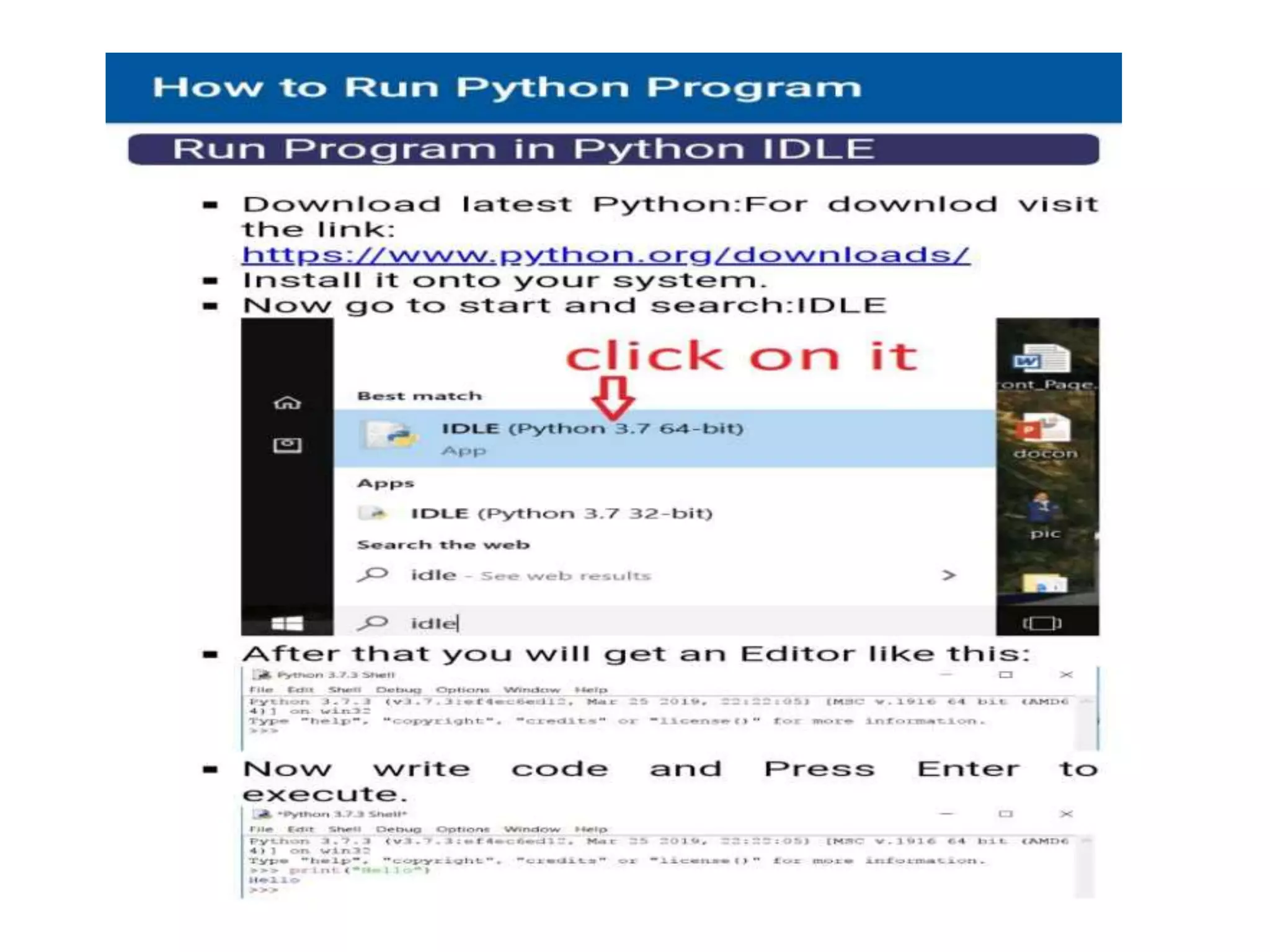
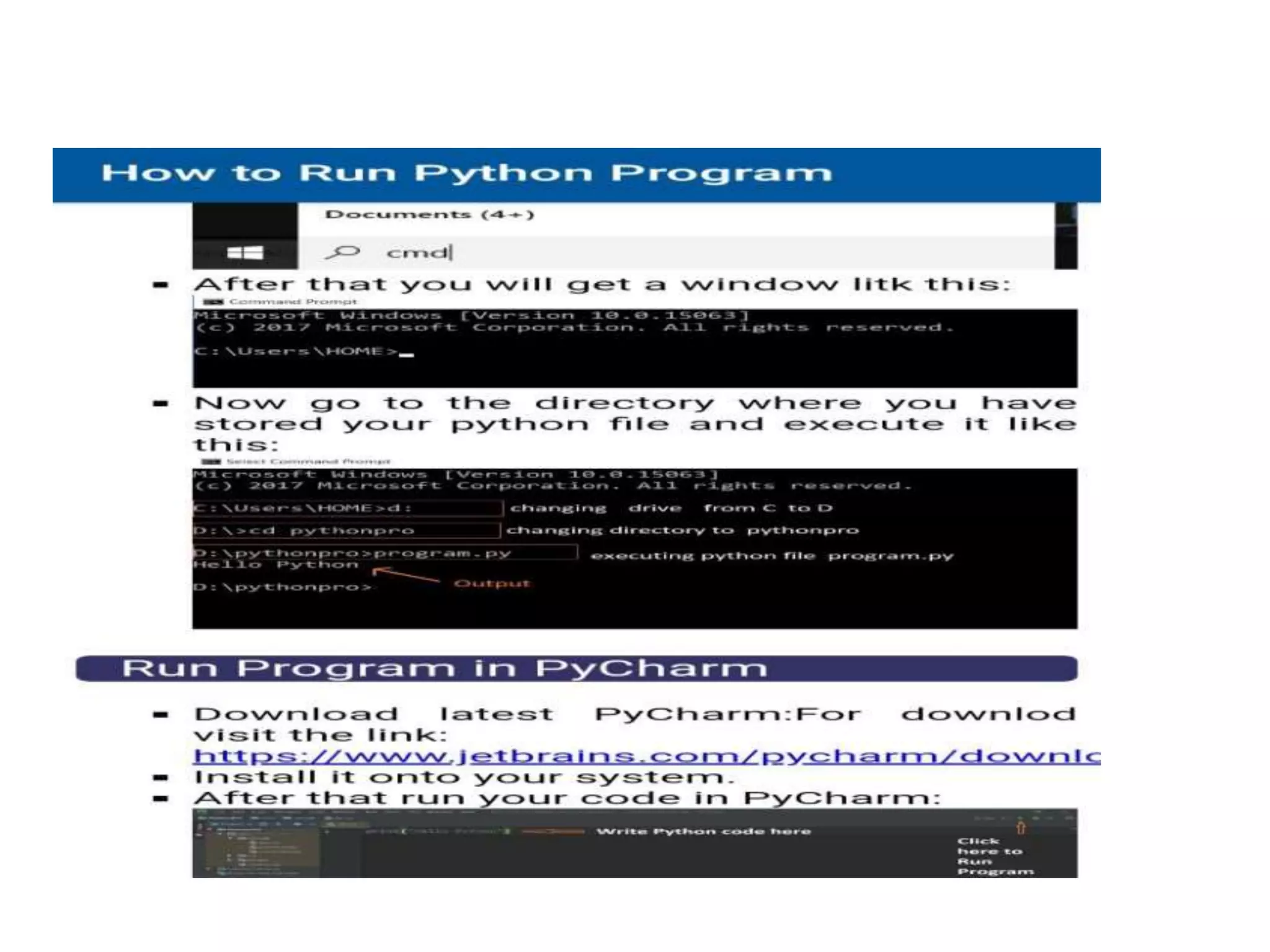
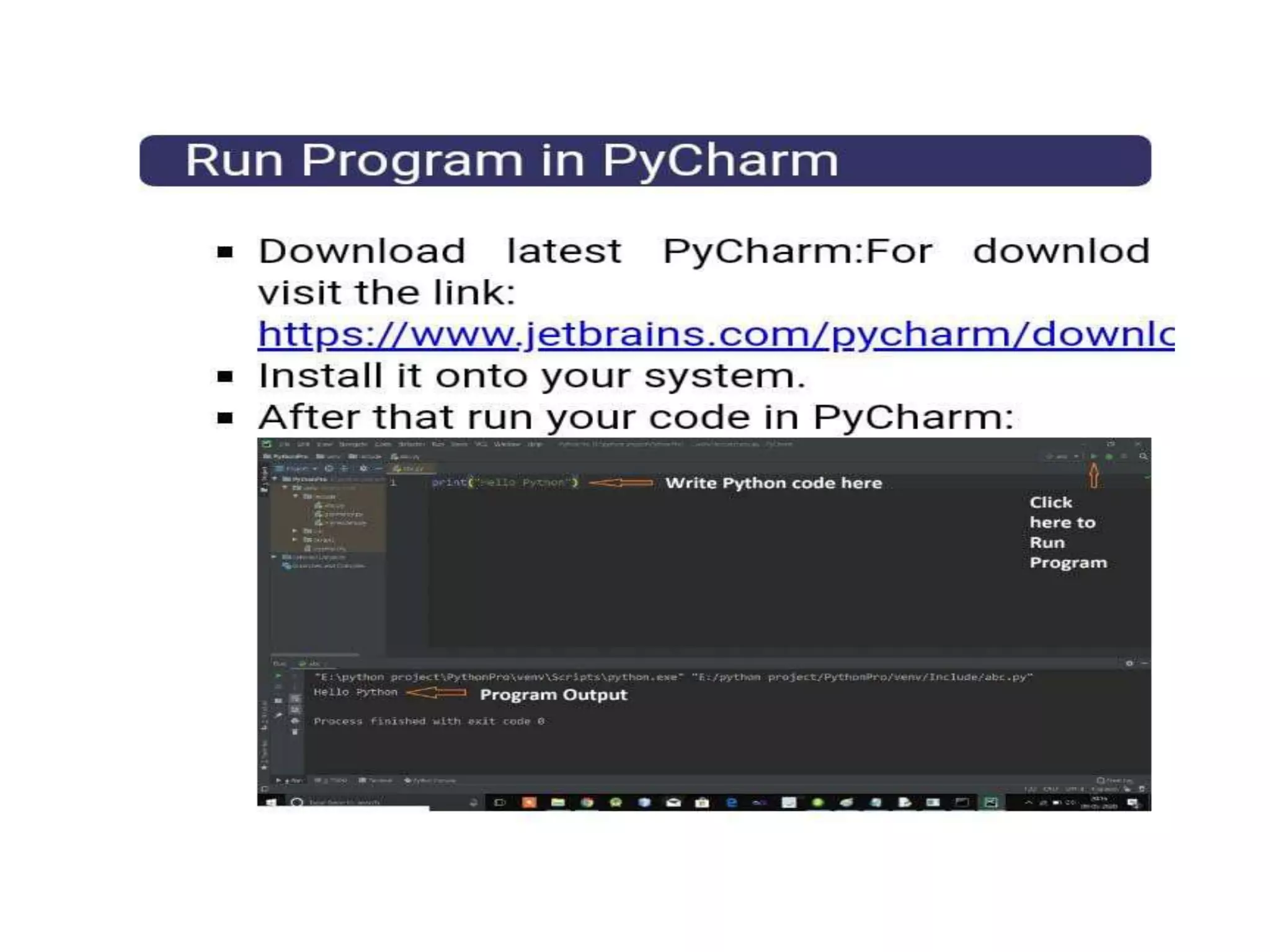
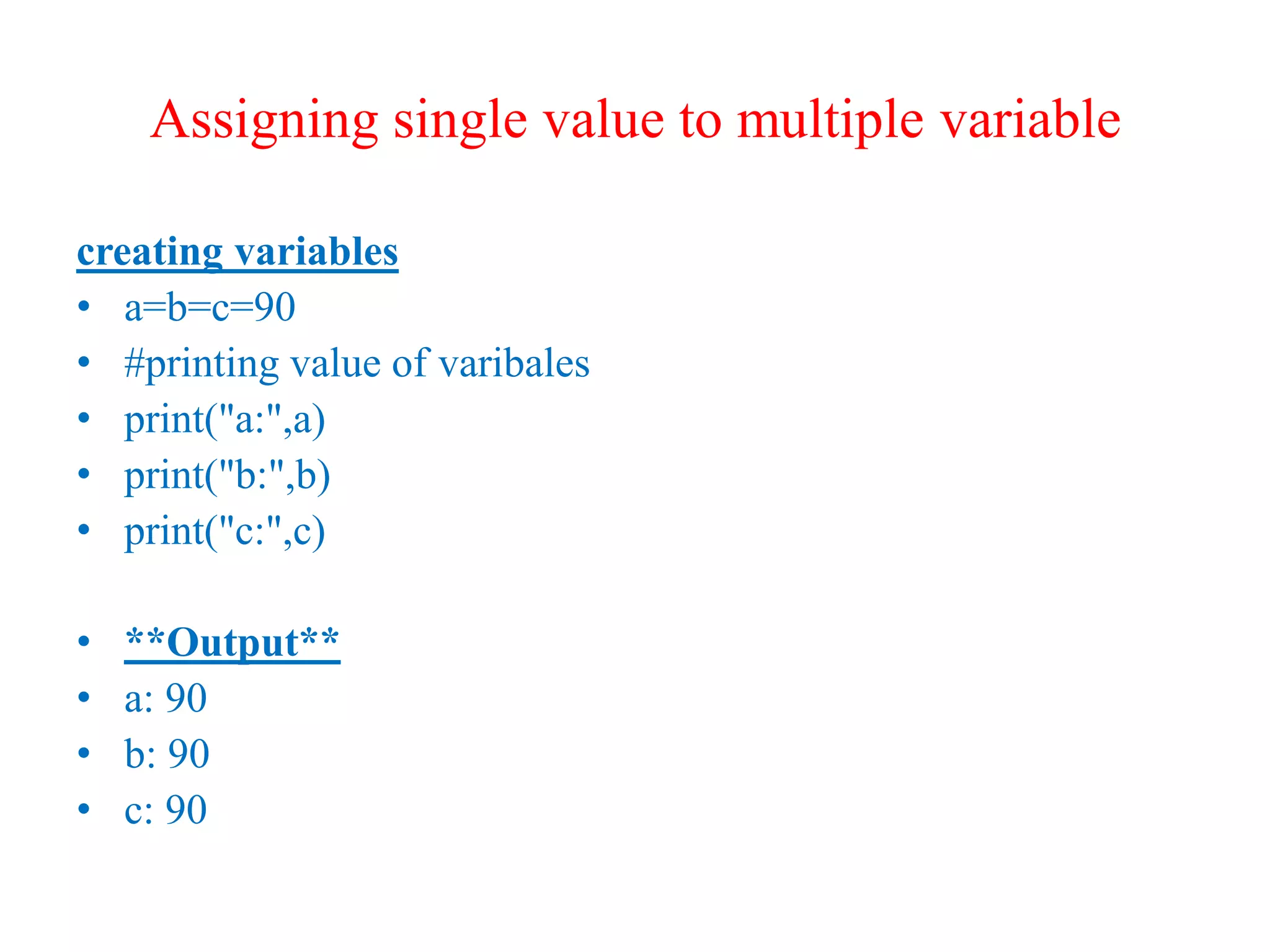
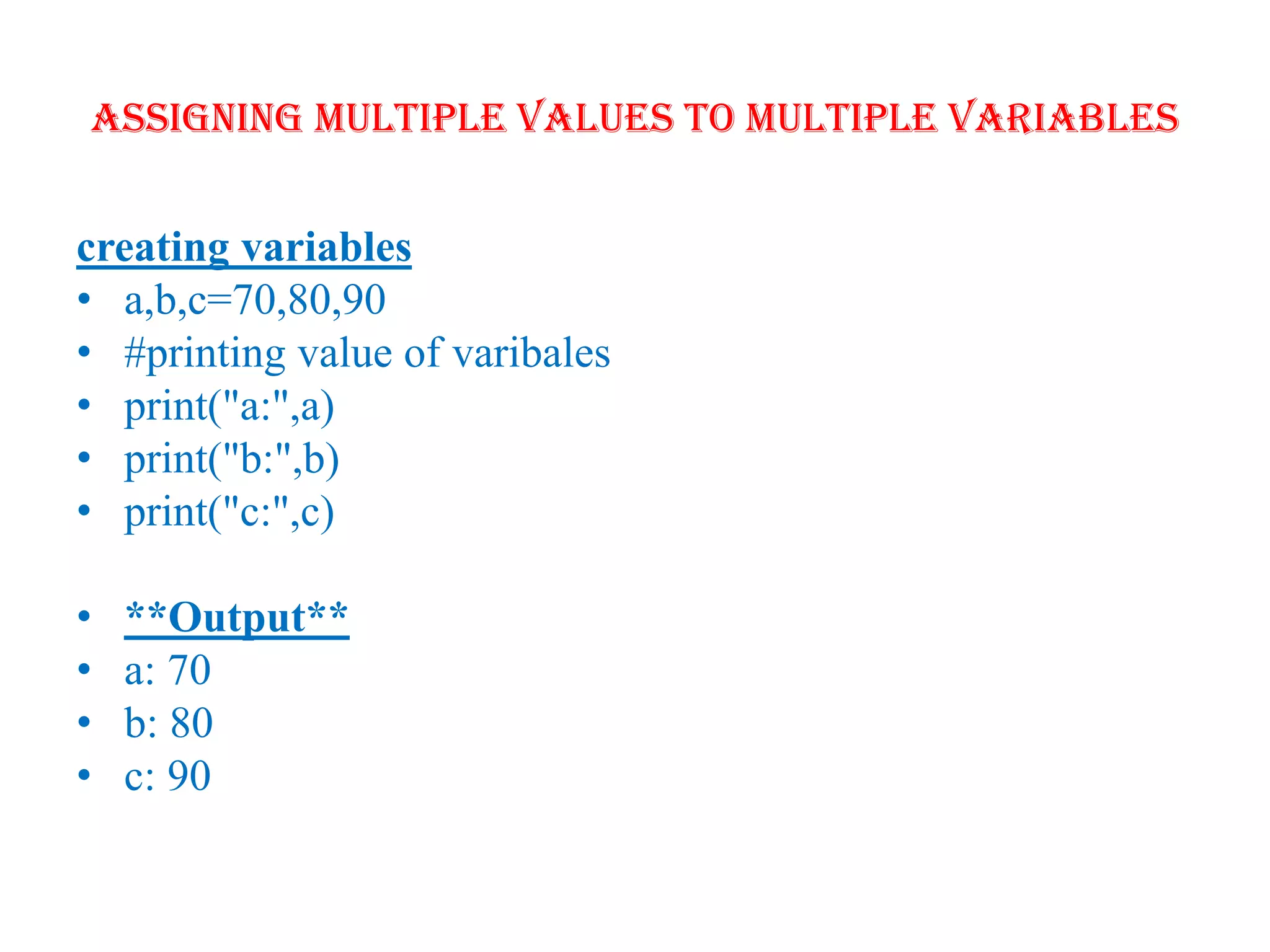
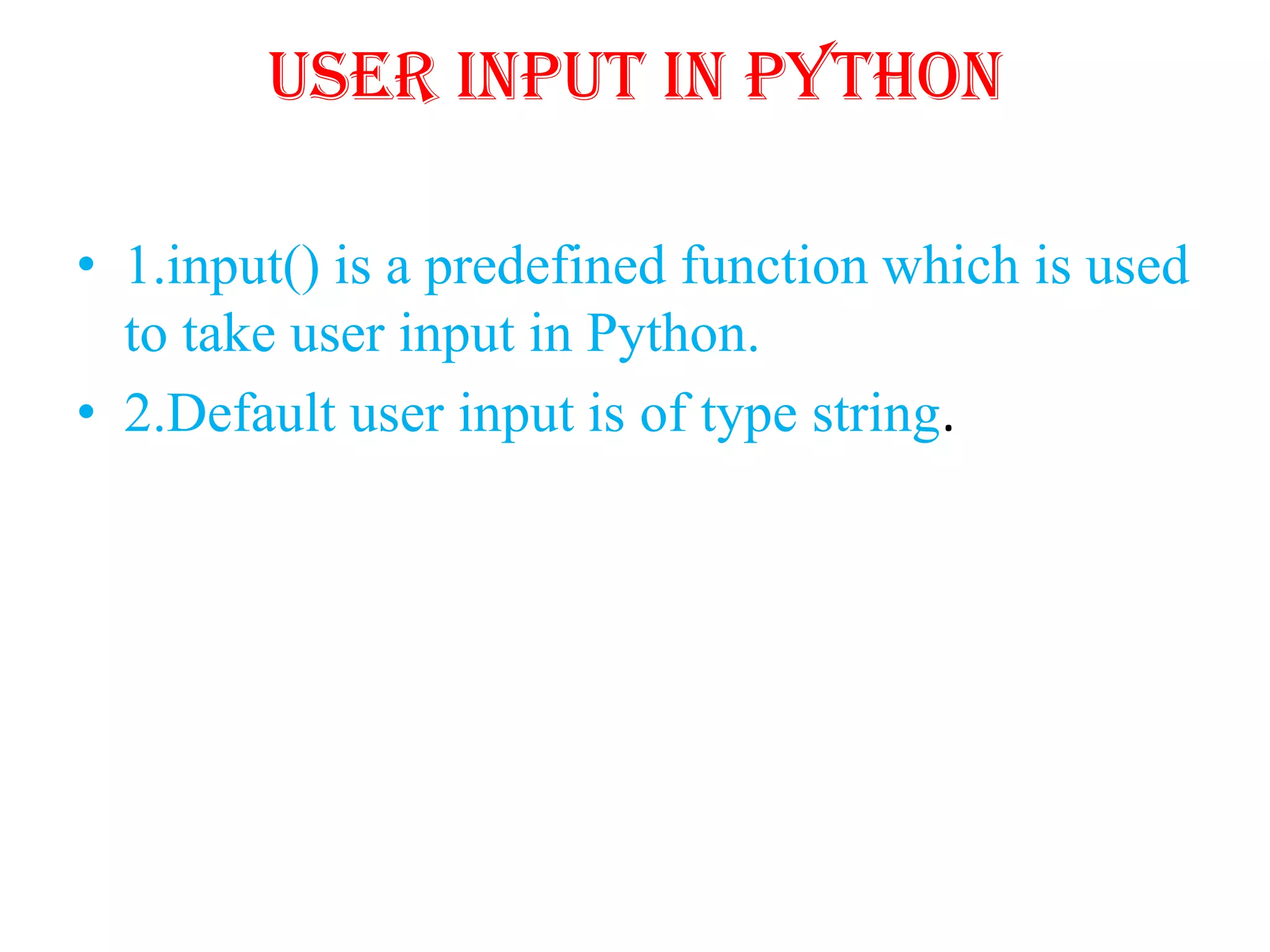
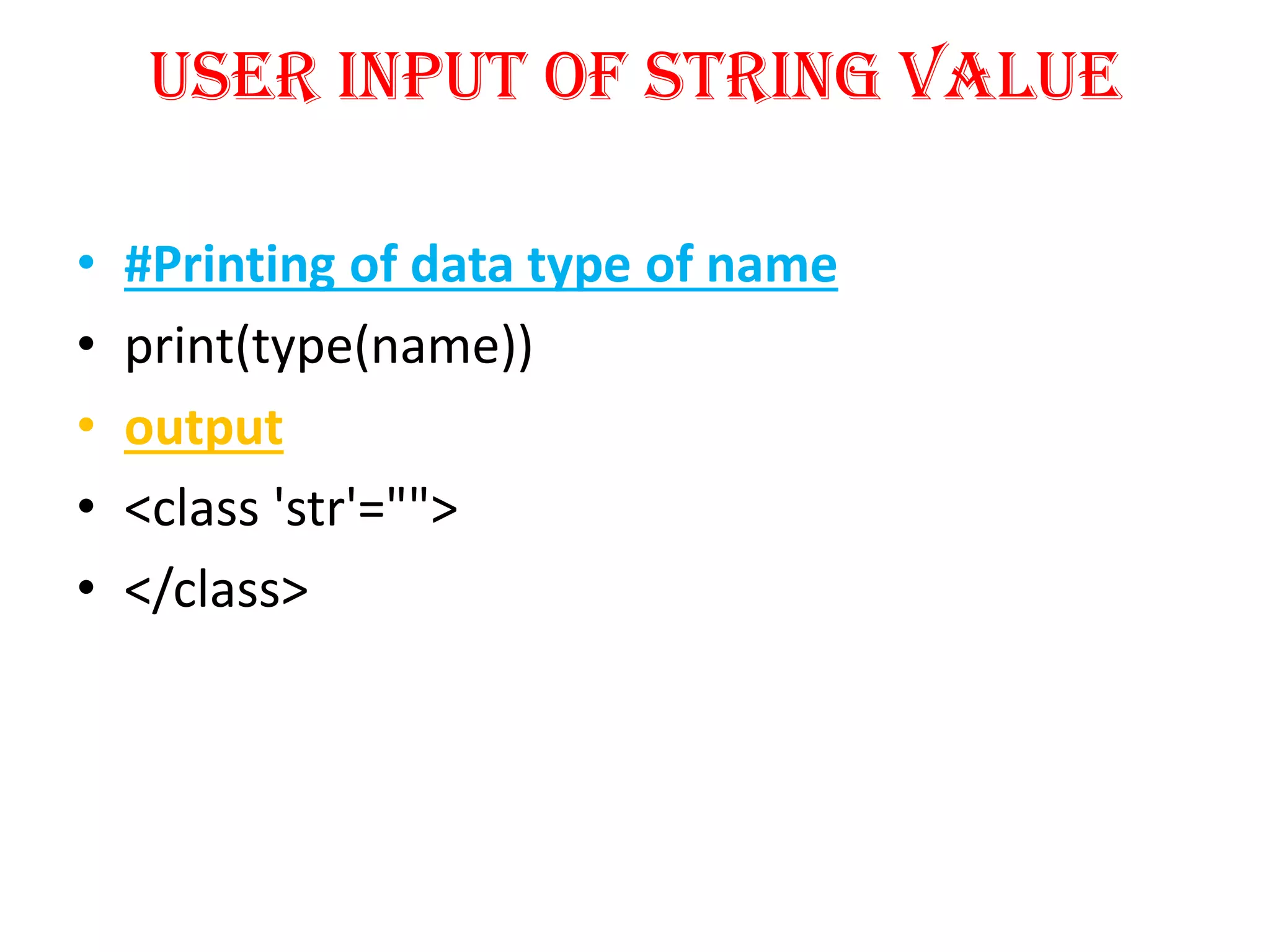
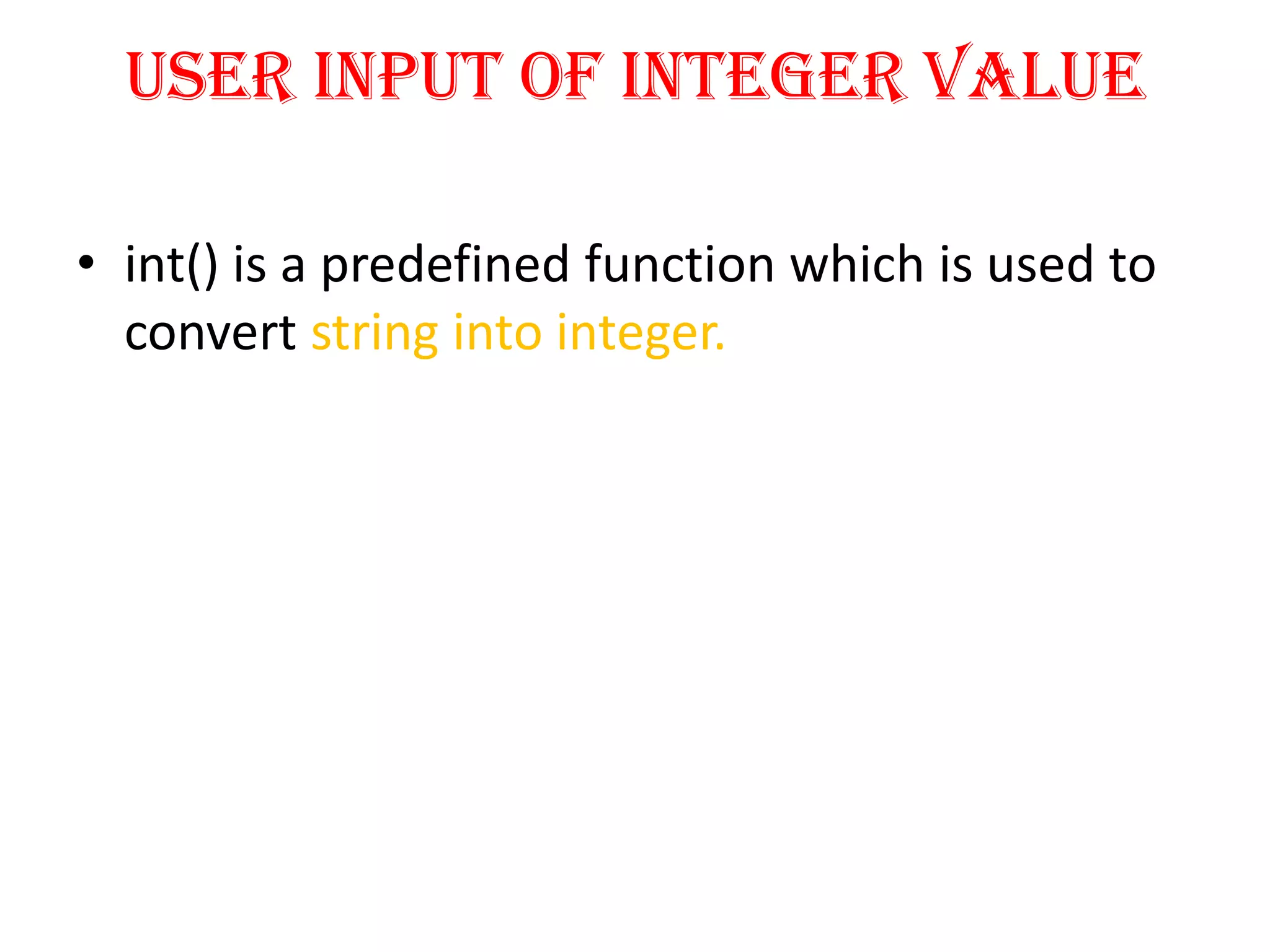
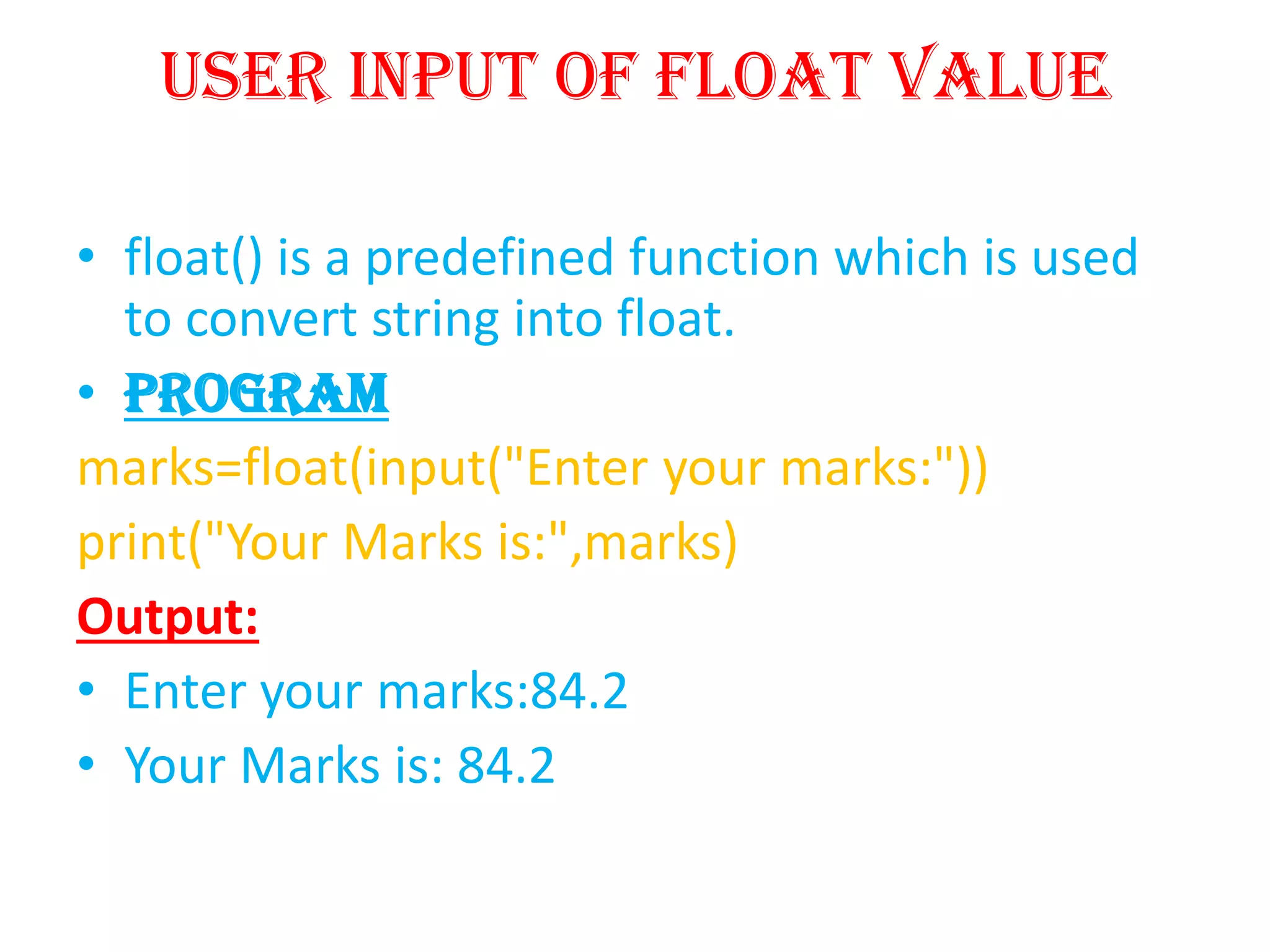
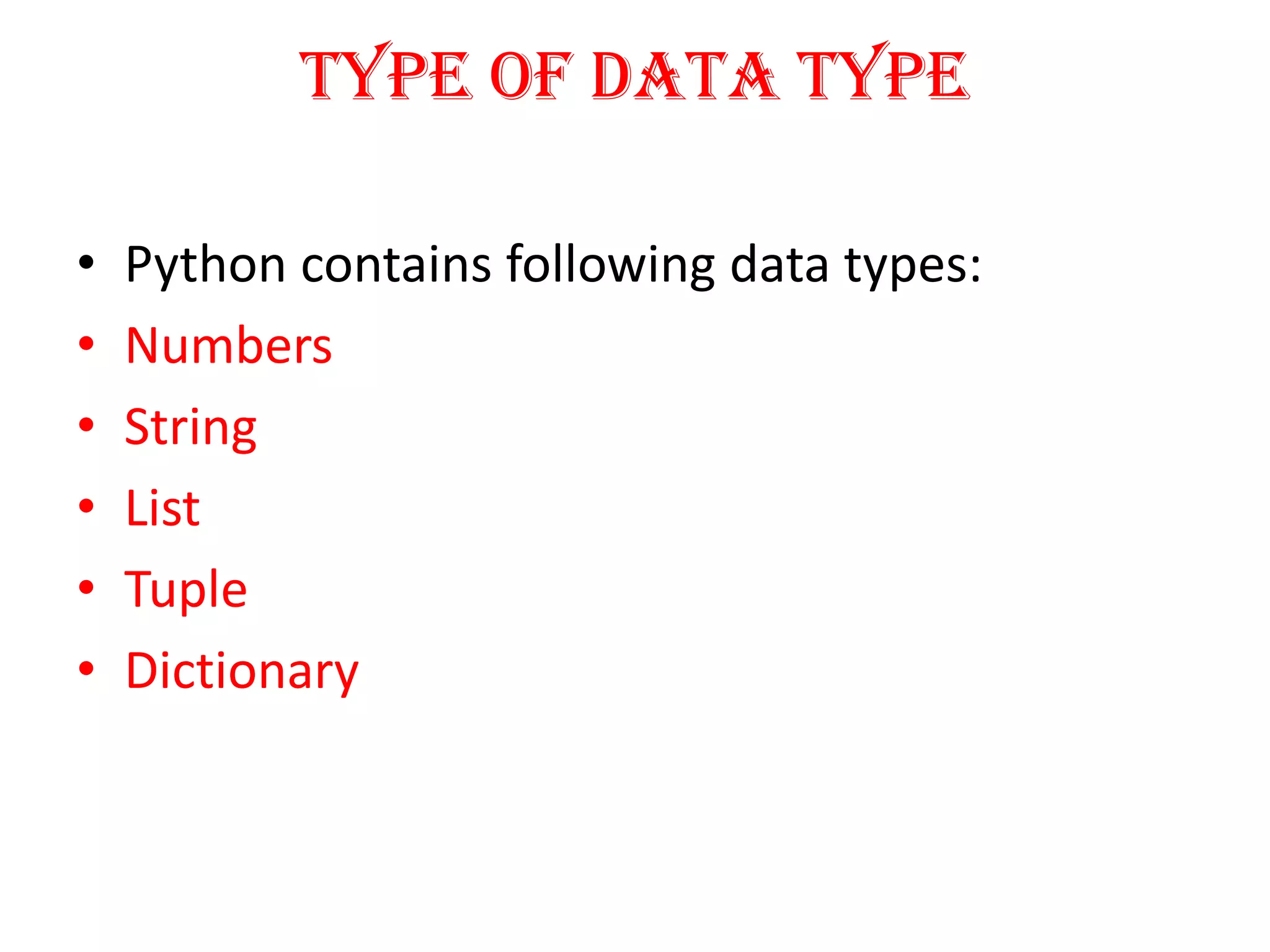
Python is a powerful, object-oriented programming language developed by Guido van Rossum and released in 1991. It is platform-independent, easy to learn, and widely used for web applications, software development, and scientific computing. Python features simple syntax, variable management, and supports various data types, enabling versatile programming solutions.