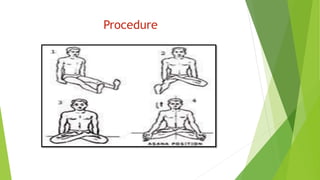
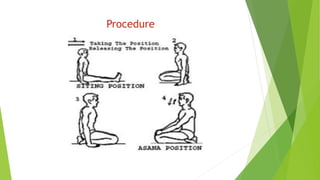
This document describes two yoga poses - Padmasana (Lotus Pose) and Vajrasana (Thunderbolt Pose). Padmasana involves sitting with each foot resting on the opposite thigh. It is said to resemble a lotus flower. The pose helps with meditation, flexibility, and digestion. Vajrasana involves sitting back on the heels with hands on knees. It strengthens the legs and aids stability. Both poses have physiological benefits like improved blood flow and nerve function, and therapeutic benefits for conditions like headaches, indigestion and knee pain.