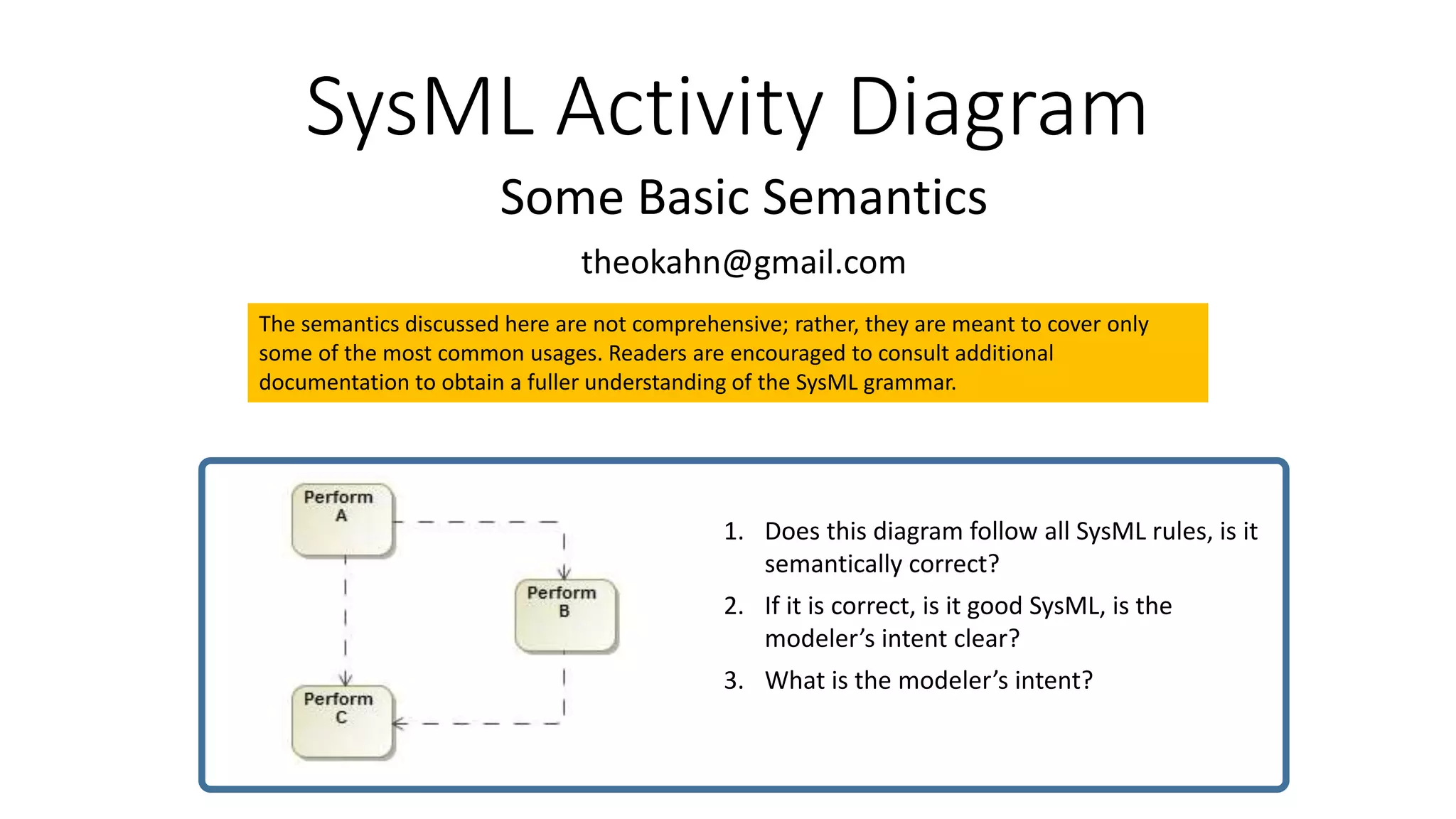
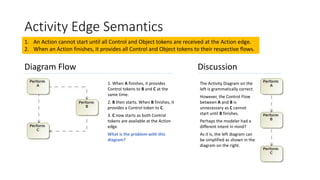
The document discusses some basic semantics of SysML activity diagrams including:
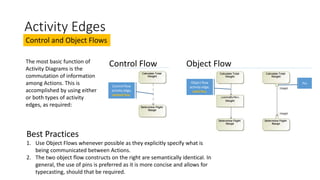
- Activity edges can be control flows or object flows to communicate information between actions. Object flows explicitly specify what is being communicated.
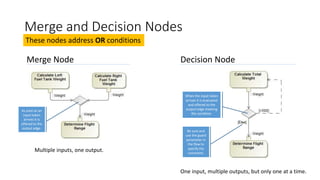
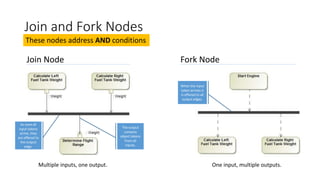
- Nodes like merge, decision, join, and fork address OR and AND conditions in activity flows.
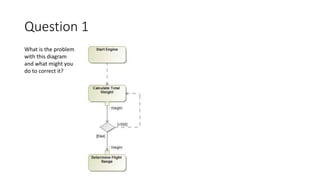
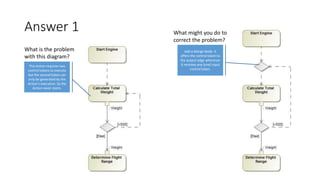
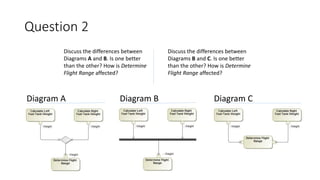
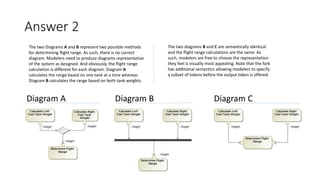
- Two activity diagrams are shown with different ways to determine flight range, with no single correct way but representing the intended system design.