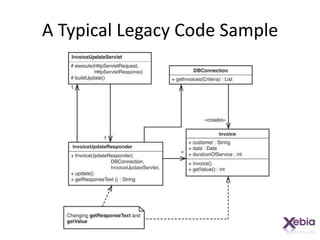
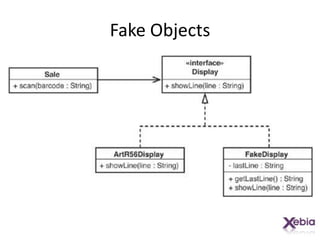
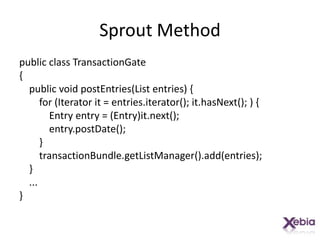
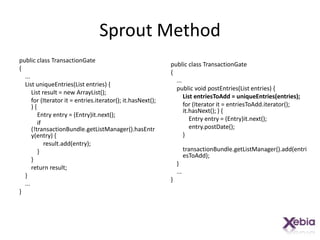
This document discusses techniques for working with legacy code, including sprout method, wrap method, and wrap class. Sprout method involves extracting part of an existing method into a new method. Wrap method surrounds an existing method with new code. Wrap class creates a new class that delegates to the original class, allowing new behavior to be added. The techniques allow new functionality to be added to legacy code in a way that does not disrupt existing behavior and allows the new code to be tested independently.













![Sprout Classstd::string QuarterlyReportGenerator::generate(){ std::vector<Result> results = database.queryResults(beginDate, endDate); std::string pageText;pageText += "<html><head><title>" "Quarterly Report" "</title></head><body><table>"; if (results.size() != 0) { for (std::vector<Result>::iterator it = results.begin(); it != results.end(); ++it) {pageText += "<tr>";pageText += "<td>" + it->department + "</td>";pageText += "<td>" + it->manager + "</td>"; char buffer [128];sprintf(buffer, "<td>$%d</td>", it->netProfit / 100);pageText += std::string(buffer);sprintf(buffer, "<td>$%d</td>", it->operatingExpense / 100);pageText += std::string(buffer);pageText += "</tr>"; } } else {pageText += "No results for this period"; }pageText += "</table>";pageText += "</body>";pageText += "</html>"; return pageText;}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workingeffectivelywithlegacycode-110426114836-phpapp01/85/Working-effectively-with-legacy-code-19-320.jpg)







