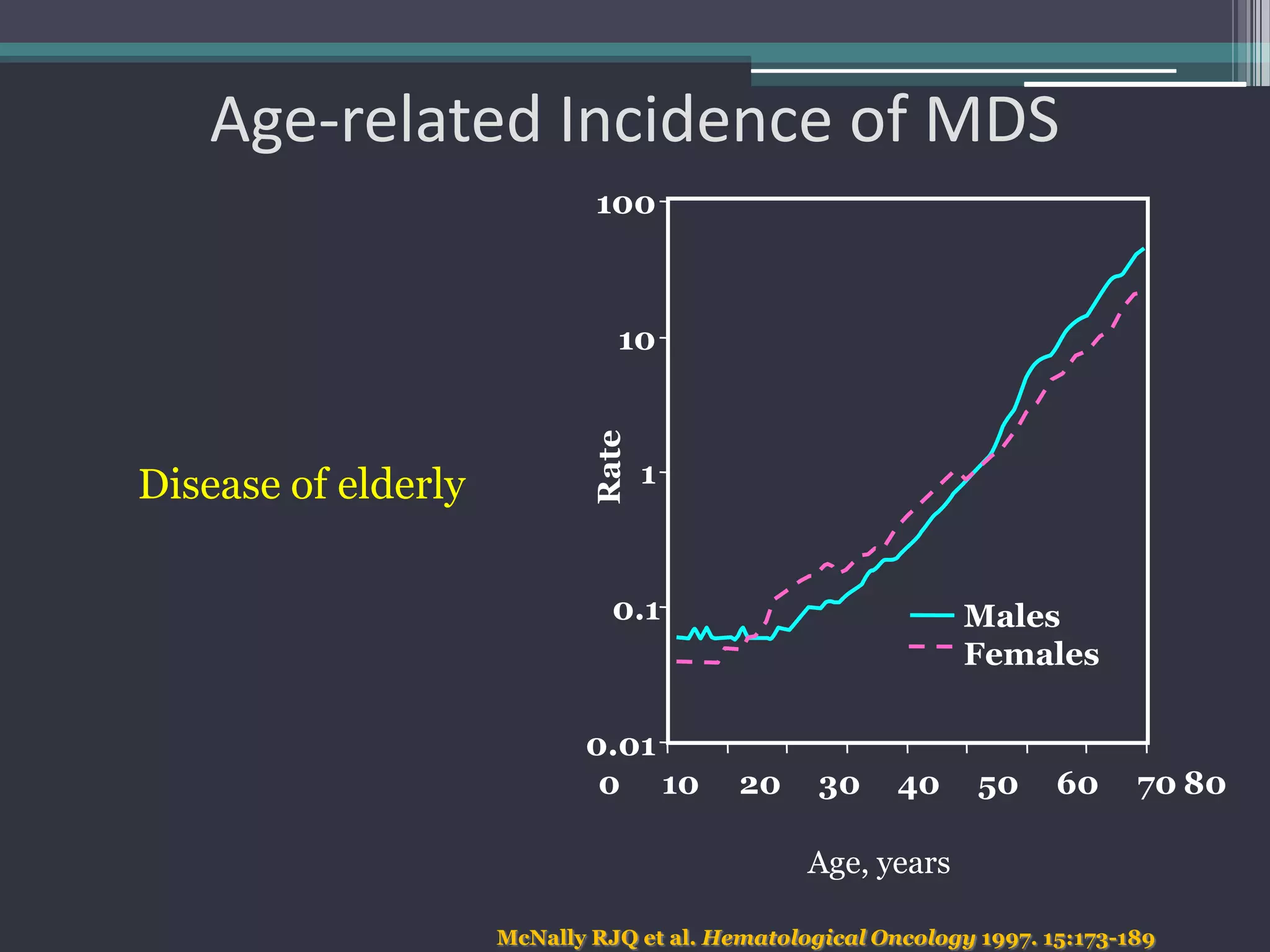
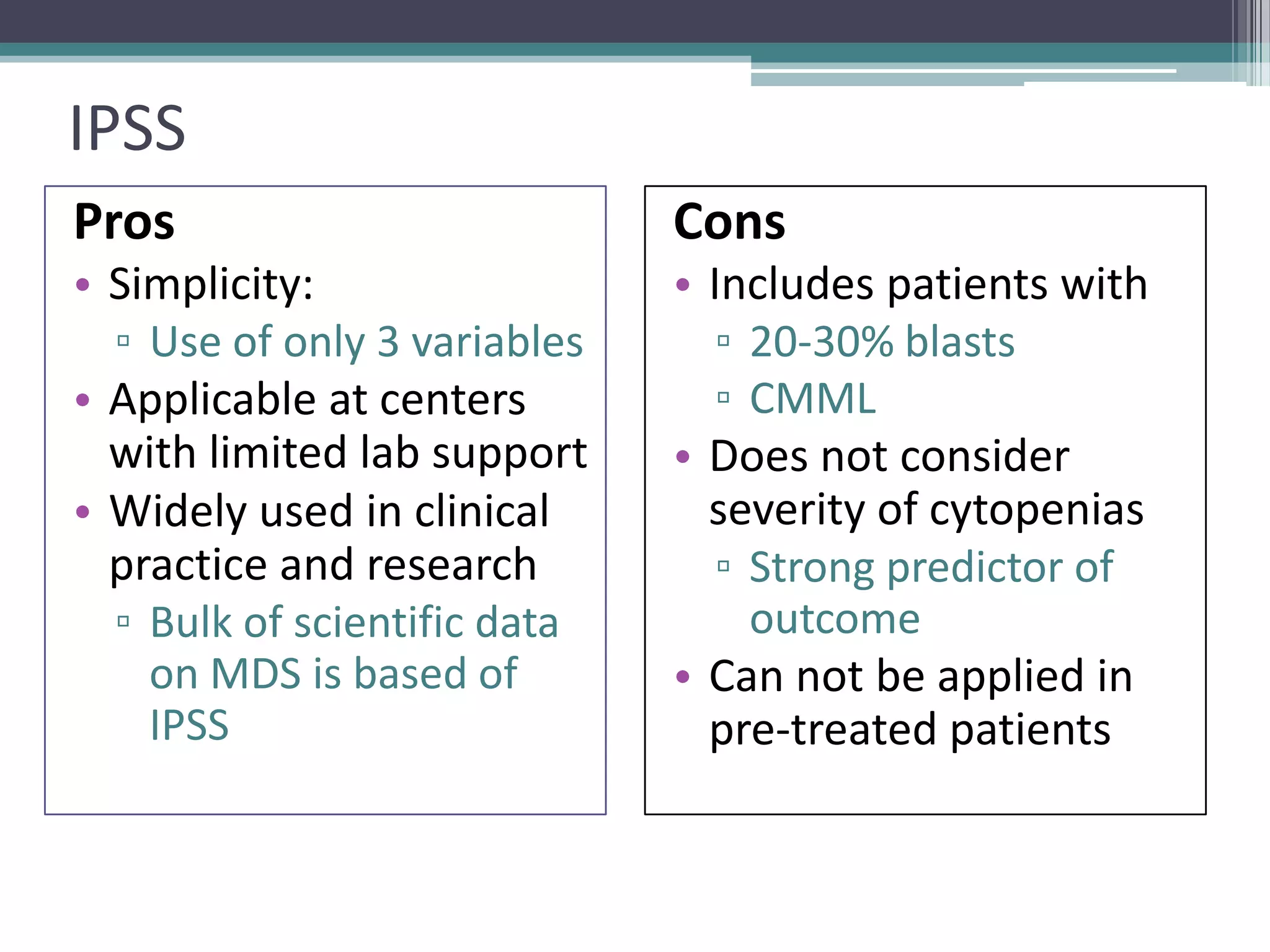
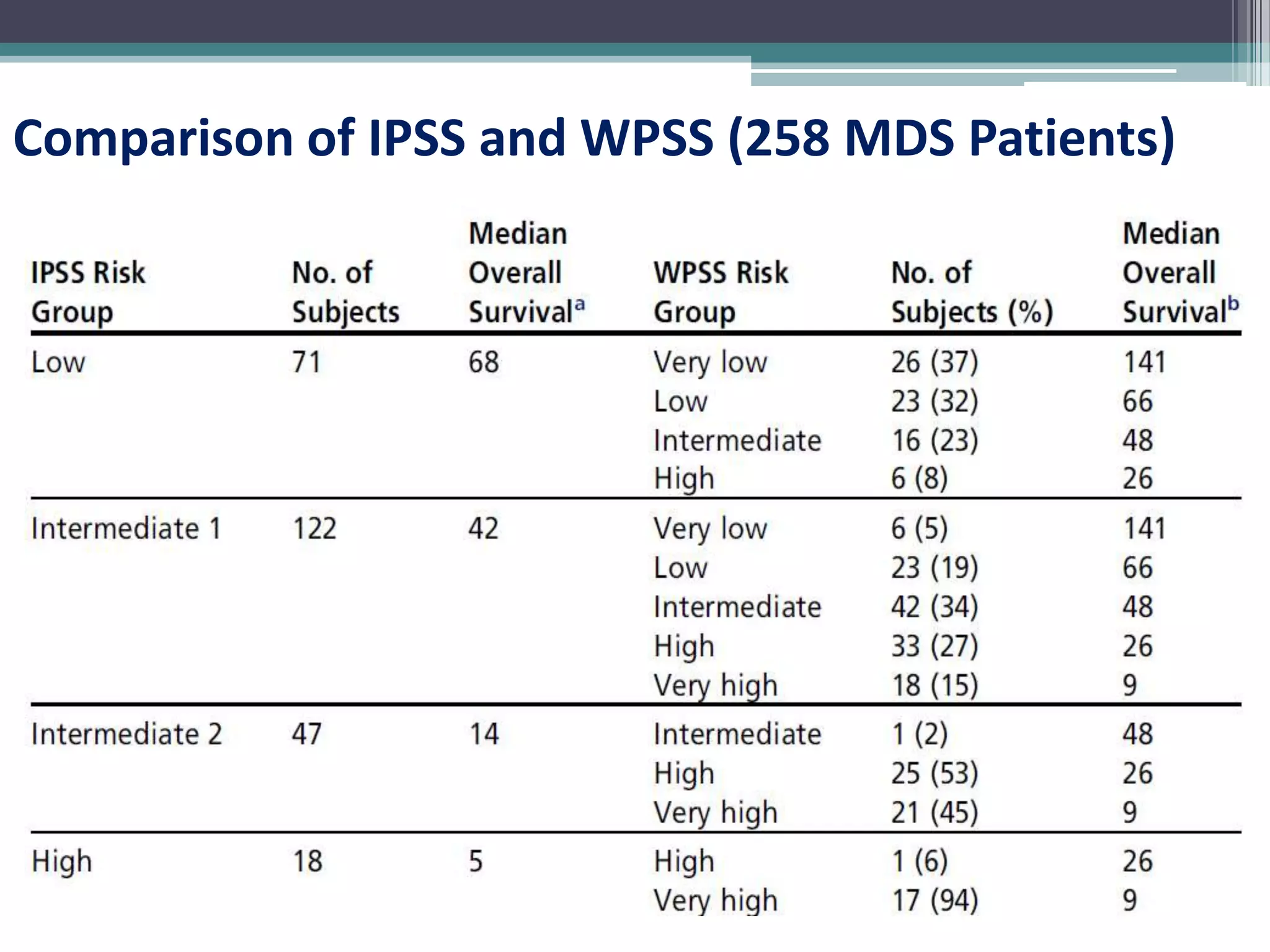
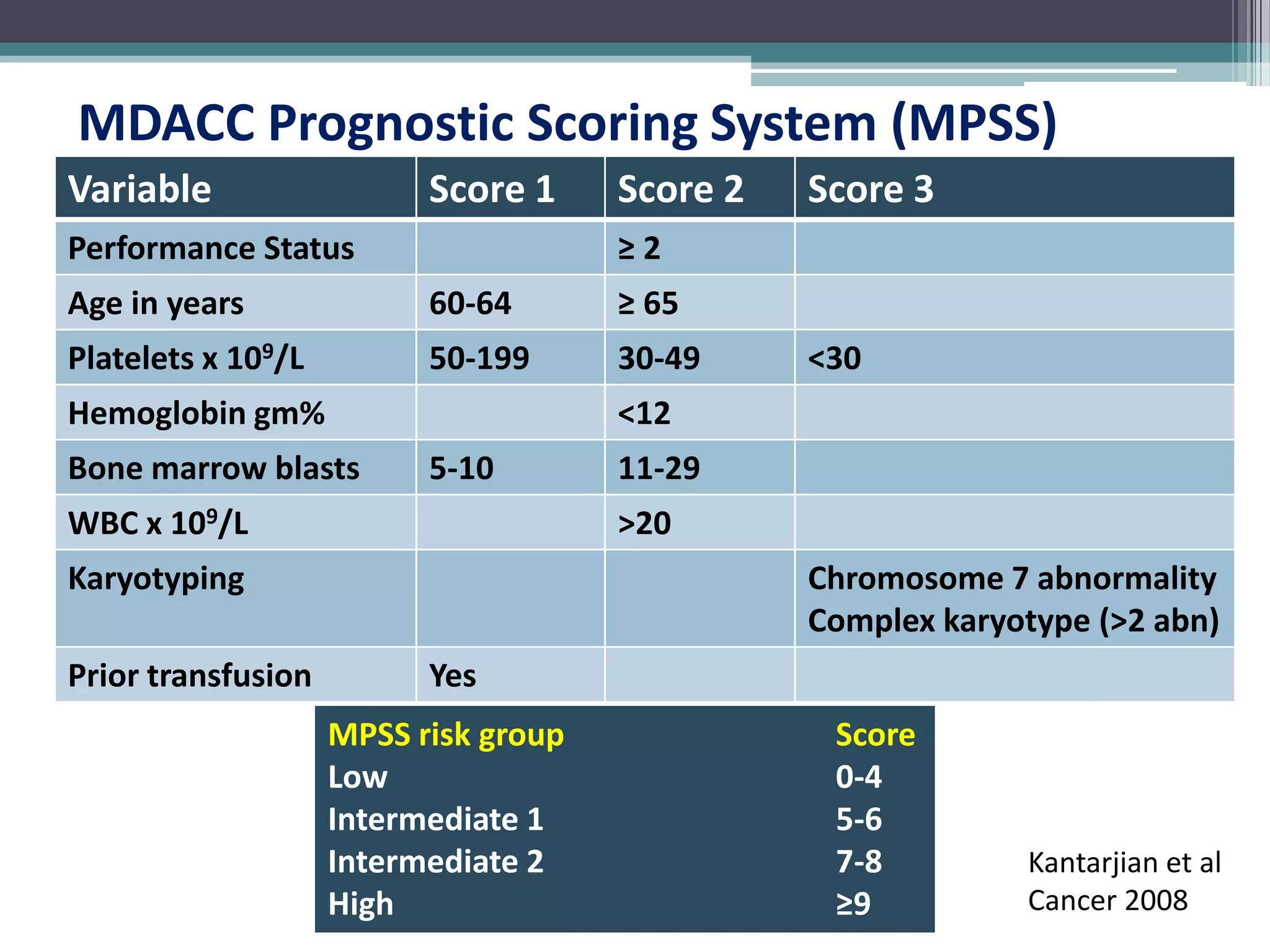
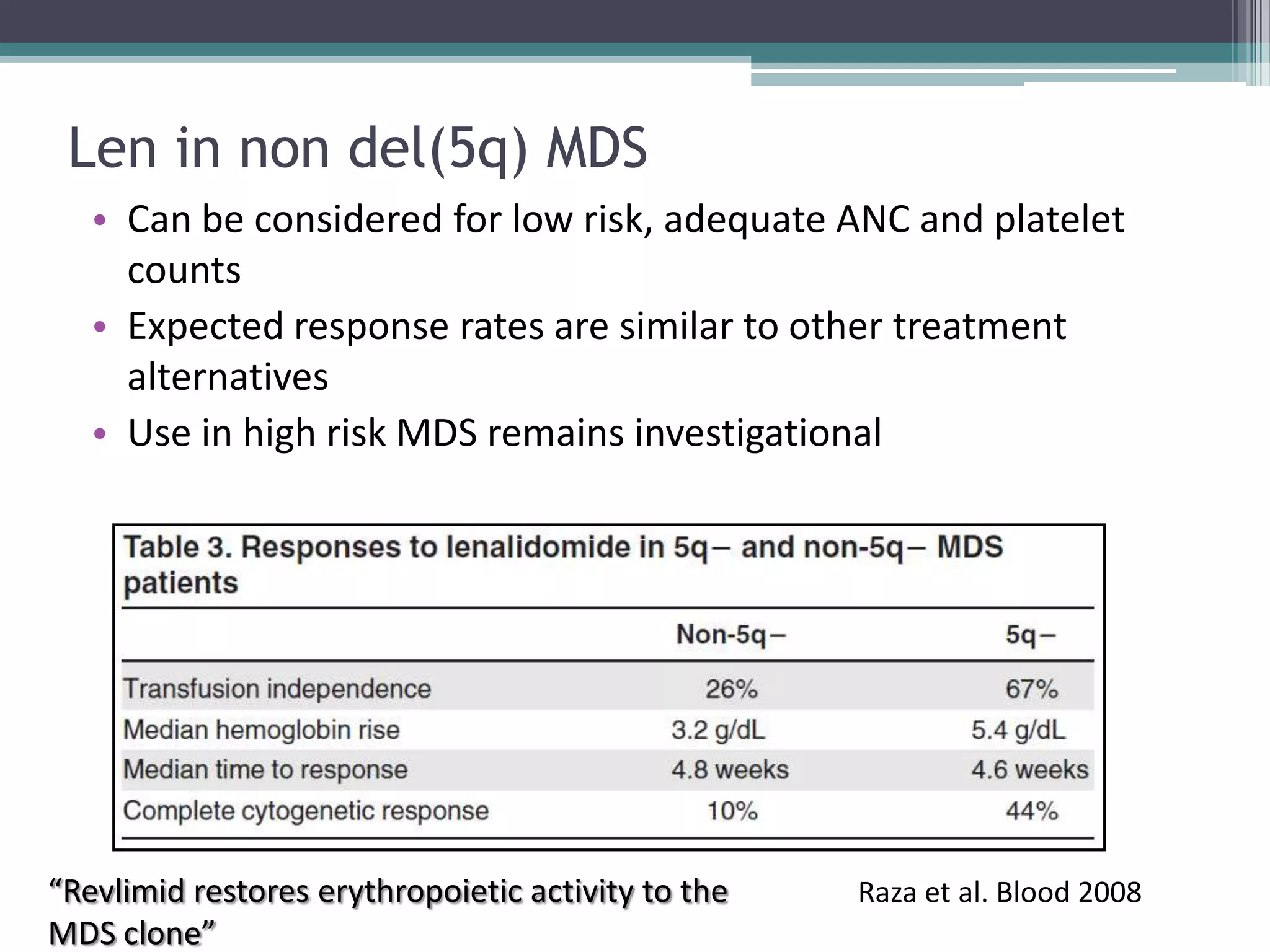
MDS is a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by variable natural history, mortality rates, and responses to therapy. The commonest causes of death are progressive bone marrow failure and conversion to acute myeloid leukemia. The WHO classification of 2008 provides improved prognostic stratification compared to previous classifications. Prognostic scoring systems like the IPSS and IPSS-R further refine risk stratification. Treatment considerations depend on risk stratification and include observation, supportive care, hematopoietic growth factors, immunosuppression, hypomethylating agents, lenalidomide and allogeneic stem cell transplant. Hypomethylating agents azacitidine and decitabine improve survival and reduce progression to AML compared to conventional