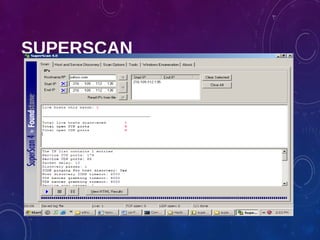
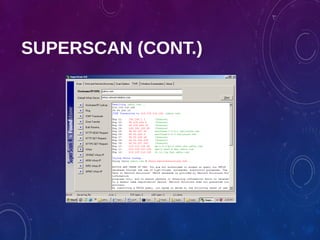
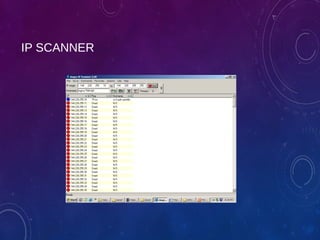
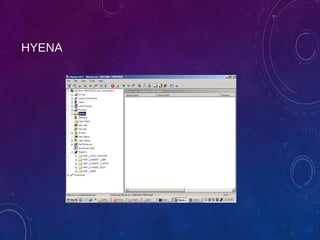
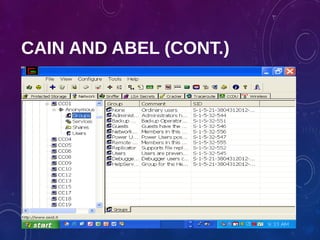
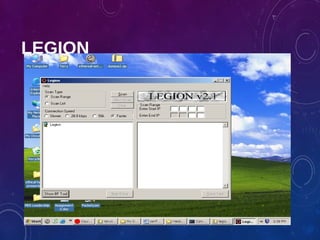
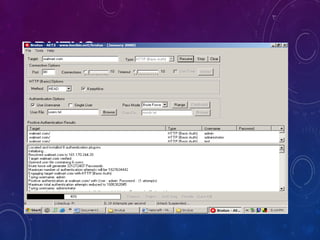
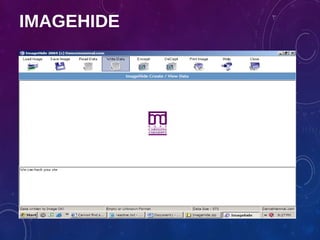
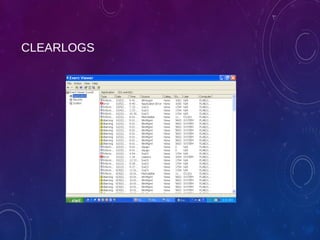
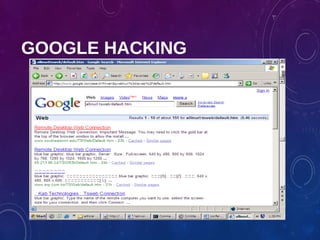
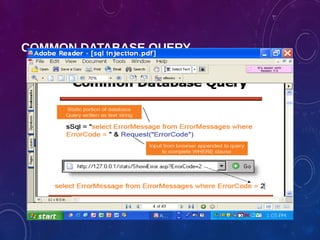
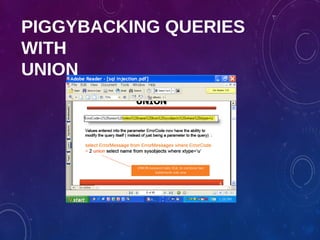
The document provides an overview of ethical hacking, including its history, the different types of hackers, and the role of certified ethical hackers in assessing system vulnerabilities. It discusses the evolution of hacking from the 1960s to the present, the skillset required for ethical hackers, and the financial compensation they can expect. Additionally, it lists various teaching resources, tools, and methodologies essential for educating future ethical hackers.