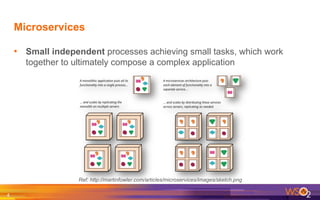
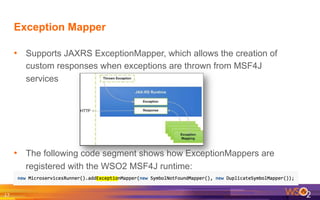
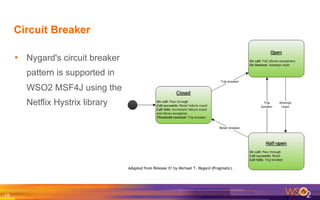
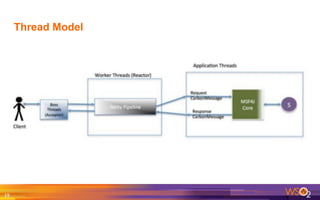
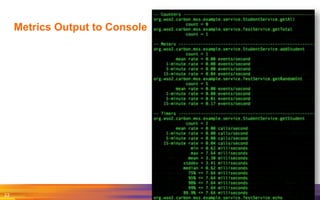
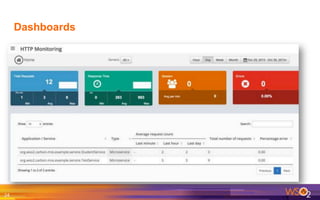
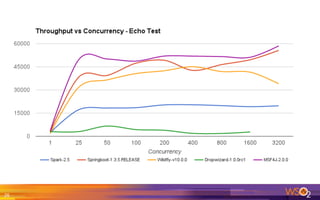
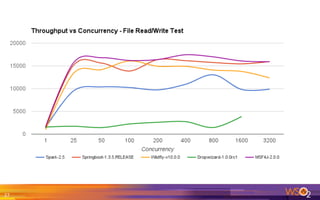
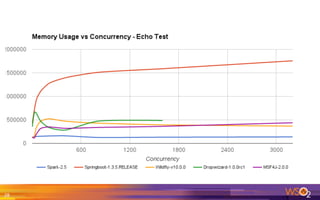
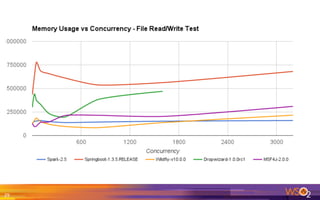
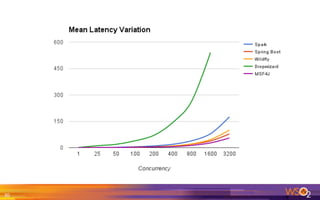
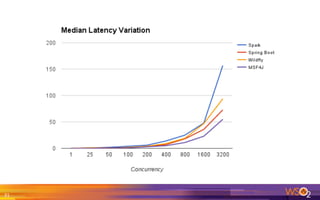
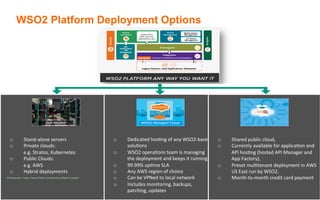
The document provides an overview of the WSO2 Microservices Framework for Java (MSF4J), highlighting its lightweight, high-performance capabilities for building Java microservices. Key features include a simple programming model with JAX-RS and Swagger annotations, fast boot-up times, support for server-less execution, and built-in analytics for monitoring. Deployment options include stand-alone servers and various cloud configurations, ensuring high availability and efficient management.