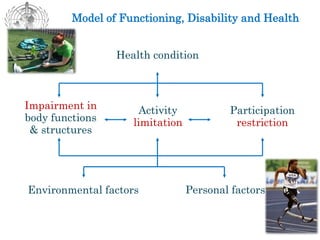
The document summarizes the WHO Global Disability Action Plan 2014-2021, which aims to improve health services for people with disabilities globally. The plan has 3 main objectives: 1) remove barriers to healthcare access, 2) strengthen rehabilitation services, and 3) improve disability data collection. It was developed in response to the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities and the 2013 UN meeting on disability. The plan is implemented through guidance documents, country support, and the Model Disability Survey to standardize disability measurement. Progress includes cognitive testing of the survey in multiple countries with pilot studies ongoing.