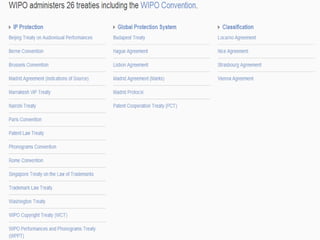
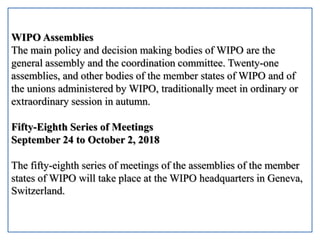
WIPO is the global intergovernmental organization responsible for intellectual property services, policy, information and cooperation. It has 191 member states and seeks to develop an international IP system that supports innovation and creativity. WIPO administers treaties such as the Paris Convention and Berne Convention, and provides global filing systems for patents, trademarks and designs. It delivers IP technical assistance and capacity building programs, and provides access to IP information through databases and search services. Key activities are carried out through committees and assemblies which determine the organization's direction.