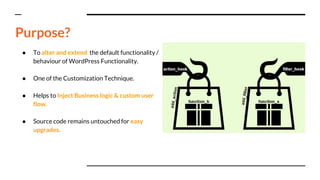
The document is a guide presented at the Bengaluru WordPress meetup discussing WordPress hooks, including their purpose, types (action and filter hooks), and best practices for custom hooks. It explains how hooks allow developers to extend WordPress functionality without altering the core code, emphasizing the importance of understanding hook parameters and priority for effective implementation. Additionally, it offers examples and practical uses of both action and filter hooks, along with advice on removing them and using dynamic hooks.