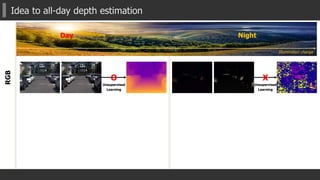
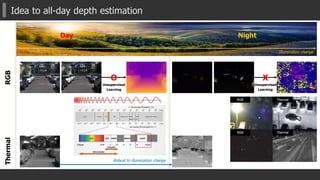
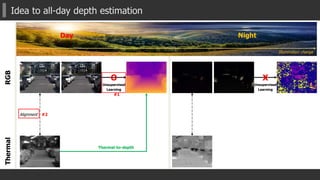
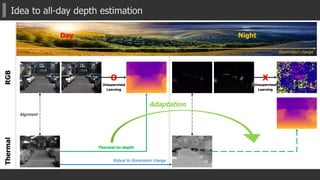
The document presents a novel multispectral transfer network (MTN) for unsupervised depth estimation that operates effectively under varying lighting conditions throughout the day and night. It discusses the architecture of MTN, which utilizes multi-task learning to predict depth, surface normals, and semantic labels from thermal and RGB inputs, along with specific components like interleaver modules and adaptive scaled sigmoid functions for enhanced training stability. Experimental results demonstrate MTN's competitive performance in both day and night scenarios compared to traditional depth estimation methods.



![Related works
Single image based depth estimation
Supervised depth estimation
Unsupervised depth estimation
Semi-supervised depth estimation
Supervised depth estimation
Supervised [NIPS’14, CVPR’15, ICCV’15, NIPS’16, PAMI’16]
Semi-supervised [CVPR’17]
Unsupervised [ECCV’16, 3DV’16, CVPR’17]
Unsupervised depth estimation
Semi-supervised depth estimation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aaai2018mtn2-180221144721/85/AAAI2018-Multispectral-Transfer-Network-Unsupervised-Depth-Estimation-for-All-day-Vision-5-320.jpg)




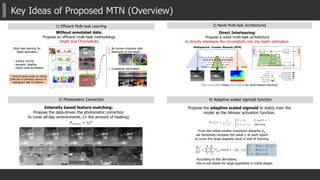


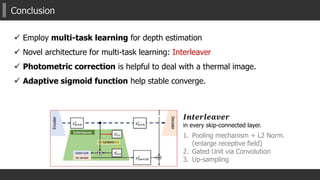
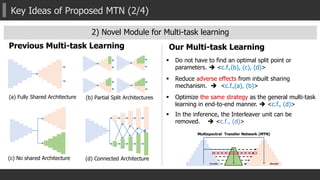
![Key Ideas of Proposed MTN (2/4)
2) Novel Module for Multi-task learning
1. Global/Un-Pooling + L2 Norm.
Enlarge receptive field [ParseNet] + feature transformation
2. Gating mechanism
Control the degree of the effectiveness of another task
to the main task. (especially in back-propagation).
3. Up-sampling and adding to previous output
Equipped in every skip-connected flows
(fully-connections between layers)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aaai2018mtn2-180221144721/85/AAAI2018-Multispectral-Transfer-Network-Unsupervised-Depth-Estimation-for-All-day-Vision-17-320.jpg)


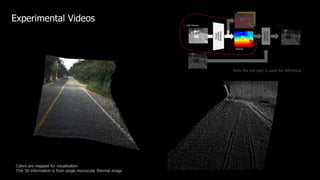
![Experimental results: Day
MTN
GT
ColorThermal
Single Task LsMTN DsMTN MTN-P DIW [NIPS’16]
Without
Binary error map (error > 3 pixels)
[Eigen, NIPS2014]
[DIW, NIPS2016]
Daytime
1~50m Methods
STN LsMTN DsMTN MTN-P MTN STN-RGB Eigen-RGB Eigen-T DIW-RGB DIW-T
Distance *Lower is better
RMS 7.7735 6.6967 6.3671 7.0058 6.0786 7.5876 10.1792 10.2660 6.4993 6.4427
Log RMS 0.2000 0.1801 0.1761 0.1951 0.1714 0.2094 0.2386 0.2384 0.1934 0.1967
Abs. Relative 0.1531 0.1325 0.1259 0.1413 0.1207 0.1570 0.1992 0.1976 0.1644 0.1697
Sq. Relative 2.2767 1.6322 1.4394 1.7251 1.3119 2.0618 4.0629 4.0835 1.8030 1.7543
Accuracy *Higher is better
δ<1.25 0.8060 0.8358 0.8407 0.8040 0.8451 0.7772 0.7551 0.7561 0.7956 0.7825
δ<1.252
0.9337 0.9492 0.9544 0.9440 0.9557 0.9378 0.8965 0.8947 0.9482 0.9454
δ<1.253
0.9776 0.9842 0.9855 0.9827 0.9868 0.9806 0.9612 0.9618 0.9842 0.9851](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aaai2018mtn2-180221144721/85/AAAI2018-Multispectral-Transfer-Network-Unsupervised-Depth-Estimation-for-All-day-Vision-22-320.jpg)
![Experimental results: Night
MTNSingle Task MTN-P DIW [NIPS’16]
Without
Nighttime
1~50m Methods
STN LsMTN DsMTN MTN-P MTN STN-RGB Eigen-RGB Eigen-T DIW-RGB DIW-T
Ordinal Accuracy *Higher is better
ξ<10 0.3233 0.3405 0.3745 0.3096 0.4666 0.2508 0.1728 0.2033 0.1404 0.3744
ξ<20 0.6237 0.6855 0.6820 0.6225 0.7026 0.3284 0.2442 0.6178 0.3176 0.7459
ξ<30 0.7317 0.7753 0.7797 0.7397 0.7757 0.3592 0.3064 0.7516 0.3805 0.8401
[Eigen, NIPS2014]
[DIW, NIPS2016]
GT
ColorThermal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aaai2018mtn2-180221144721/85/AAAI2018-Multispectral-Transfer-Network-Unsupervised-Depth-Estimation-for-All-day-Vision-23-320.jpg)