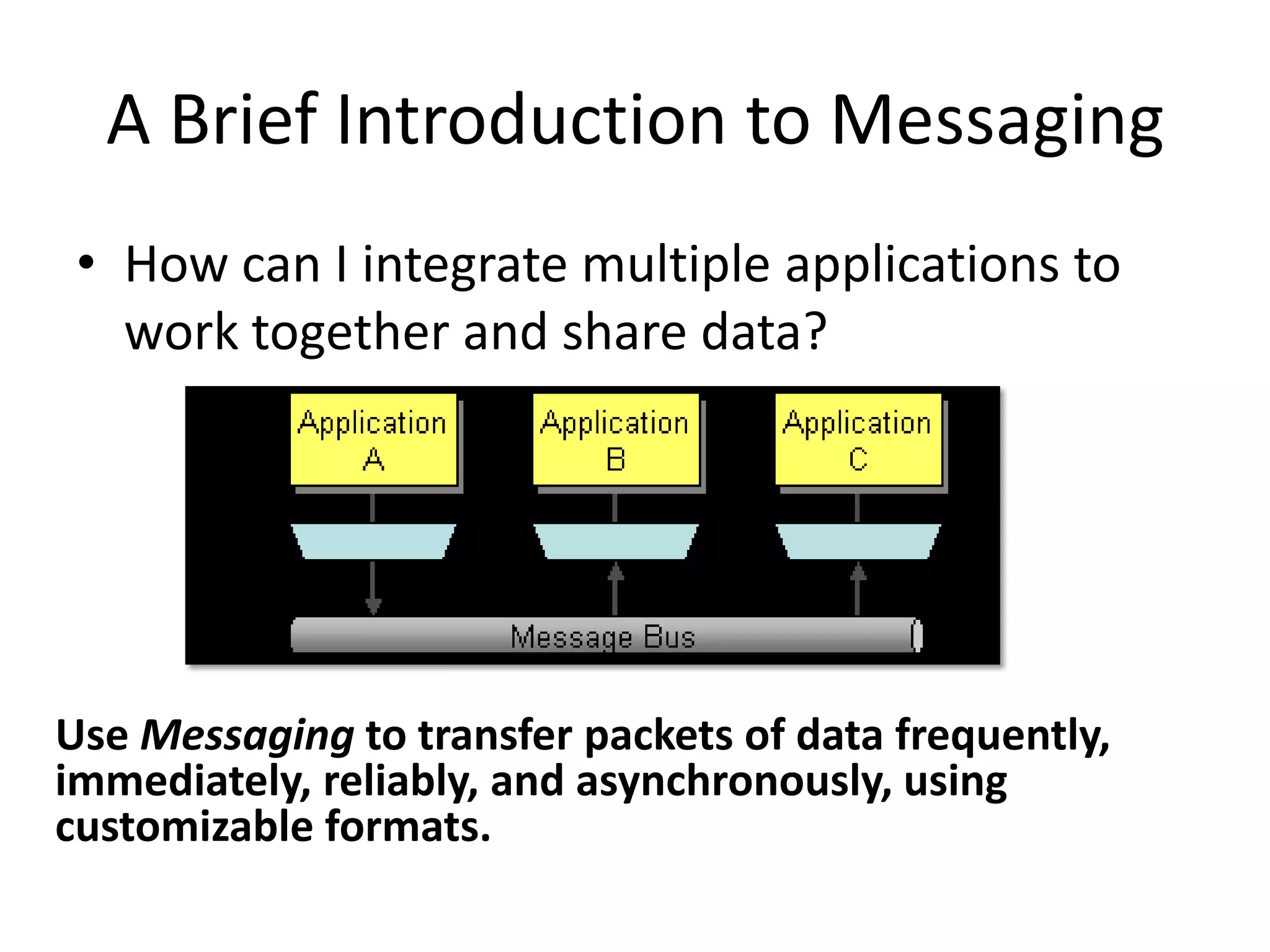
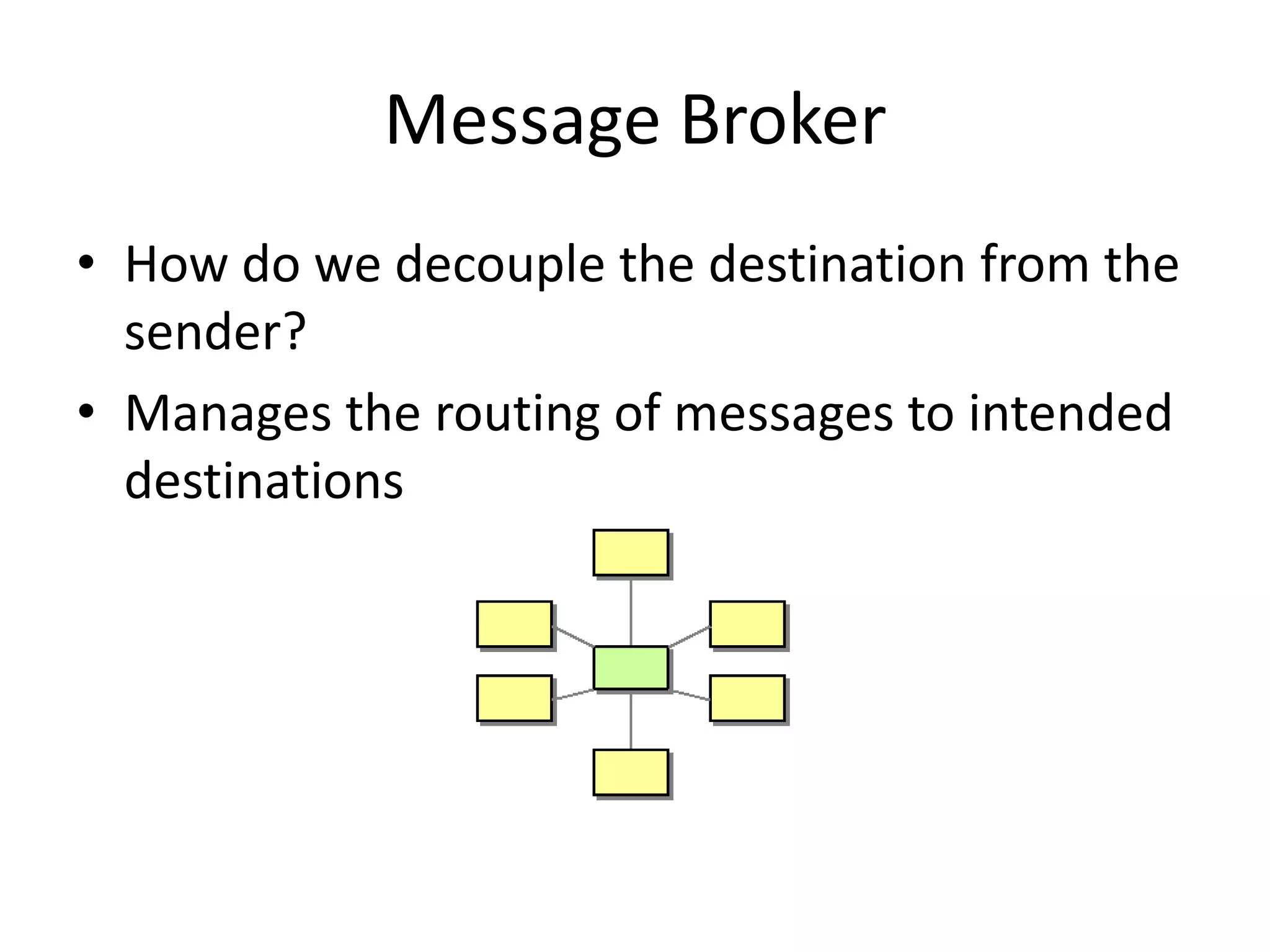
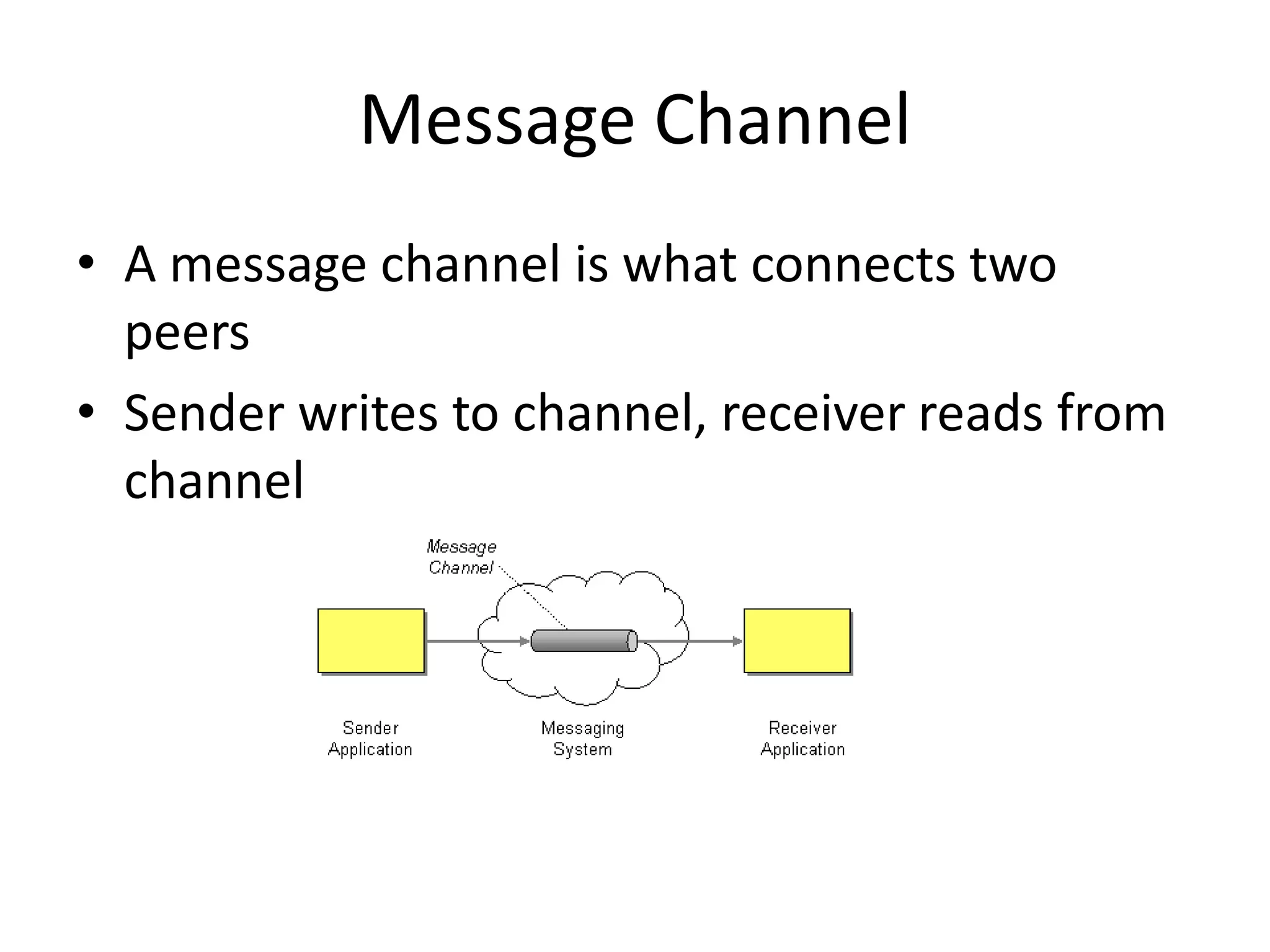
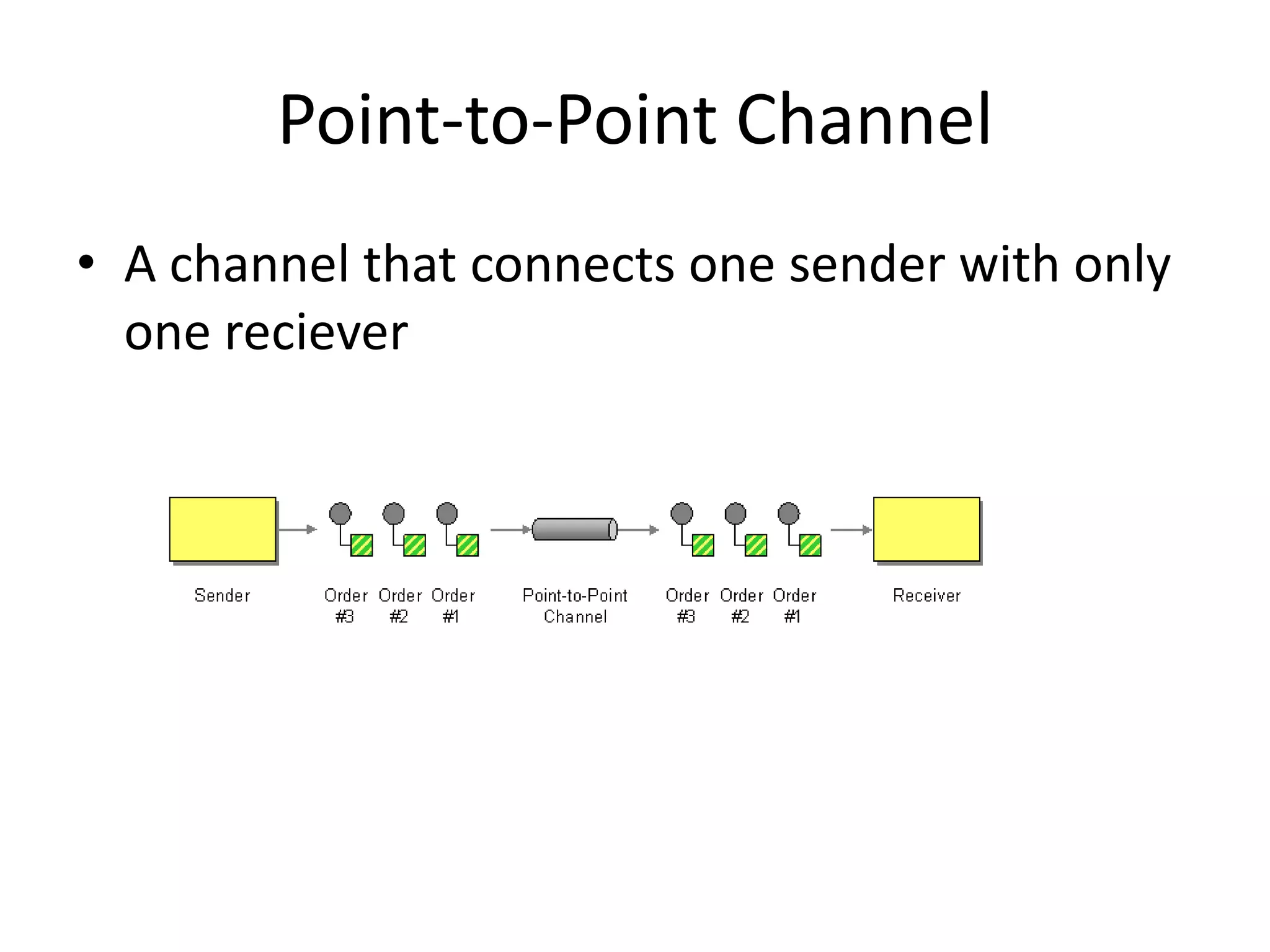
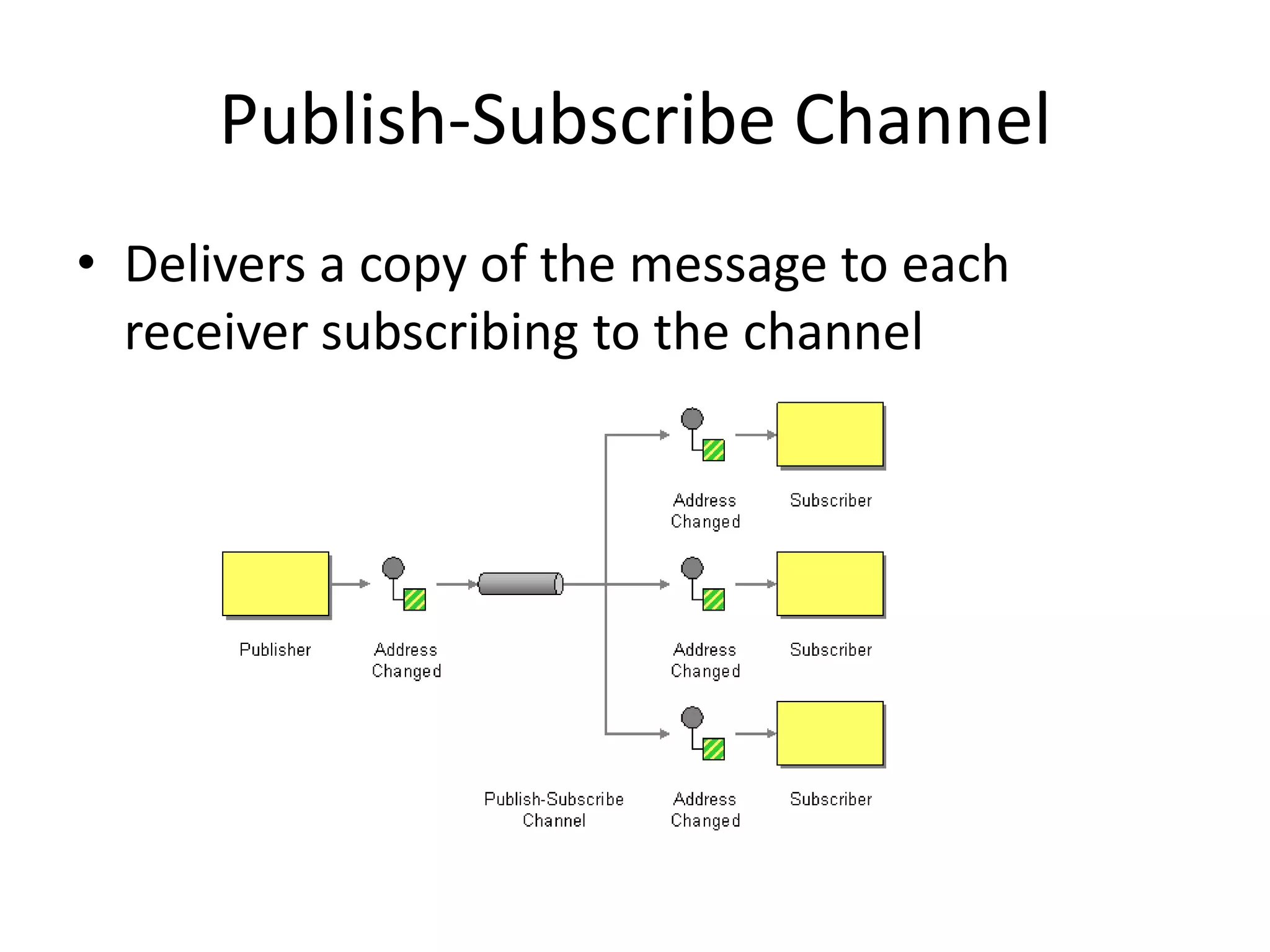
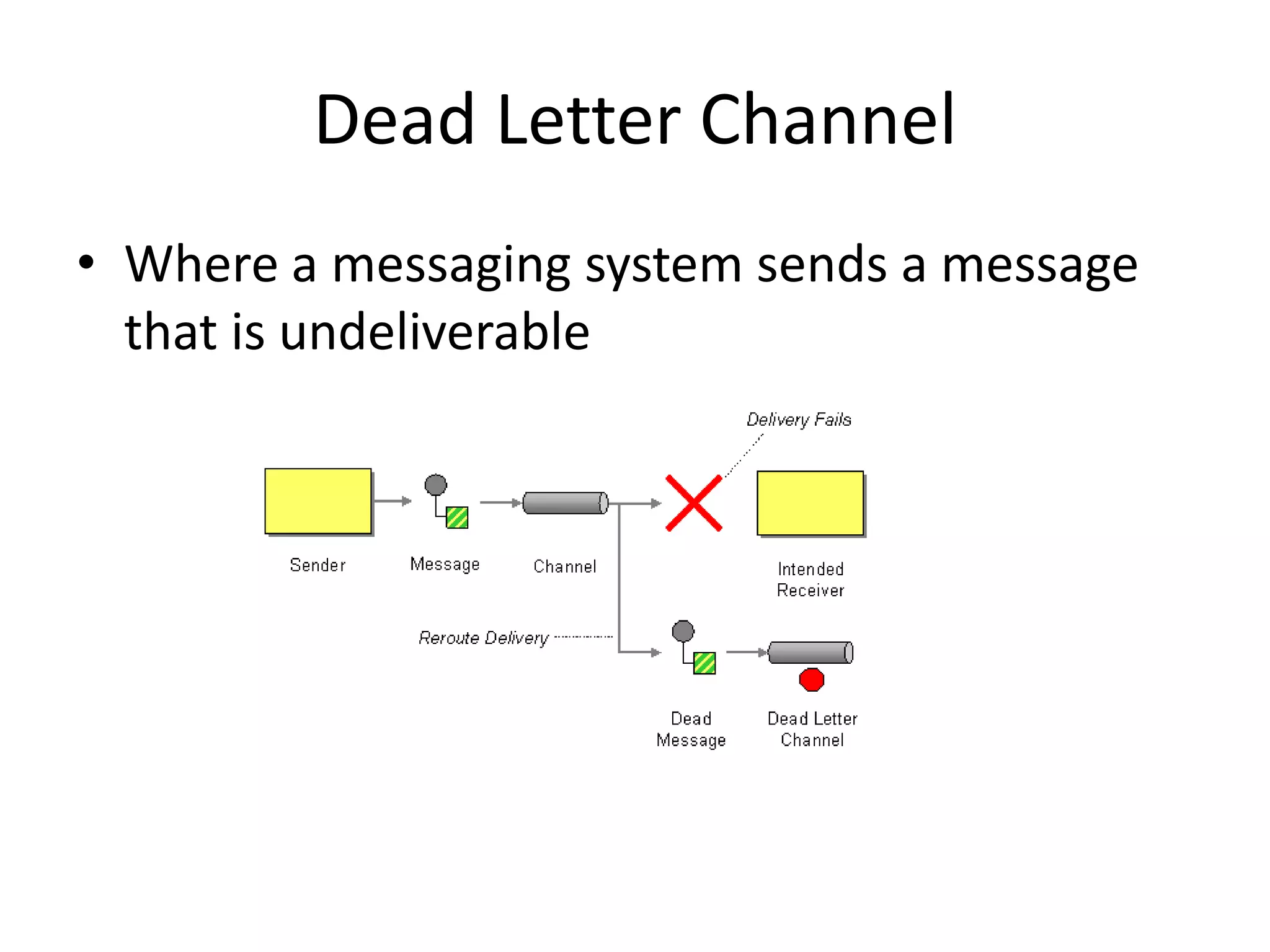
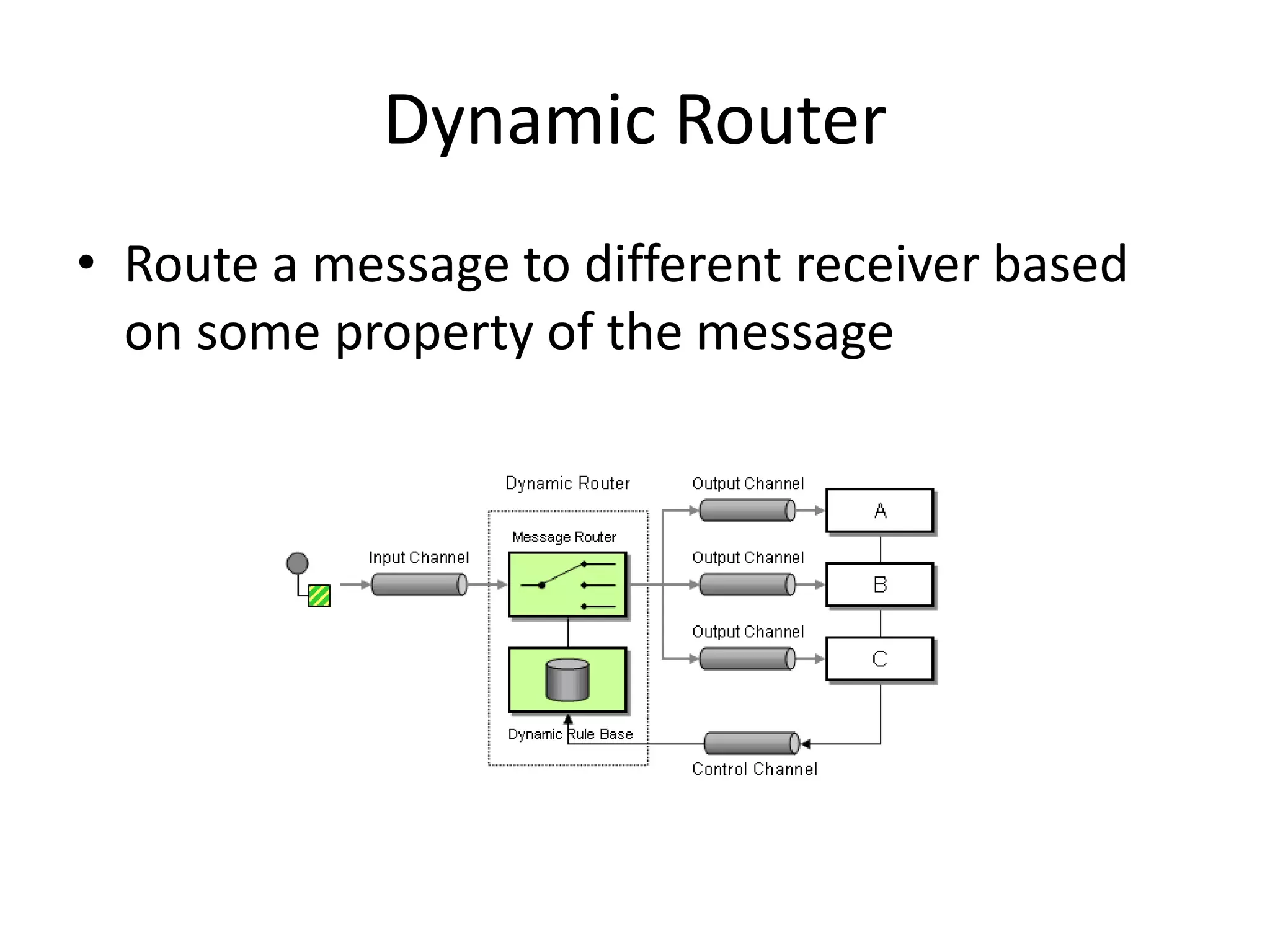
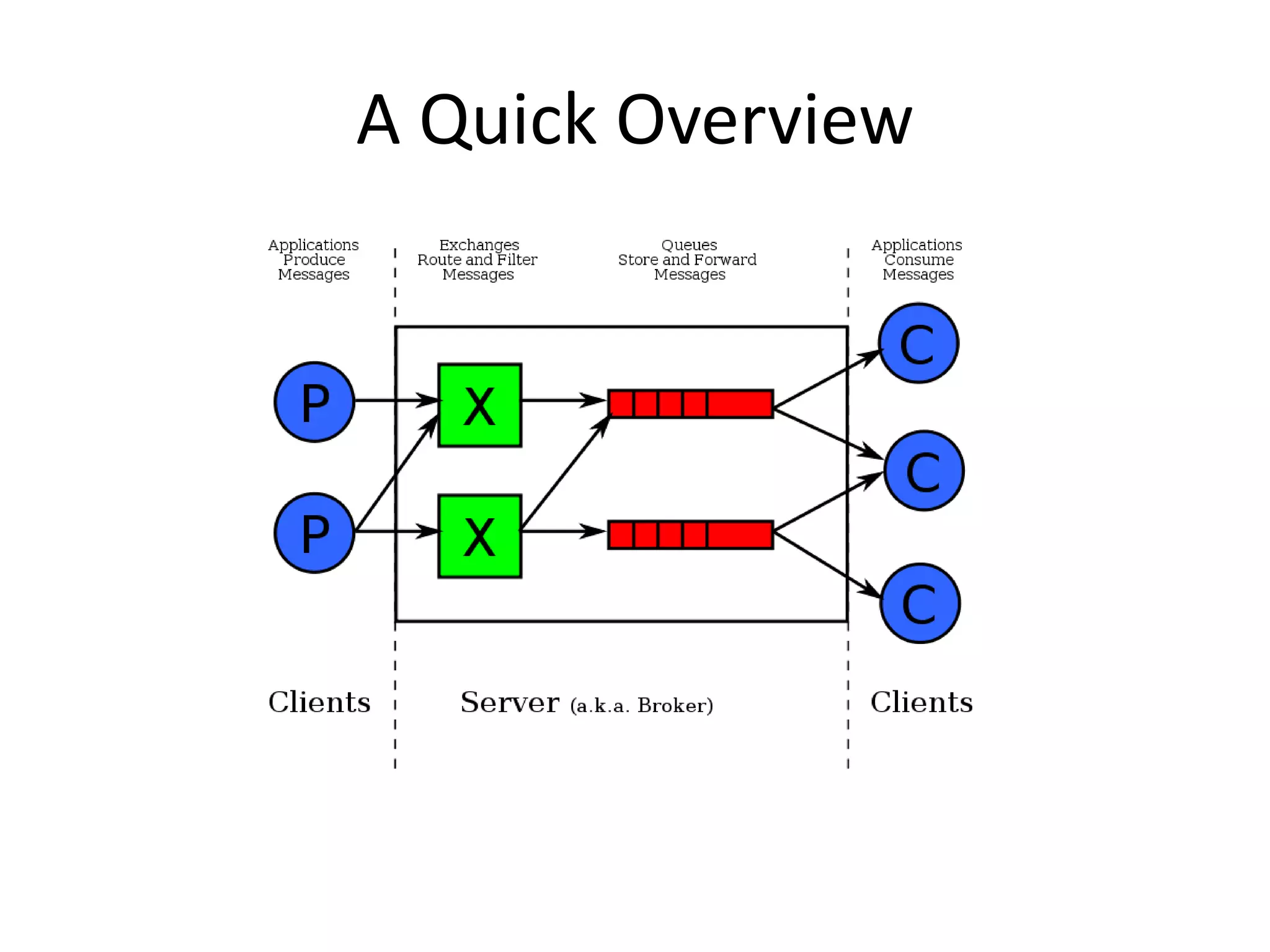
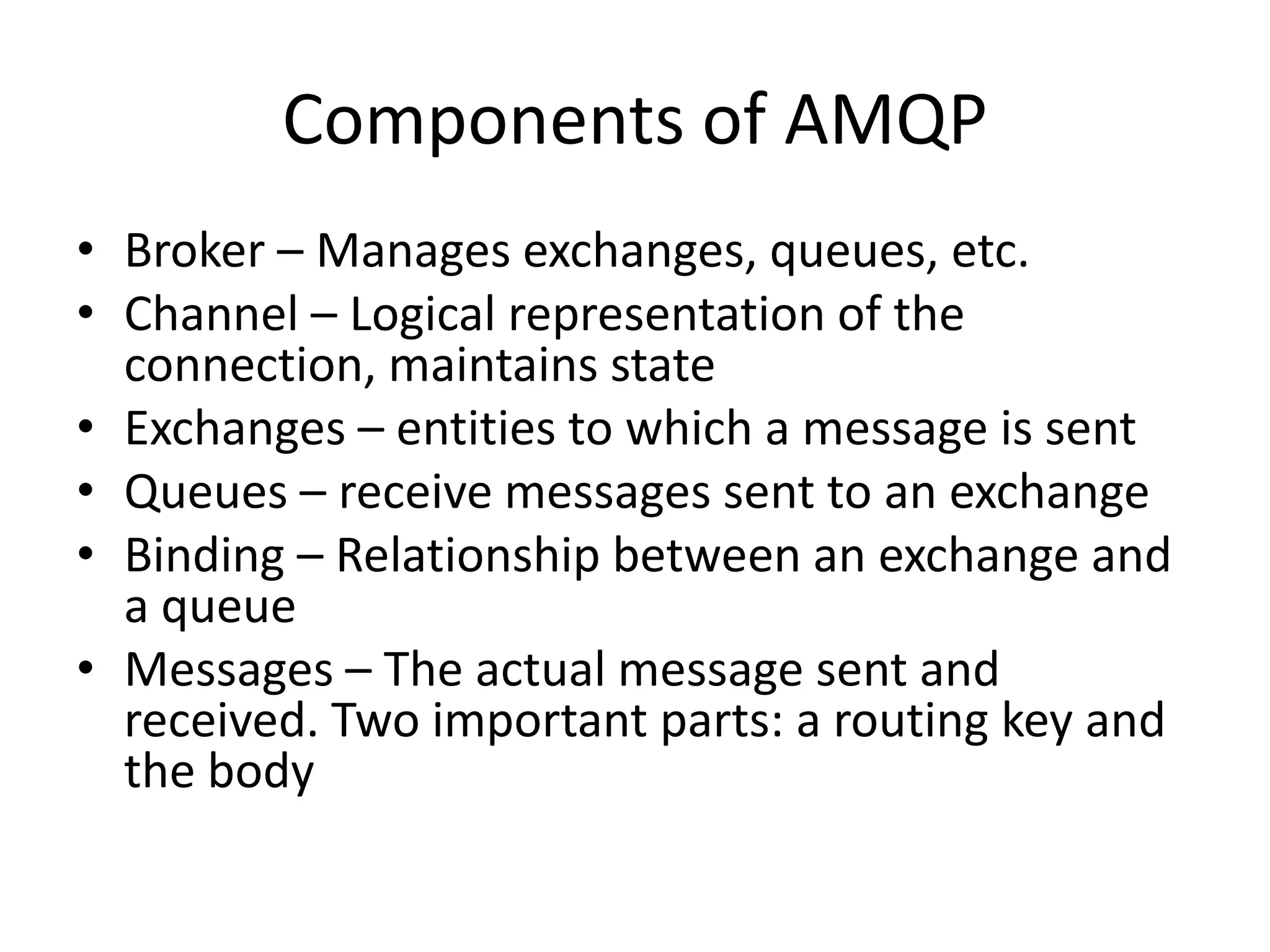
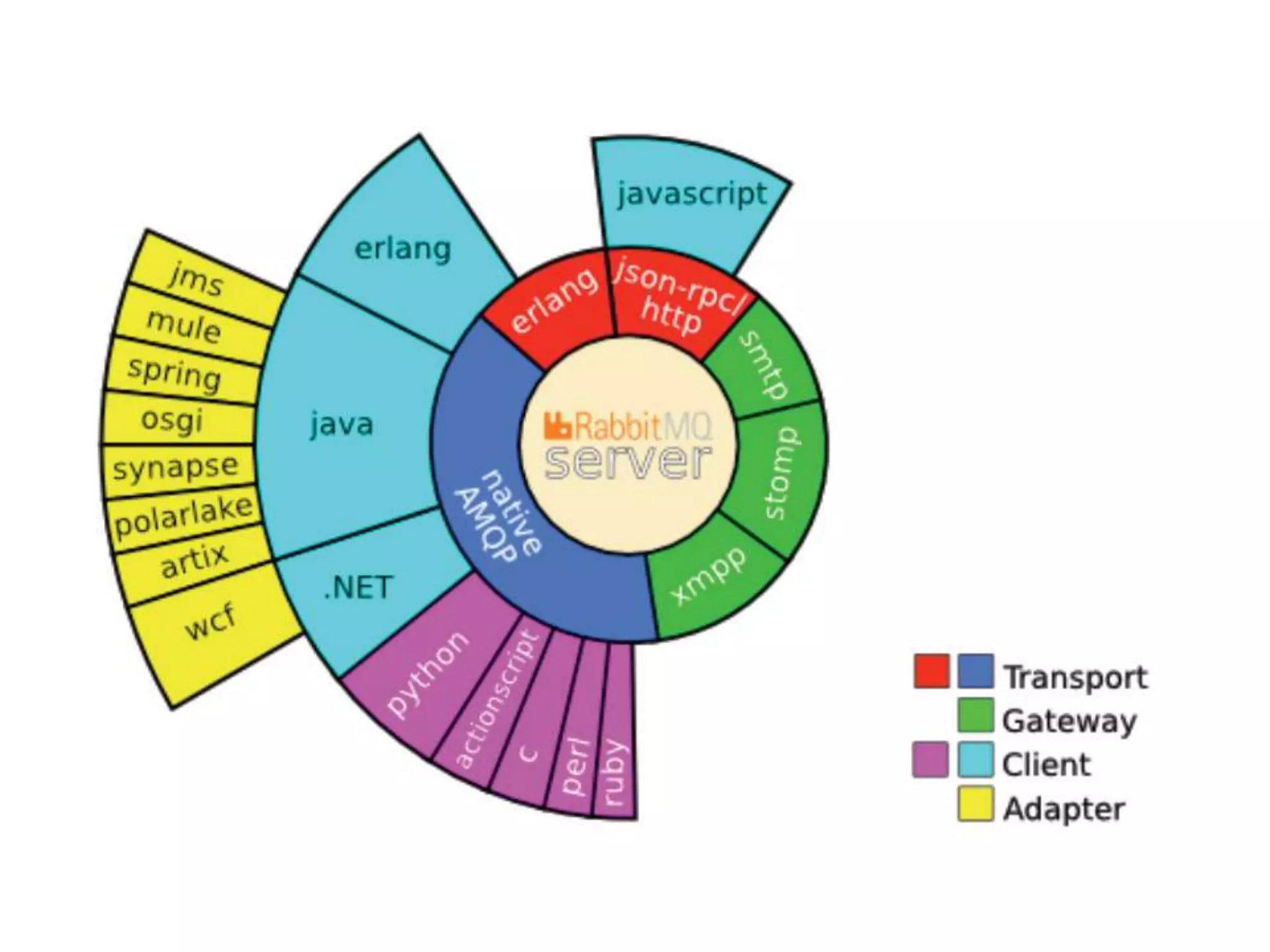
Messaging can be used to integrate different systems and applications to work together by transferring data packets asynchronously using customizable formats. It allows for decoupling of publishers and subscribers. RabbitMQ is an open source message broker that implements the AMQP standard for high performance messaging. It can be used from Java applications using the RabbitMQ client library, Apache Camel AMQP component, or Spring AMQP framework.