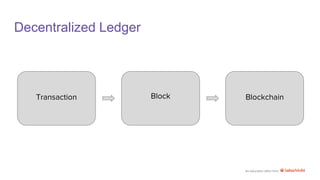
Blockchain is a decentralized ledger technology consisting of linked blocks containing transactions, which enhances transparency and prevents fraud. It features transaction processing, immutable ledgers, and various consensus mechanisms like proof of work and proof of stake. Notable examples include Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Hyperledger.