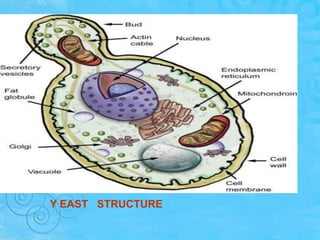
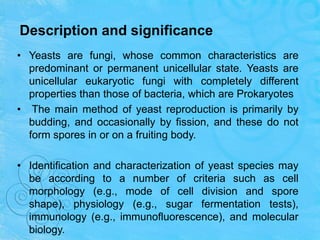
Yeasts are single-celled fungi that reproduce primarily through budding. They contain organelles like eukaryotic cells. Yeasts can be identified by characteristics like morphology, physiology, and molecular techniques. Common habitats include soil, plants, animals, and insects. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is important industrially for producing ethanol and carbon dioxide in baking and brewing. It undergoes aerobic respiration or anaerobic fermentation. Another use is for leavening bread. Candida albicans is an opportunistic pathogen of humans that can cause candidiasis when immunity is compromised.