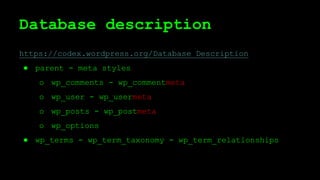
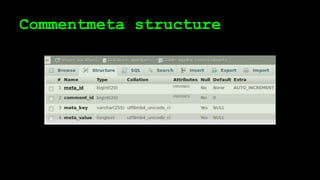
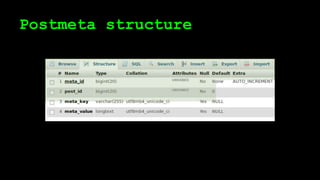
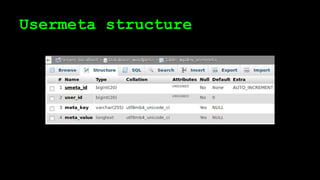
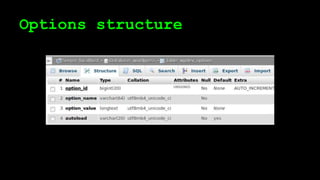
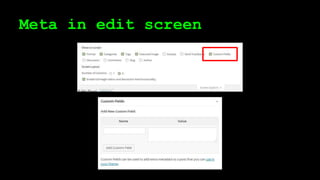
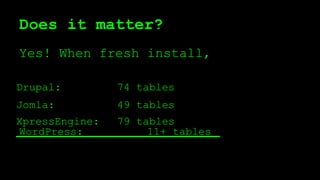
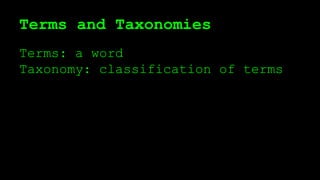
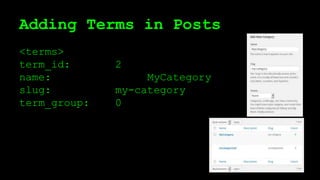
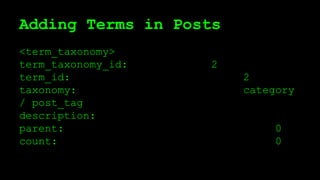
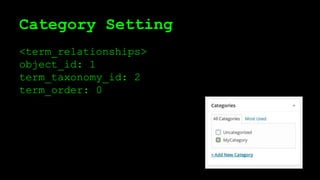
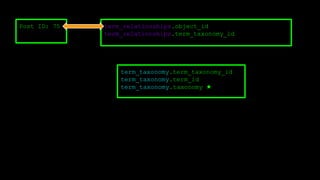
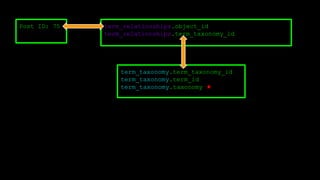
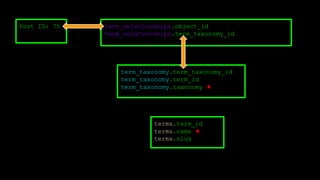
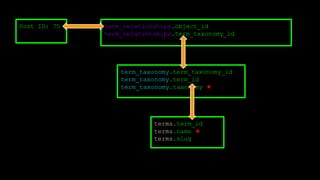
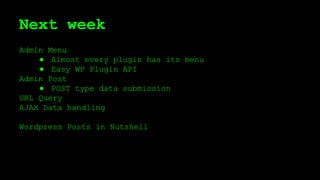
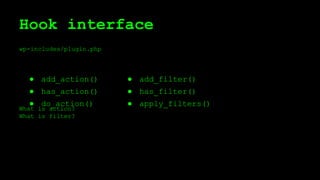
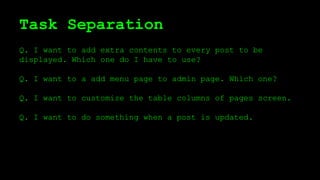
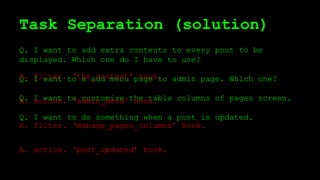
This document discusses WordPress plugins and database tables. It covers hooks, which allow plugins to connect functions to events. Hooks are either actions or filters. Database tables in WordPress use a metadata structure, with meta tables containing key-value pairs that provide flexibility. Taxonomies classify terms and allow terms to be associated with posts through term relationships and term taxonomies. Next week's topics will include adding admin menus and handling POST data for plugins.







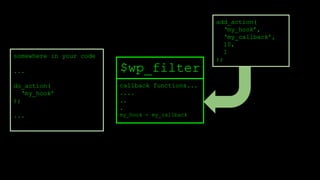
![do_action
inside of do_action:
● retrieve the callback functions by their tags (hook)
● sort by priority
● call_user_func()
do {
foreach ( (array) current($wp_filter[$tag]) as $the_ )
if ( !is_null($the_['function']) )
call_user_func_array($the_['function'],
array_slice($args, 0, (int) $the_['accepted_args']));
} while ( next($wp_filter[$tag]) !== false );](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wordpressplugin2-150522045453-lva1-app6891/85/WordPress-plugin-2-24-320.jpg)
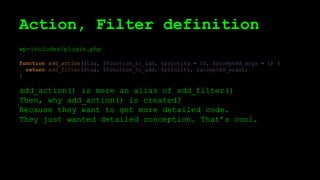
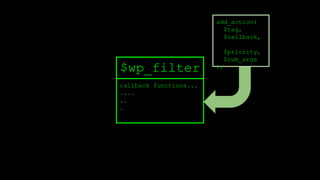
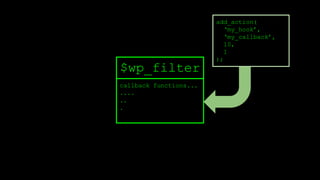
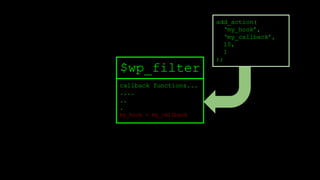
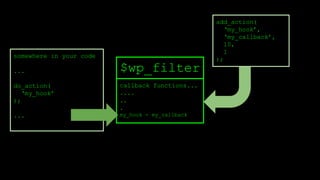
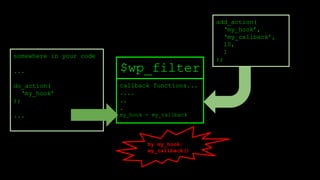
![add_action
function add_filter( $tag, $function_to_add, $priority = 10, $accepted_args = 1 ) {
global $wp_filter, $merged_filters;
$idx = _wp_filter_build_unique_id($tag, $function_to_add, $priority);
$wp_filter[$tag][$priority][$idx] = array('function' => $function_to_add,
'accepted_args' => $accepted_args);
unset( $merged_filters[ $tag ] );
return true;
}
$wp_filter is an array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wordpressplugin2-150522045453-lva1-app6891/85/WordPress-plugin-2-25-320.jpg)