Recommended
PPT
PPTX
PDF
BINARY SEARCH - A - DATA STRUCTURE AND ALGORITHM.pdf
PPTX
Analysis of Algorithm - Binary Search.pptx
PPTX
Binary Searching Algorithm PowerPoint Presentation
PDF
In the binary search, if the array being searched has 32 elements in.pdf
PPTX
PPTX
DAA-23UJ1A0504.pptx design and analysis algorithm search
PPTX
Binary search algorithm.pptx
DOCX
PPS 5.5.BASIC ALGORITHMS SEARCHING (LINEAR SEARCH, BINARY SEARCH ETC.), BASI...
PPTX
DOCX
PDF
PPT
PDF
Binary Search - Design & Analysis of Algorithms
PPTX
Binary_Search_PPT_Final.pptx dddddddddddddddddddddddd
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Searching in DSA that follow a dsa searching.pptx
PPT
PPTX
A binary tree is a hierarchical data structure where each node has at most tw...
PPT
PPTX
an Introduction to binary search algorithm
PPTX
Binary search in data structure
PPTX
A presentation on the comparison on complexity between
PPTX
PPTX
Search-Algorithm (2025 Edition)
PPTX
3.Problem Solving Techniques and Data Structures.pptx
PPT
Computer System Architecture Notes for CS students Binary Codes.ppt
PPT
Computer System Architecture Notes for Computer Science Students K-Maps.ppt
More Related Content
PPT
PPTX
PDF
BINARY SEARCH - A - DATA STRUCTURE AND ALGORITHM.pdf
PPTX
Analysis of Algorithm - Binary Search.pptx
PPTX
Binary Searching Algorithm PowerPoint Presentation
PDF
In the binary search, if the array being searched has 32 elements in.pdf
PPTX
PPTX
DAA-23UJ1A0504.pptx design and analysis algorithm search
Similar to working of binary search .BINARY_SEARCH.ppt
PPTX
Binary search algorithm.pptx
DOCX
PPS 5.5.BASIC ALGORITHMS SEARCHING (LINEAR SEARCH, BINARY SEARCH ETC.), BASI...
PPTX
DOCX
PDF
PPT
PDF
Binary Search - Design & Analysis of Algorithms
PPTX
Binary_Search_PPT_Final.pptx dddddddddddddddddddddddd
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Searching in DSA that follow a dsa searching.pptx
PPT
PPTX
A binary tree is a hierarchical data structure where each node has at most tw...
PPT
PPTX
an Introduction to binary search algorithm
PPTX
Binary search in data structure
PPTX
A presentation on the comparison on complexity between
PPTX
PPTX
Search-Algorithm (2025 Edition)
PPTX
3.Problem Solving Techniques and Data Structures.pptx
More from trahul9
PPT
Computer System Architecture Notes for CS students Binary Codes.ppt
PPT
Computer System Architecture Notes for Computer Science Students K-Maps.ppt
PPT
Understanding 8085 Architecture( For computer science students).ppt
PPT
Memory Hierarchy Notes of Computer Science students.ppt
PPTX
Notes of Software Engineering for class MCA
PPT
Digital Notes of Database Management System
PPTX
Computer System Architecture Notes SEC-B.pptx
PPTX
Computer System Architecture Notes SEC-A.pptx
PPTX
Unit-4 Notes on Deep learning-compressed.pptx
PPTX
Unit-4 Notes on Deep learning-compressed.pptx
PPTX
Unit-3 Notes on deep Learning Machine Translation.pptx
PPTX
Unit-3 Notes on deep Learning-compressed.pptx
PPTX
Unit-3 deep Learning.pptx Notes of Deep Learning)
PPTX
Unit-2 Structured.pptx( Notes of Deep Learning)
PPT
Linear Regression in Machine Learning Notes for MCA.ppt
PPTX
Linear Regression in Machine Learning Notes for MCA.pptx
PPT
KNN and SVM algorithm in Machine Learning for MCA
PPTX
KNN algorithm in Machine Learning for MCA
PPTX
Machine Learning Notes on Decision Trees.pptx
PPT
Lecture notes on Software Engineering MCA
Recently uploaded
PPTX
Fitting Infiltration Models to Infiltration using Excel (1).pptx
PPTX
Designing Work for Humans, Not Machines: Human-Centered Maintenance Excellence
PPTX
Week 2.1.pptxdynamics particle kinetics introduction 2
PPT
Integer , Goal and Non linear Programming Model
PPTX
ISO 13485.2016 Awareness's Training material
PPTX
Optimized access control techniques in Cloud Computing with Security and Scal...
PDF
Infinite Sequence and Series: It Includes basic Sequence and Series
PPTX
uADPF Topology_SFP requirements_locked slides.pptx
PDF
Rajesh Prasad- Brief Profile with educational, professional highlights
PDF
Decision-Support-Systems-and-Decision-Making-Processes.pdf
PPTX
A professional presentation on Cosmos Bank Heist
PPTX
This Bearing Didn’t Fail Suddenly — How Vibration Data Predicts Failure Month...
PDF
Basics of Electronics Task by Vivaan Jo Varghese.pdf
PDF
Soil Compressibility (Elastic Settlement).pdf
PDF
Computer Network Lab Manual ssit -kavya r.pdf or Computer Network Lab Manual ...
PPT
Ceramic Matrix Composites Slide from Composite Materials
PDF
Chad Ayach - An Accomplished Mechanical Engineer
PDF
Shear Strength of Soil/Mohr Coulomb Failure Criteria-1.pdf
PDF
Computer Graphics Fundamentals (v0p1) - DannyJiang
PDF
engineering management chapter 5 ppt presentation
working of binary search .BINARY_SEARCH.ppt 1. Binary Search
Let ai 1≤ i ≤ n be a list of elements that are
sorted in non decreasing order.
Consider the problem of determining
whether a given element x is present in
the list. If x is present , we are to
determine a value j such that aj = x. If x is
not in the list , then j is to be set to zero
2. Iterative Binary Search
Algorithm BinSearch(a,n,x)
{
low:=1;high:=n;
while( low ≤ high) do
{
mid:=(low+high)/2;
if(x<a[mid]) then high:=mid -1;
else if (x>a[mid])then low:=mid+1;
else return mid;
}
return 0
}
3. Recursive Binary Search
Algorithm BinSearch(a,i ,I ,x)
//Given an array a[i:l]of elementsin nondicreasing
//order 1i≤l,determine whether x is present
{
if (l=i) then
{
x=a[i] then return i;
else return 0;
}else
{
mid:=(i+l)/2;
4. if(x=a[mid]) then return mid ;
else if (x<a[mid])then
return Binsrch(a,i,mid-1,x);
else return Binsrch(a, mid+1,l,x);
}
}
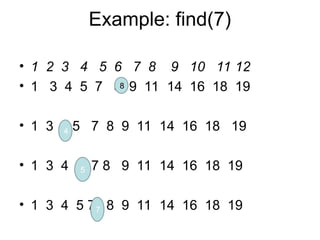
5. Example: find(7)
• 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
• 1 3 4 5 7 8 9 11 14 16 18 19
• 1 3 4 5 7 8 9 11 14 16 18 19
• 1 3 4 5 7 8 9 11 14 16 18 19
• 1 3 4 5 7 8 9 11 14 16 18 19
8
4
5
7
6. • Example:-
-15, -6, 0, 7, 9, 23, 54, 82, 101,
112,125, 131, 142,151
X=151 low high mid
1 14 7
814 11
1214 13
14 14 14
found that a[14]=151
7. 8. If n is in the range [2k-1
2k
),then BinSearch
makes at most k elements of comparison
for successful search and either k-1 or k
comparison for an unsuccessful search. In
other words time for successful search is
O(log n) and for an unsuccessful search is
(log n)

![Iterative Binary Search
Algorithm BinSearch(a,n,x)
{
low:=1;high:=n;
while( low ≤ high) do
{
mid:=(low+high)/2;
if(x<a[mid]) then high:=mid -1;
else if (x>a[mid])then low:=mid+1;
else return mid;
}
return 0
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-250722051813-090270d6/85/working-of-binary-search-BINARY_SEARCH-ppt-2-320.jpg)
![Recursive Binary Search
Algorithm BinSearch(a,i ,I ,x)
//Given an array a[i:l]of elementsin nondicreasing
//order 1i≤l,determine whether x is present
{
if (l=i) then
{
x=a[i] then return i;
else return 0;
}else
{
mid:=(i+l)/2;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-250722051813-090270d6/85/working-of-binary-search-BINARY_SEARCH-ppt-3-320.jpg)
![if(x=a[mid]) then return mid ;
else if (x<a[mid])then
return Binsrch(a,i,mid-1,x);
else return Binsrch(a, mid+1,l,x);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-250722051813-090270d6/85/working-of-binary-search-BINARY_SEARCH-ppt-4-320.jpg)
![• Example:-
-15, -6, 0, 7, 9, 23, 54, 82, 101,
112,125, 131, 142,151
X=151 low high mid
1 14 7
814 11
1214 13
14 14 14
found that a[14]=151](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-250722051813-090270d6/85/working-of-binary-search-BINARY_SEARCH-ppt-6-320.jpg)