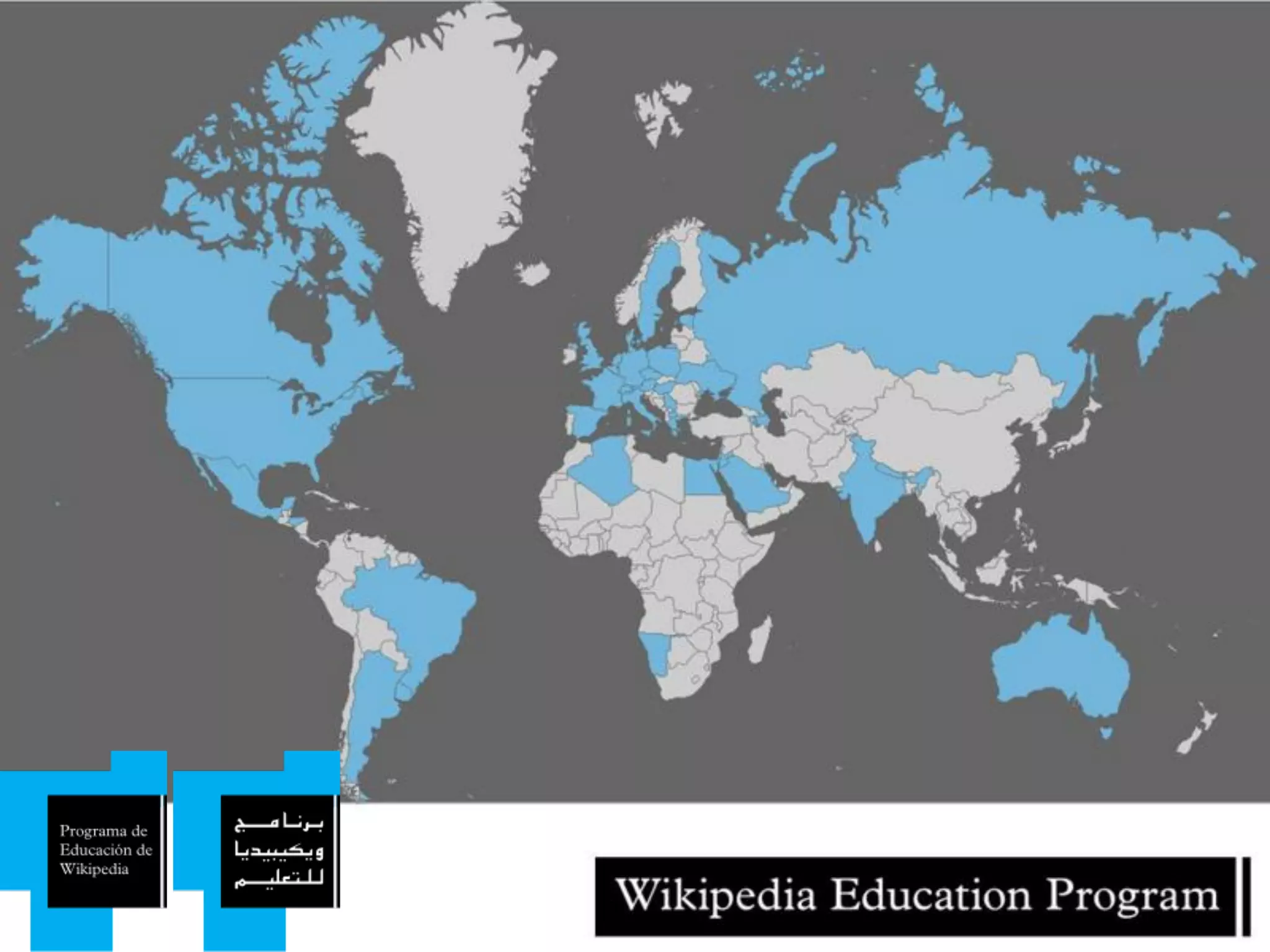
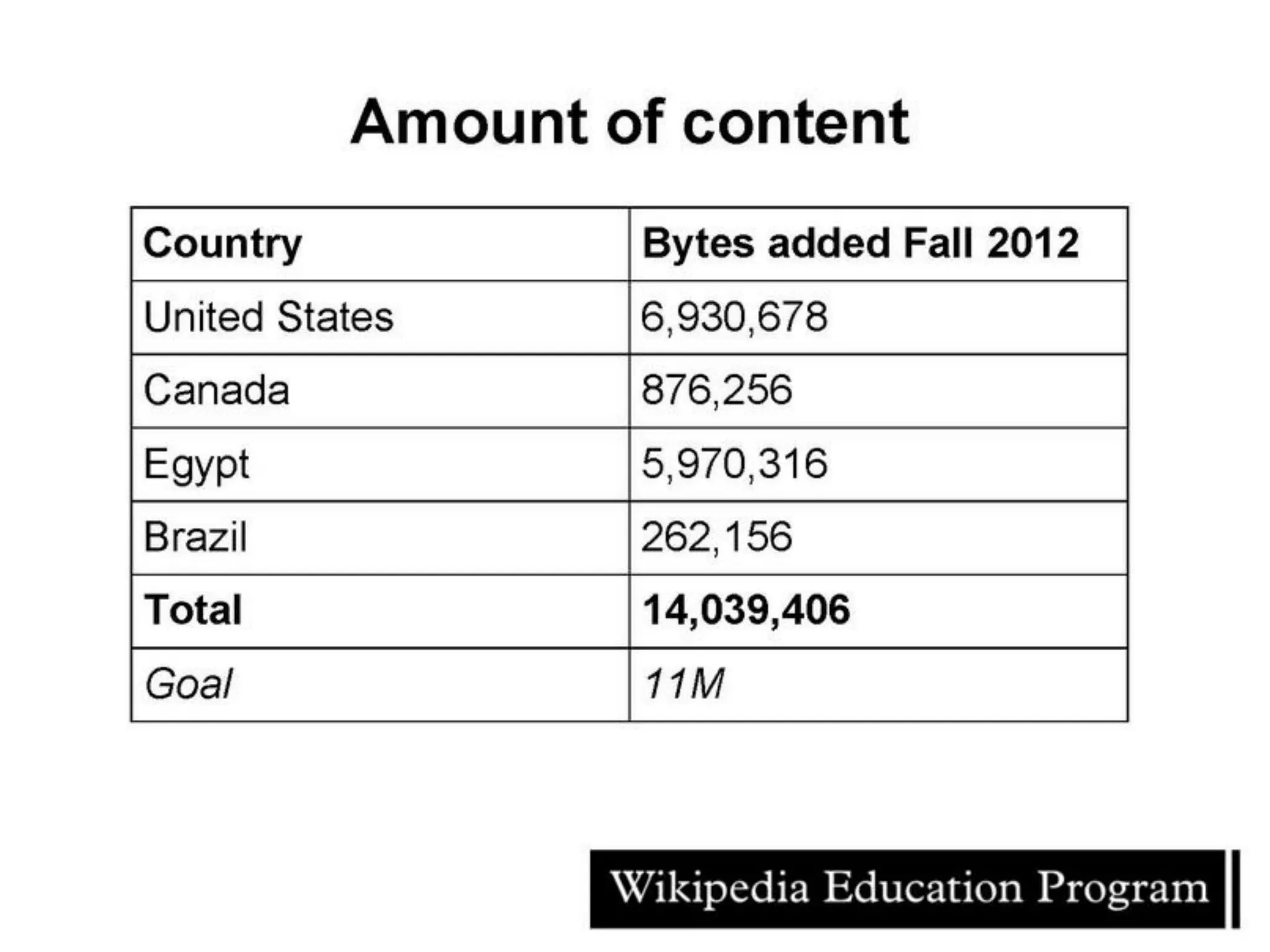
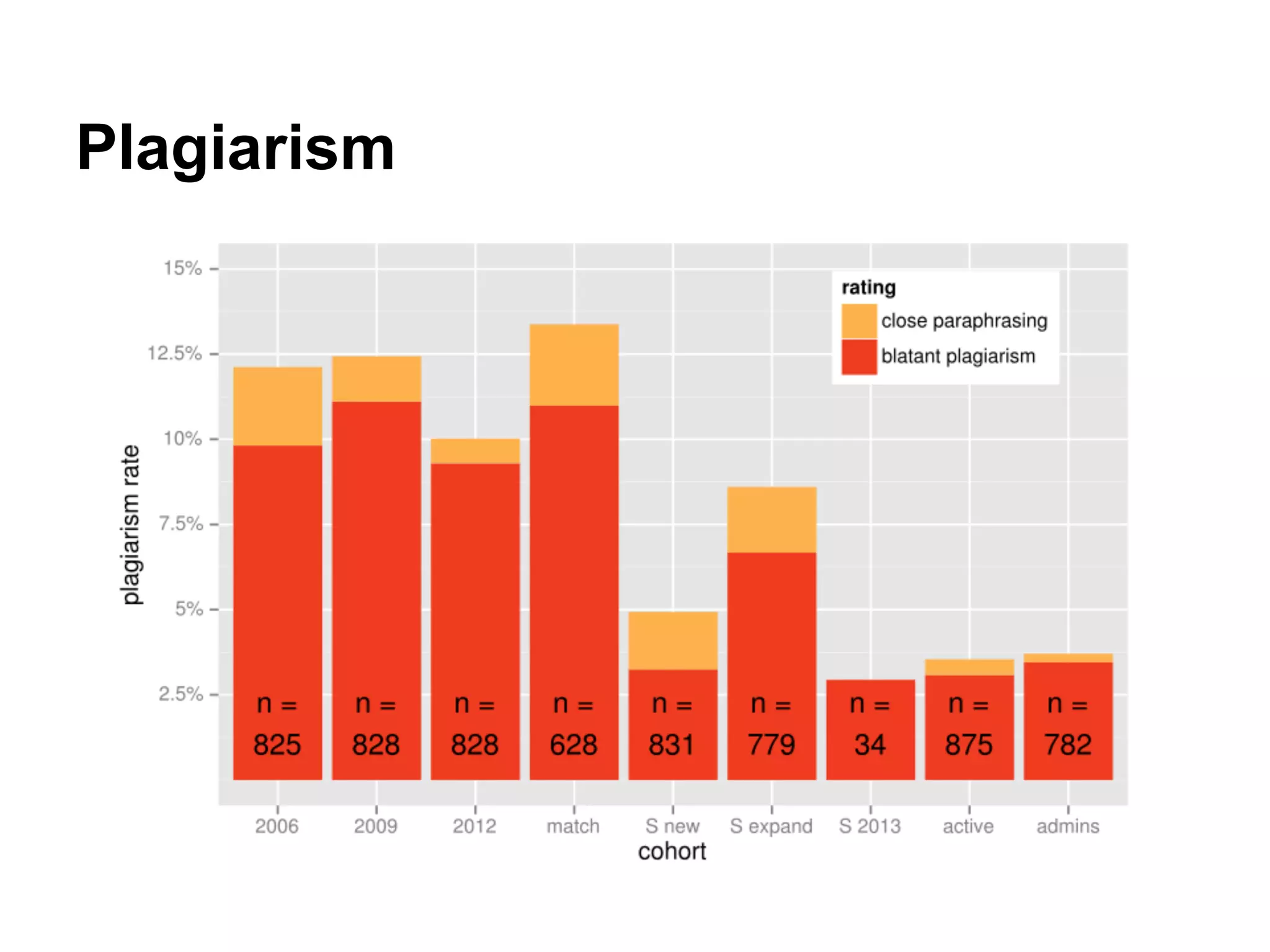
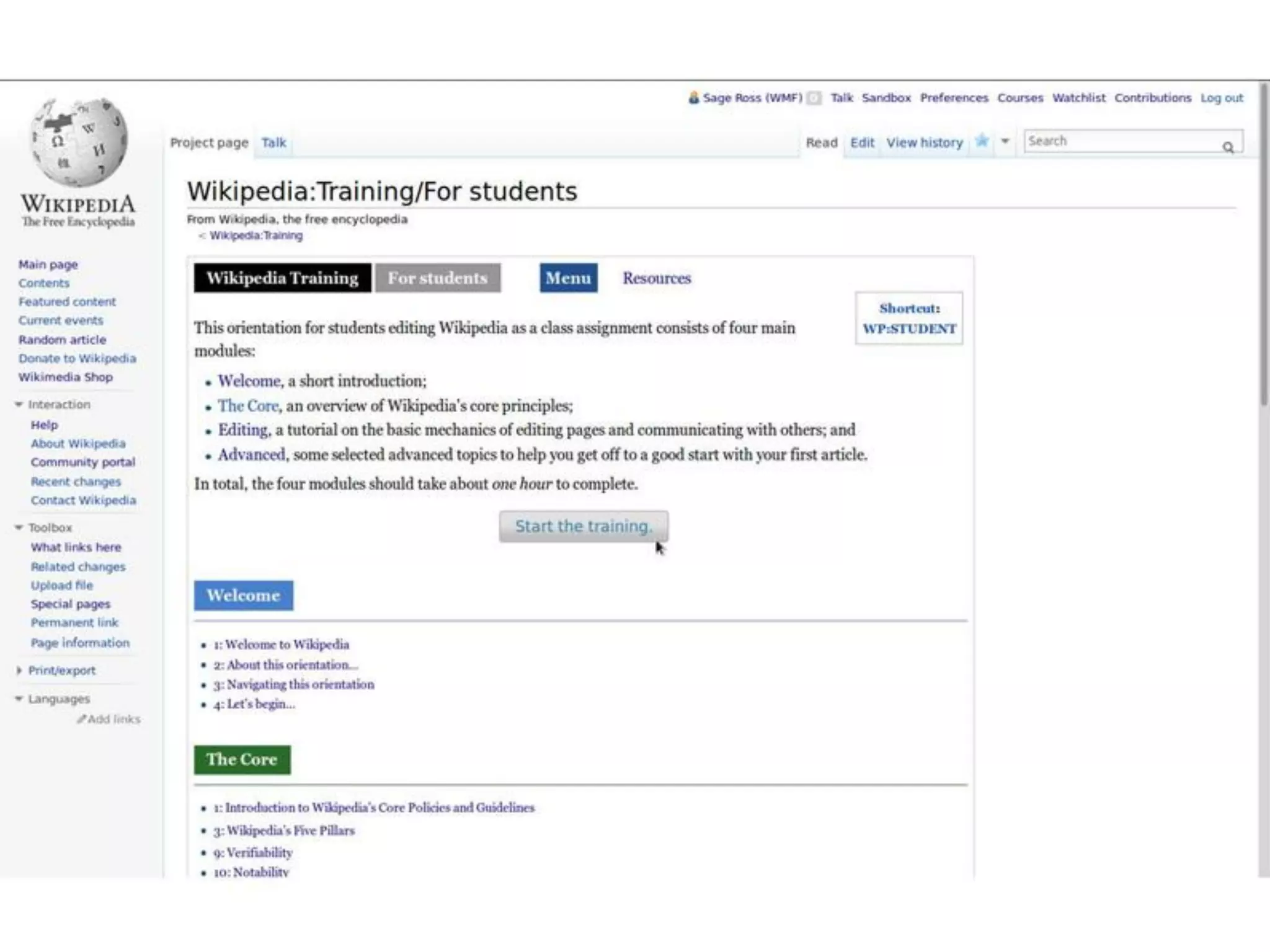
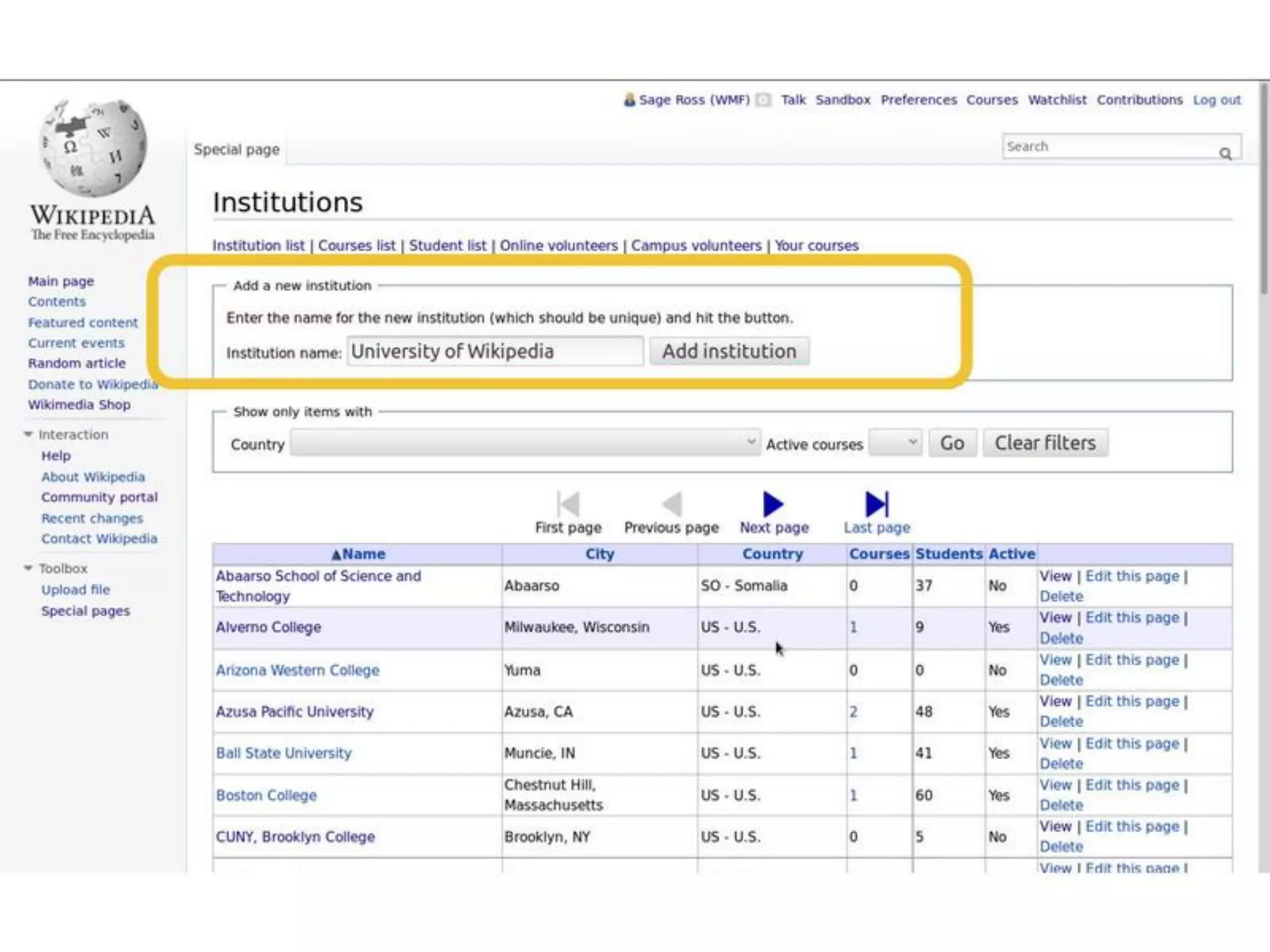
The document discusses the role of Wikipedia in education, highlighting its reliability and usage among medical professionals and students. It outlines Wikipedia's mission of sharing knowledge freely and the diverse efforts of volunteers in maintaining its content accuracy. The pedagogical benefits of using Wikipedia in education are emphasized, such as promoting media literacy, critical thinking, and digital citizenship.

![An early study in the journal Nature said that in 2005,
Wikipedia scientific articles came close to the level of
accuracy in Encyclopædia Britannica and had a similar
rate of "serious errors".[2]
Between 2008 and 2012, articles in medical and scientific
fields such as pathology,[5] toxicology,[6] oncology,[7]
pharmaceuticals,[8] and psychiatry[9] comparing Wikipedia
to professional and peer-reviewed sources found that
Wikipedia's depth and coverage were of a high
standard.
--Reliability of Wikipedia, Wikipedia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wikischolar-theintersectionoftheworldslargestreferenceworkandacademia-140113082853-phpapp01/75/The-Future-of-Wikipedia-in-Education-2-2048.jpg)









![Featured, Good articles
Semi-formal peer review
Total: 4,000 FAs and 10,000 GAs
Frequently written by experts
Primarily by one or by a few people
[20]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wikischolar-theintersectionoftheworldslargestreferenceworkandacademia-140113082853-phpapp01/75/The-Future-of-Wikipedia-in-Education-14-2048.jpg)