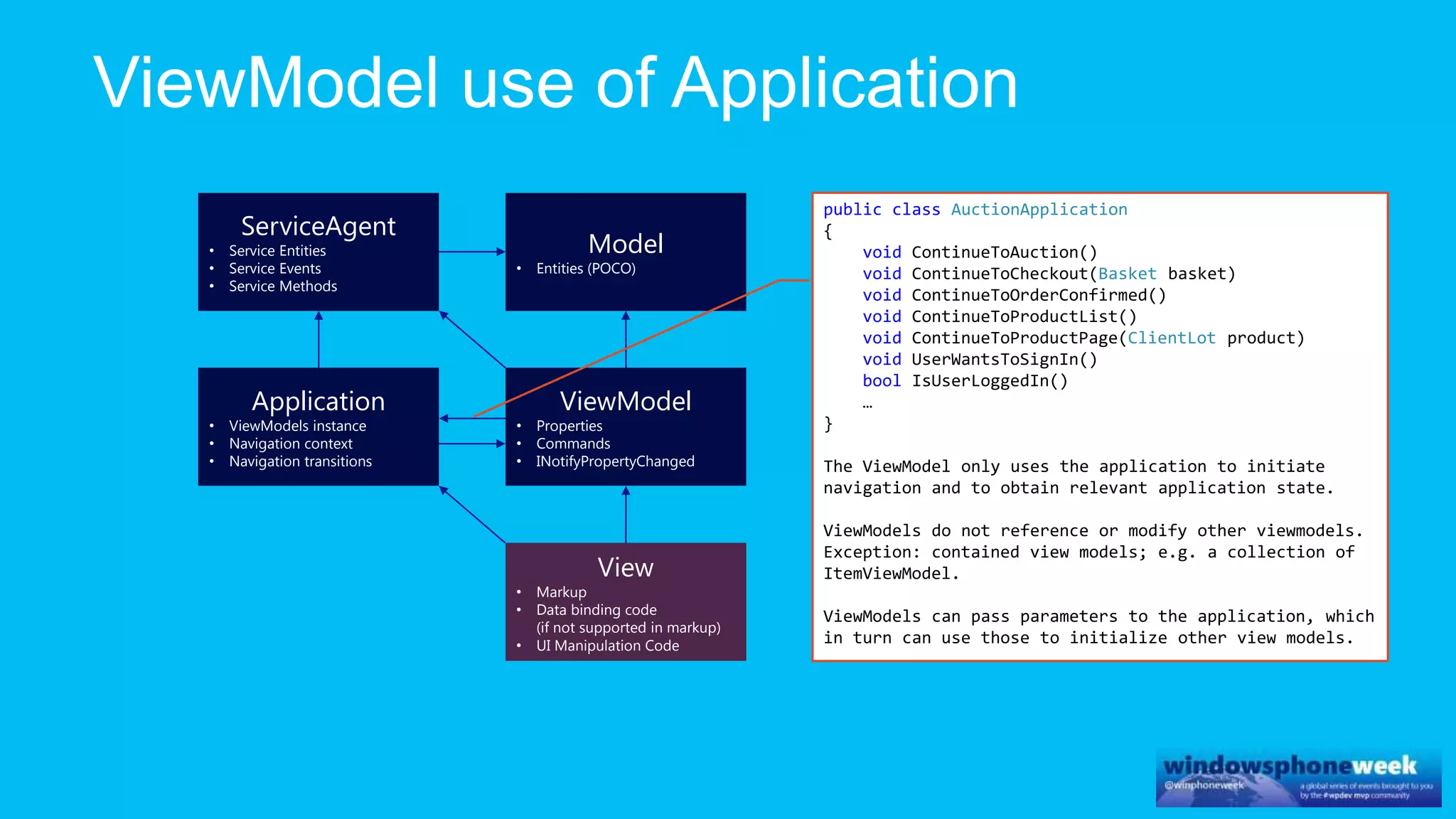
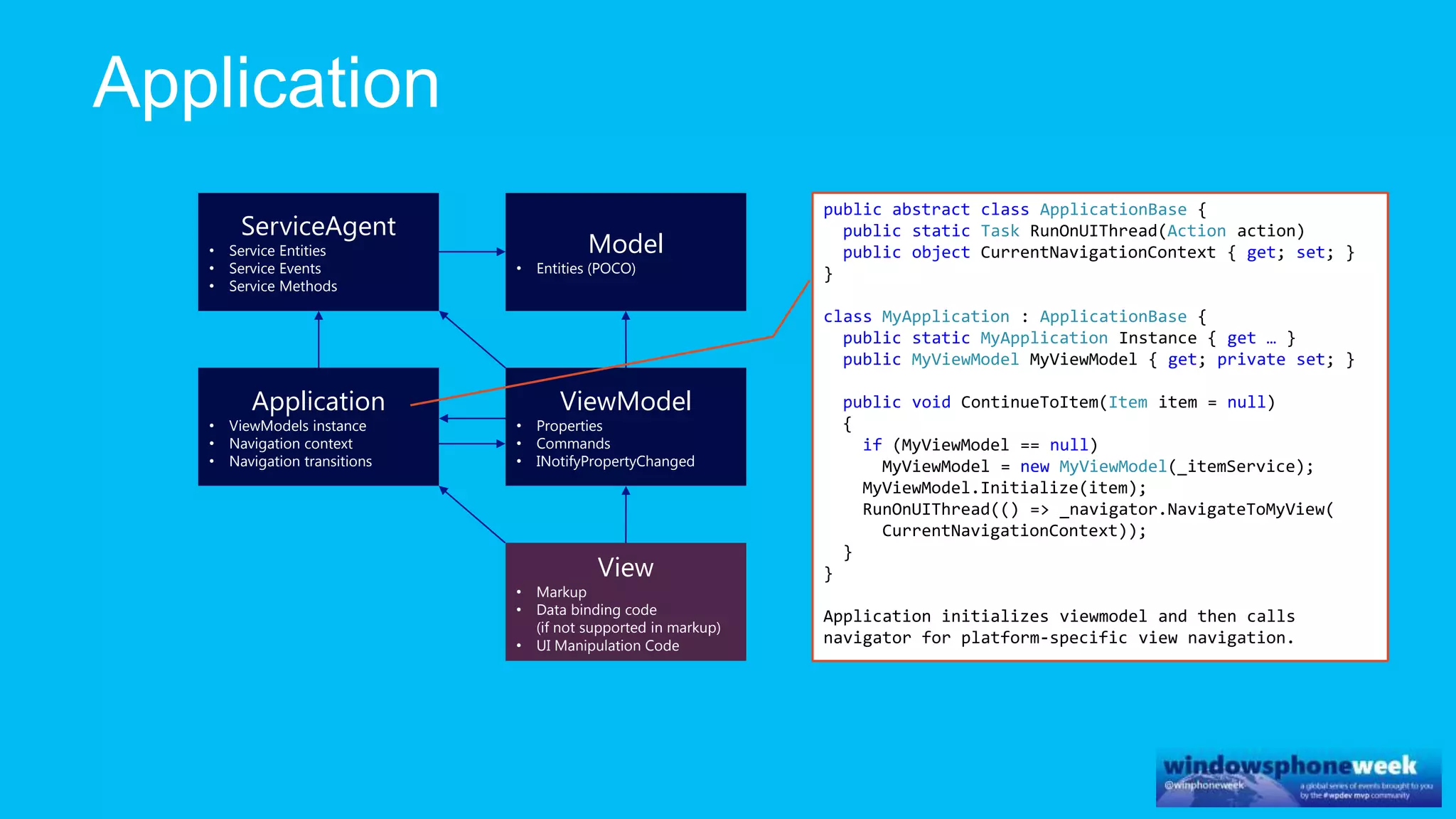
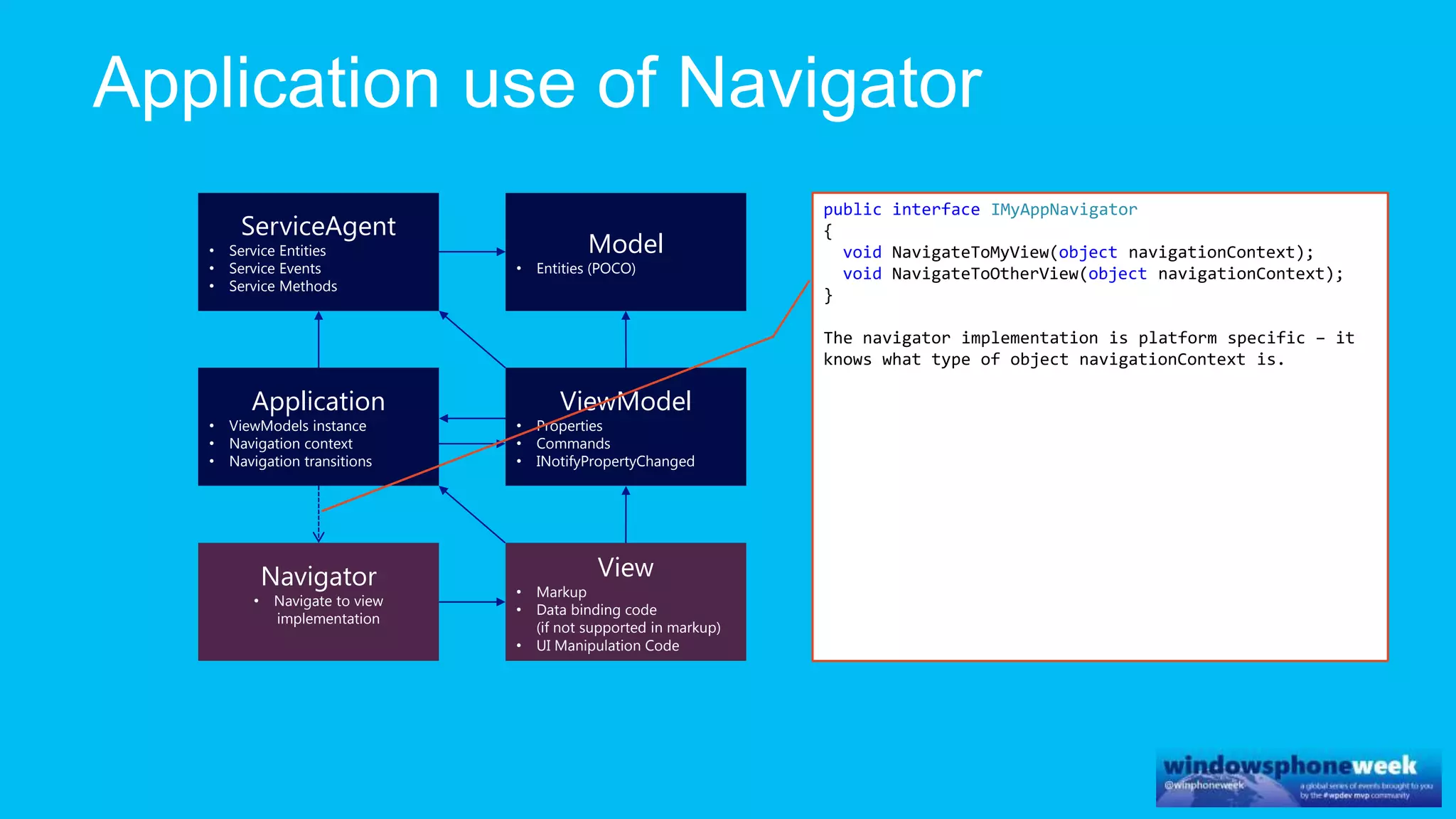
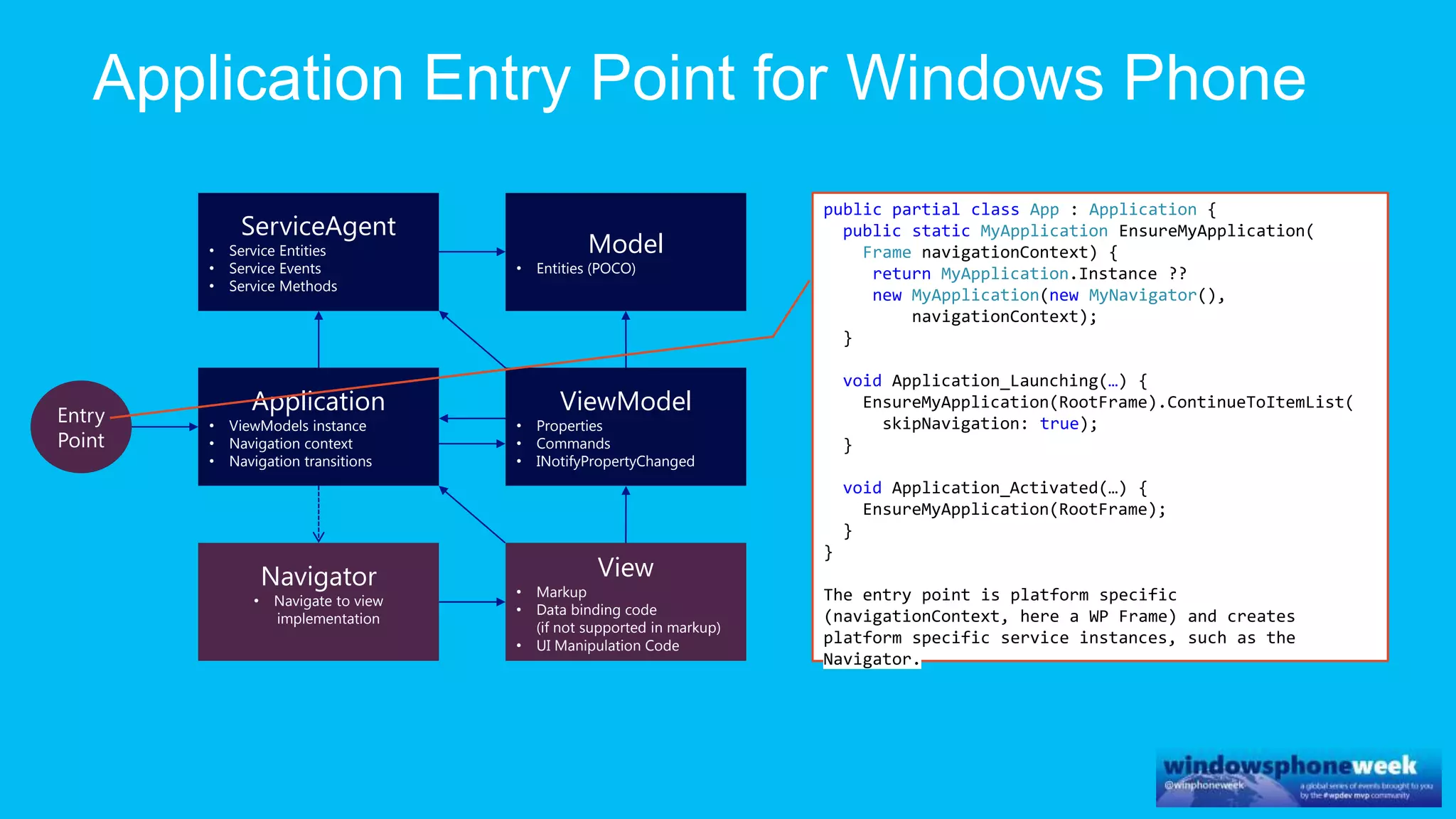
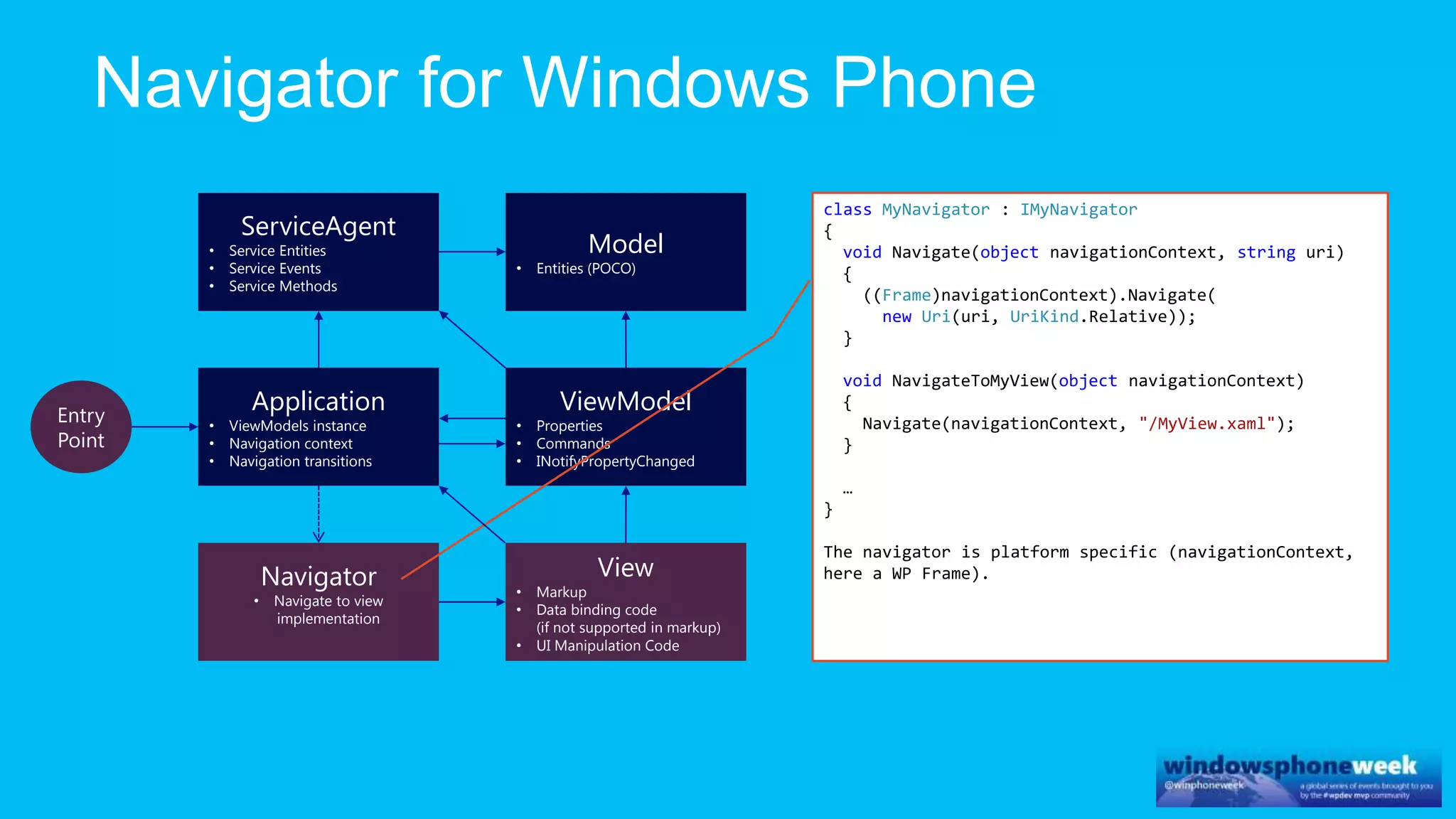
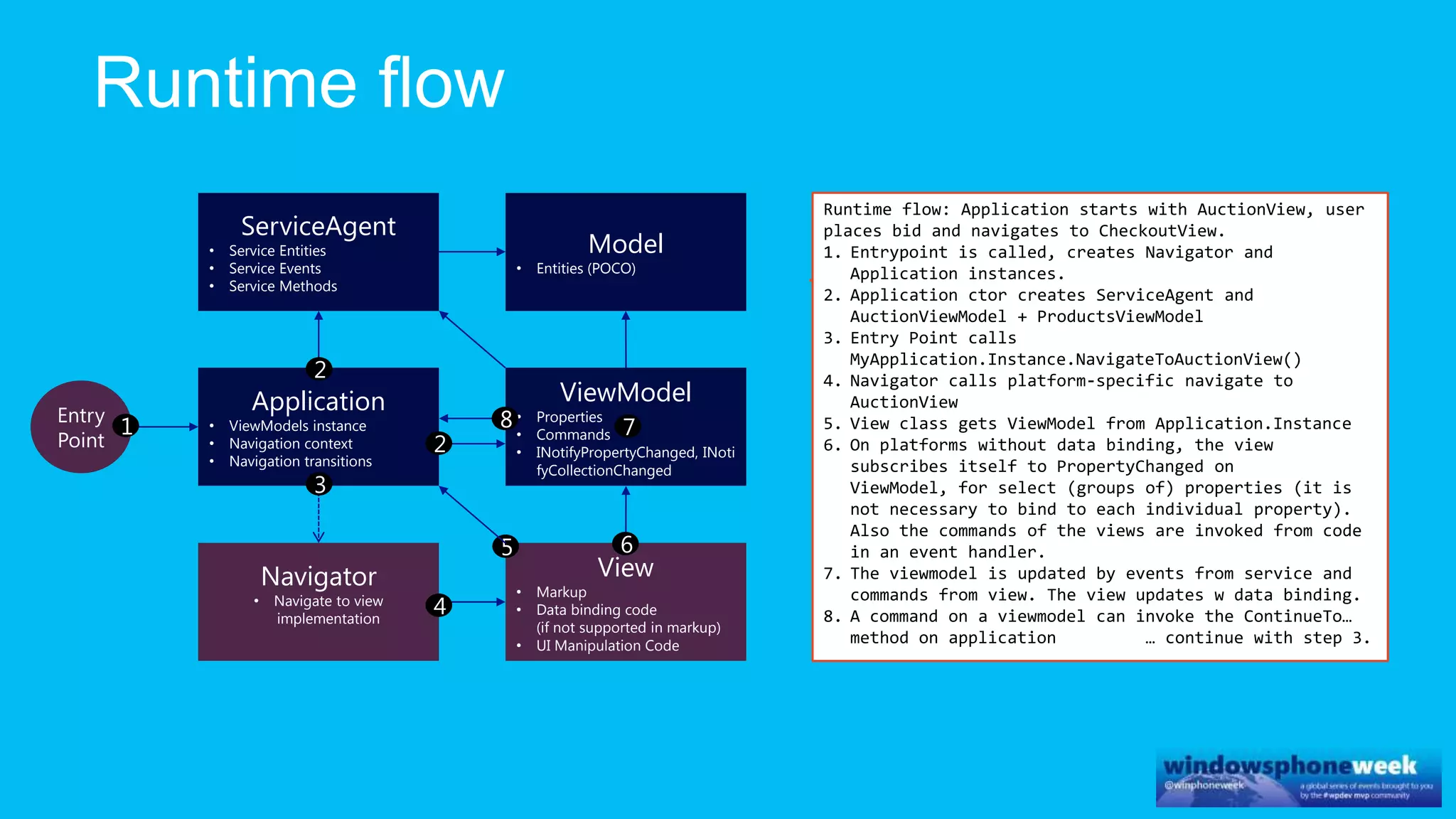
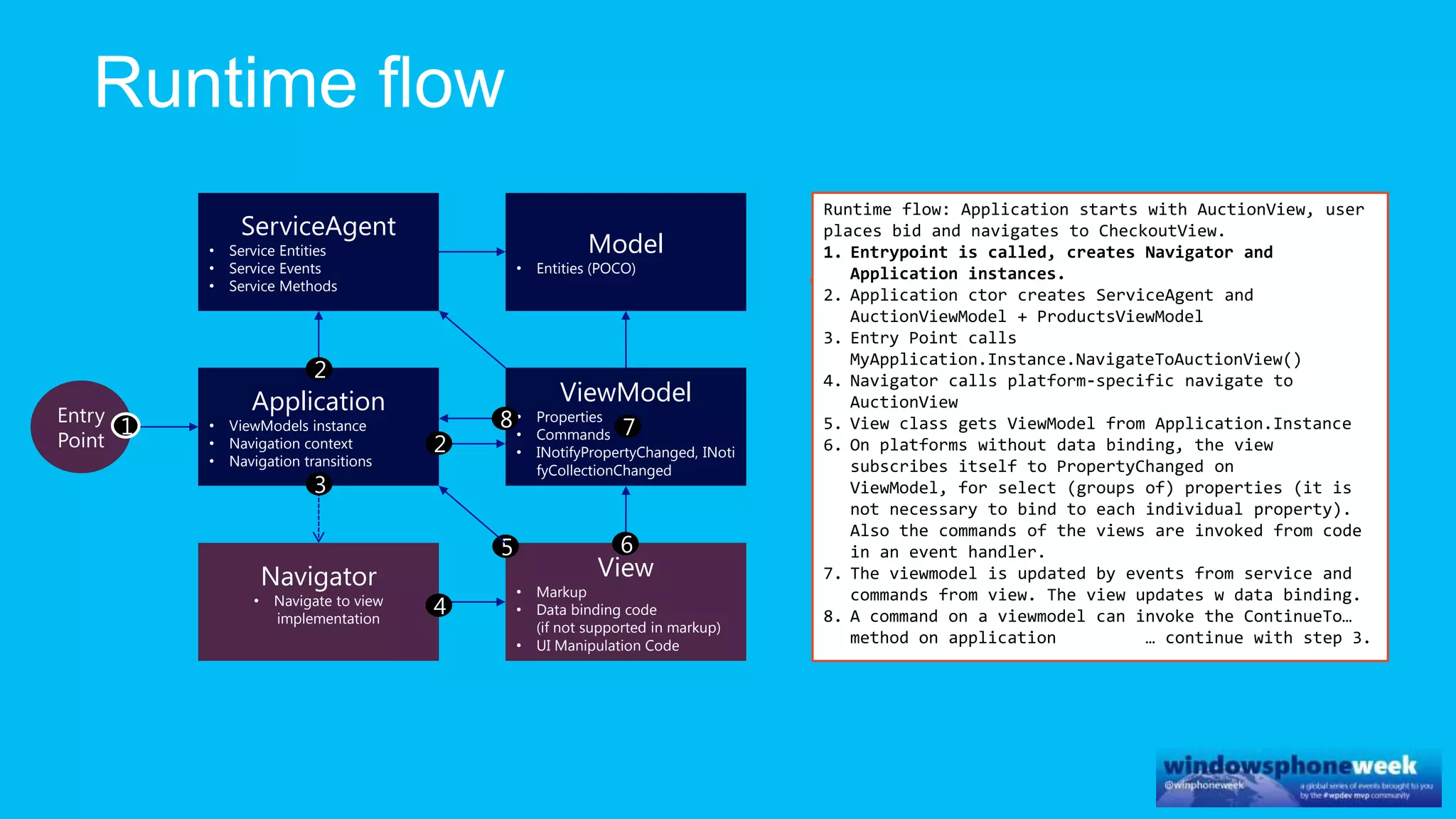
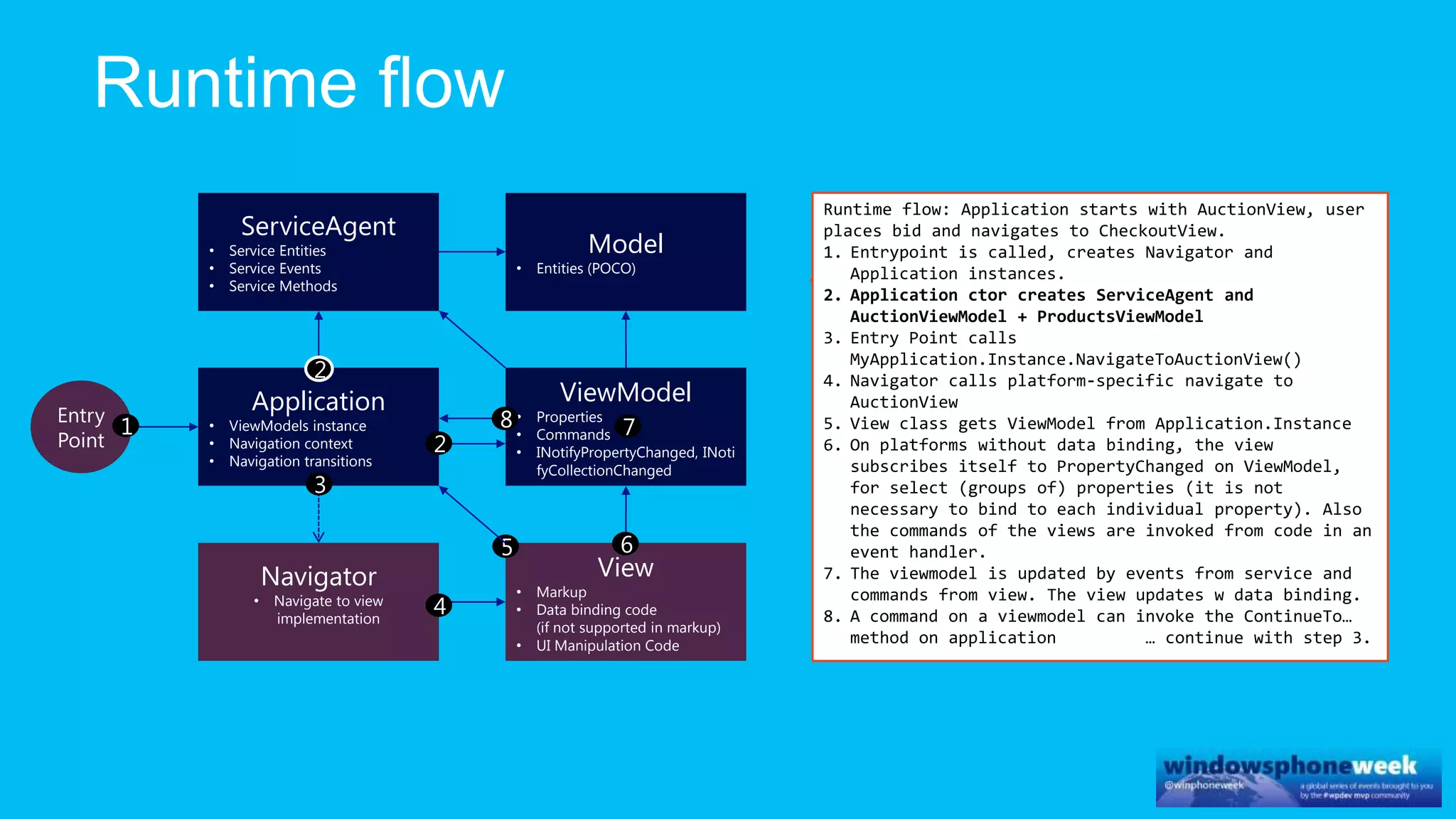
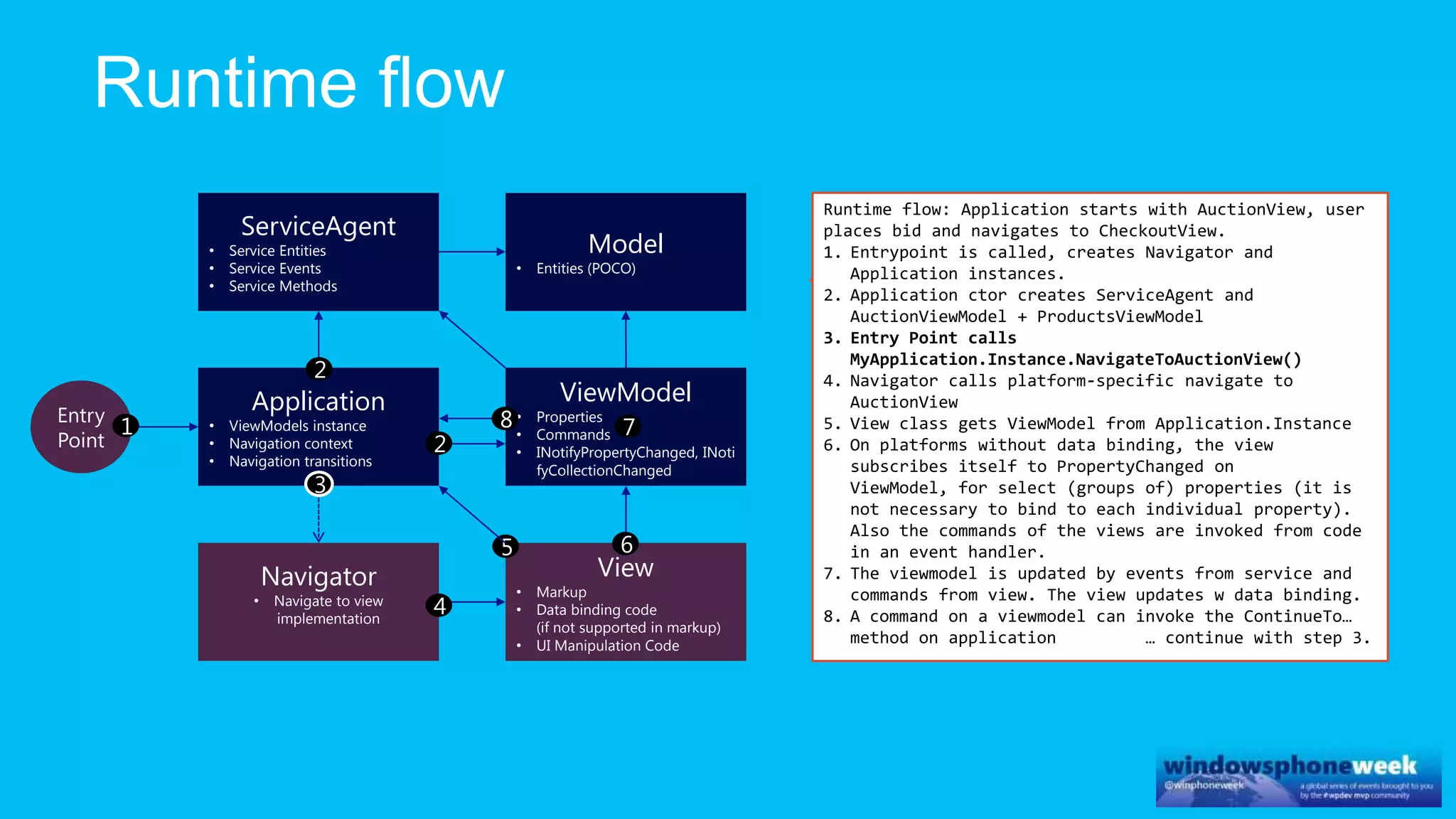
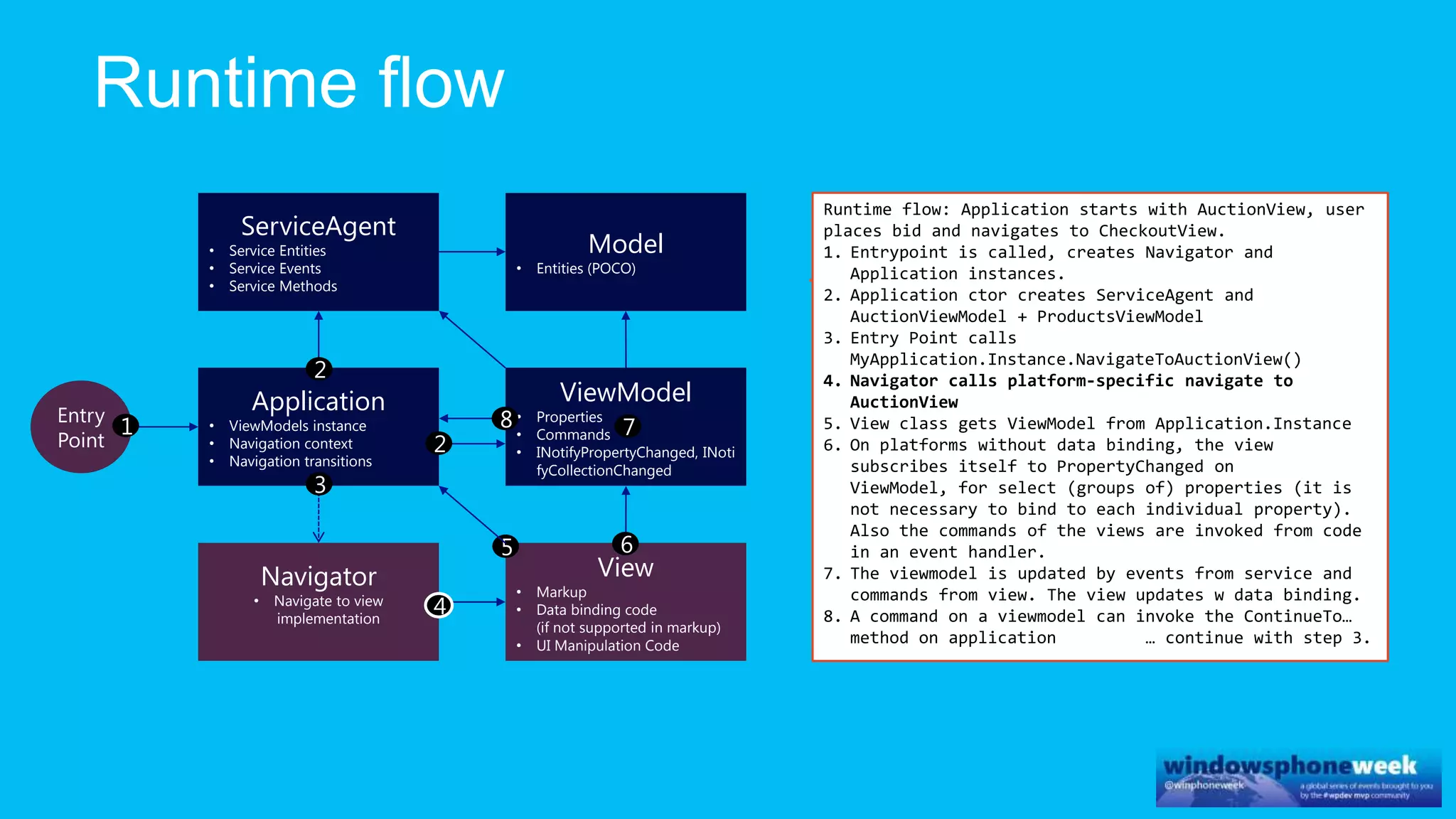
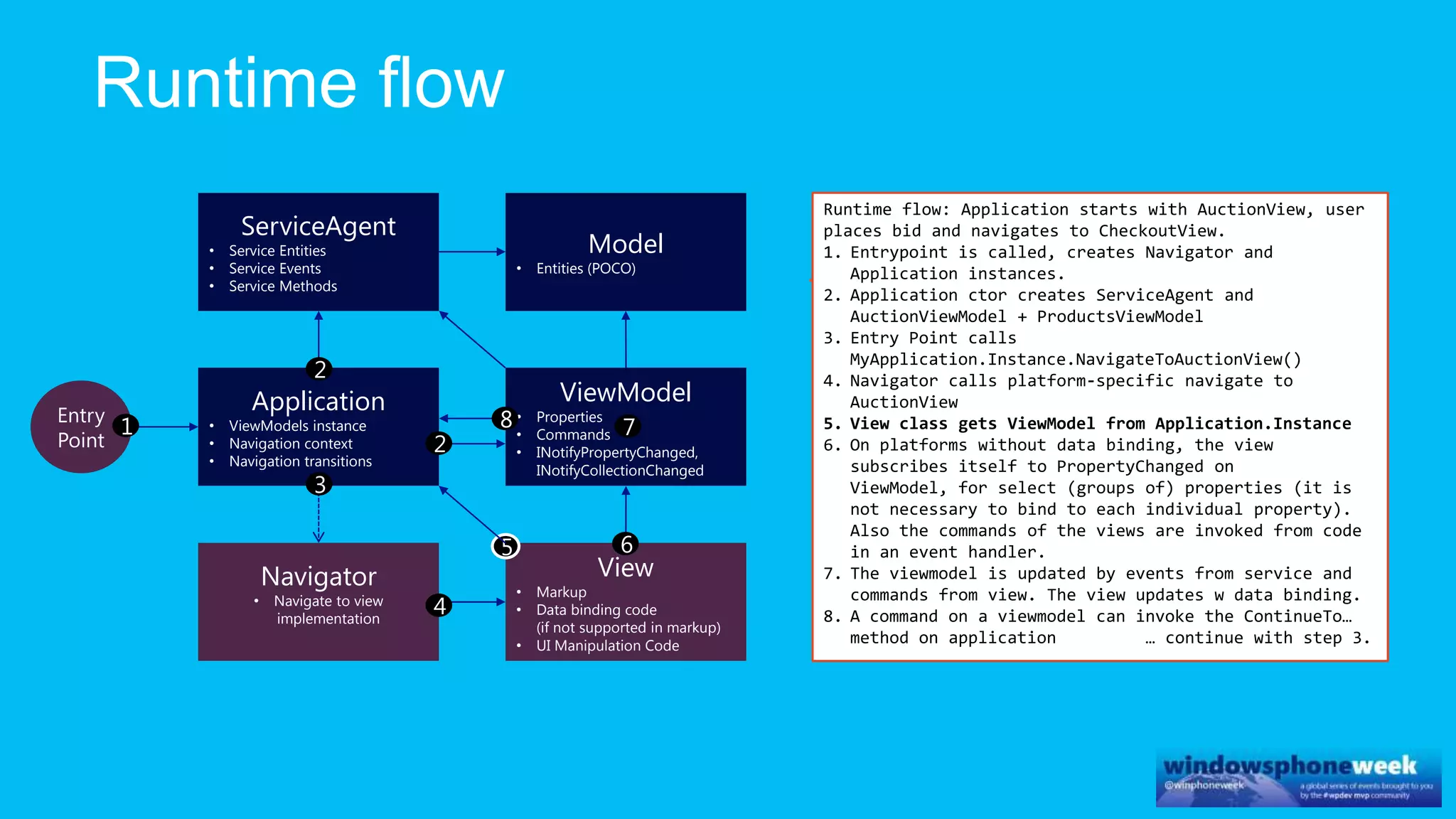
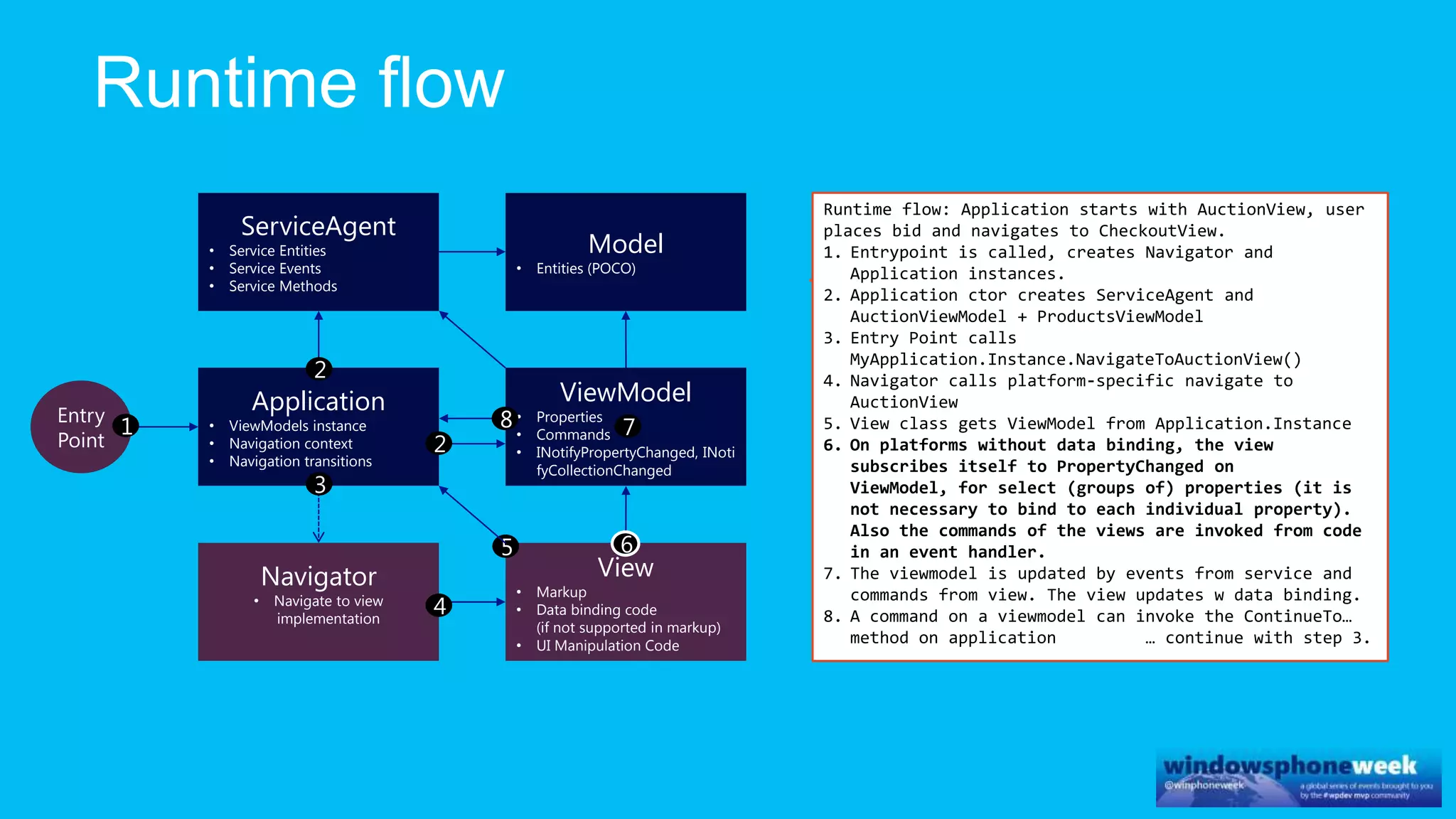
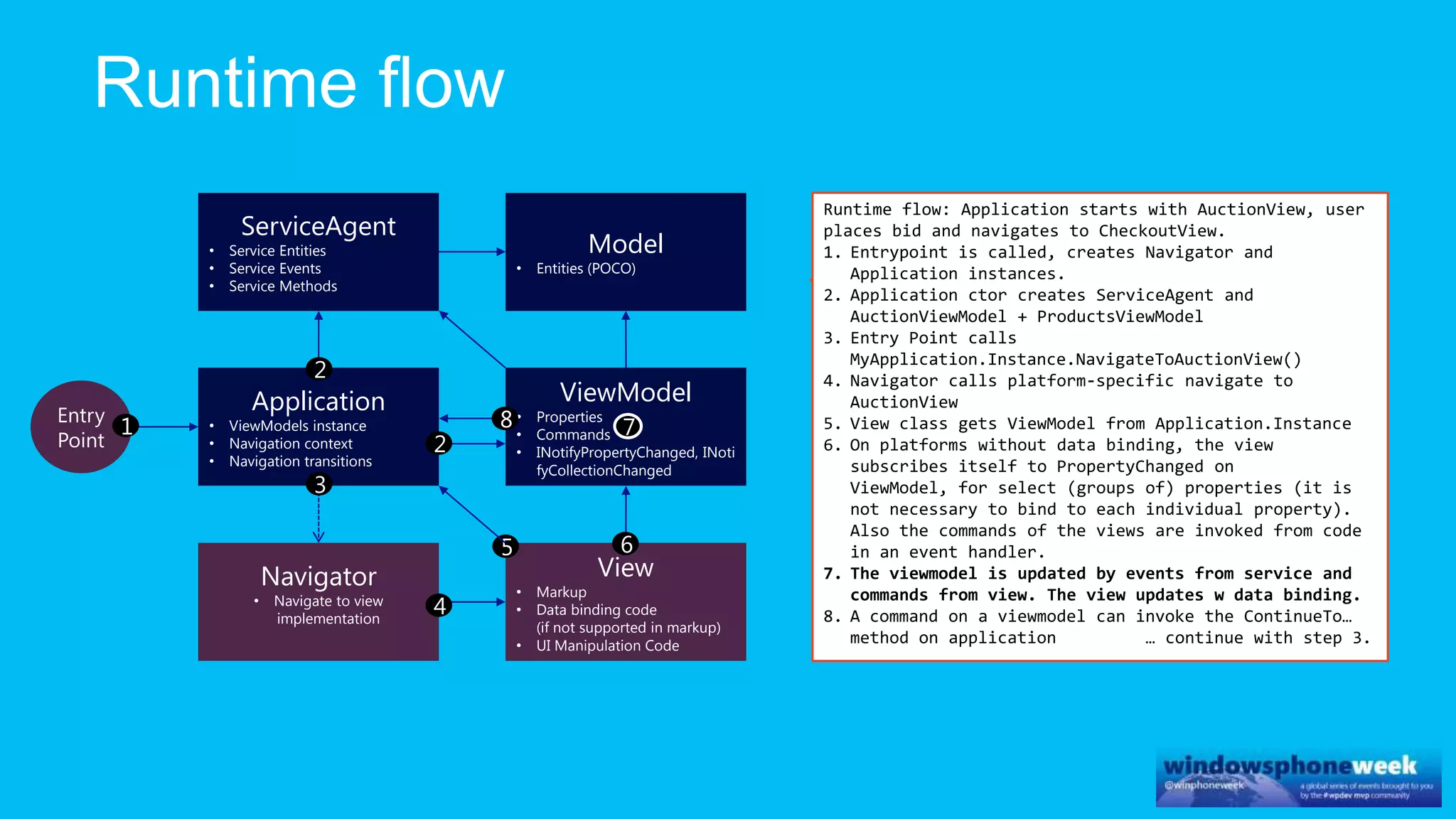
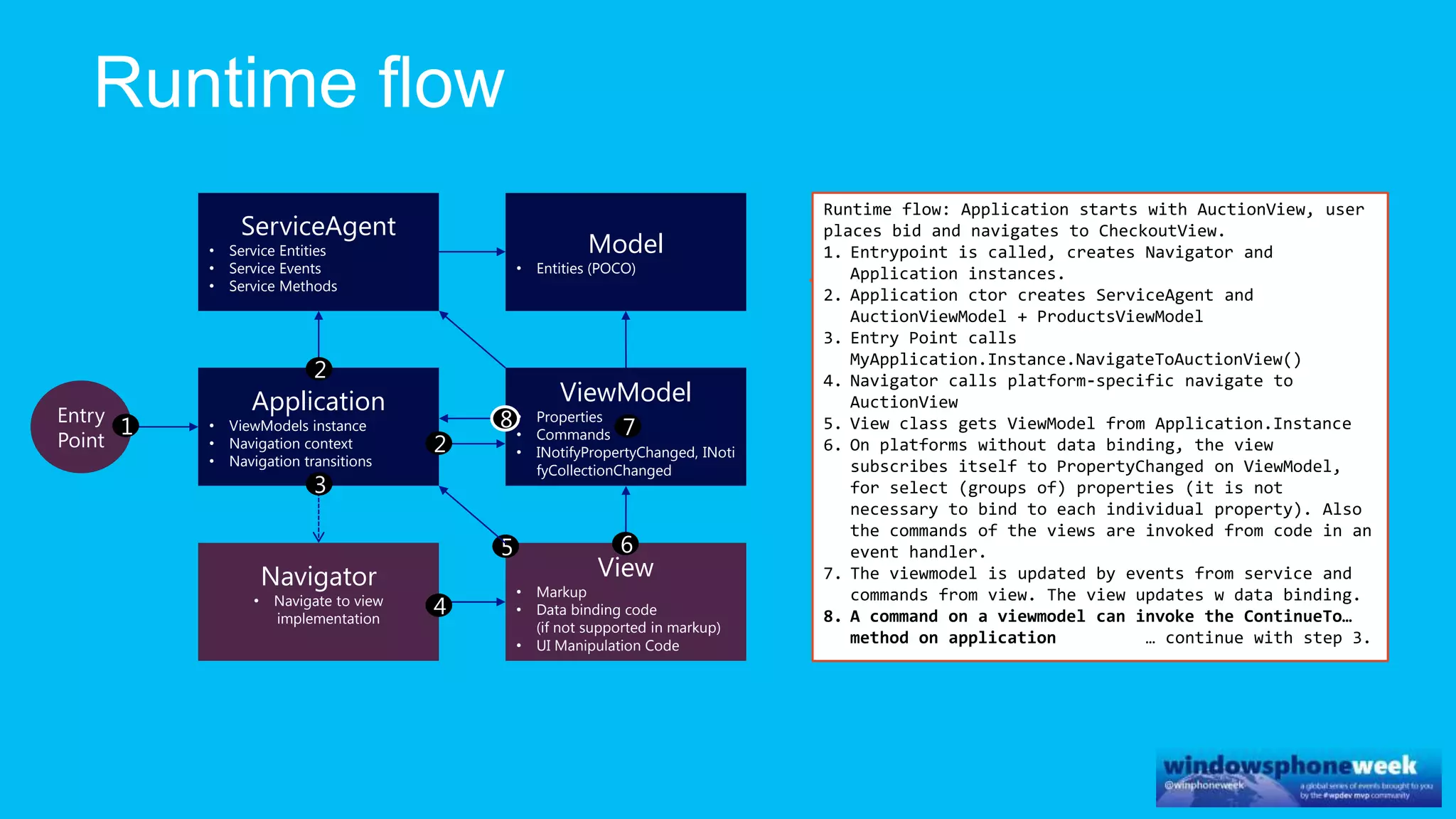
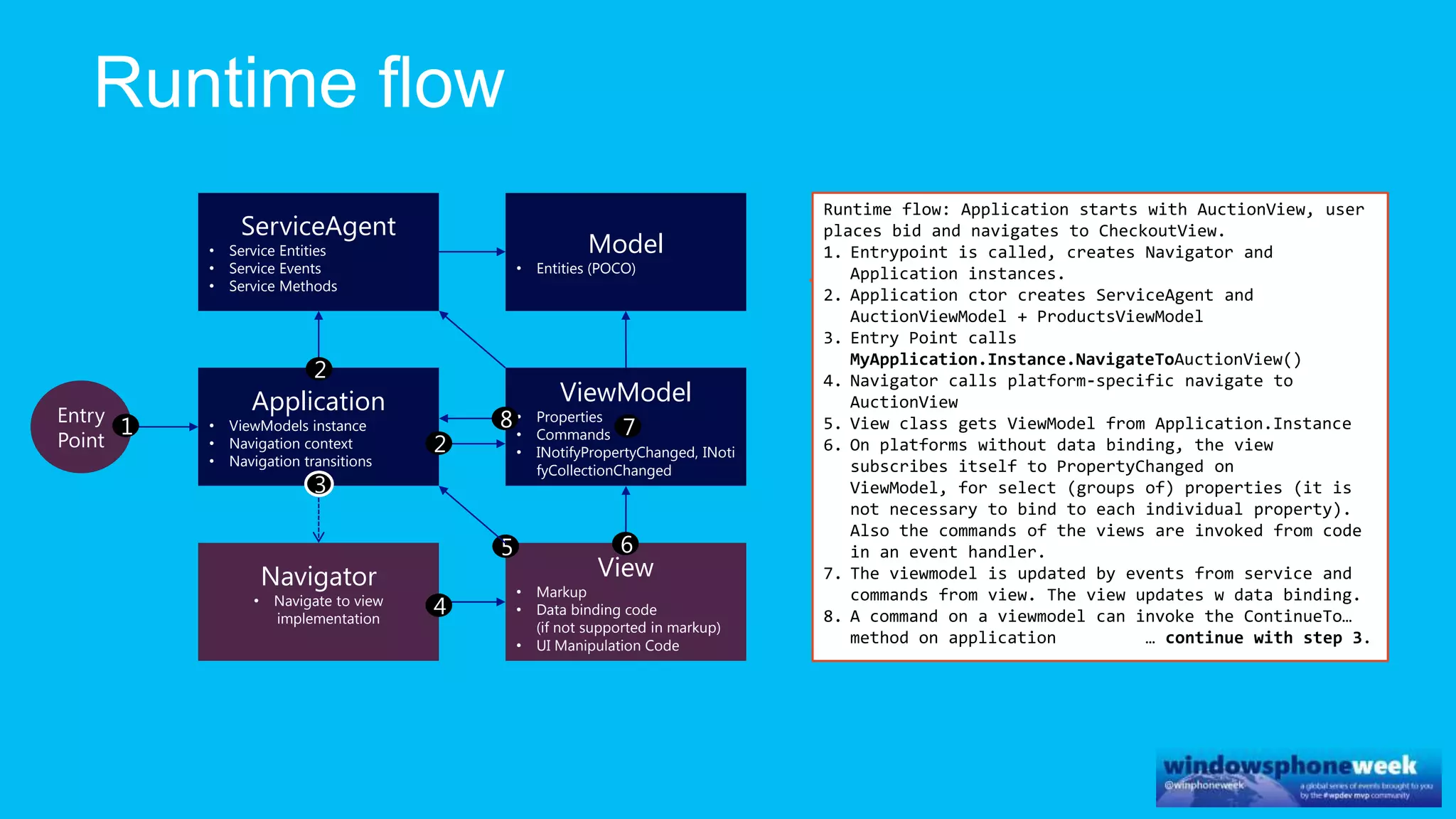
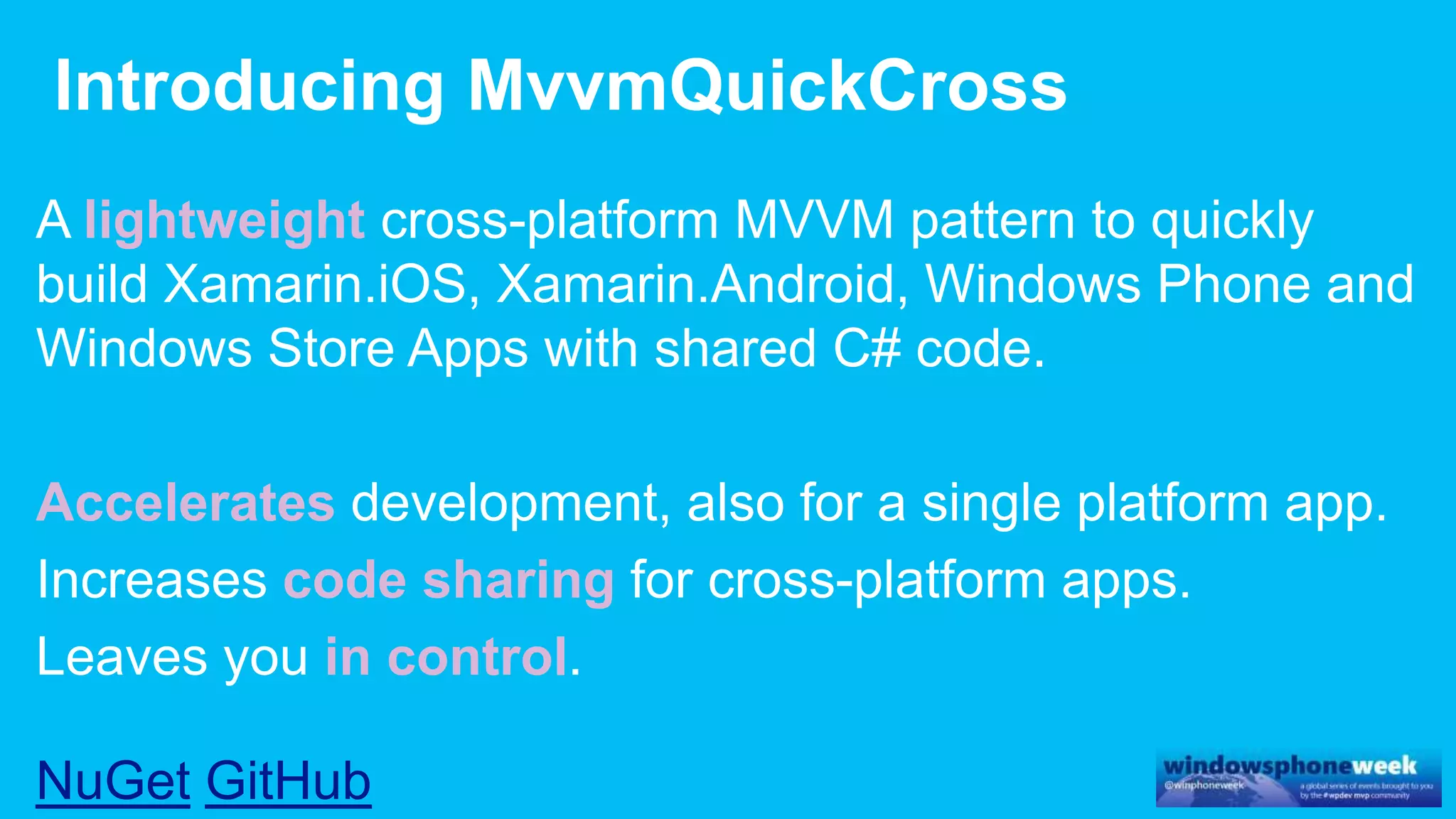
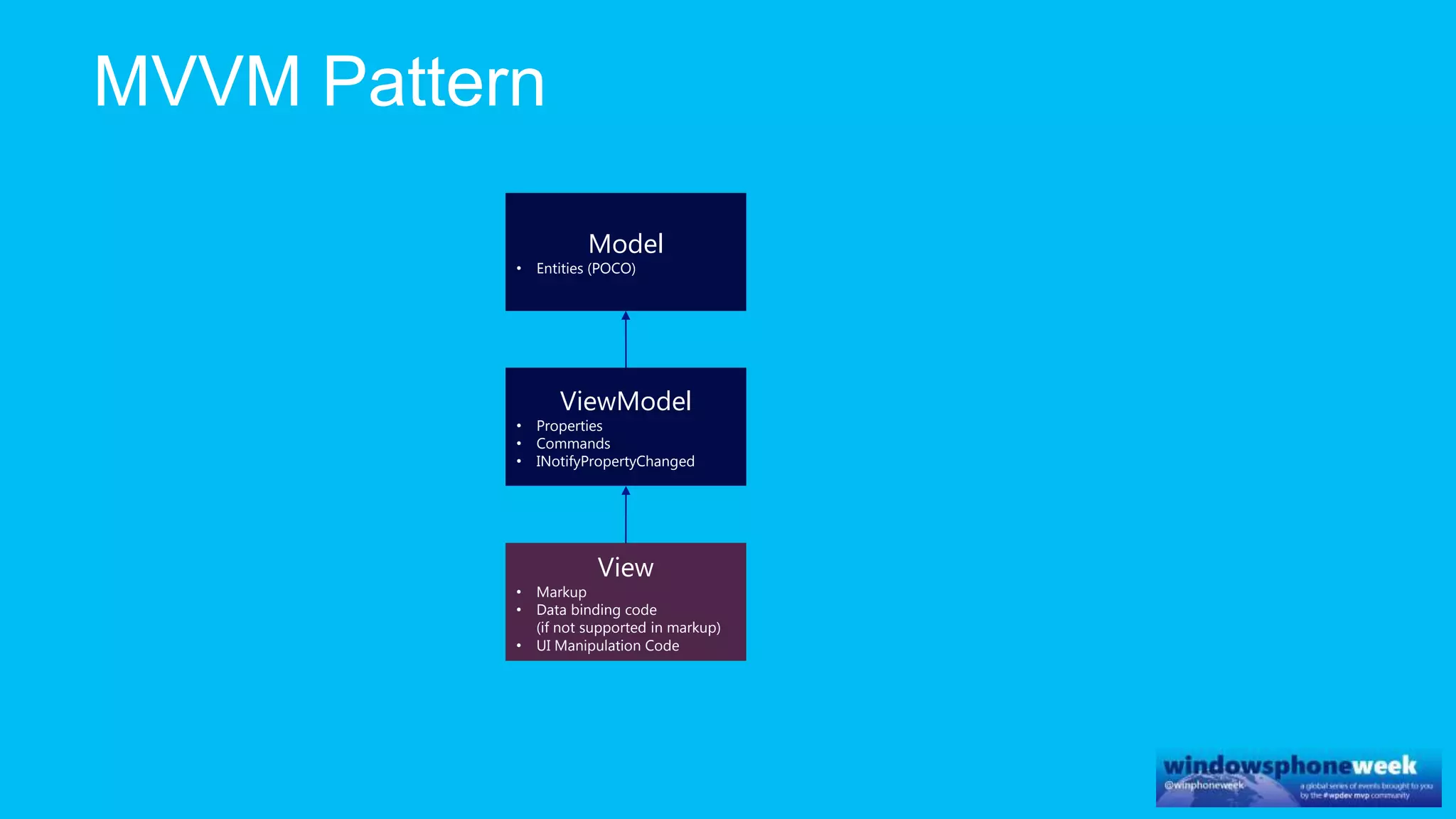
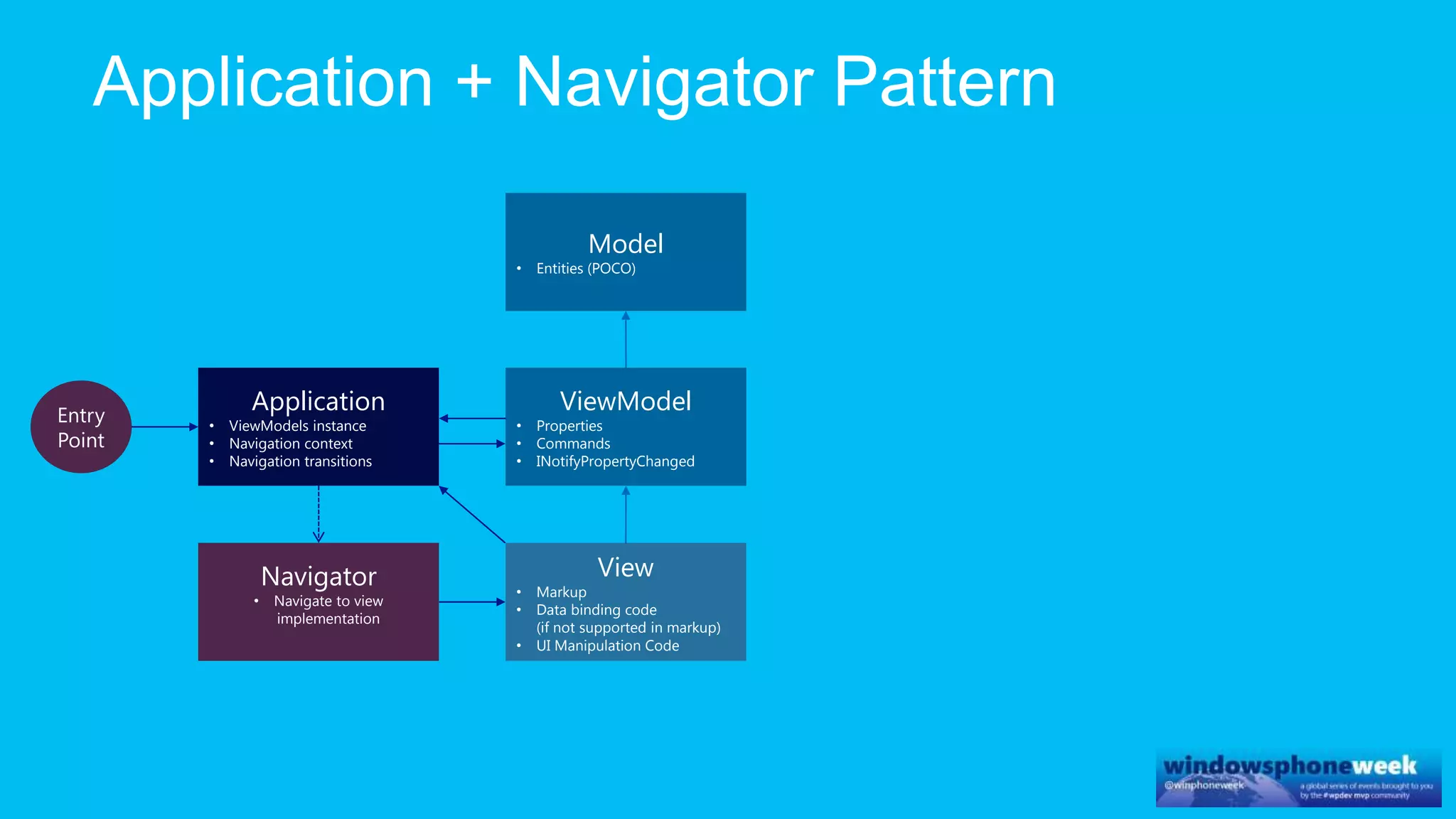
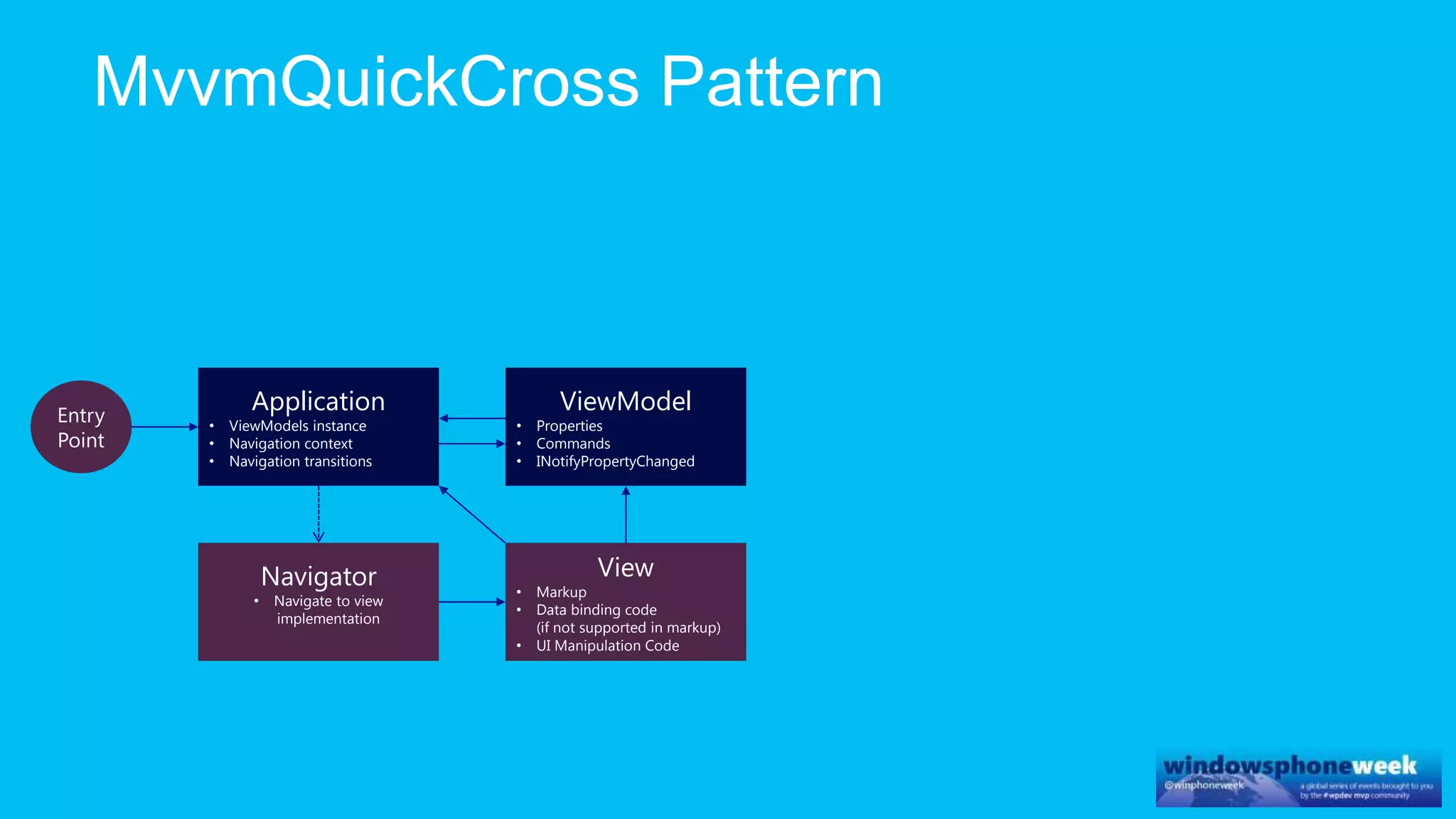
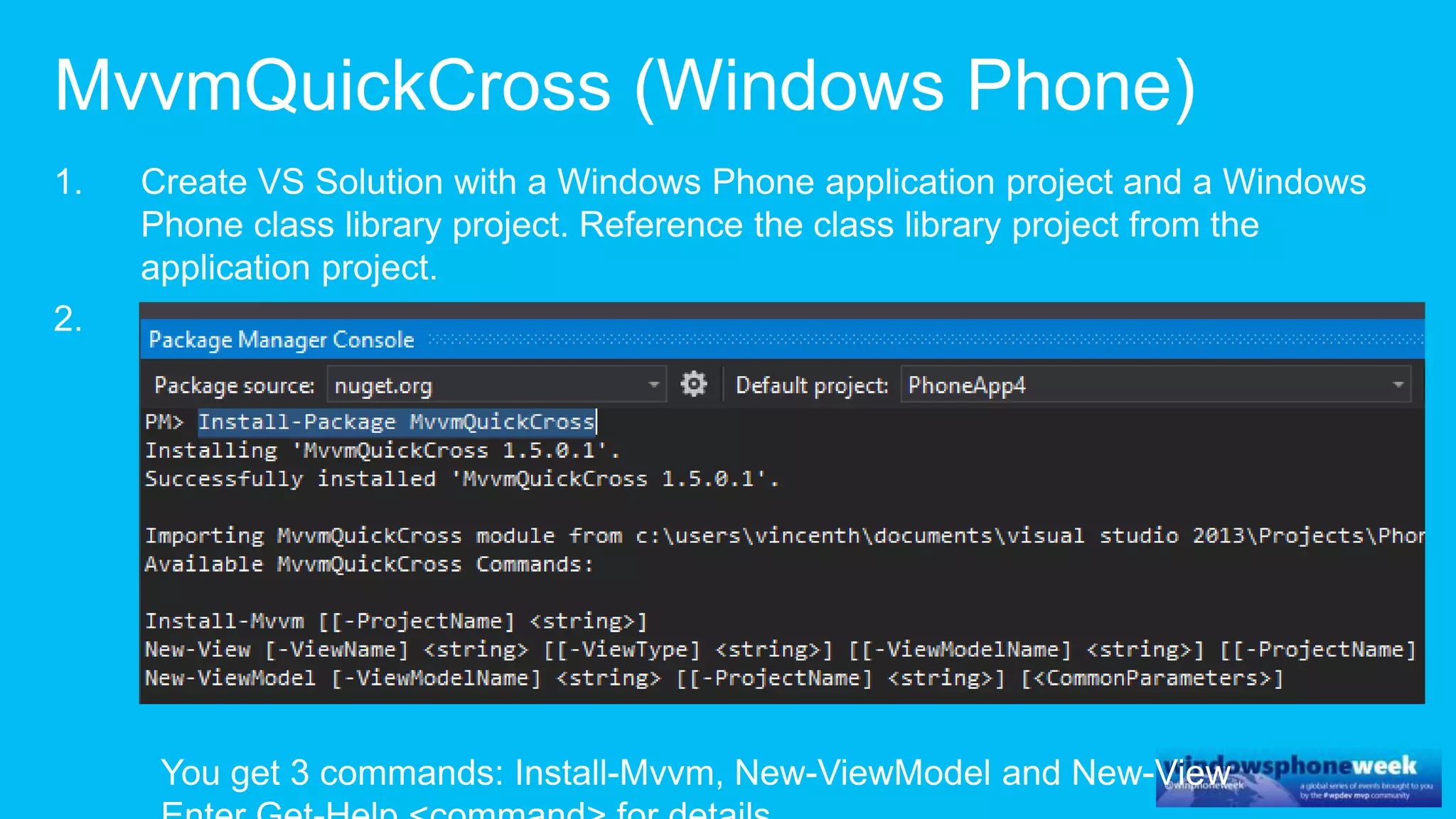
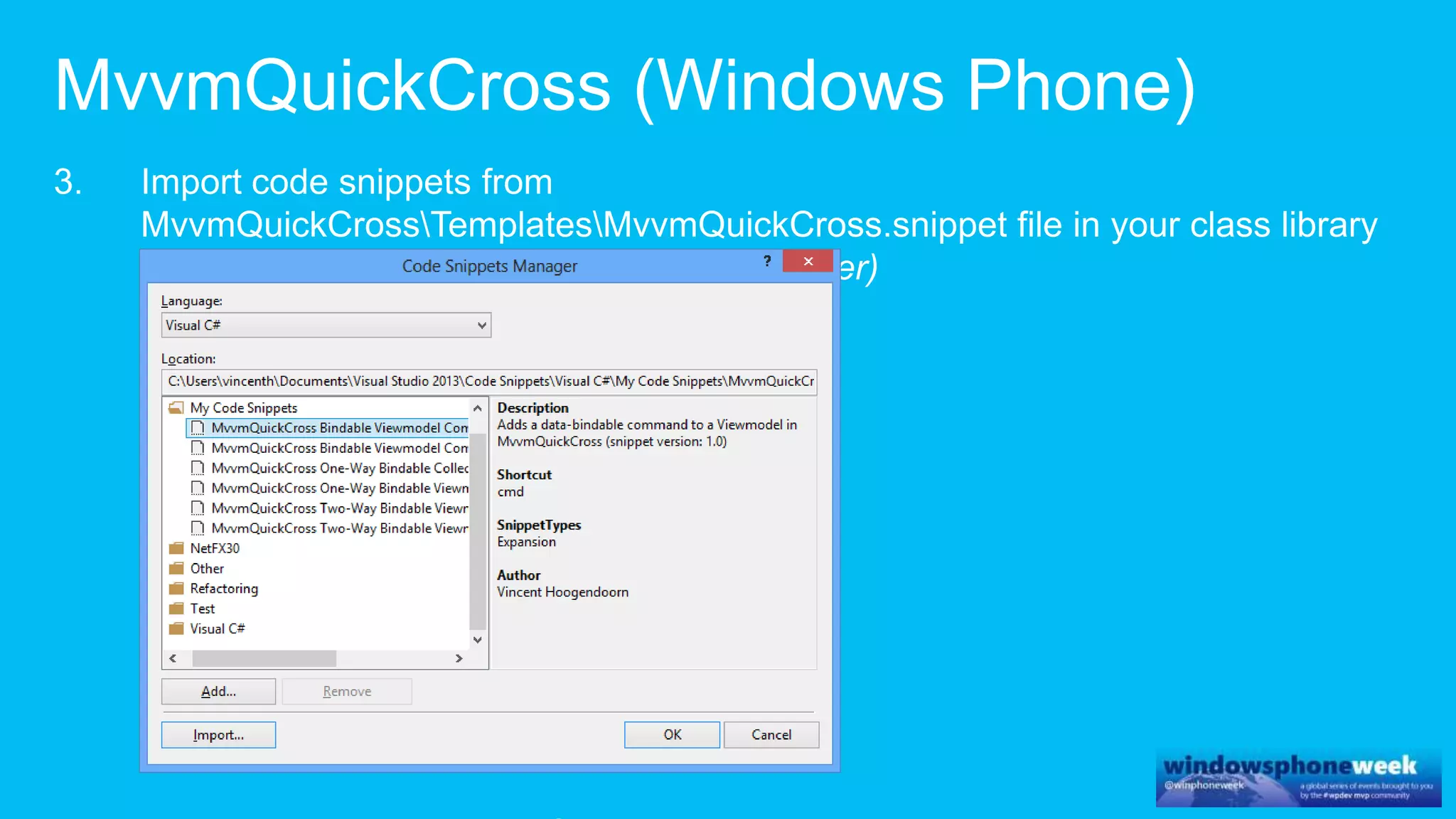
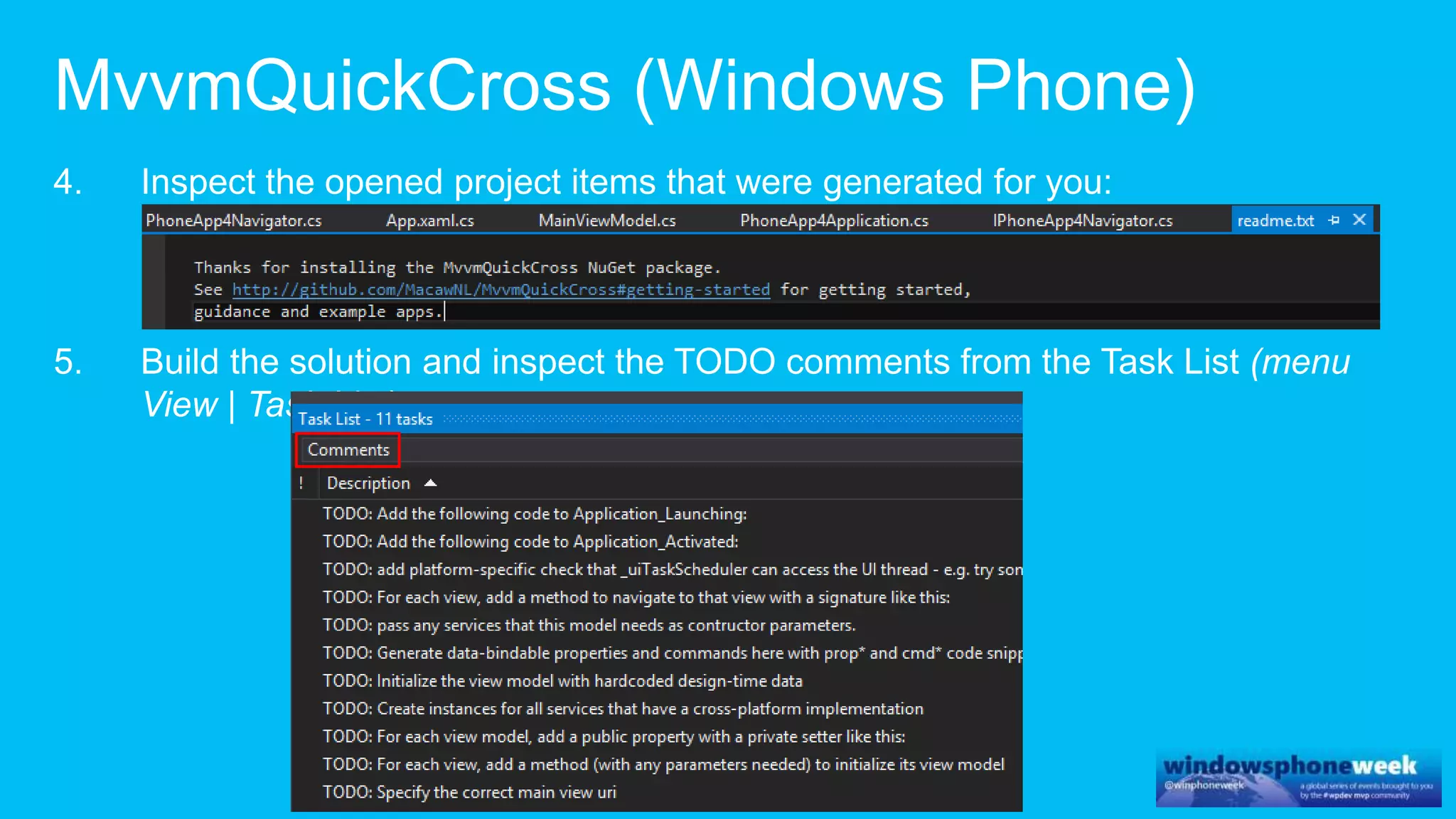
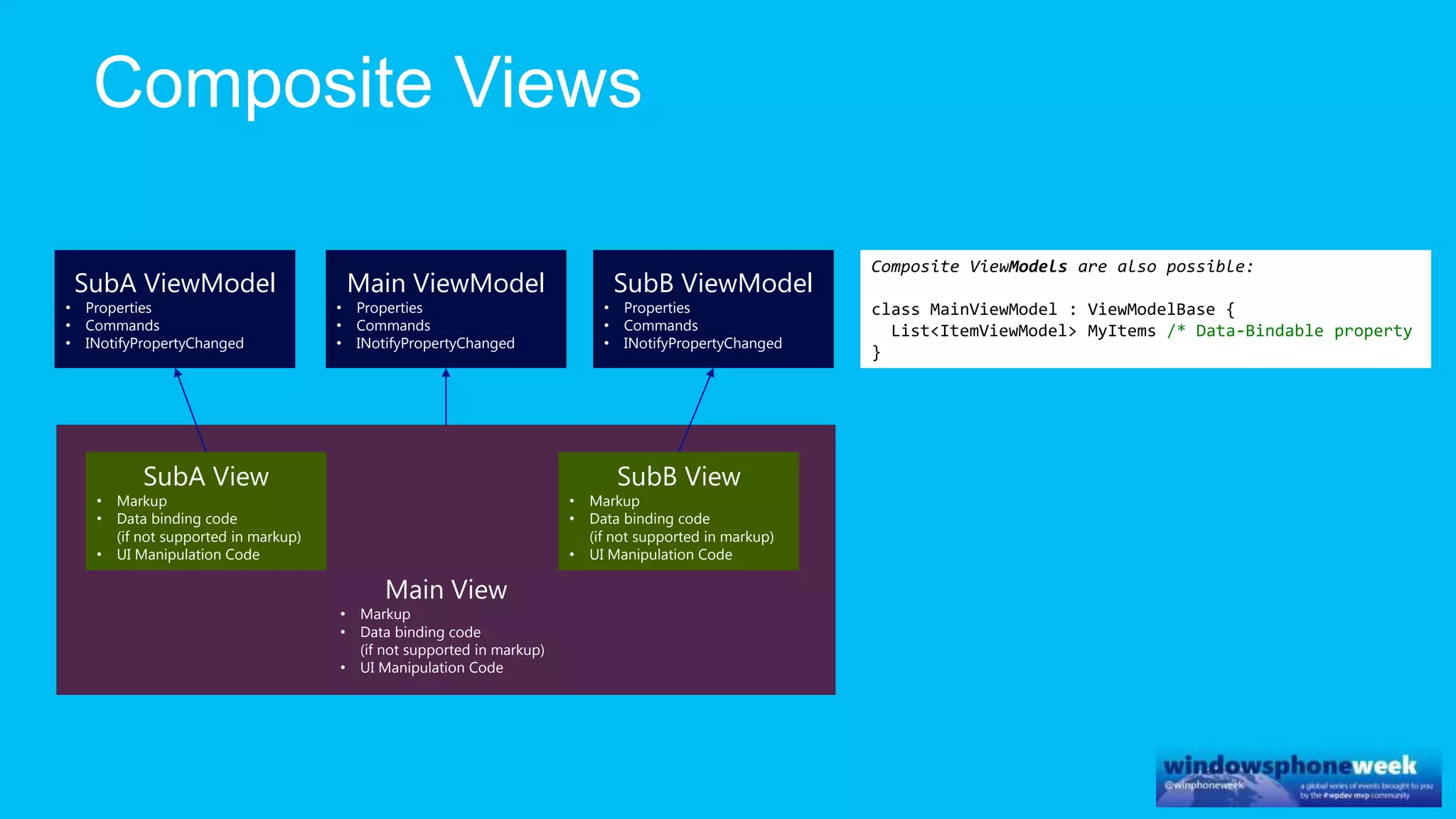
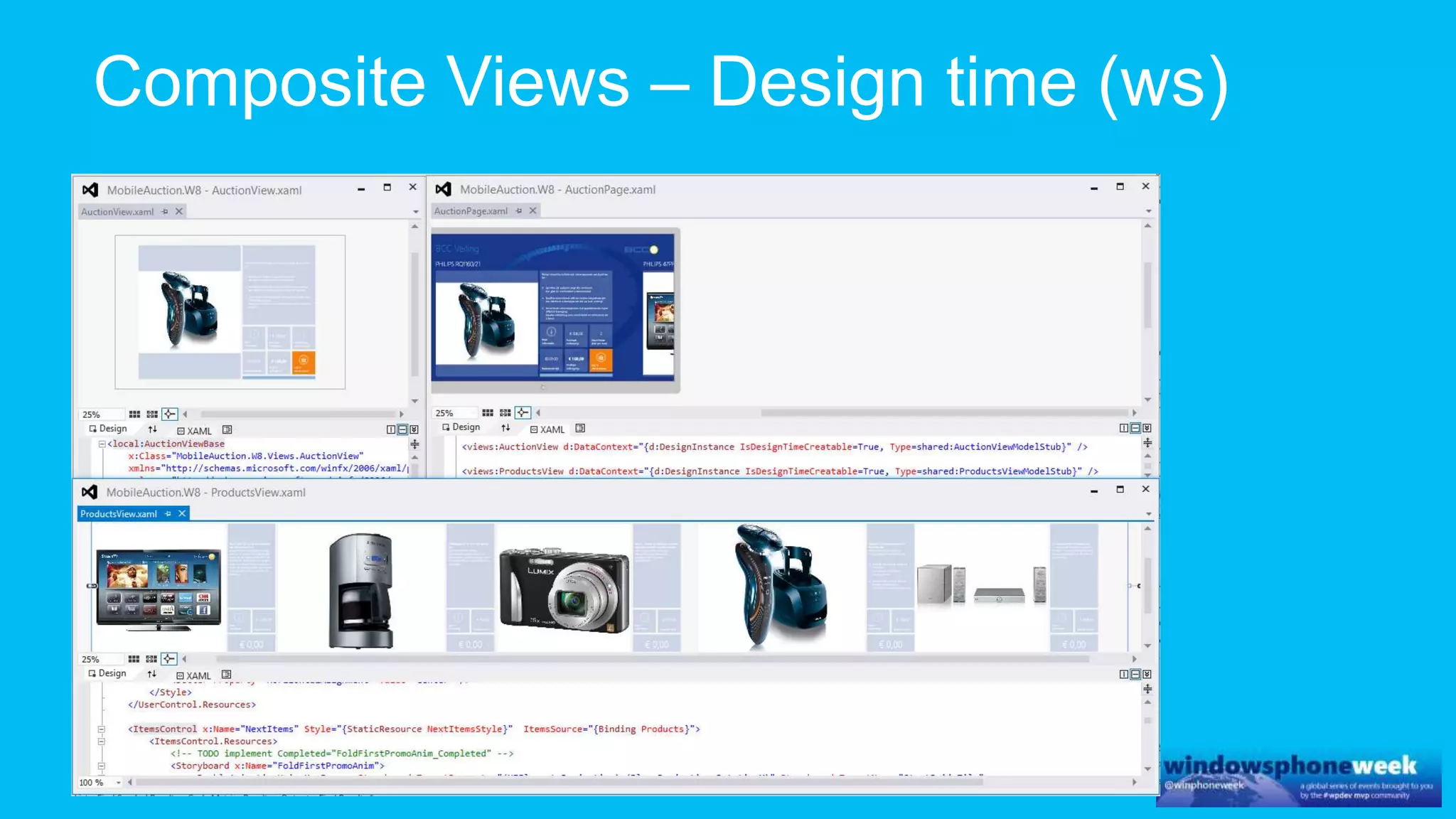
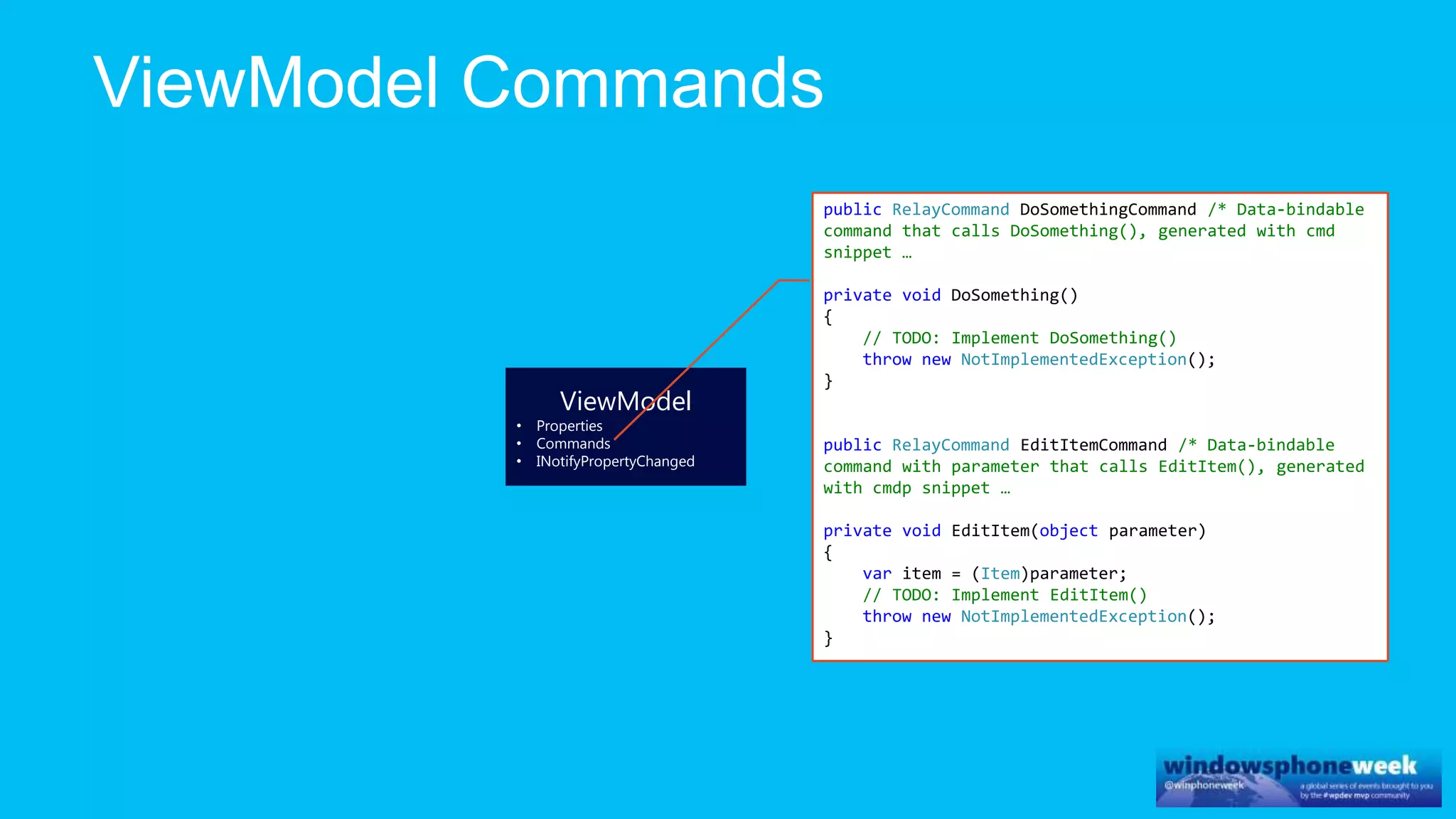
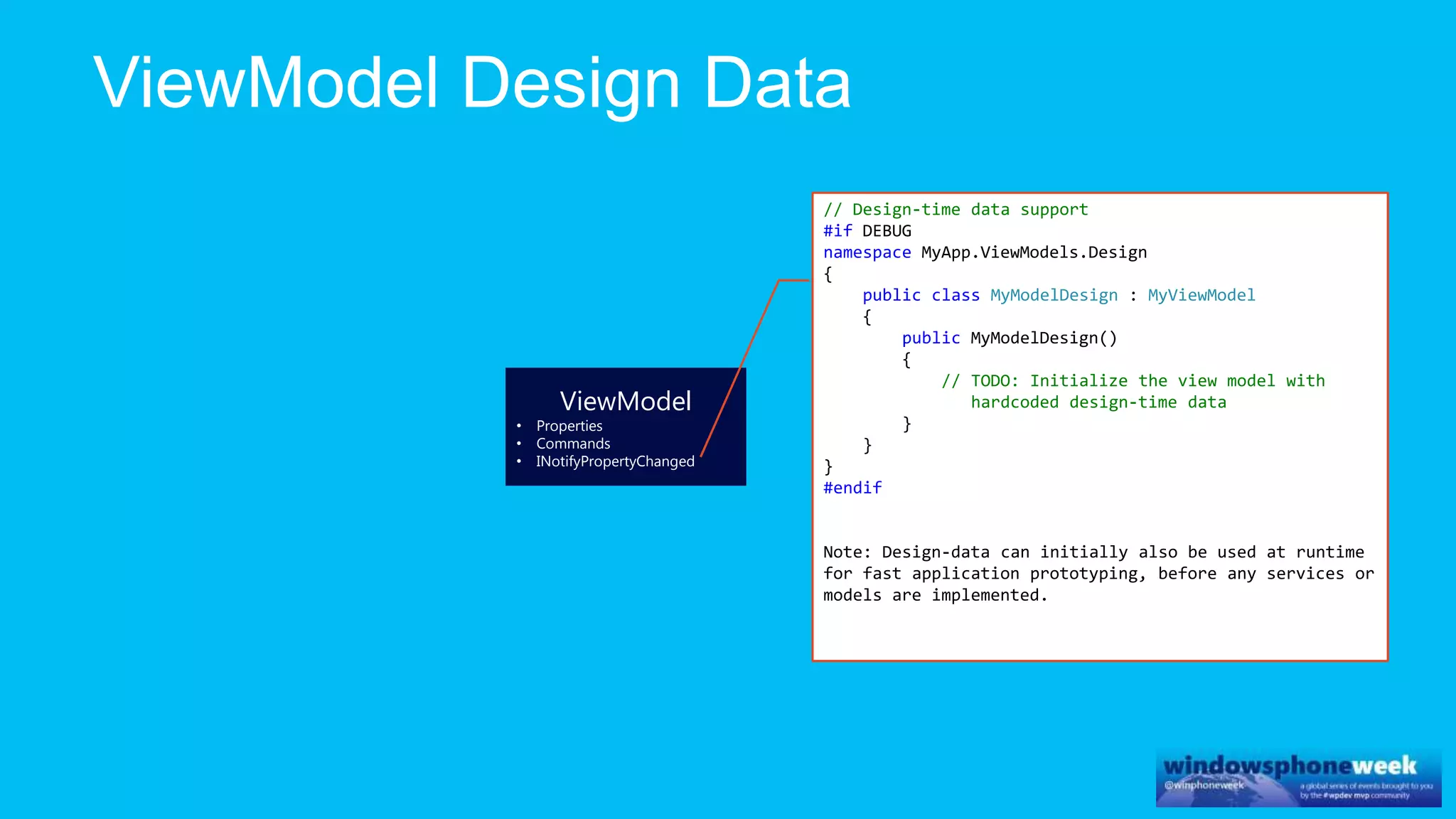
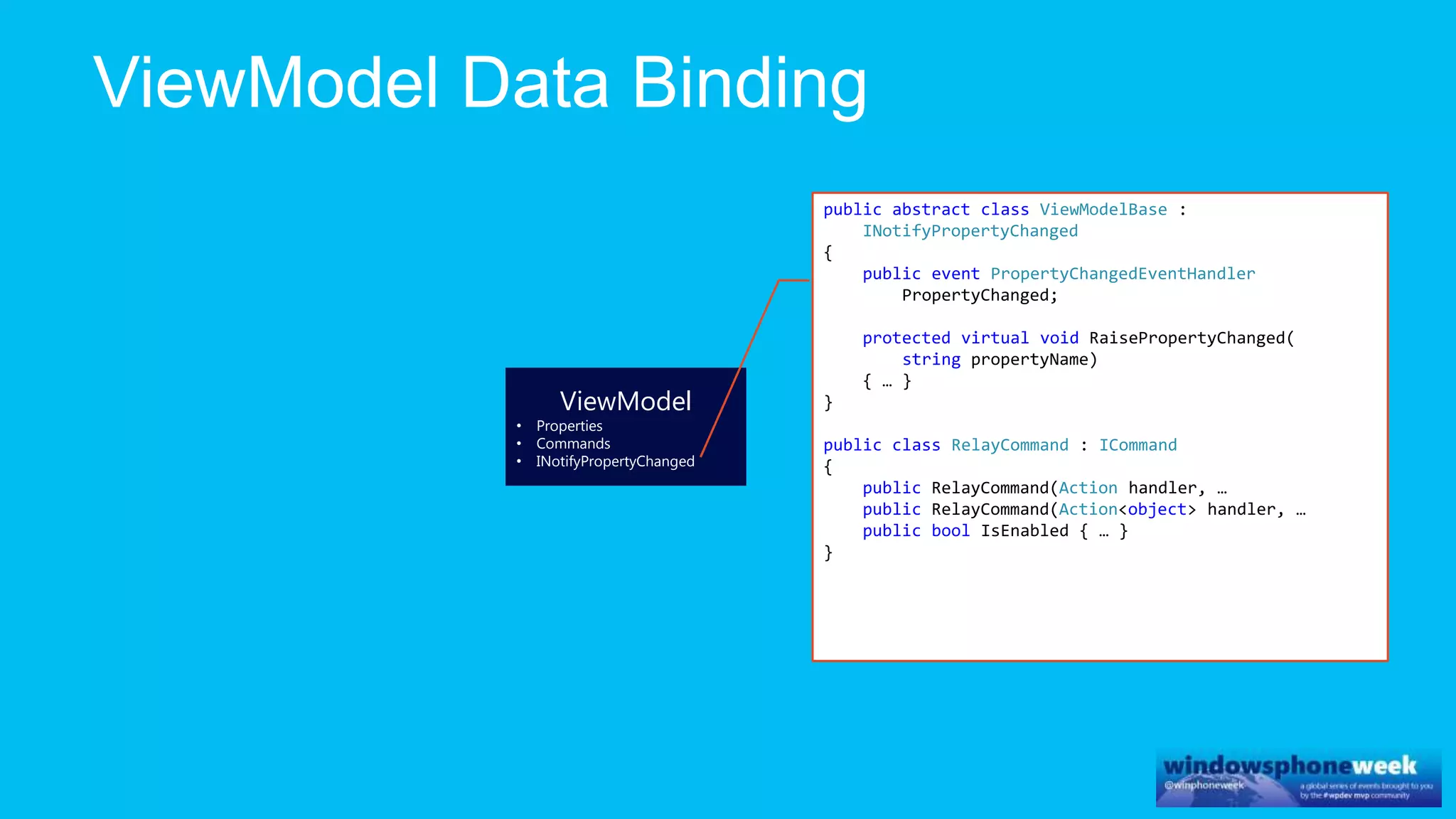
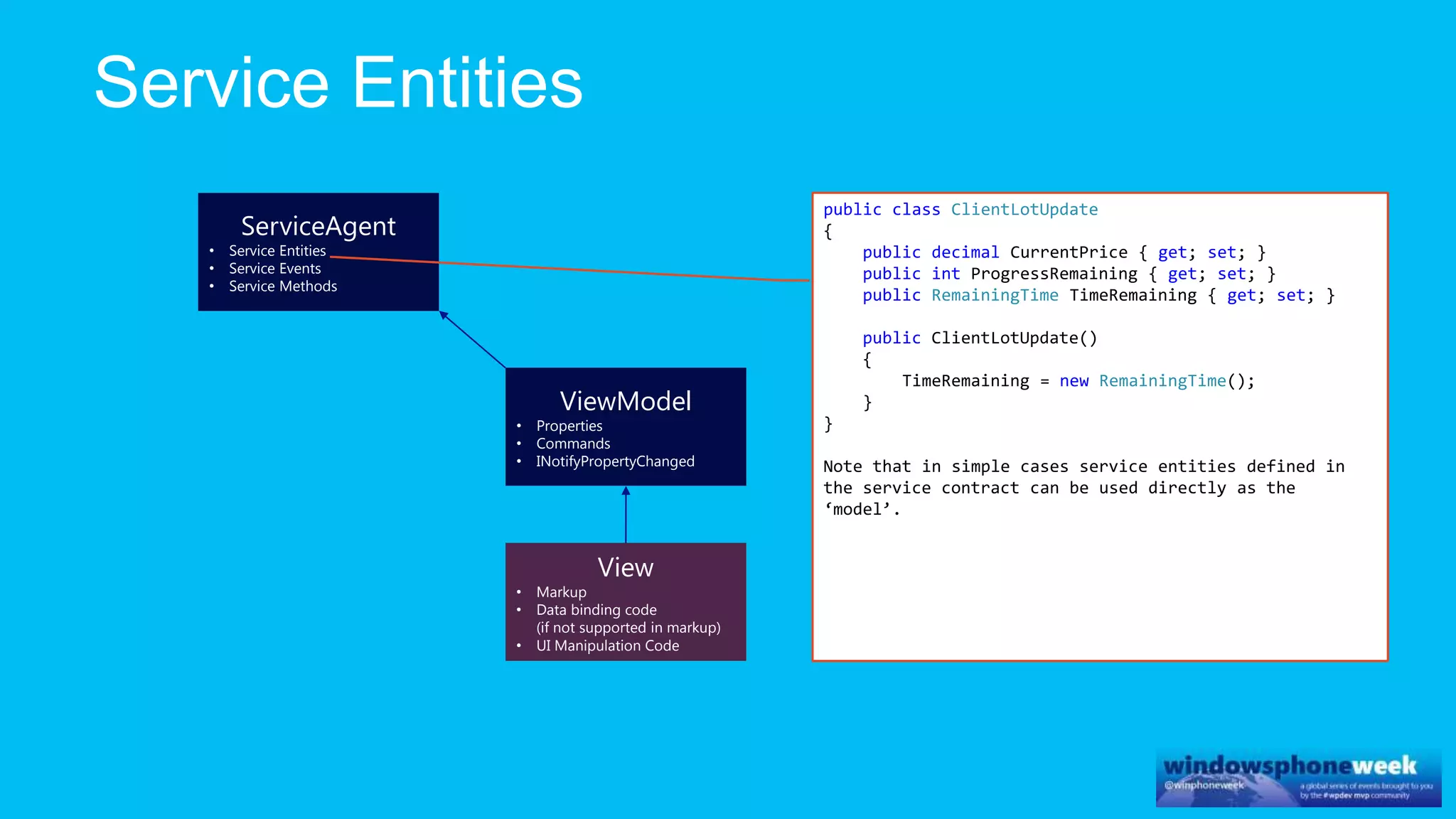
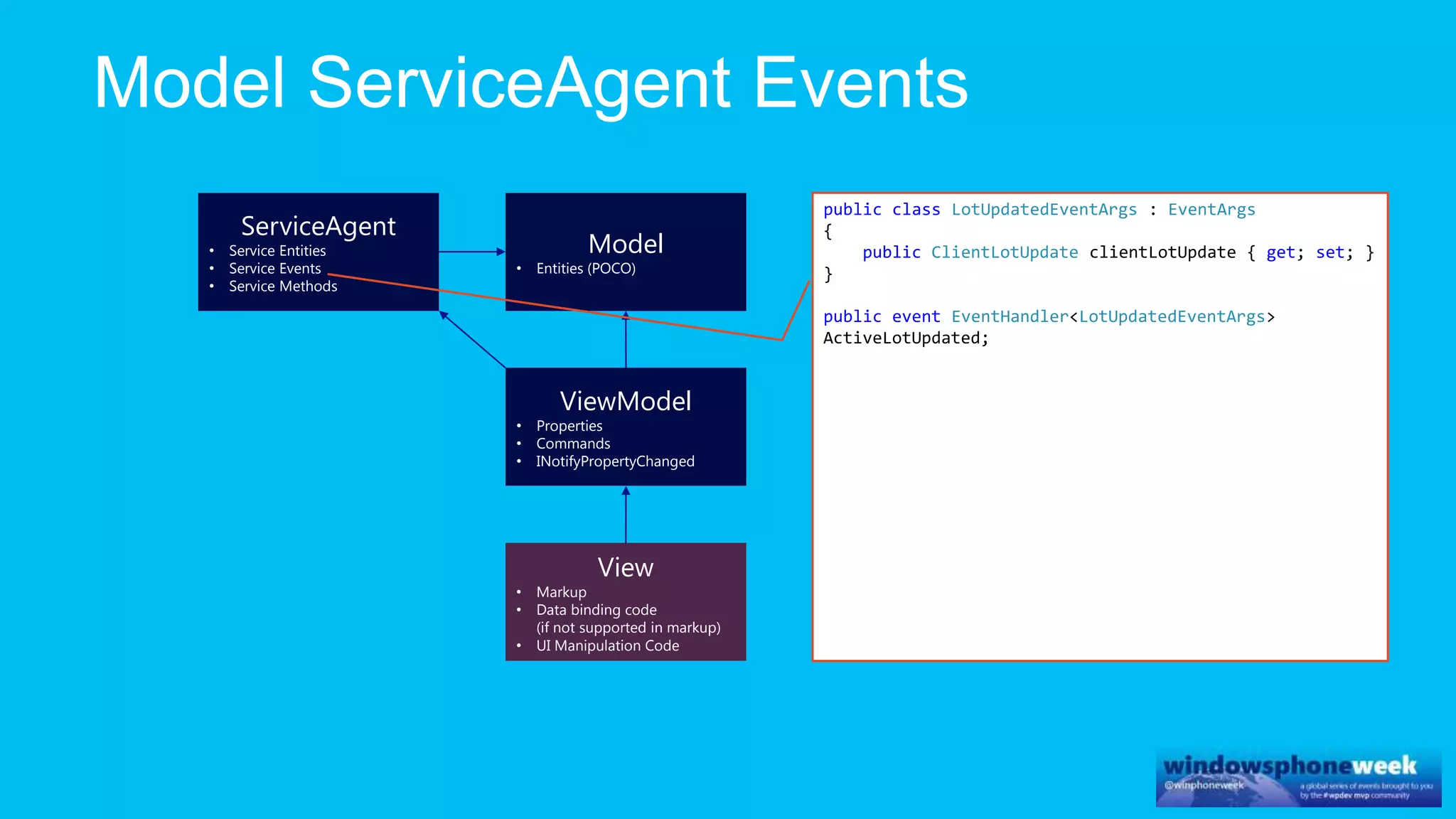
MvvmCross is a cross-platform MVVM framework that allows for sharing code and user interfaces across platforms. It uses the MVVM pattern with ViewModels, Models, and Views. ViewModels contain properties, commands, and notify of property changes. Models contain plain-old CLR object entities. Services can be used to access back-end services and events. The Application handles navigation between ViewModels and application states. The Navigator performs platform-specific navigation between Views. Runtime flow involves the EntryPoint instantiating Application and Navigator, then navigating between Views and ViewModels in response to user input and service events.








![ViewModel
• Properties
• Commands
• INotifyPropertyChanged
Model
• Entities (POCO)
ServiceAgent
• Service Entities
• Service Events
• Service Methods
View
• Markup
• Data binding code
(if not supported in markup)
• UI Manipulation Code
public class PlaceBidRequest
{
public int LotId { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
}
public Task RaisePlaceBidAsync(PlaceBidRequest
placeBidRequest)
{
return _hubProxy.Invoke(
"PlaceBid",
new object[] { placeBidRequest });
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mvvmquickcross-windowsphonedevday2013-131005125610-phpapp01/75/MvvmQuickCross-for-Windows-Phone-25-2048.jpg)