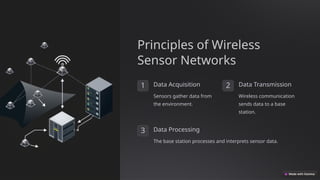
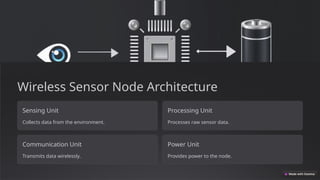
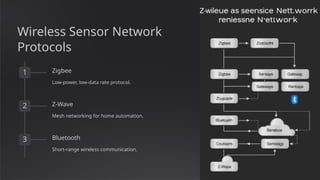
The document discusses the fundamentals of wireless sensor technology, including key principles, applications, and challenges. It outlines the architecture of wireless sensor nodes, types of sensors, and various protocols used for communication, as well as power management strategies. Future trends highlighted include AI integration, IoT convergence, and miniaturization of sensors.