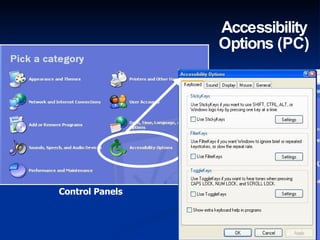
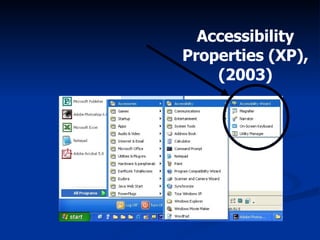
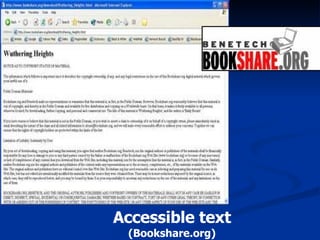
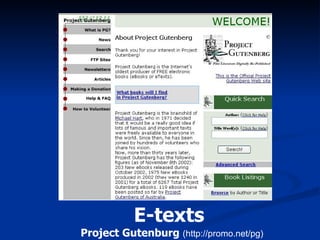
The document discusses making assistive technology available to all students in inclusive classrooms. It notes that up to 300,000 students need specialized assistive technology and that with appropriate access, 75% can remain in regular classrooms and 45% can reduce services. It provides examples of assistive technologies like audio support, alternative outputs for computers, accessible texts and library books. It emphasizes the importance of evidence-based practices and removing obstacles to collaboration between general and special educators to support all students.








































![Contact info. Betty Nelson [email_address] http://www.slideshare.net/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cec-2008-1207198134070963-9/85/Why-Not-Make-Assistive-Technology-Available-50-320.jpg)