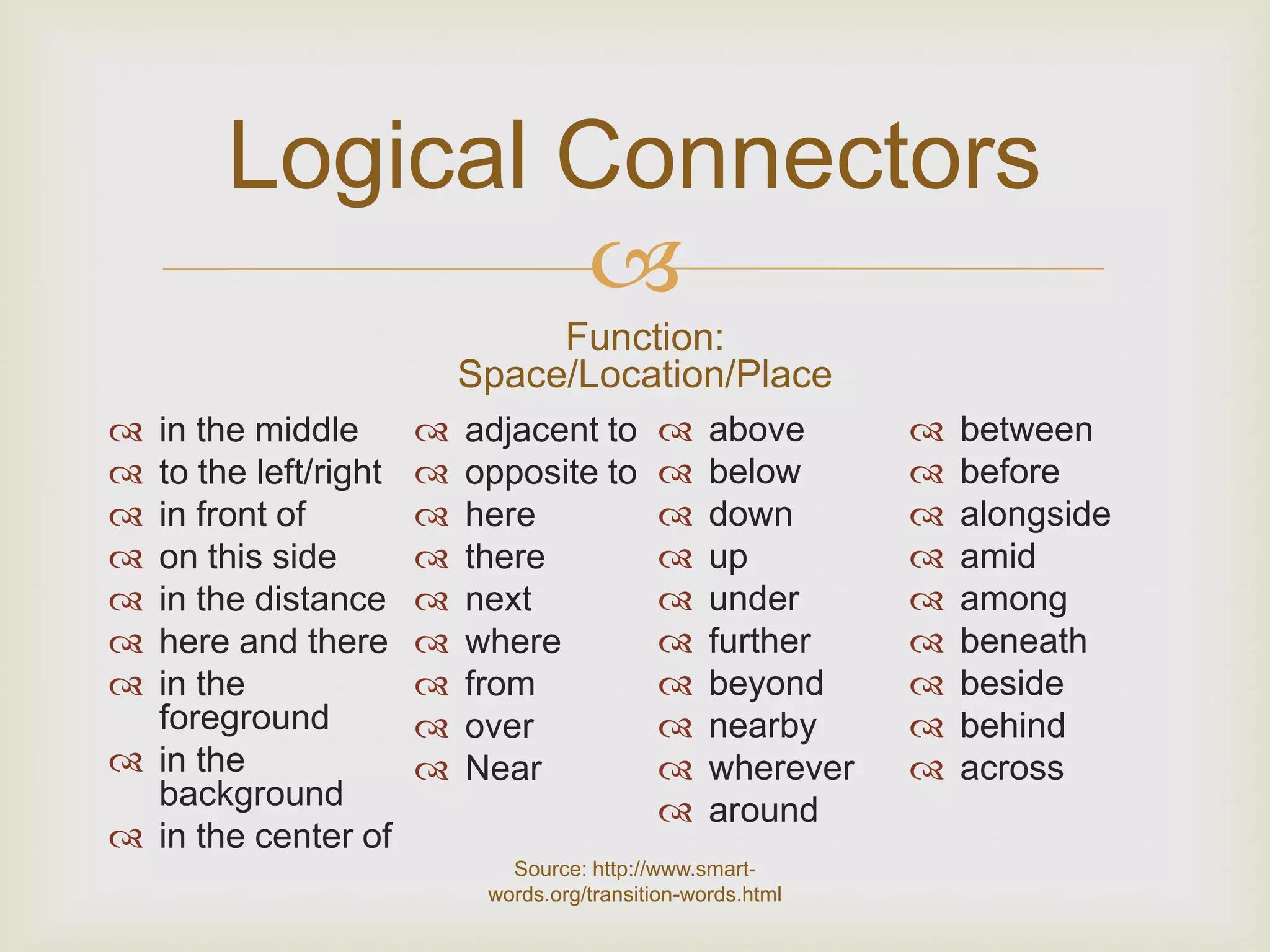
3. Logical connectors are transition words that help signal relationships between ideas and improve coherence.