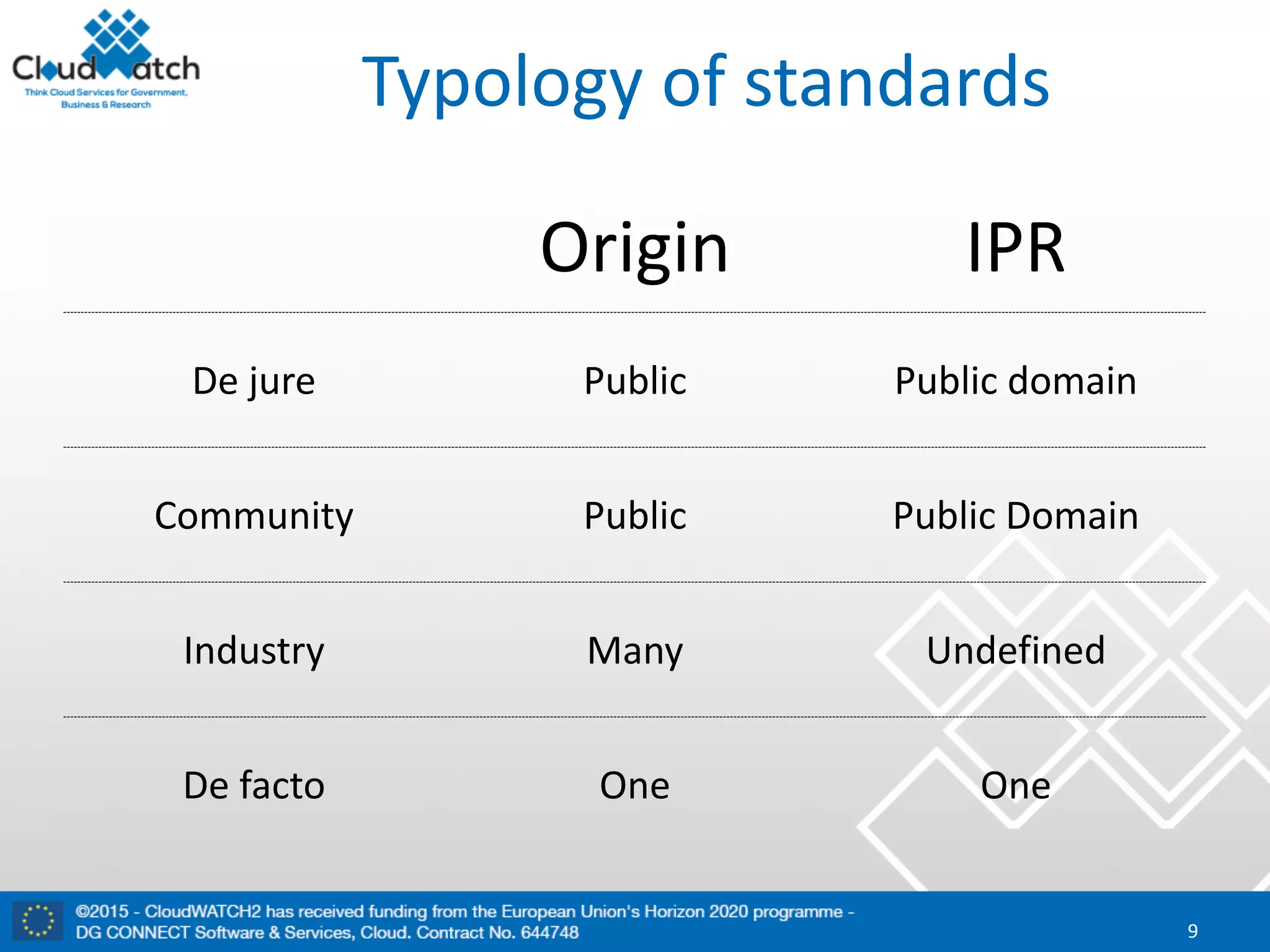
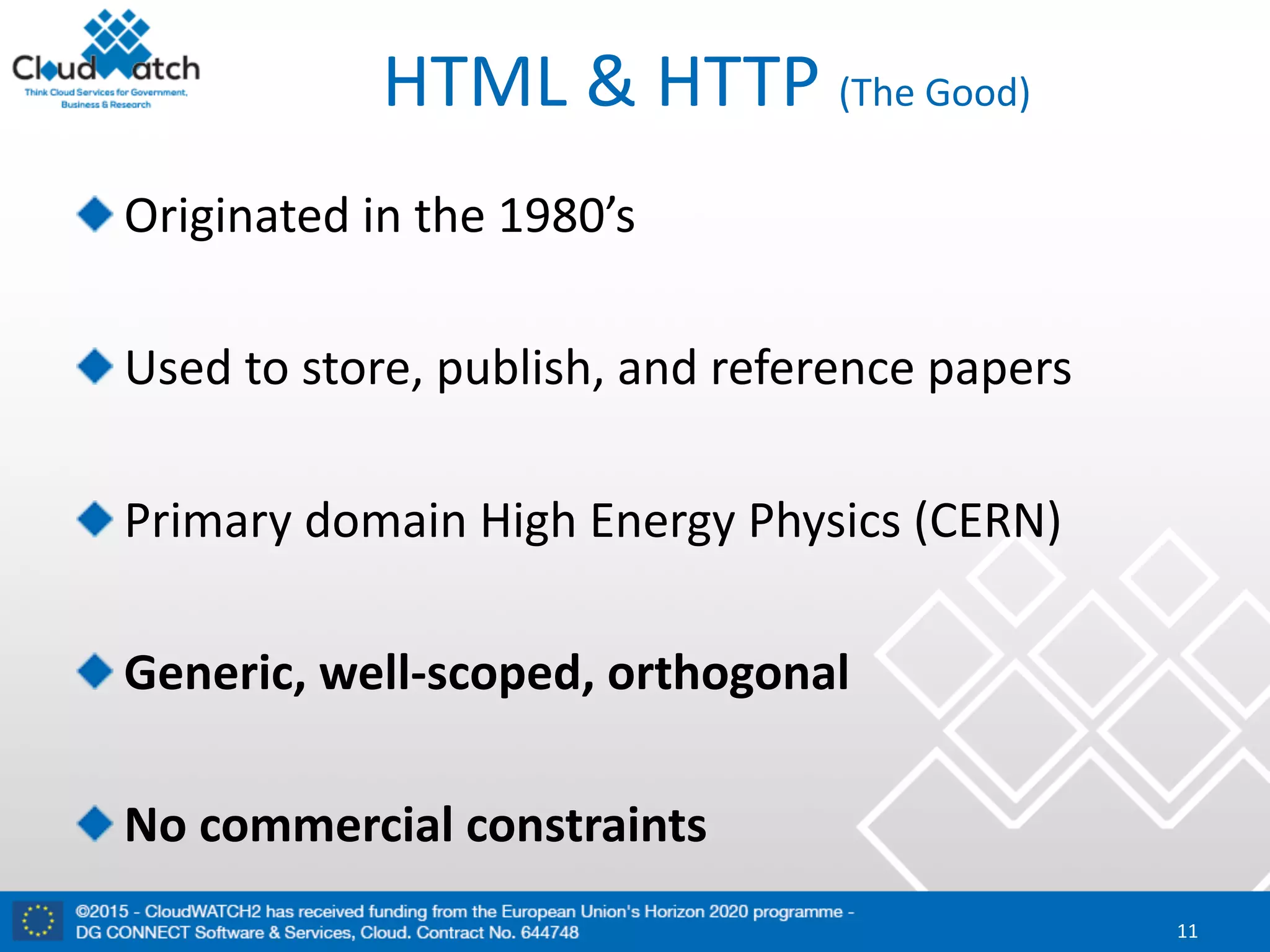
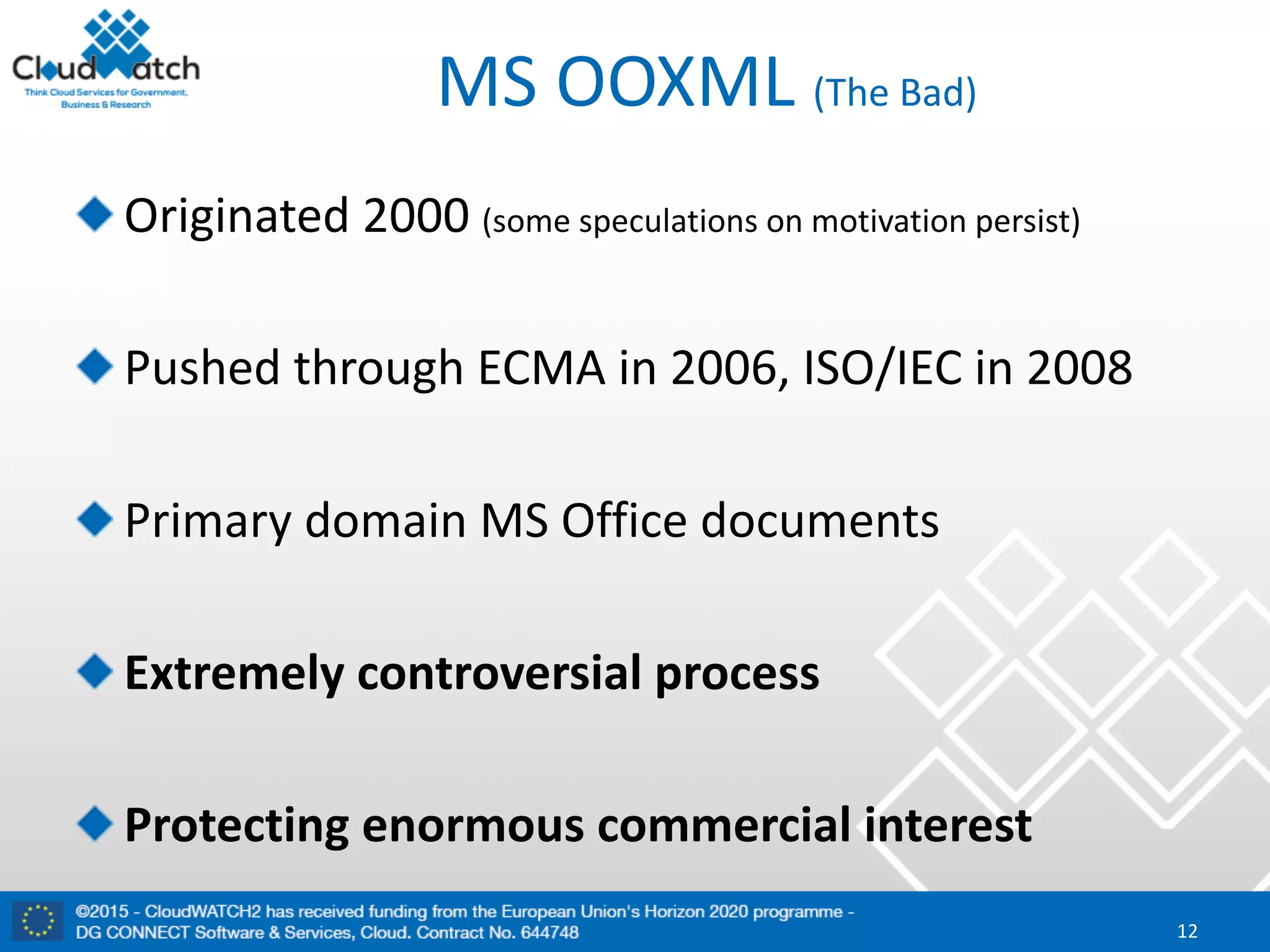
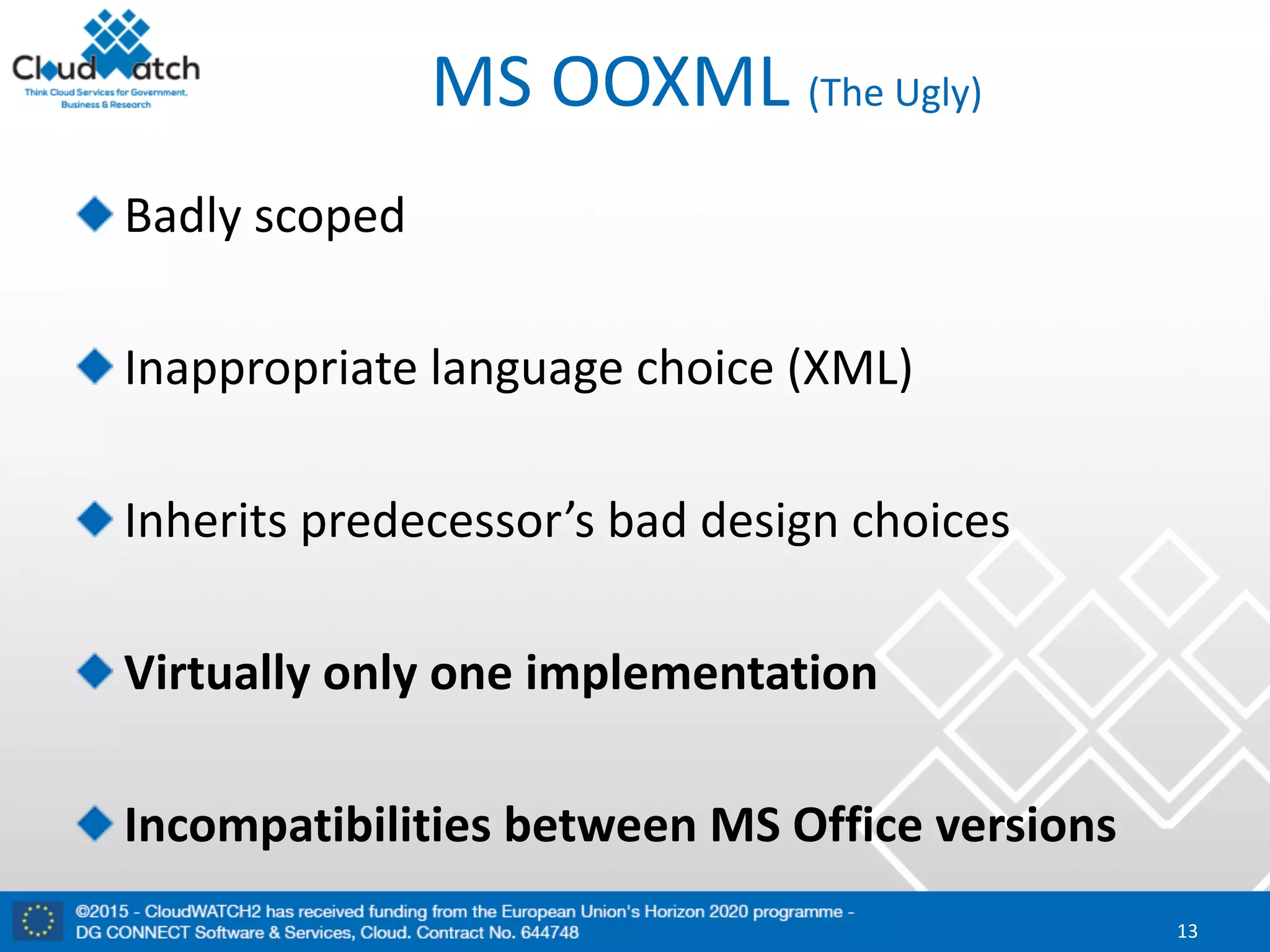
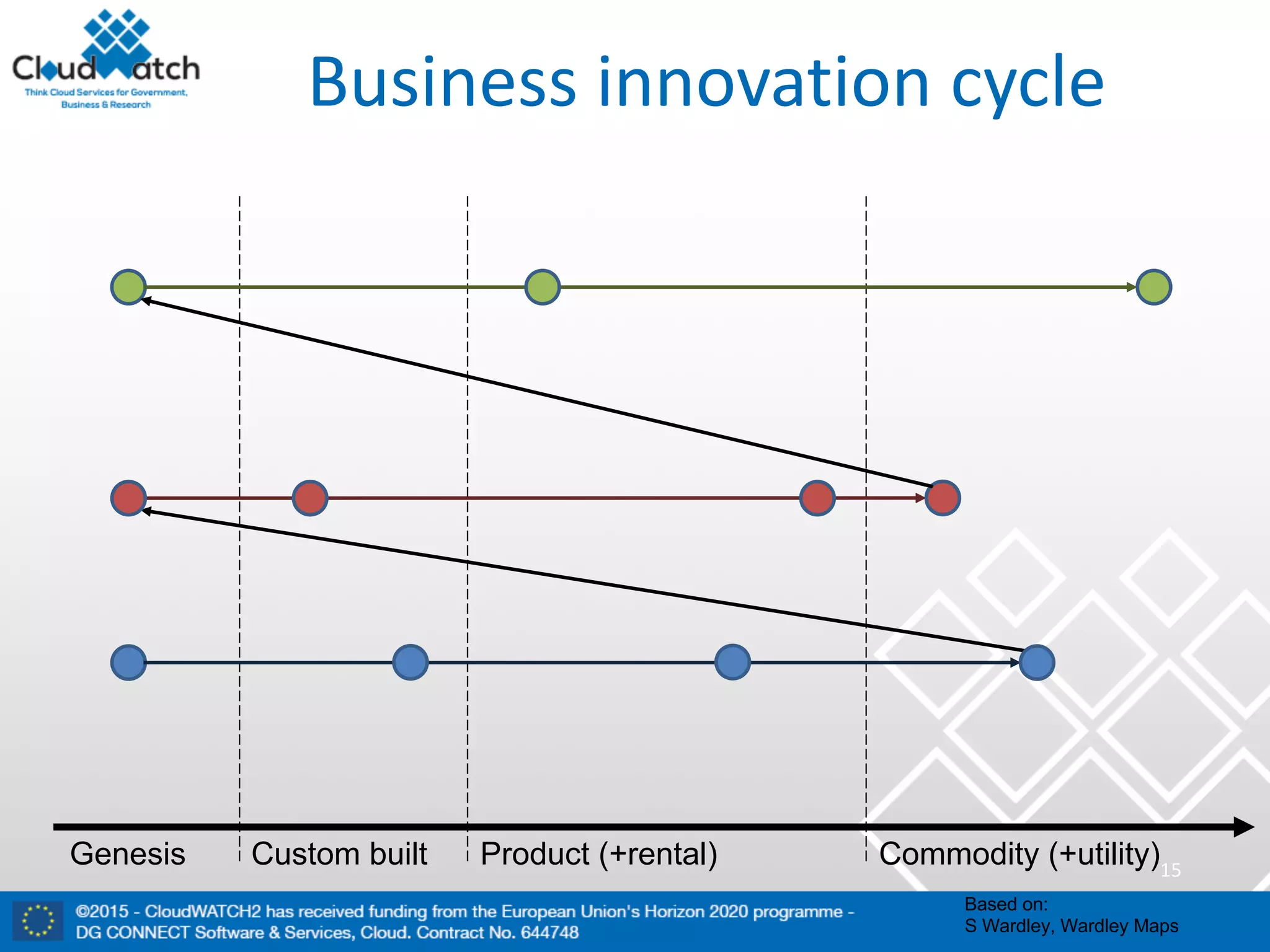
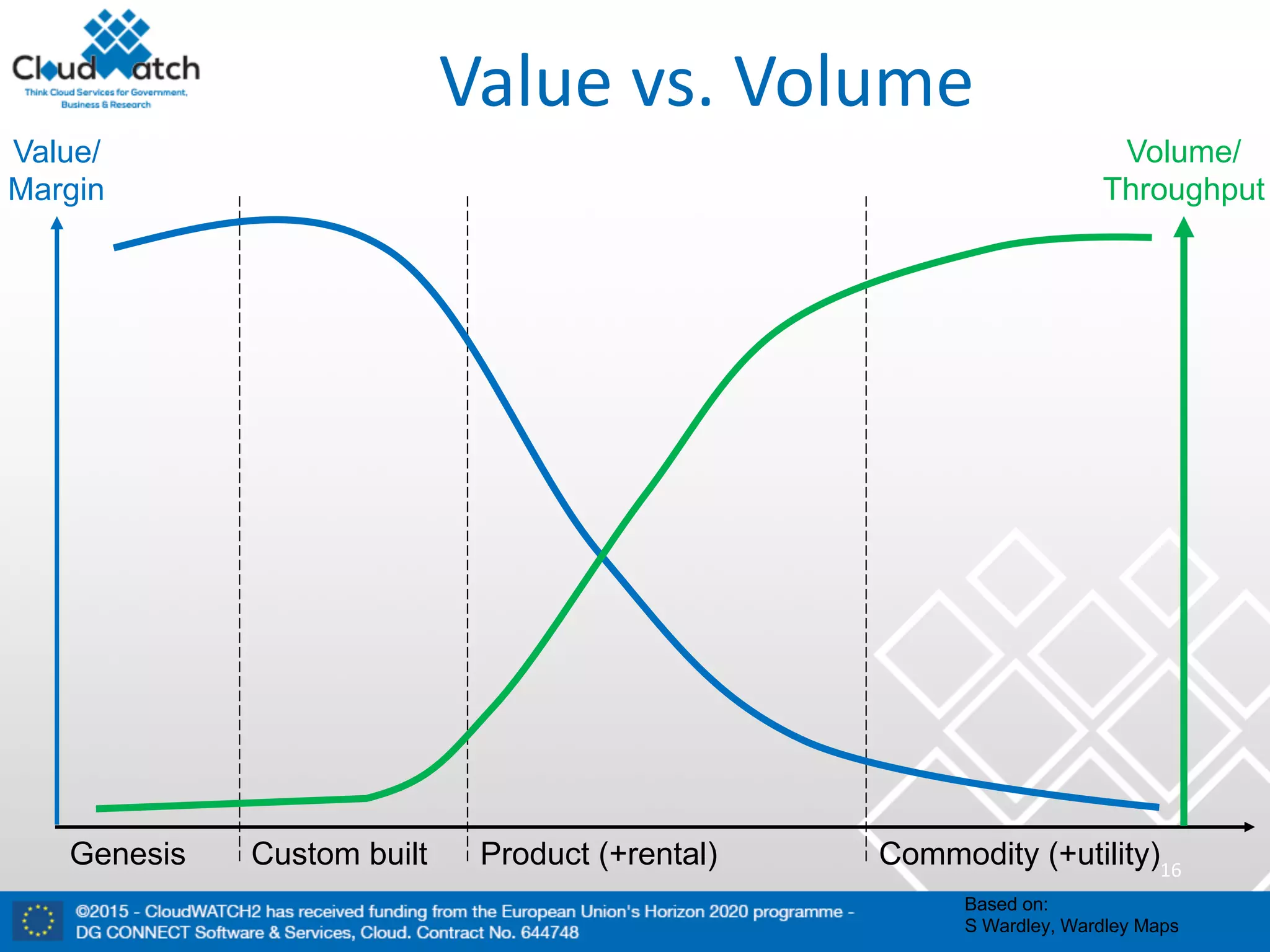
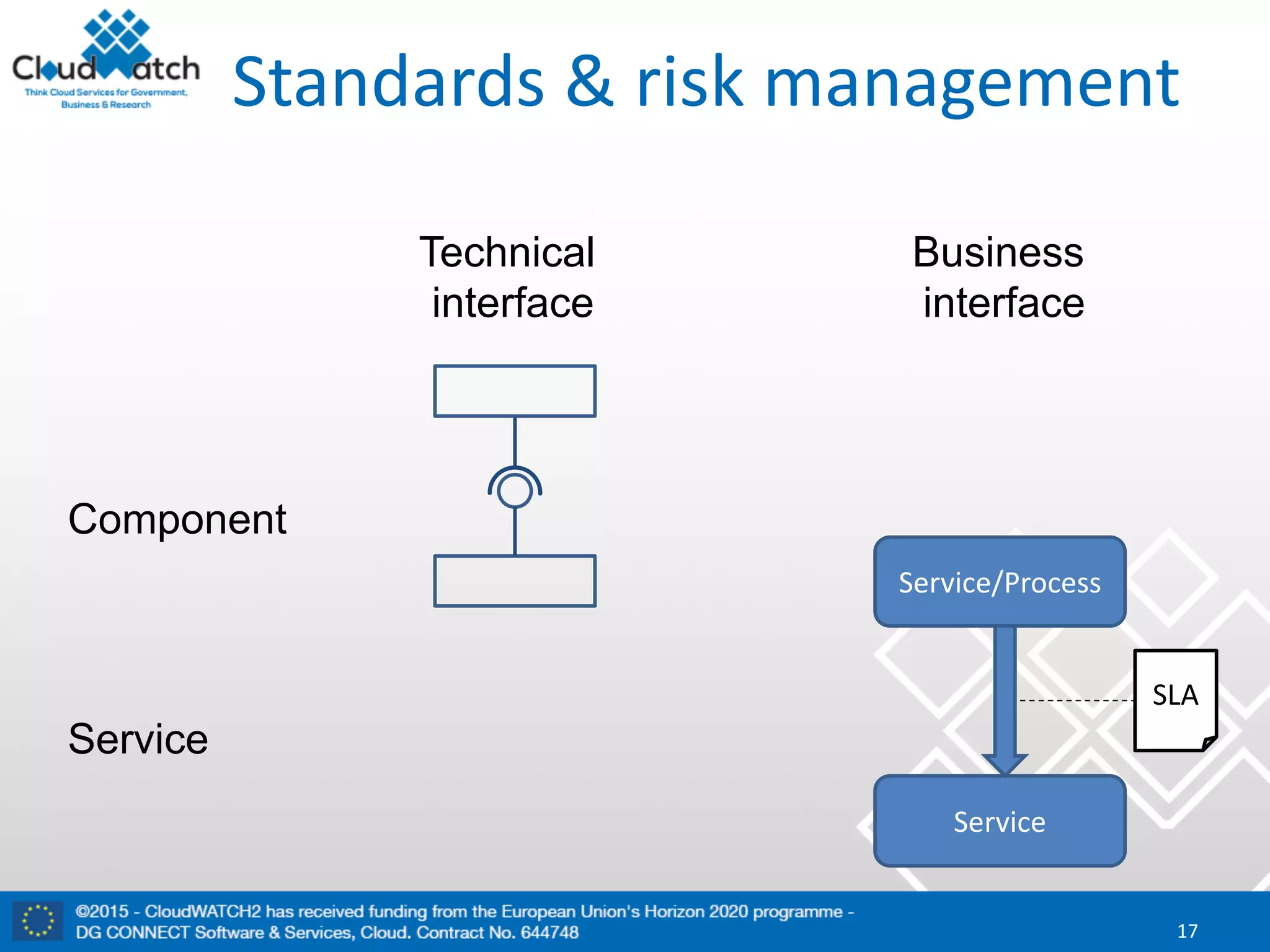
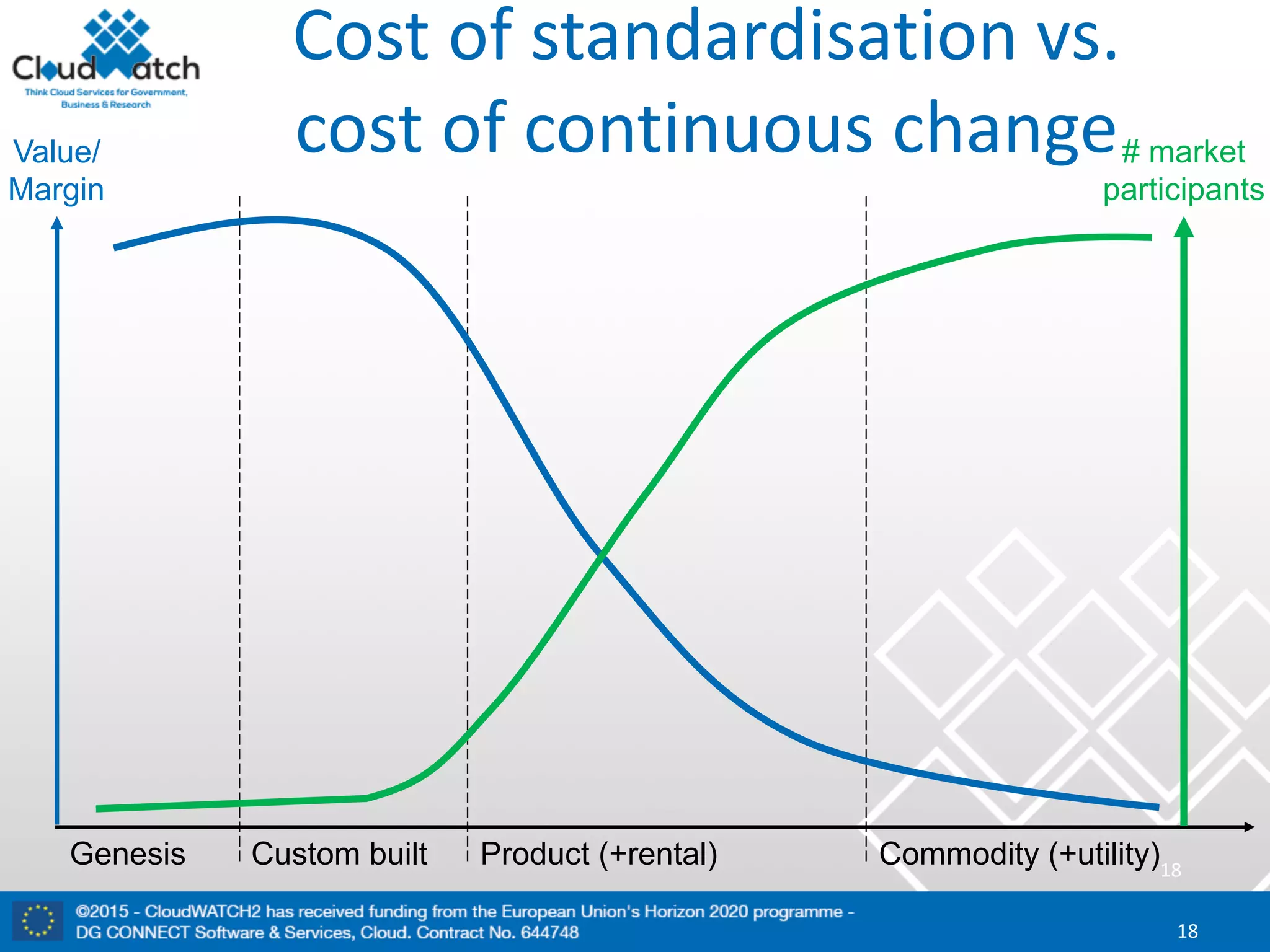
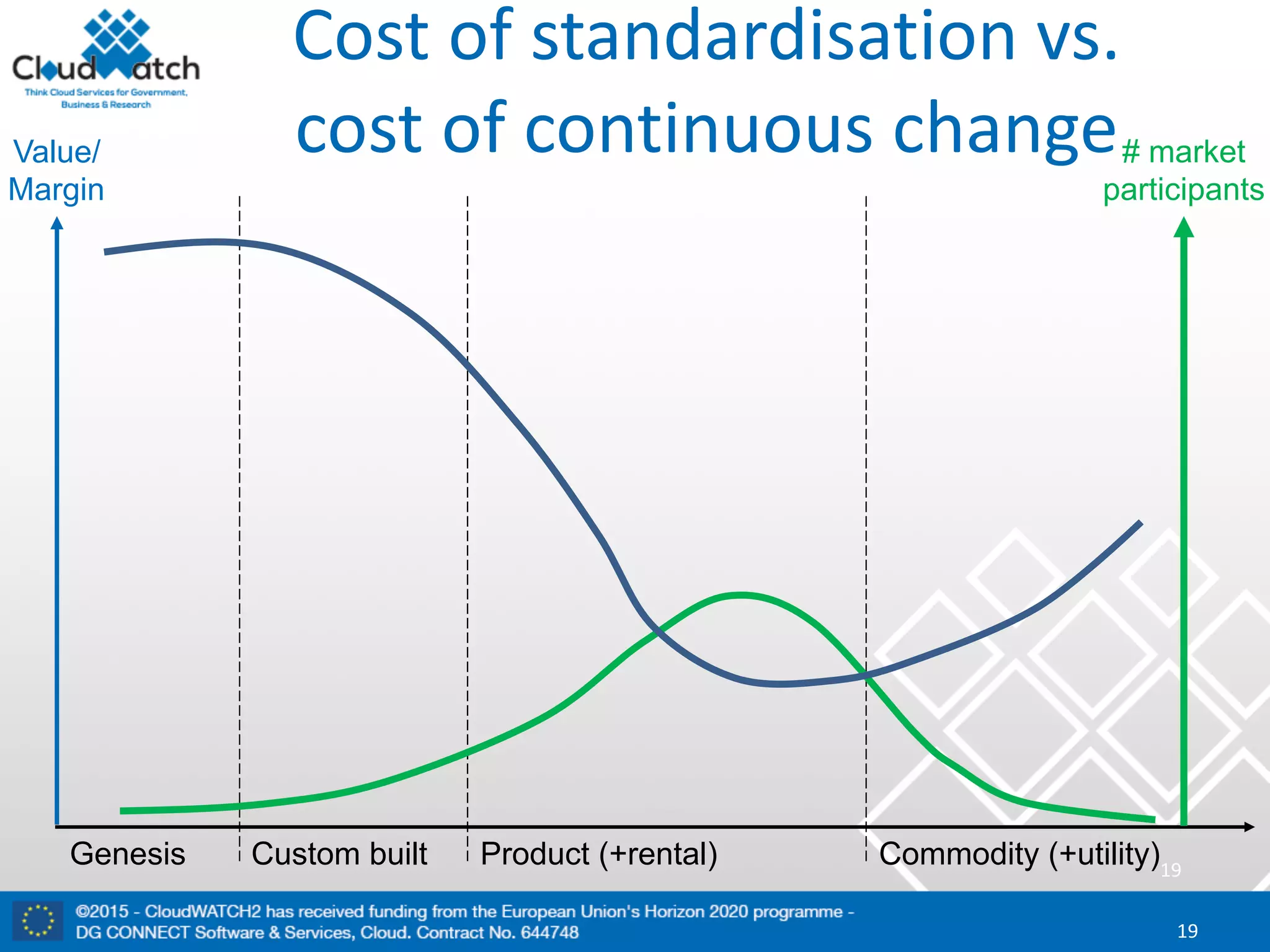
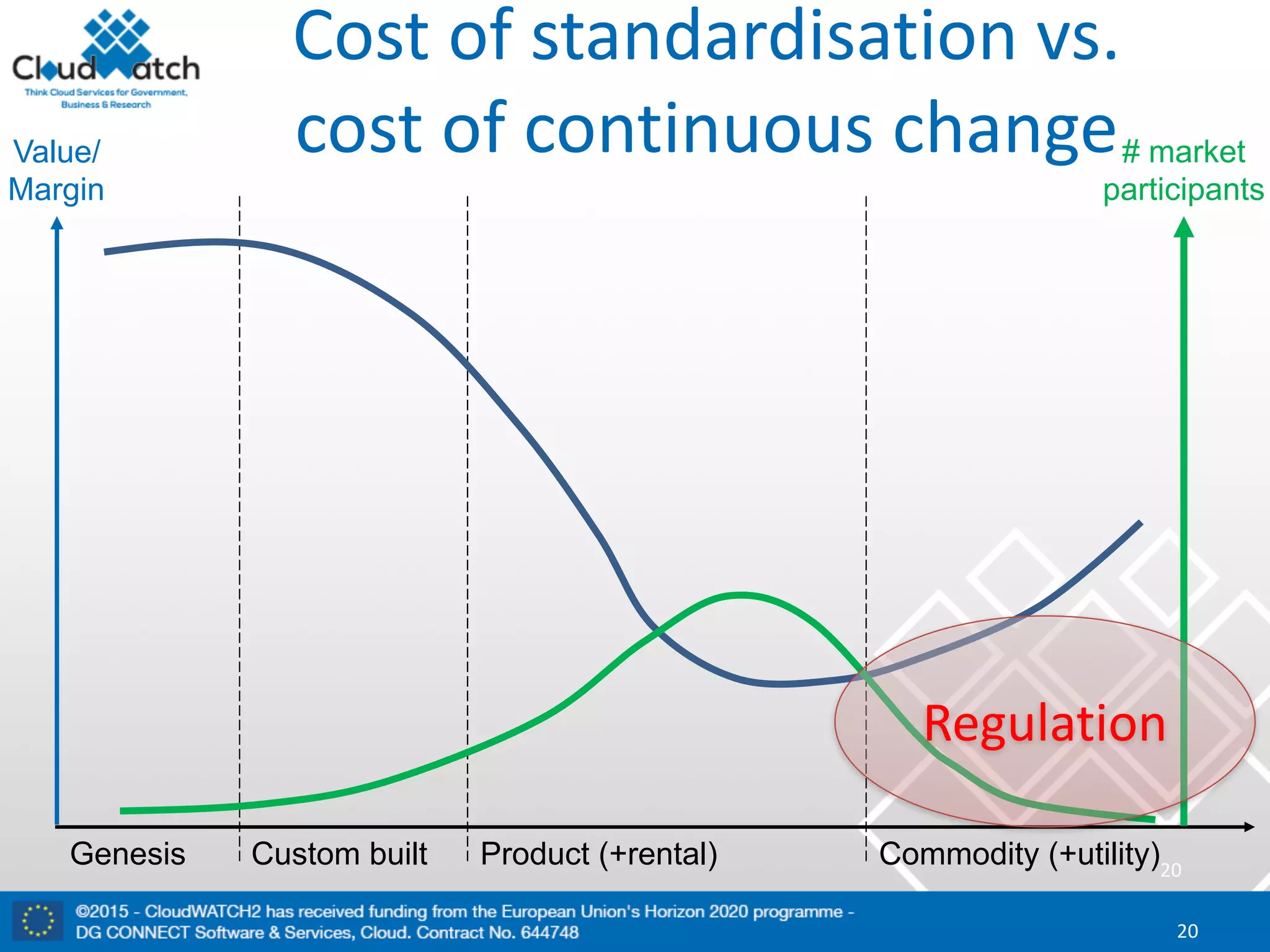
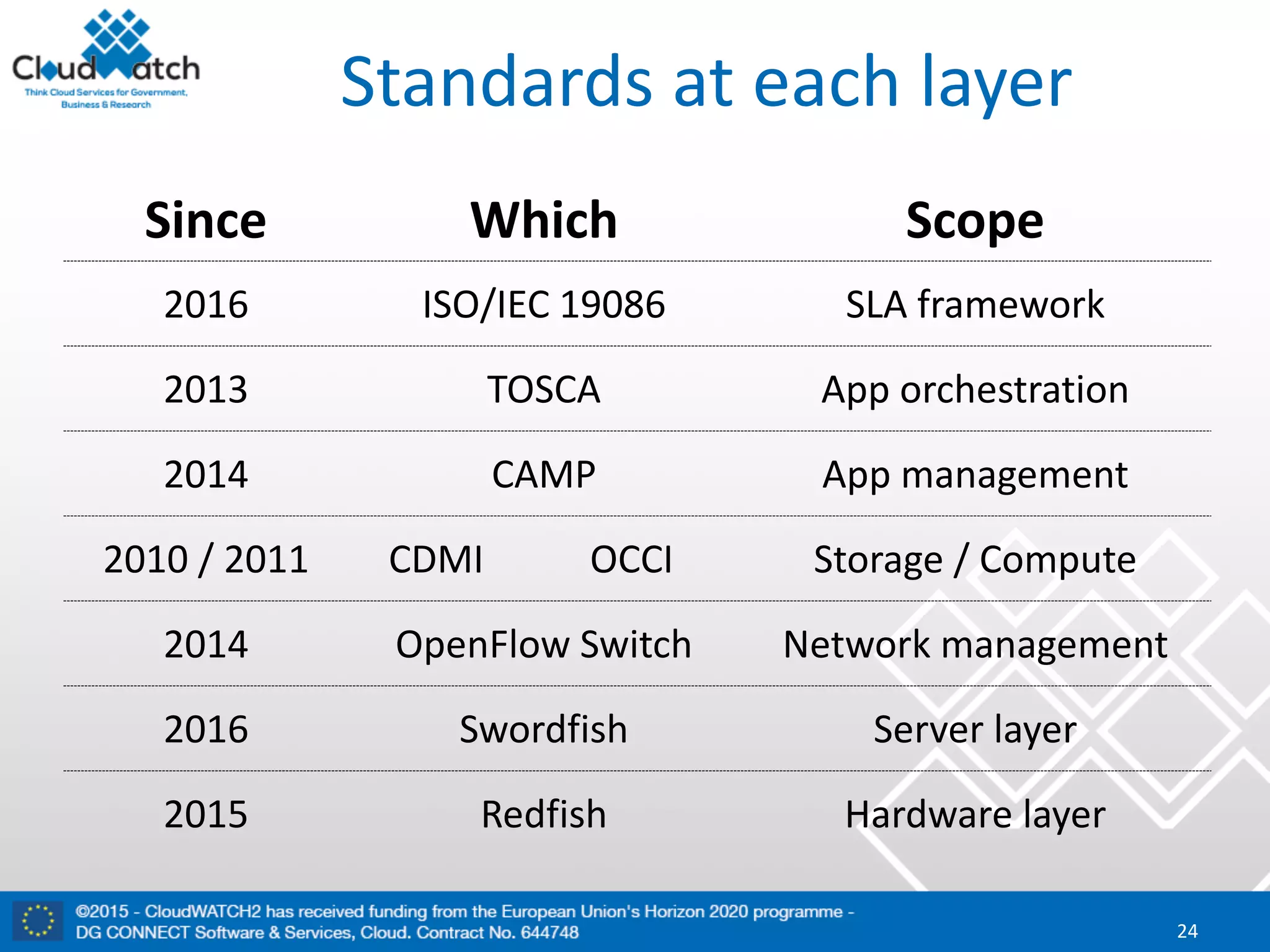
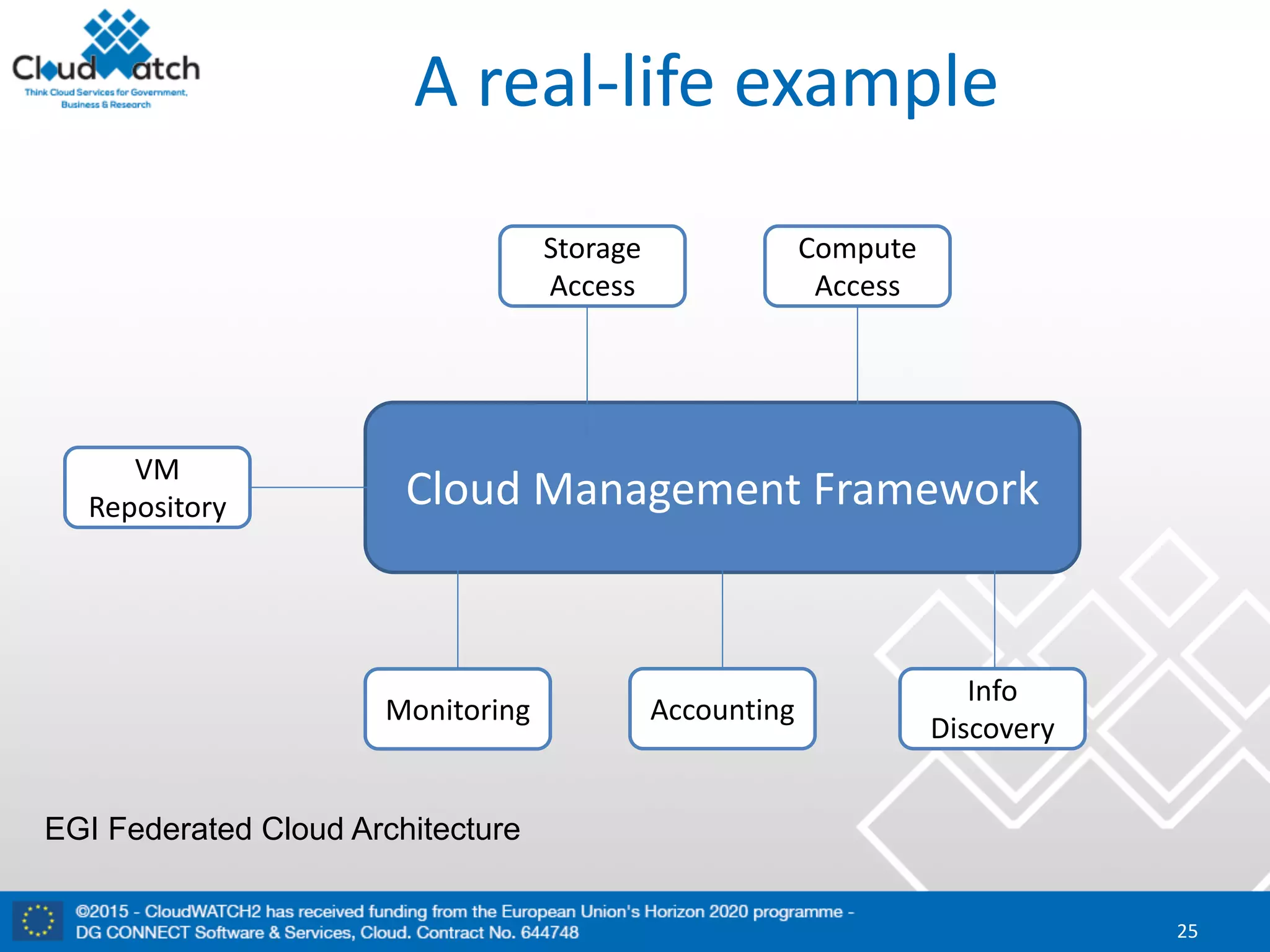
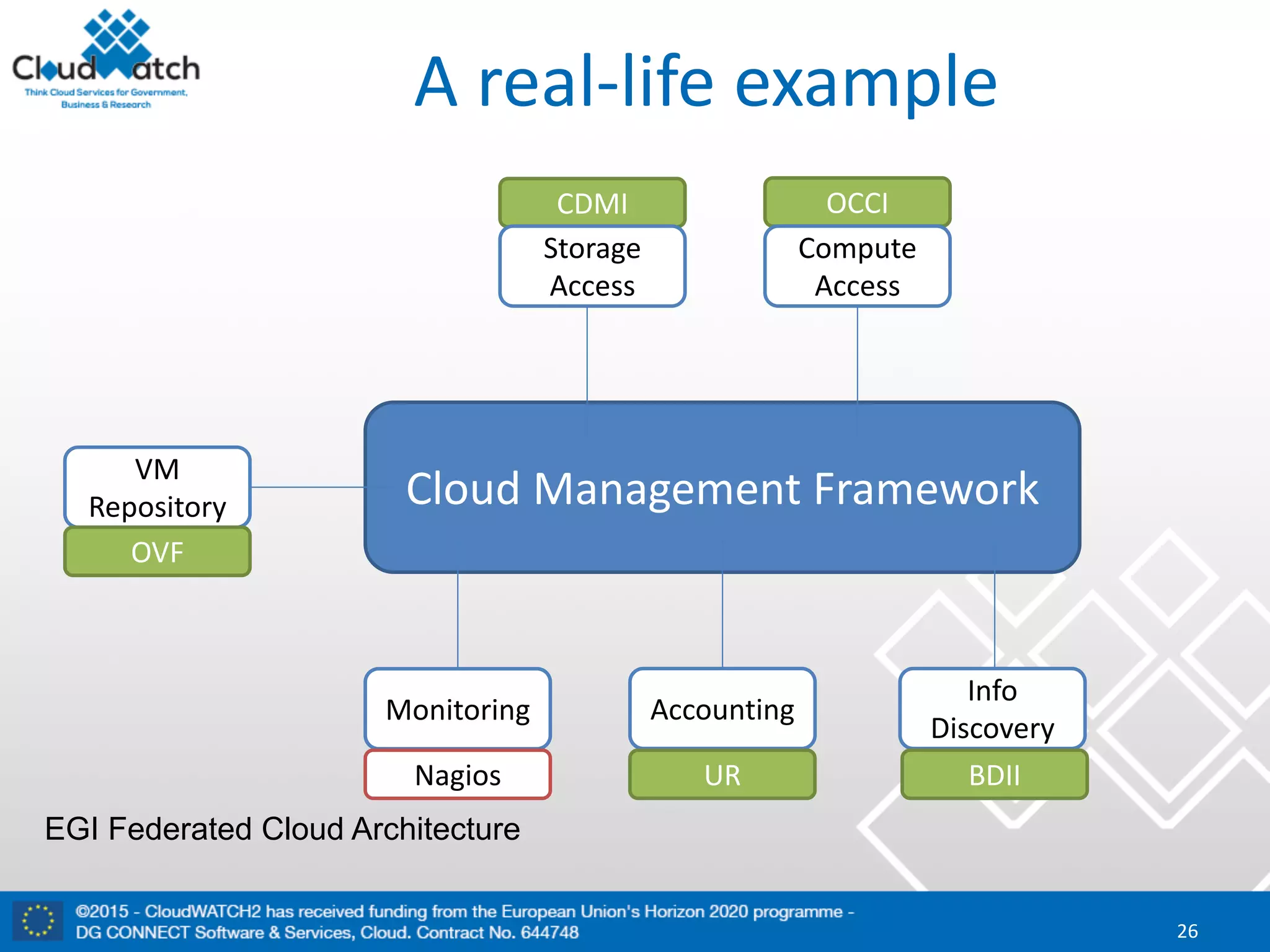
The document discusses the complexities and significance of standards in cloud computing, including historical examples and their impacts on various technologies. It presents a detailed exploration of different types of standards, their development processes, and their implications for both large corporations and startups. Additionally, it raises critical questions about balancing standardization with innovation and the varying perceptions of stakeholders within the industry.













![The EC and the DSM
Four Freedoms
1. Free movement of goods
2. Free movement for workers
3. […] Freedom to provide services
4. Free movement of capital
… applied to Digital Single Market
1. Harmonising of trading standards
2. Convergence on common standards
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05whystandardiseataleoficeandfirev6-170928124350/75/Why-standardise-The-business-case-for-the-adoption-of-cloud-standards-29-2048.jpg)