1. The document discusses issues related to lack of sanitation facilities in India, particularly in rural areas, and its negative impacts on human dignity, health, and education outcomes.
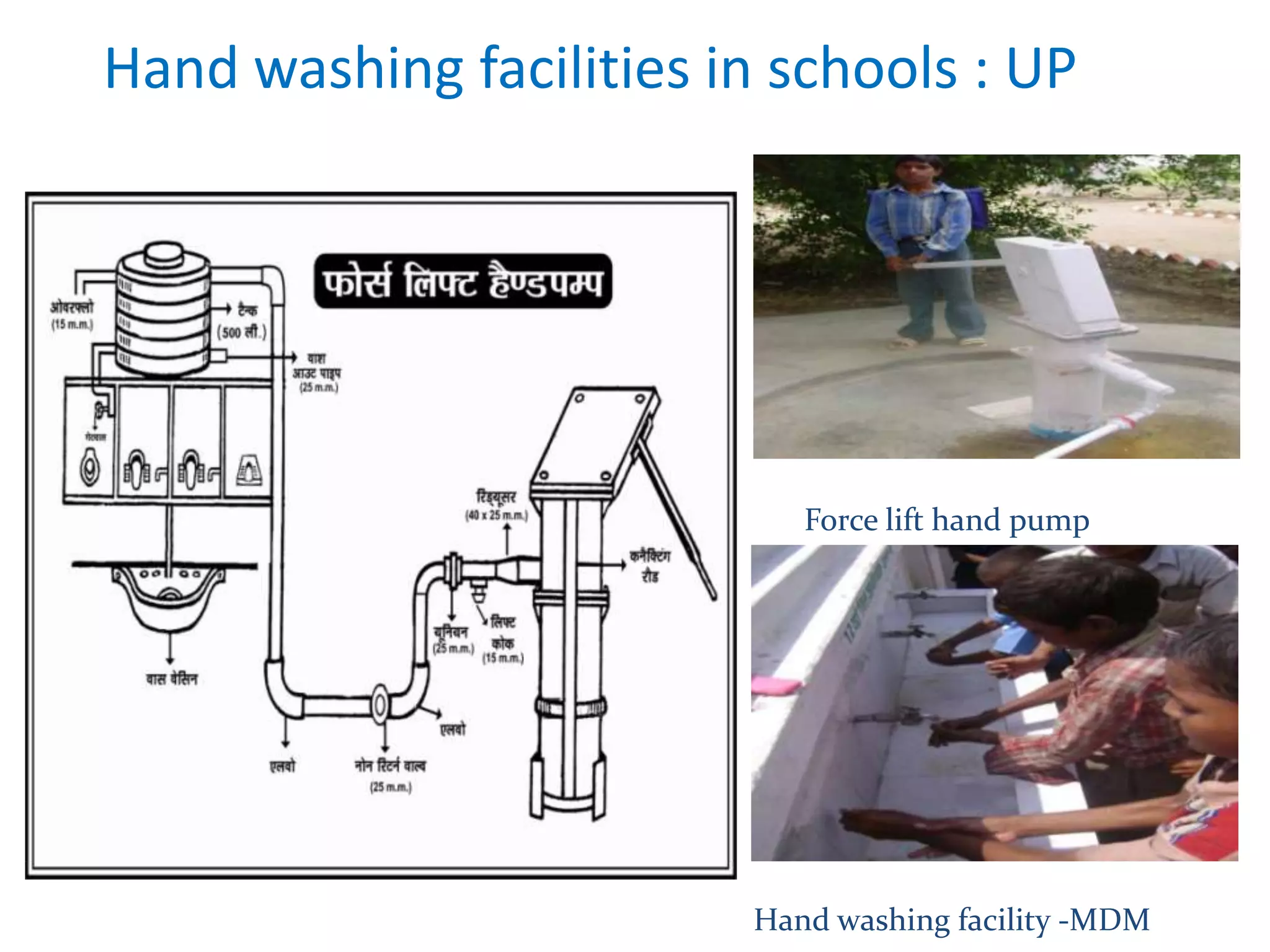
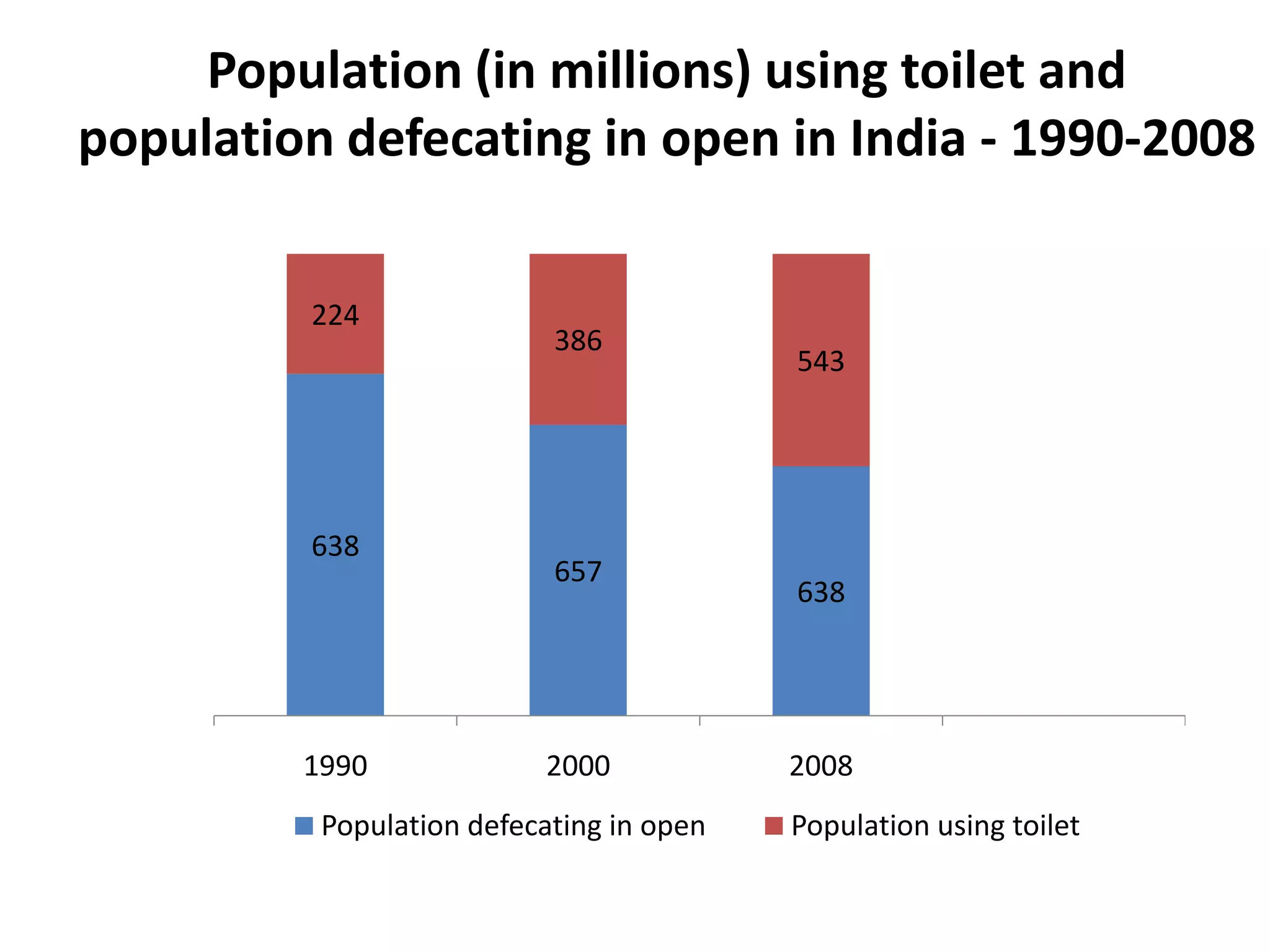
2. Over 60% of the world's open defecators live in India, most in rural areas, negatively impacting public health. Lack of toilets and sanitation facilities prevents many girls from continuing their education.
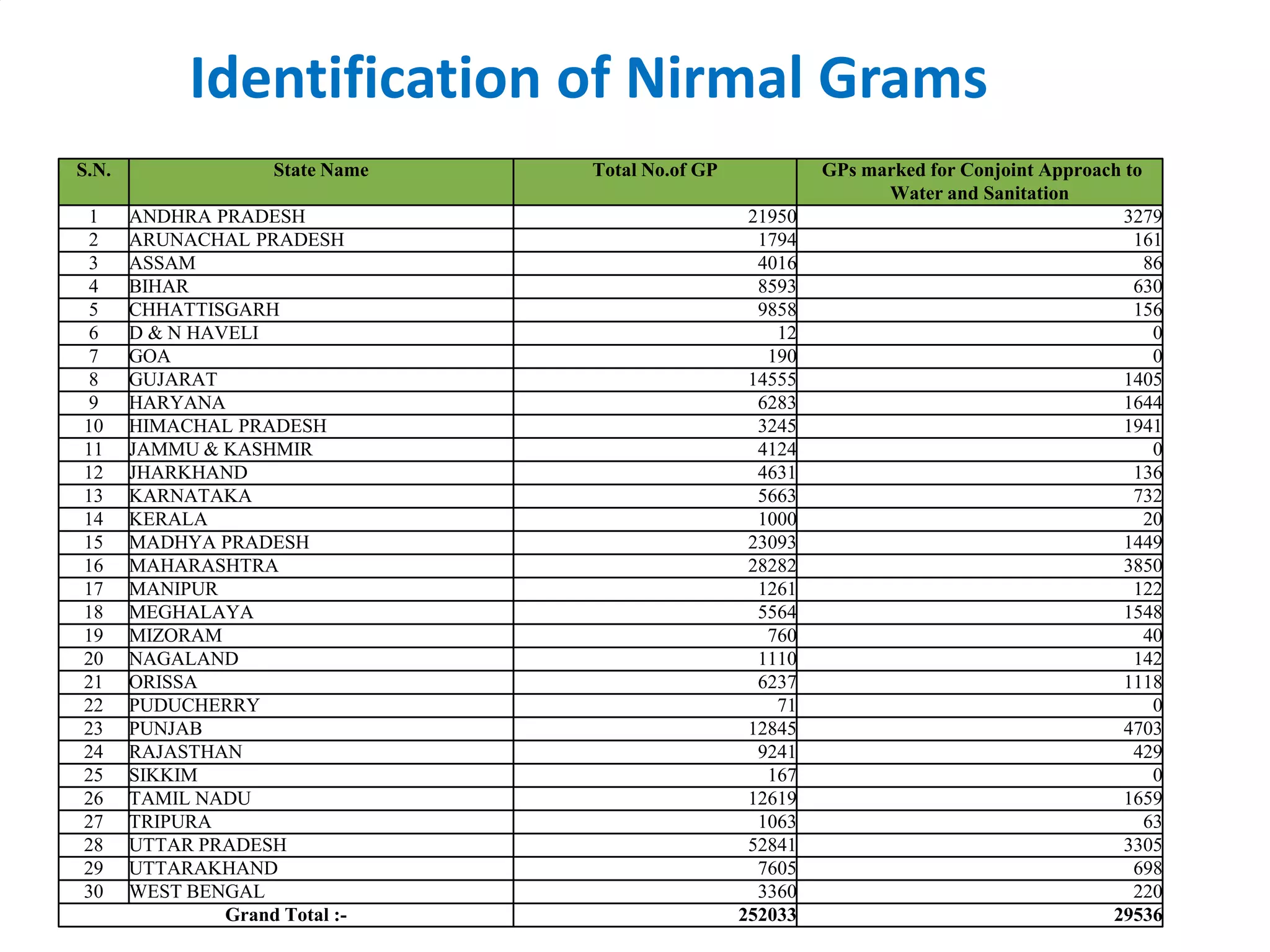
3. Several government programs and initiatives aim to improve sanitation coverage in India, but at current rates, the country will not meet its Millennium Development Goals for sanitation until 2054. Concerted efforts are needed to accelerate progress and ensure access to basic sanitation for








![• Improving the existing school infrastructure by
ensuring functional girls toilets in each
school, review and provision of gender
sensitive curriculum [Karnataka towards
actualizing the Vision 2020, Report of the
Social Empowerment Planning
Department, Government of Karnataka March
2010]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workshop-130202091504-phpapp02/75/Workshop-10-2048.jpg)

![Nirmal Bharat Abhiyan (NBA)
• Financial incentive to eligible categories of
upto Rs 10,000 for IHHLs [Individual
Household Latrine] Rs 5500 TSC plus Rs
4500 MNREGS
• Involving local bodies
• Increased Central funding with increase of
133% in 2012-13 over previous year
• All schools/anganwadis to be covered with
toilet units by March 2013
• Private players roles
• NGO’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workshop-130202091504-phpapp02/75/Workshop-12-2048.jpg)