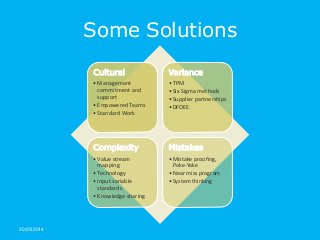
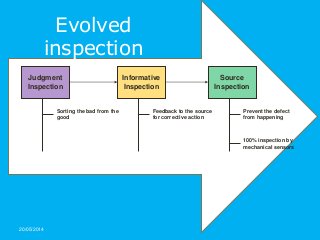
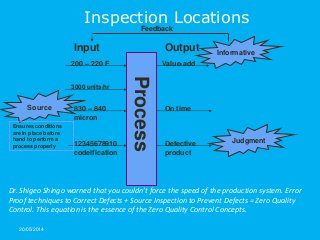
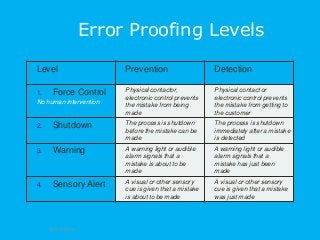
Today the achievement of world class quality levels or zero defect is the new competitive edge. With highly and global competitive markets even one error can cause the loss of a customer or expensive corrective actions. Error proofing techniques are required to achieve these world class levels