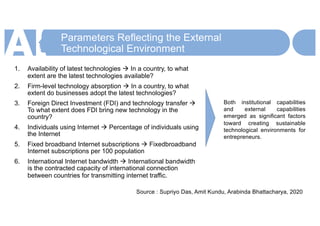
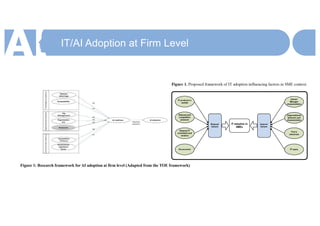
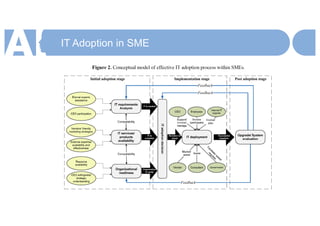
SMEs need to adopt AI to gain a competitive advantage and survive in an increasingly digital economy transformed by AI. They should begin by mapping important economic networks and data flows to identify opportunities to create and capture value through AI at scale. An action plan includes evaluating each network's potential and strengthening values. While AI removes constraints, it also changes competition. Traditional businesses must understand how to leverage strengths in new ways and transform operating capabilities. Adopting cutting-edge technology ahead of competitors is important for SME survival in this new environment.