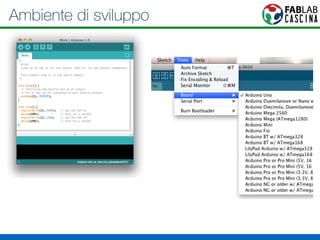
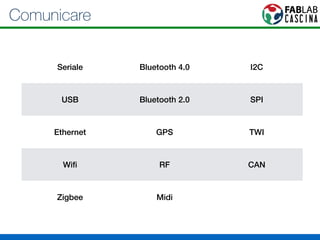
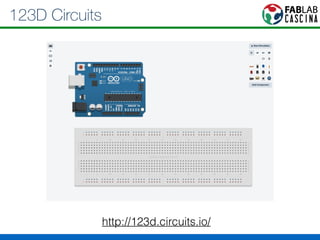
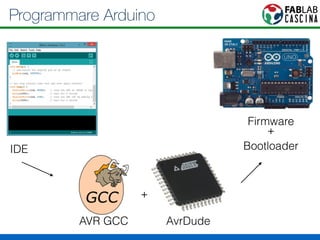
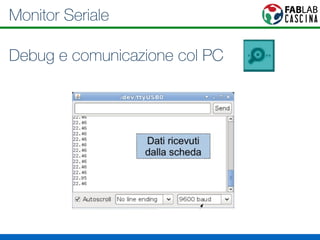
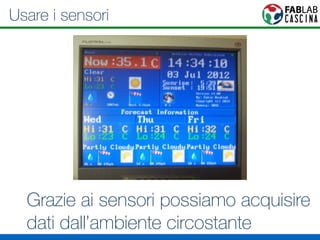
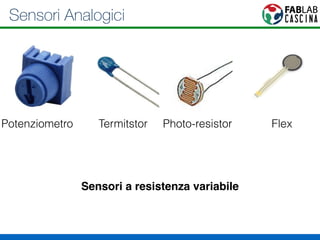
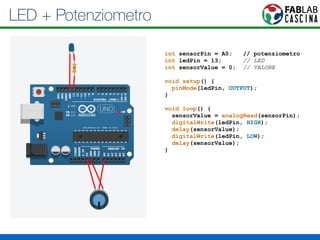
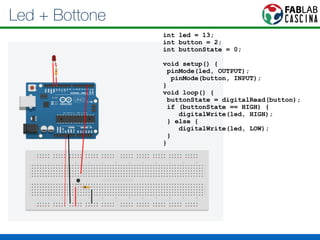
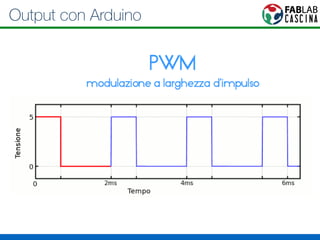
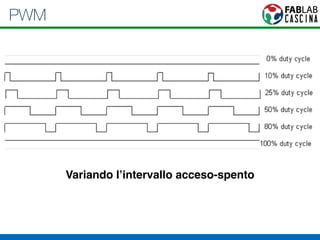
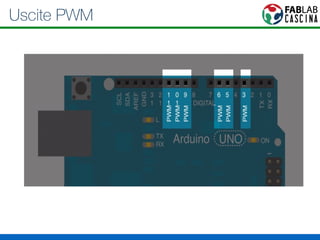
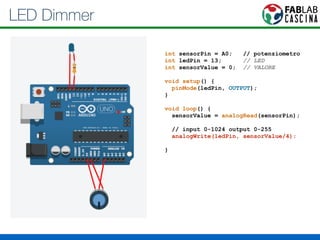
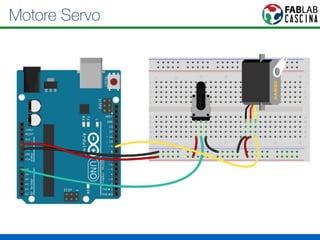
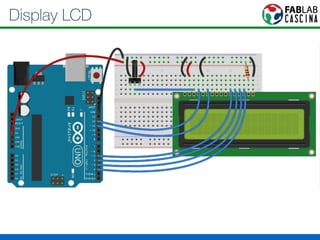
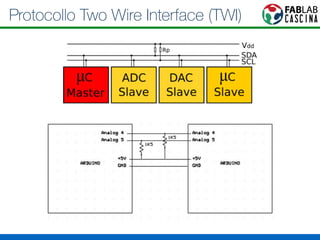
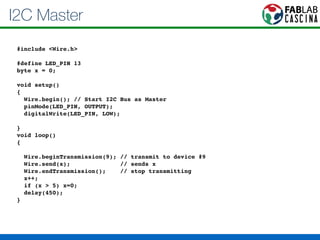
Il documento fornisce una panoramica di Arduino, descrivendo le schede elettroniche, l'ambiente di sviluppo e la comunità. Vengono presentati vari tipi di sensori e modalità di programmazione, utilizzando esempi di codice per accendere un LED e acquisire dati dai sensori. Inoltre, si discutono protocolli di comunicazione e applicazioni pratiche con dispositivi come motori e display.