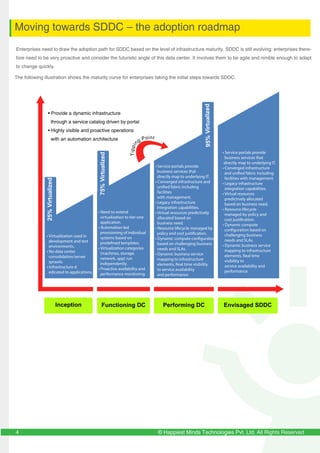
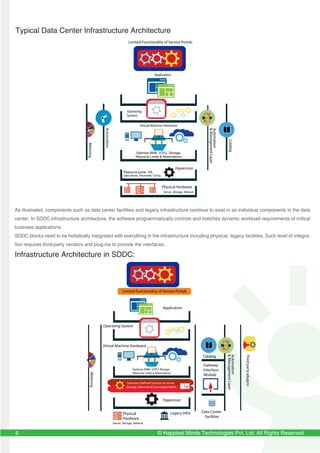
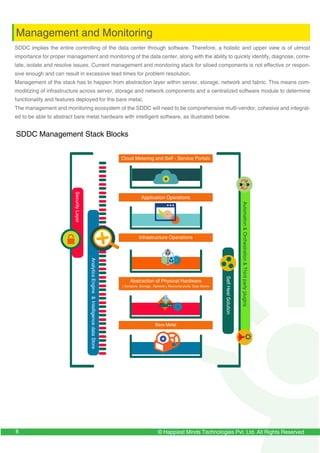
The document discusses the evolution and importance of Software-Defined Data Centers (SDDC) in transforming IT infrastructure by prioritizing software over hardware for efficiency and flexibility in resource management. It outlines a roadmap for enterprises to adopt SDDC, the potential benefits, and challenges faced during the transition, including the need for comprehensive management solutions and vendor interoperability. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of power and cooling systems in supporting SDDC infrastructure and highlights the role of technology in meeting business demands in a cloud-centric world.