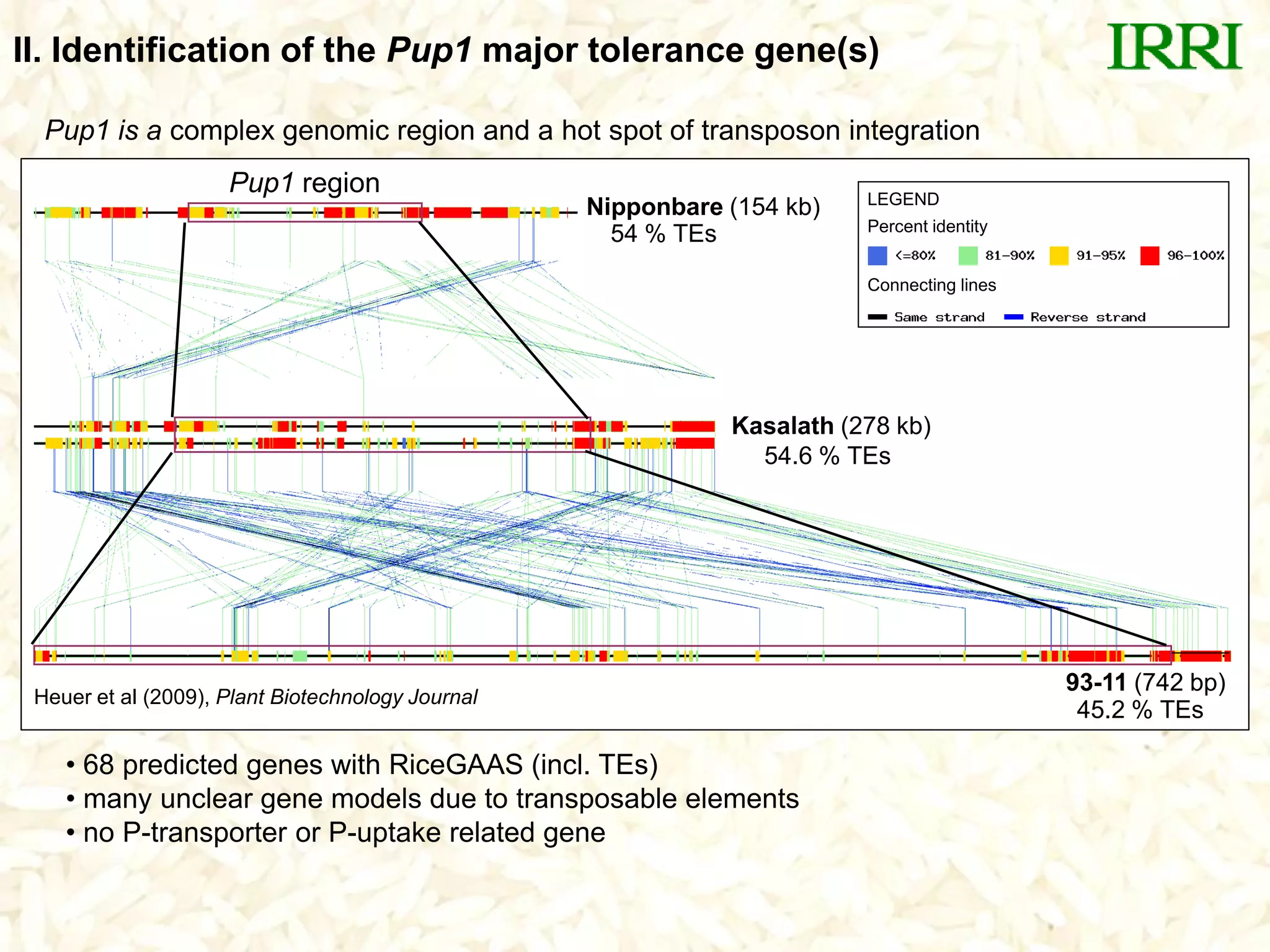
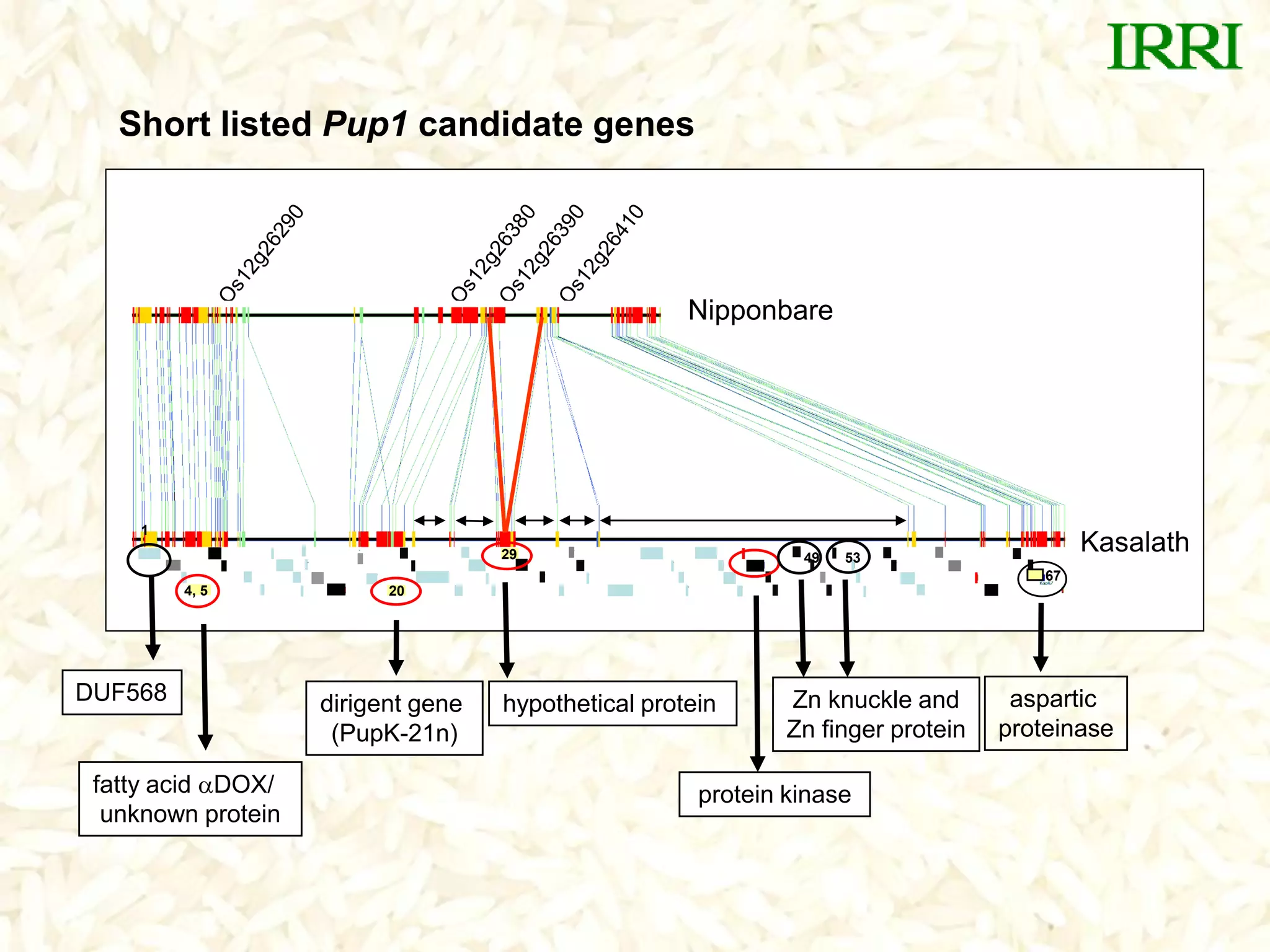
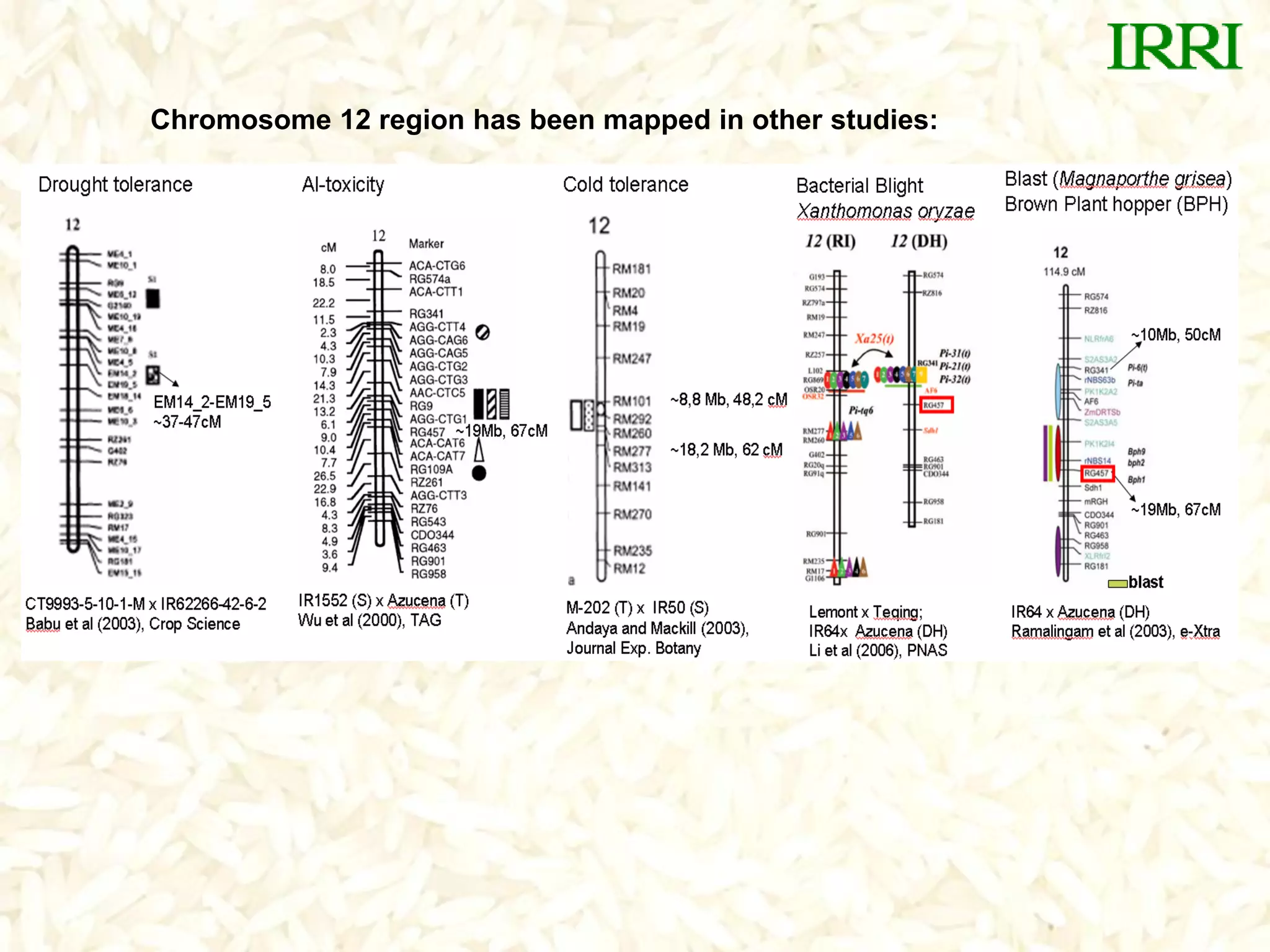
The document discusses research on developing rice varieties with tolerance to phosphorus deficiency and aluminum toxicity. Key points include:
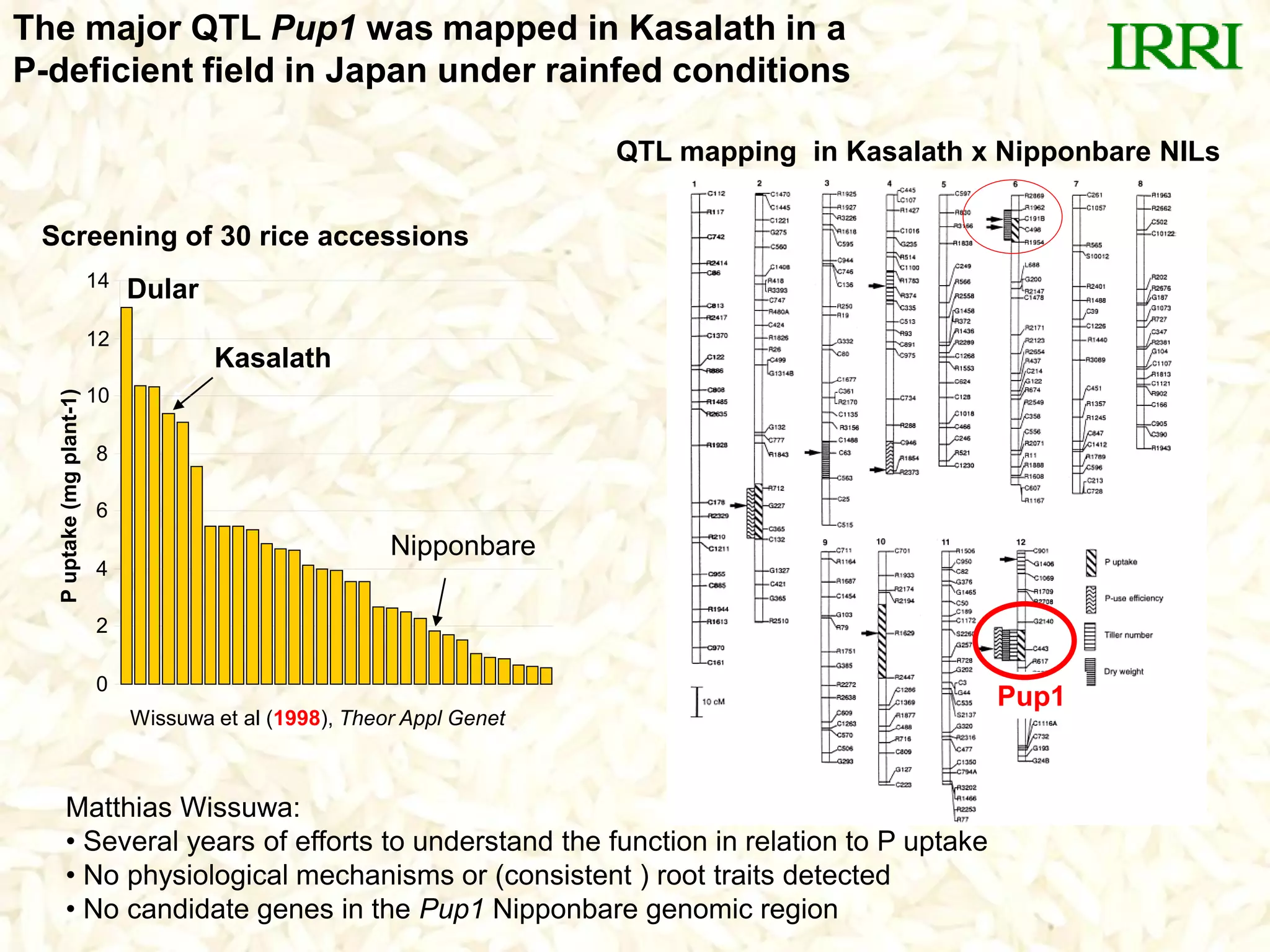
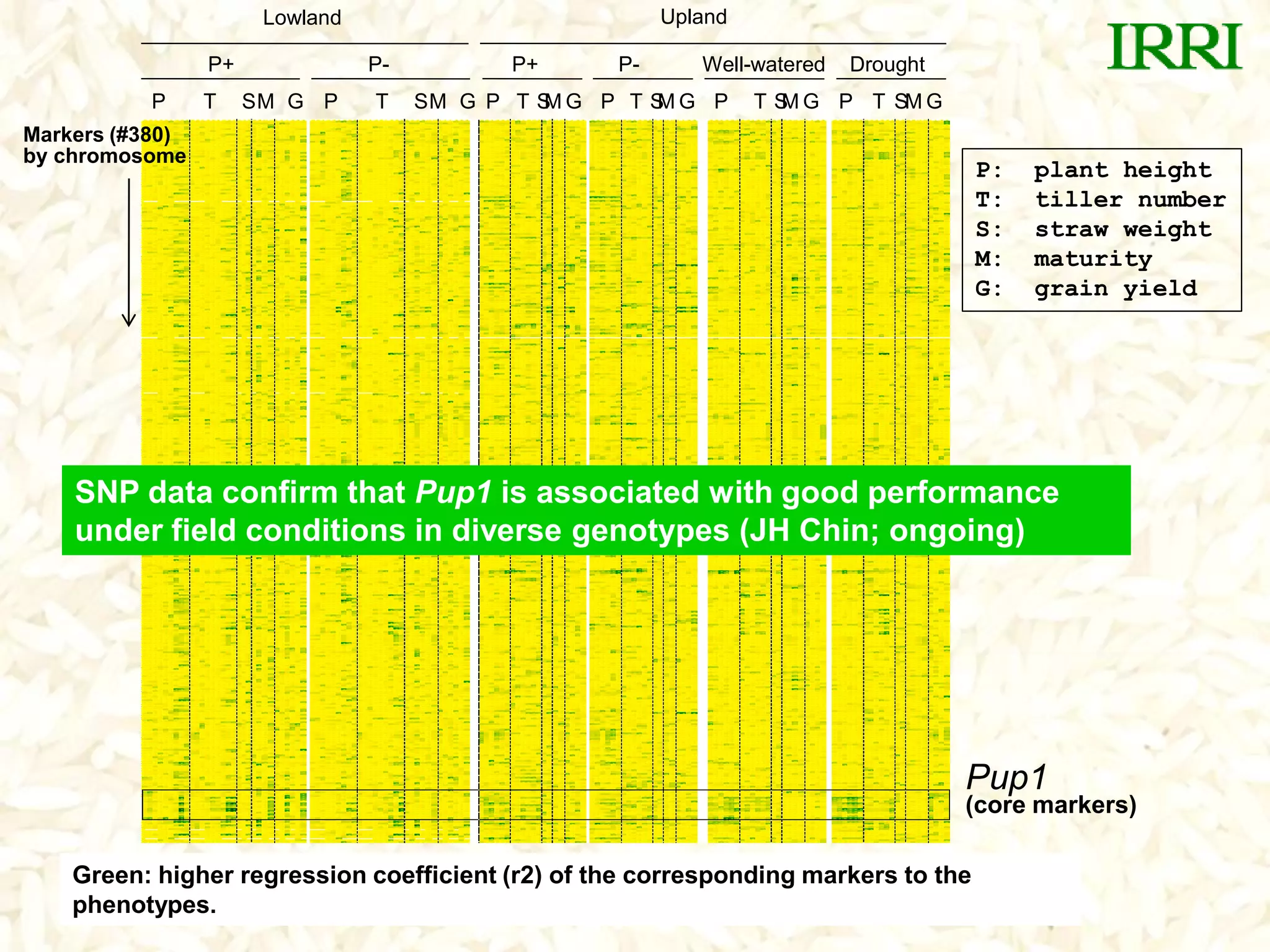
- The Pup1 QTL for phosphorus uptake was mapped in the rice variety Kasalath. Several years of research was unable to identify the physiological mechanism or candidate genes responsible for this trait.
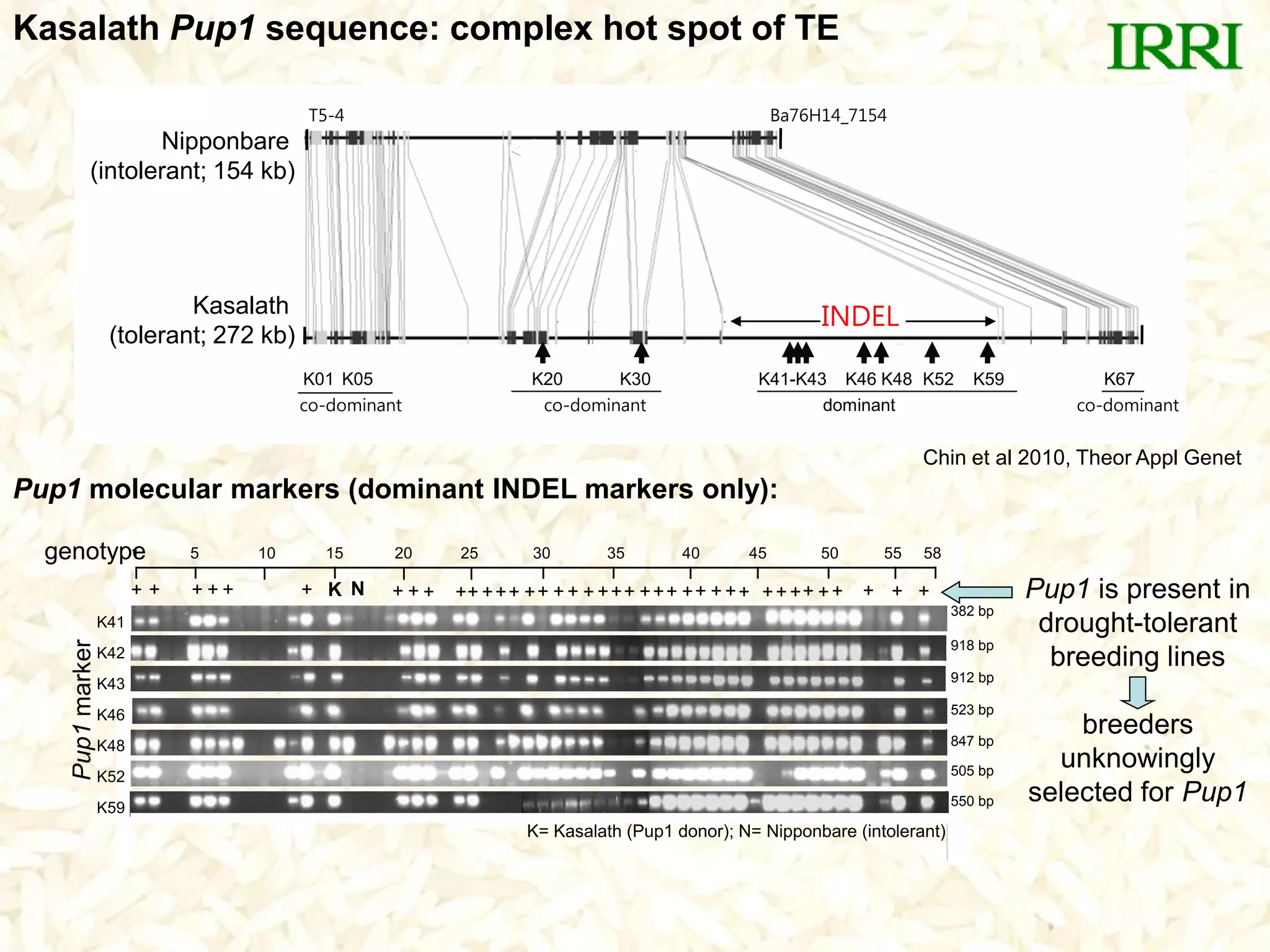
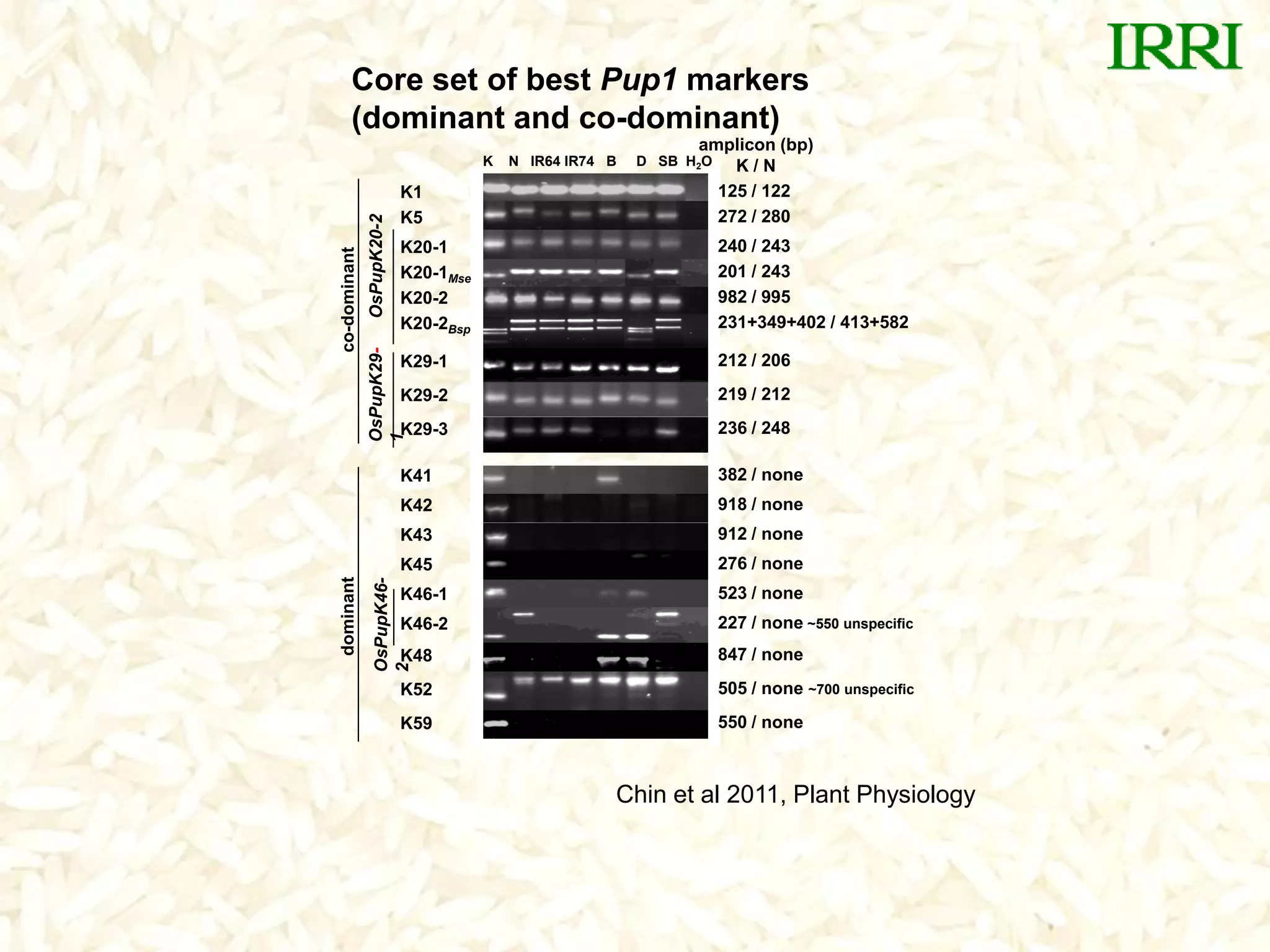
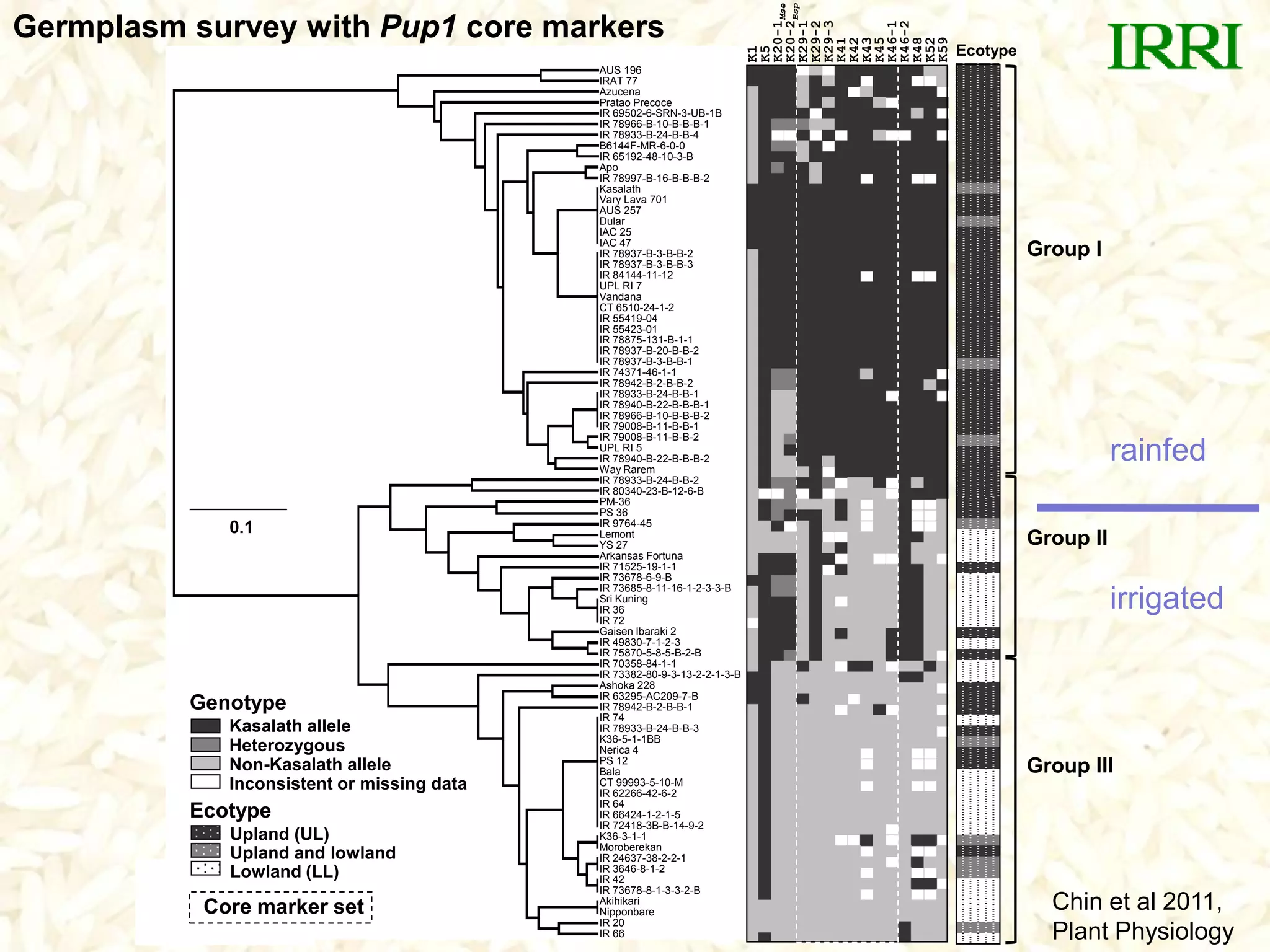
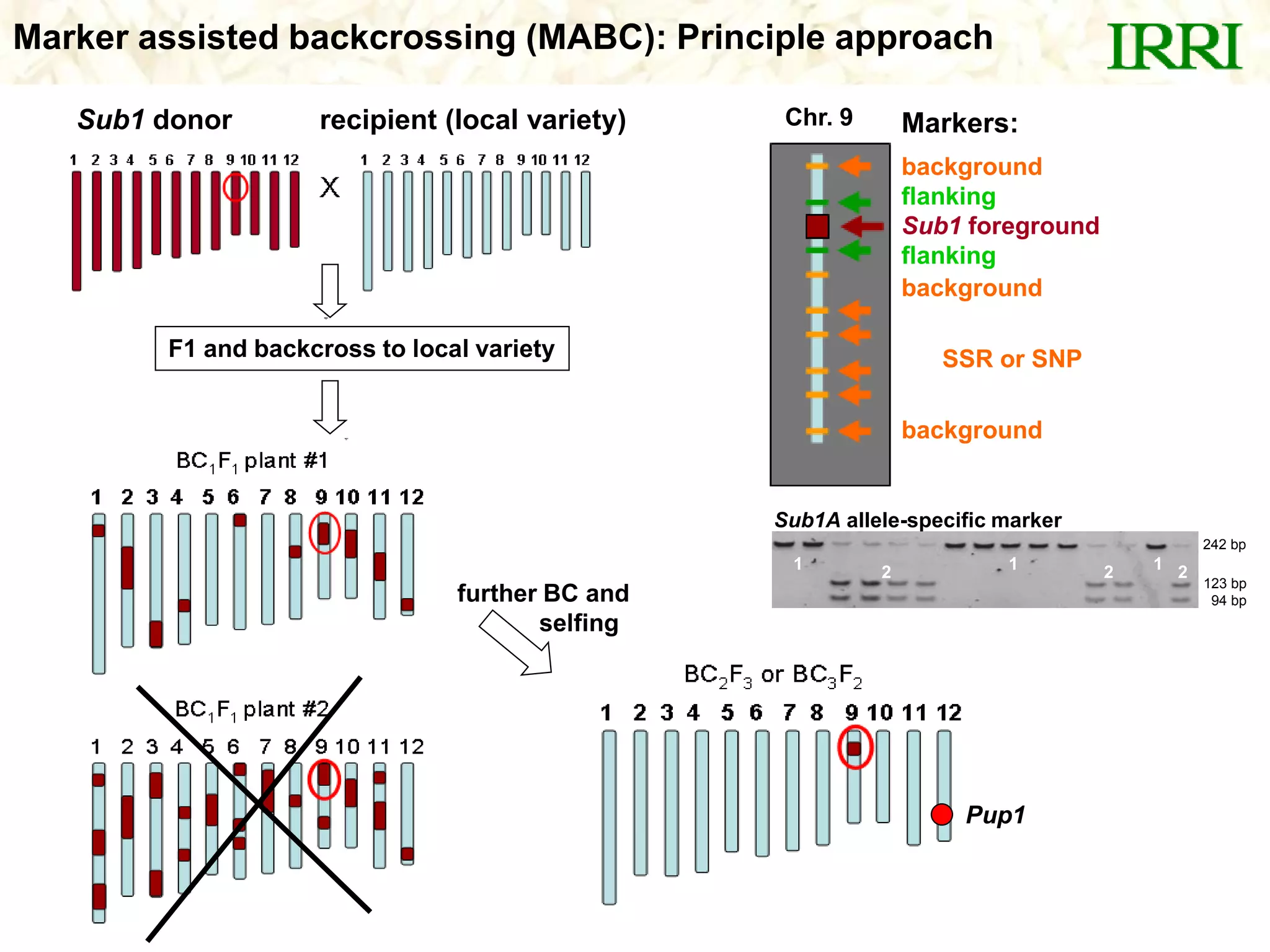
- A set of Pup1 gene-specific markers were developed, including dominant and co-dominant markers. These were used to survey germplasm and identify varieties possessing the Pup1 allele.
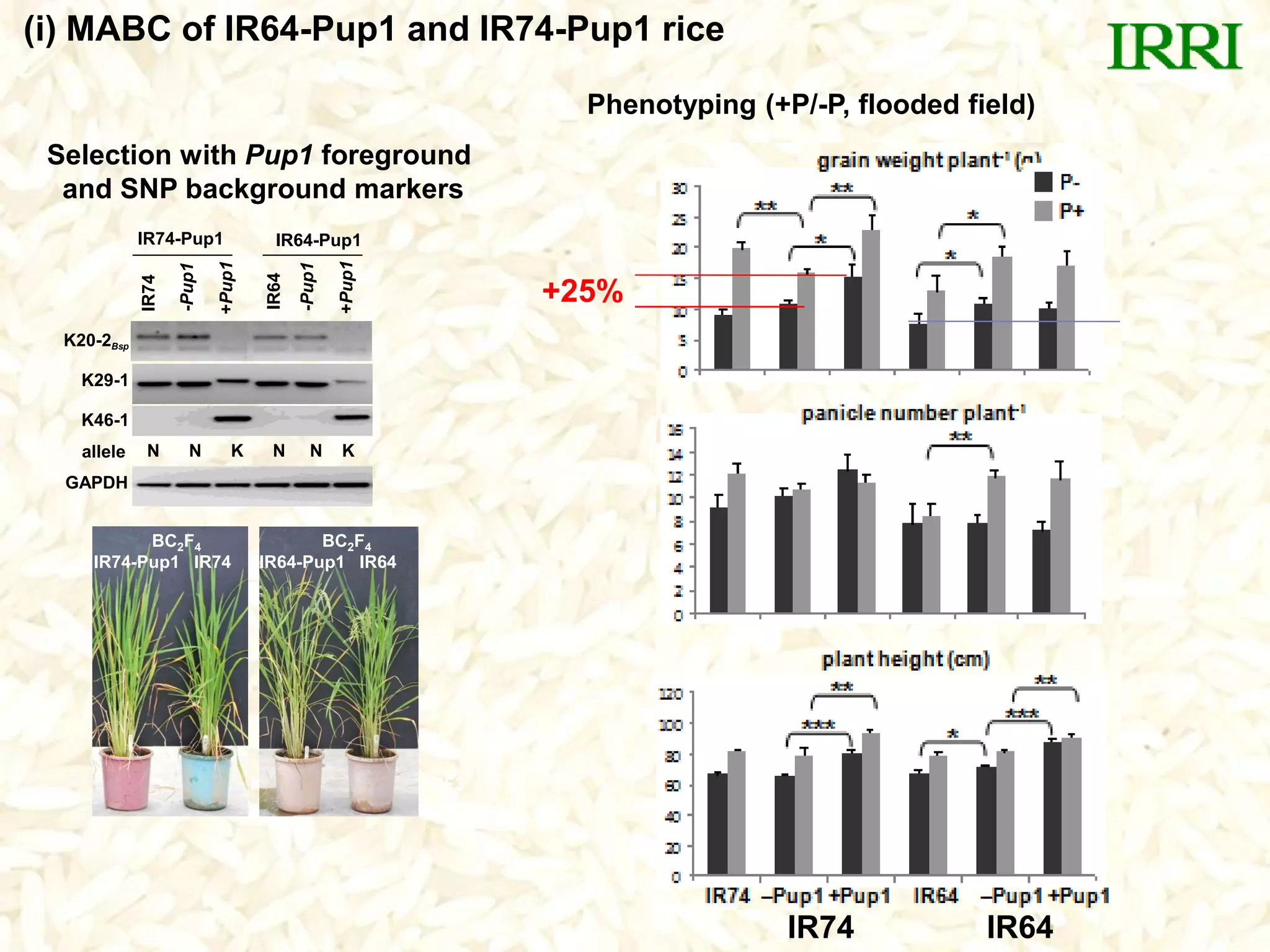
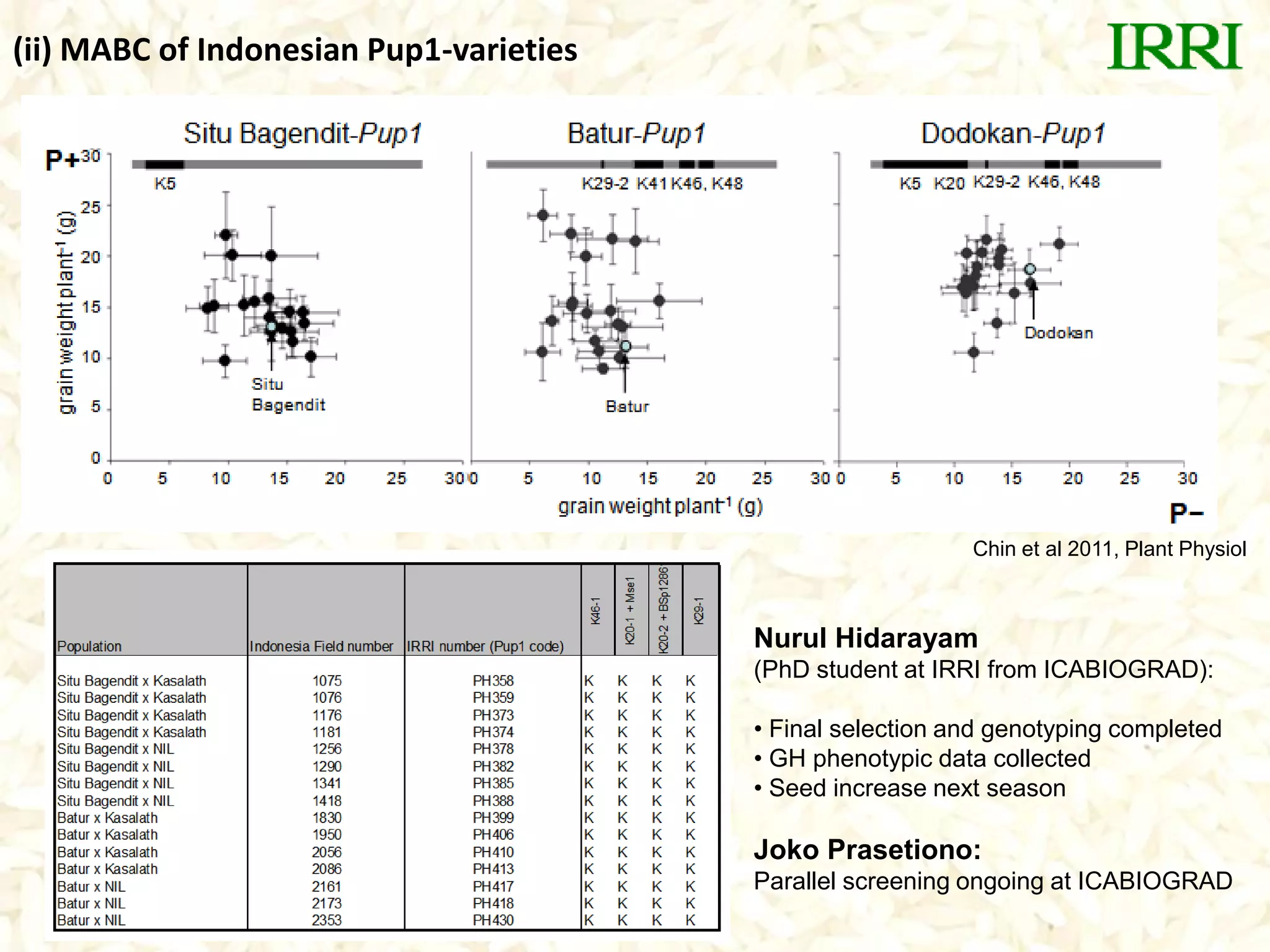
- Marker-assisted backcrossing was used to introgress the Pup1 allele into high-yielding recipient varieties like IR64 and IR74. Initial field trials show the introgressed lines have improved