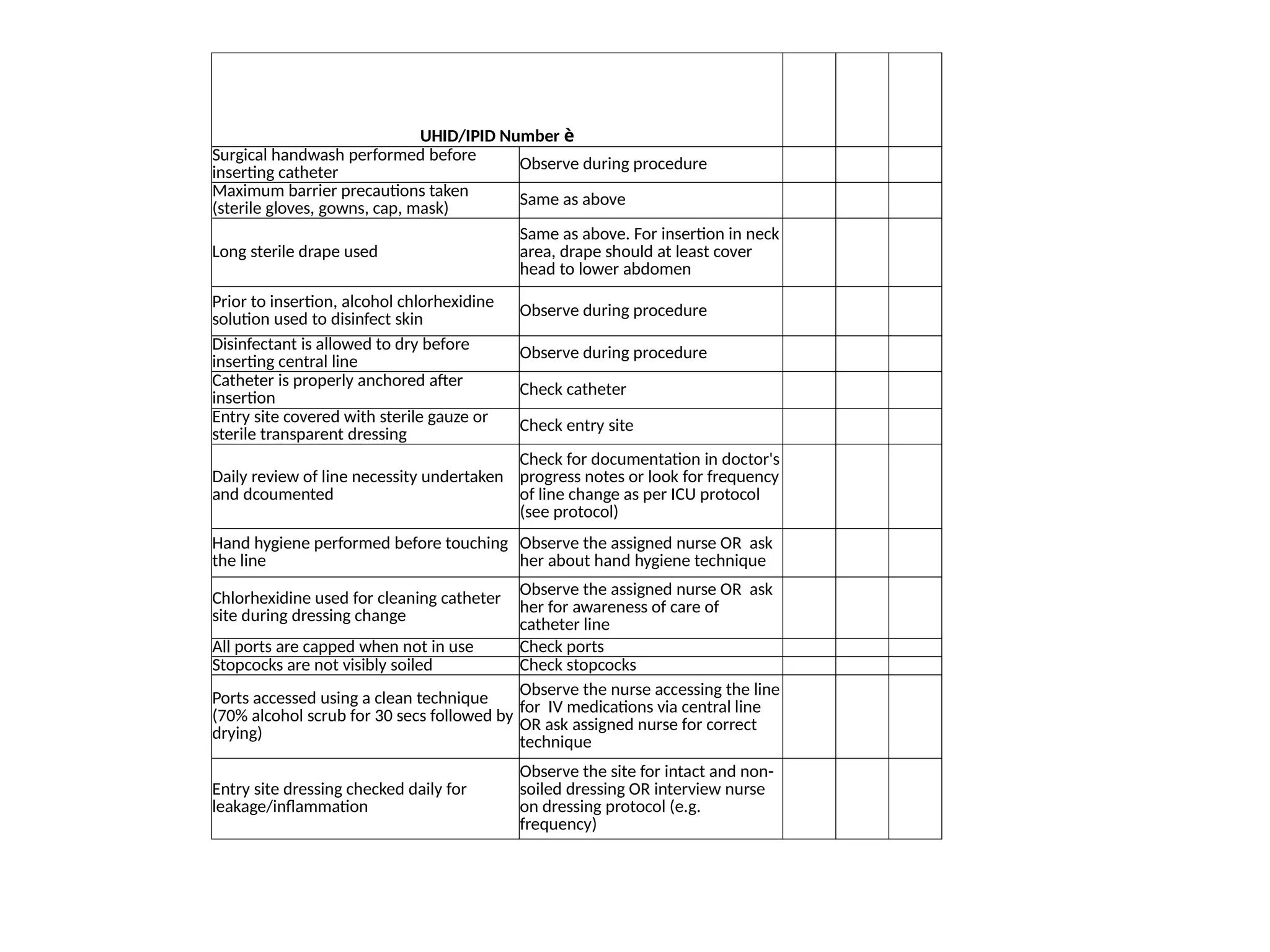
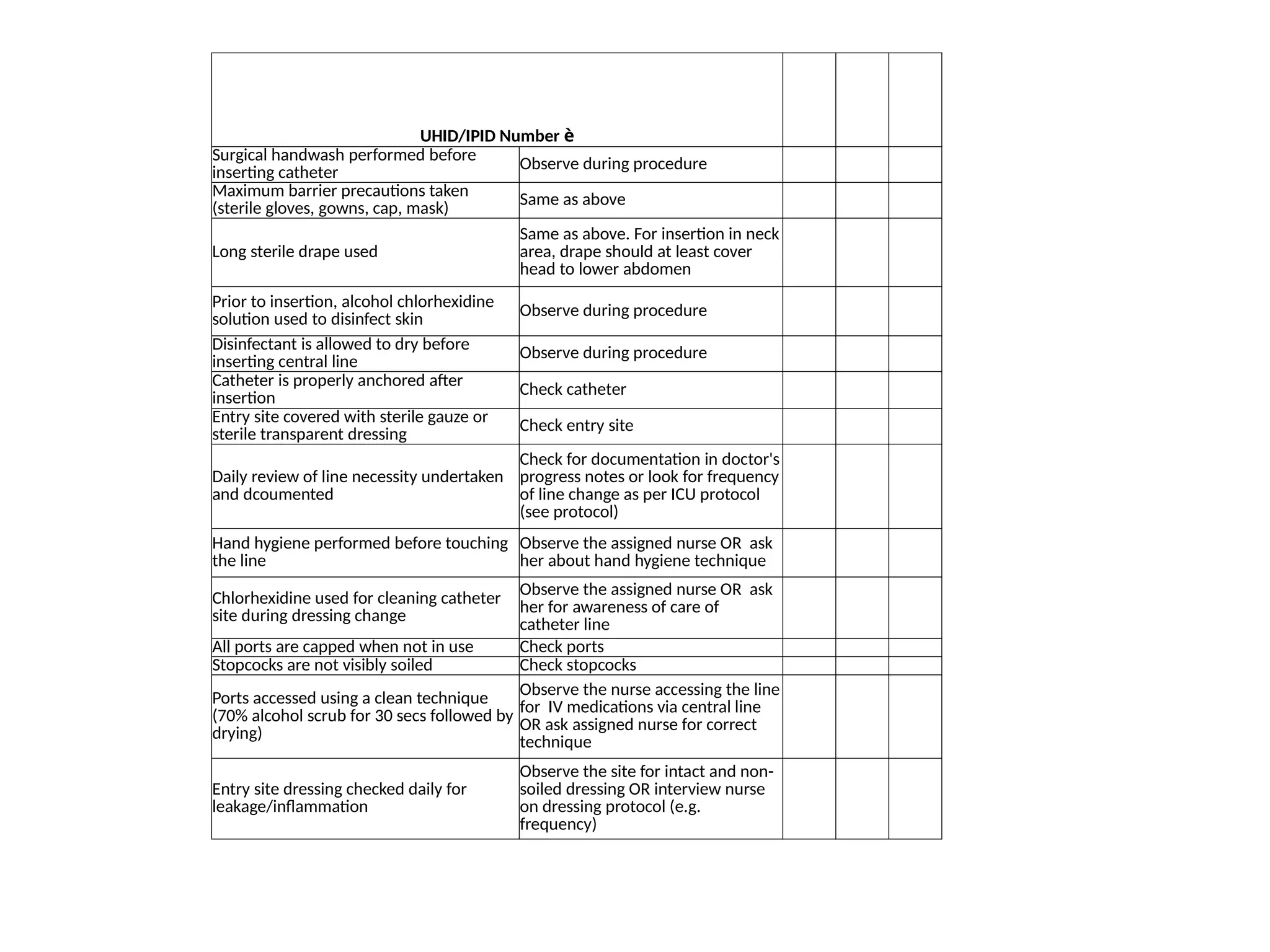
The document outlines multiple case scenarios of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) involving patients with different medical conditions and catheter use, providing specific infection types, culture results, and clinical management. It includes questions for identifying HAIs, dates of events, and exclusions for specific infection surveillance methods. Additionally, it includes calculation methodologies for infection rates, monitoring criteria, and validation processes to track HAIs and surgical site infections (SSIs).








































![Patient ID:
Patient Name:
Gender: M/ F Date of Birth/ Age:
Event Type: CLABSI Date of Event:
Date of Procedure:
Date Admitted to Facility: Location:
Diagnosis
Location of Central Line Insertion:
________________
Date of Line Insertion: ___ /___ /________
Date of Line Removal : ___ /___ /________
Date of Line Reinsertion (if applicable): ___
/___ /____
Any hemodialysis catheter present: Yes/ No
Any other device: __________________________
Event Details
Specific Event: Laboratory-confirmed
Specify Criteria Used:
Signs & Symptoms (check all that apply)
□ Fever
□ Chills
□ Hypothermia
□ Hypotension
□ Bradycardia
Laboratory (check one)
□ Recognized pathogen from one or more blood
cultures
□ Common commensal from ≥ 2 blood cultures
Pathogens Identified: Yes/ No [If Yes, specify]
COMMENTS:
CLABSI Form – Simplified version](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workshoponhai1-241223181410-75c3968a/75/Workshop-on-HOSPITAL-ACQUIRED-INFECTIONS-1-pptx-41-2048.jpg)